Engineering > EXAM > ENMF 417 Final Exam | Questions and Answers (All)
ENMF 417 Final Exam | Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
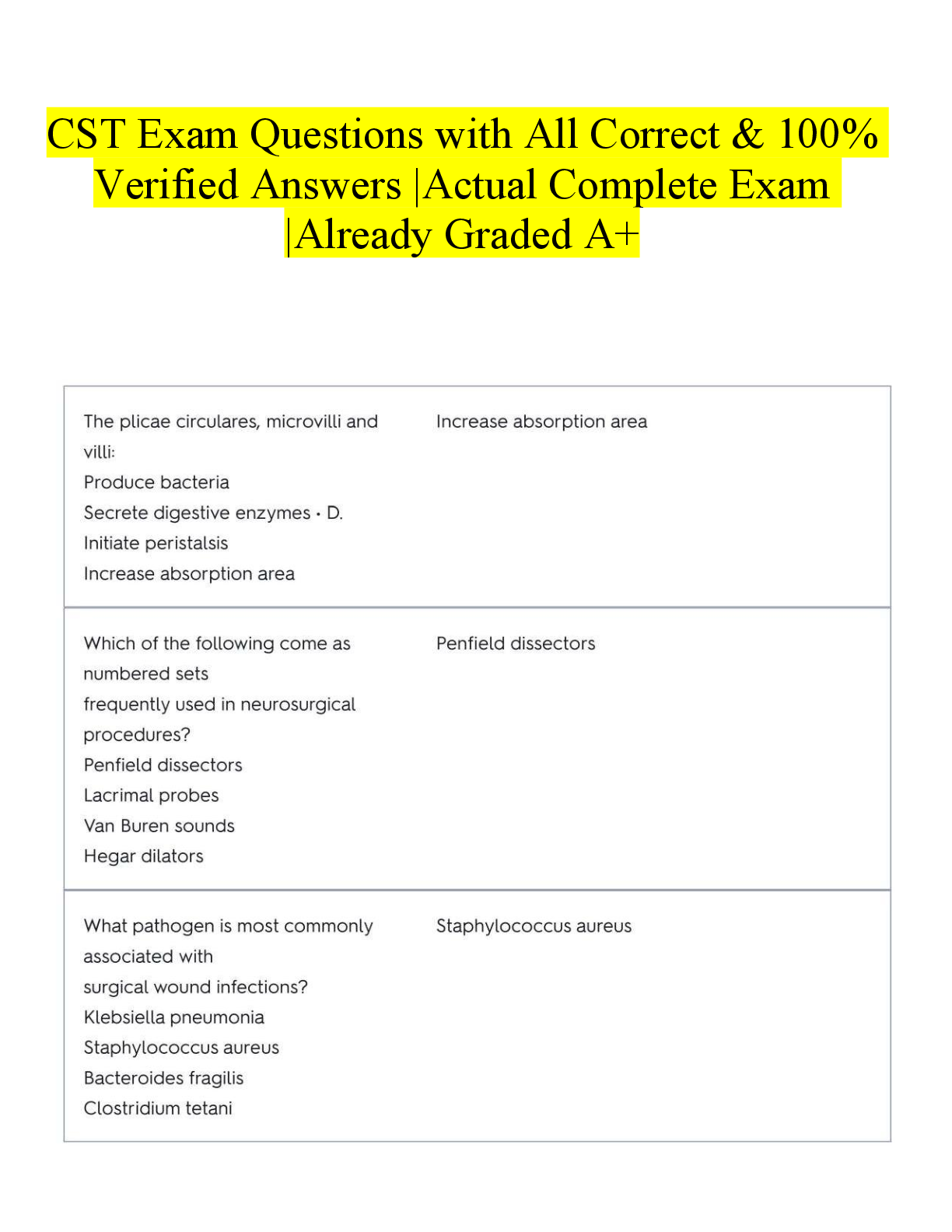
ENMF 417 Final Exam | Questions and Answers What are important factors for surfaces? Friction and Wear, Safety, Aesthetic, Fatigue, Surface Contact, Mechanical Integrity What is Tribology? Study of ... surfaces like friction, wear, and lubricants What are the different kinds of wear? Adhesive, Corrosive, Abrasive, Fatigue What is adhesion? It is a force between the surface of two materials, that doesn't form chips What is abrasion? It's a force between surfaces where roughness causes chips to form. What are common surface treatments Shot peening, Carburizing, Physical vapor deposition (PVD), Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), Electroplating, Anodizing, Painting What is shot peening? A process where a workpiece is repeatedly bombarded with high velocity particles. These high hardness spherical balls form a hardened layer on the surface due to work hardening What is PVD? Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a process where a material is turned into a vapor, and then deposited onto a surface, creating a thin coating. What is CVD? Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where a material is chemically applied to a surface. What is carburizing? Heating a part of low carbon steel in a carbon-rich environment so that carbon is diffused into its surface What is Metrology? The science of measurement. What is a CMM? It is a coordinate measuring machine. It functions by mapping a probes movements to software. What is an LDV? It is a laser-doppler vibrometer. It functions by measuring using the doppler effect on laser light to measure vibrations and velocity. What is an SEM? It is a scanning electron microscope. It functions by firing electrons through magnetic lenses, releasing secondary surface electrons, which are detected by the microscope. What is an AFM? It is an atomic force microscope. It functions by using laser light to detect the changes in force via a small probe. What are common non-destructive tests? Ultrasonic, Radiography (x-ray), Acoustic emission, Eddy Current Inspection, Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) How does ultrasonic inspection work? Anomalies absorb or deflect the sound waves, whichare then detected as changes in the waves. How does radiology (x-ray) inspection work? By imaging using x-ray light. How does Acoustic Emission work? Sounds made by a material, structure, or machines in use or under load are heard and analyzed to determine its "state of health" How does eddy current inspection work? Works on the principle of determining the ease at which a material will accept induced current. How does magnetic flux leakage (MFL) work? The basic principle is that a powerful magnet is used to magnetize steel. At areas where there is corrosion or missing metal, the magnetic field "leaks" from the steel. What is machining? Material removal process in which a sharp cutting tool is used to mechanically cut away material so that the desired part geometry remains What are the pros and cons of machining? Pros: Dimensional accuracy, Complex shapes, Surface finish, Can process a variety of materials, Can be economical for small batches Cons: Can be expensive for large amount of batch, Waste of materials, Lubricants may be necessary, Can take longer compared to shaping, May have adverse effects to surface integrity. What is the difference btw orthogonal and oblique cutting? Orthogonal is along the line of the cut. Oblique is at some angle to the cut What are the conventional machining methods? Milling, Sawing, Turning, Broaching, Drilling, Boring What are the abrasive machining methods? Grinding, Polishing, Lapping What are some Non-Conventional machining? Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Eletro-Chemical Machining (ECM), Waterjet, Laser What is single point machining? Processes like: Turning, Boring, Facing. Workpiece is rotating and the bit is a signal point and stationary. What is facing? To make a flat surface on a part. What is Boring? Enlarging an existing hole in a workpiece, typically larger holes than drilling. What is the difference between conventional and climb milling? What is broaching? Broaching is a machining process that uses a toothed tool called a broach to remove material from a workpiece. What is abrasion (flank) wear? It is the wearing away of hard tool material due to frictional forces. What is adhesion wear? Soft workpiece material that adheres to the tool. Creates a BUE (built up edge) What is diffusion wear? Workpiece material diffusing into tool, causing chemical reactions and changes in physical properties. What is machinability? A relative measure of how easily a material can be machined. 1 is good. < 1 bad, > 1 great. What are important properties for tools? Toughness, Hardness and Wear resistance (i.e. chemically inert etc.) What is chatter? Chatter is the self induced undesirable vibrations that occur between the cutting tool and the workpiece, resulting in a wavy or rough surface finish. What are some ways to reduce chatter? Improve workpiece and tool stiffness, Modify tool and/or geometry for cutting, Change machine parameters (rpm, feed rate, depth of cut, etc.) What is grinding? Grinding is a form of abrasive machining where a surface of a part is smoothed. What is Honing? Honing is a grinding operation for internal surfaces performed after drilling, boring and reaming. What is Lapping? Lapping is a precise surface finishing process that uses abrasive particles in slurry to refine and smooth a surface. What is Dressing? Dressing refers to the process of restoring or shaping a grinding wheel's cutting ability by removing dull or worn abrasive grains. How does ultrasonic machining work? Ultrasonic machining (USM) utilizes a vibrating tool and an abrasive slurry to remove material from a workpiece. How does a water jet work? Water jet work by using high pressure water and often a abrasive power (SiC or aluminum oxide) within to saw materials. How does chemical machining work? Material is removed via contact with a strong chemical. The area of the material that isn't being removed must be masked. Then the material is submerged and the material is melted away. then the mask is removed. How does electrochemical machining (ECM) work? Electrochemical machining is a method of removing metal by an electrochemical process. An electrolyte is used to do this which is normally an inorganic salt solution. How does electrical discharge machining (EDM) work? Electrical discharge machining works by an electrode using a spark to erode a workpiece submerged in dielectric fluid. Usually used for delicate parts How does laser machining work? Laser machining uses high powered lasers to cut materials. How does electron beam machining work? Electron beam machining uses VERY fast electrons to cut a workpiece. Requires a vacuum What is casting? Casting is the act of pouring hot metal liquids into molds to form a near-net-shape. In casting, what is a flask? Is the container for the liquid metal, contains all the other parts for casting In casting what is the mold? The mold is made up of the cope (upper half) and drag (lower half) contains the necessary features to preform a cast. In casting what is the pattern? It is the casing in which the part will be formed. In casting what is the gating system? The gating system is made up the cup, the sprue, and the runner. The cup is where liquid metal enters, the sprue directs the metal to pattern, and the runner is a horizontal channel leading to the pattern as well. In casting what is a riser? The riser is a store of extra molten metal to compensate for shrinkage errors. It should take longer to solidify than the rest of the part. What is sand casting? A type of permanent pattern, expendable mold casting that involves casting in a 90% sand, 7% clay, 3% water mixture that makes up the flask of the mold. This mold must be destroyed to free the part after each use. What is shell casting? Shell casting is a type of sand casting where instead of just sand a thin resin shell is used as a pattern withing the sand flask. This creates a better surface finish and greater dimensional accuracy. What is evaporative pattern casting? Evaporative pattern casting (lost-foam casting) is a type of expendable pattern, expendable mold casting that involved liquid metal replacing a foam pattern inside of a sand flask. What is investment casting? Investment casing (lost-wax casting) is form of casting where a wax pattern is attached to a pattern tree and covered in slurry and stucco coatings. The was is them melted out of the mold and then molten metal is poured in. The mold is then broken to get the final results. What is die casting? Die casting is a process where molten metal is injected at a high pressure into a permeant mold called a die. What are the seven categories of casting defects? 1. Metallic projections 2. Cavities 3. Discontinuities 4. Defective surface 5. Incomplete casting 6. Incorrect dimensions or shape 7. Inclusions What causes and how do you prevent cold shots? Cold shots are cause by splattering of metal within the pattern. To fix them pouring procedures must be changed or the gating system must adjusted. What causes and how do you precent shrinkage cavities? Shrinkage cavities are caused by the difference in densities between the solid and liquid phases of metals. Some ways to prevent this is to include risers, reduce the casting temperature, and increase local head dissipation. What is a misrun and how to prevent it? A misrun is when a metal in a cast fails to fill a mold due to early solidification. To prevent this changes to the mold or gating system will be needed. What is a sand blow and how to prevent it? A sand blow is void in the surface of the part caused by excess moisture and low mold permeability. To prevent this, ensure that molds and cores are dry before use and that there is sufficient gas permeability. What is and how to prevent a cold shunt? A cold shunt is when two steams of molten metal solidify just before the fuse. To prevent them ensure correct design of the gating system and consider mold preheating. What is a wash and how to prevent it? A wash is when molten metal enters a mold to quickly and erodes the pattern. To prevent this ensure that the gating system is designed correctly, that the mold and core are sufficiently strong, and that the mold sand contains sufficient binder. What is a hot tear and how do you prevent it? A hot tear occurs when under cooling the metal doesn't have sufficient tensile to prevent cracking. To prevent this either ensure a expendable mold has sufficient collapsibility or remove the part quickly after solidification. What is porosity caused by and how to prevent it? Porosity is small holes in the product caused by trapped gasses and/or shrinkage. It can be prevented by increasing the cooling rate, or adding cills to the mold. What are some important design considerations for a cast part? Avoid sharp corners. Deep cavities should be on one side of the mold. Wall sections should be of uniform thickness. Add ribs or fillets to boss extrusions. Always include a shrinking allowance. What are the pros and cons of cold forming? Pros: Better accuracy and surface finish, High final strength and hardness Cons: Requires higher forces, Limitations to possible deformations, requires additional annealing, Limited to certain materials What are the pros and cons of warm forming (30 - 60% of melting)? Pros: Lower forces, Able to produce parts with increased complexity, no annealing required Cons: Strict temperature control resulting in complexity and cost increases What are the pros and cons of hot forming (>60% of melting temp)? Pros: Large deformations possible, lowest forces, possible with more materials, no annealing required Cons: Lower accuracy, High productions costs, Possible warping of parts when cooling. Why use forming over casting? Some reasons are: To create geometry unstable for casting, better control over material microstructure, able to process materials unable to be reasonably melted. What is foraging? Inducing plastic deformation of a workpiece by a compressive force. What is rolling? Rolling is reducing the cross-sectional area or thickness of a long workpiece between two rollers. What is extrusion? Extrusion is the PUSHING of material through a die to form it [Show More]
Last updated: 7 months ago
Preview 4 out of 13 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ENMF 417 MIDTERM AND FINAL EXAM BUNDLE
ENMF 417 MIDTERM AND FINAL EXAM BUNDLE
By Nurse Henny 7 months ago
$15
2
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 04, 2025
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 04, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
18