*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NUR 530|Pharmacology and Pathophysiology| Exam 1 Study Guide. (All)
NUR 530|Pharmacology and Pathophysiology| Exam 1 Study Guide.
Document Content and Description Below
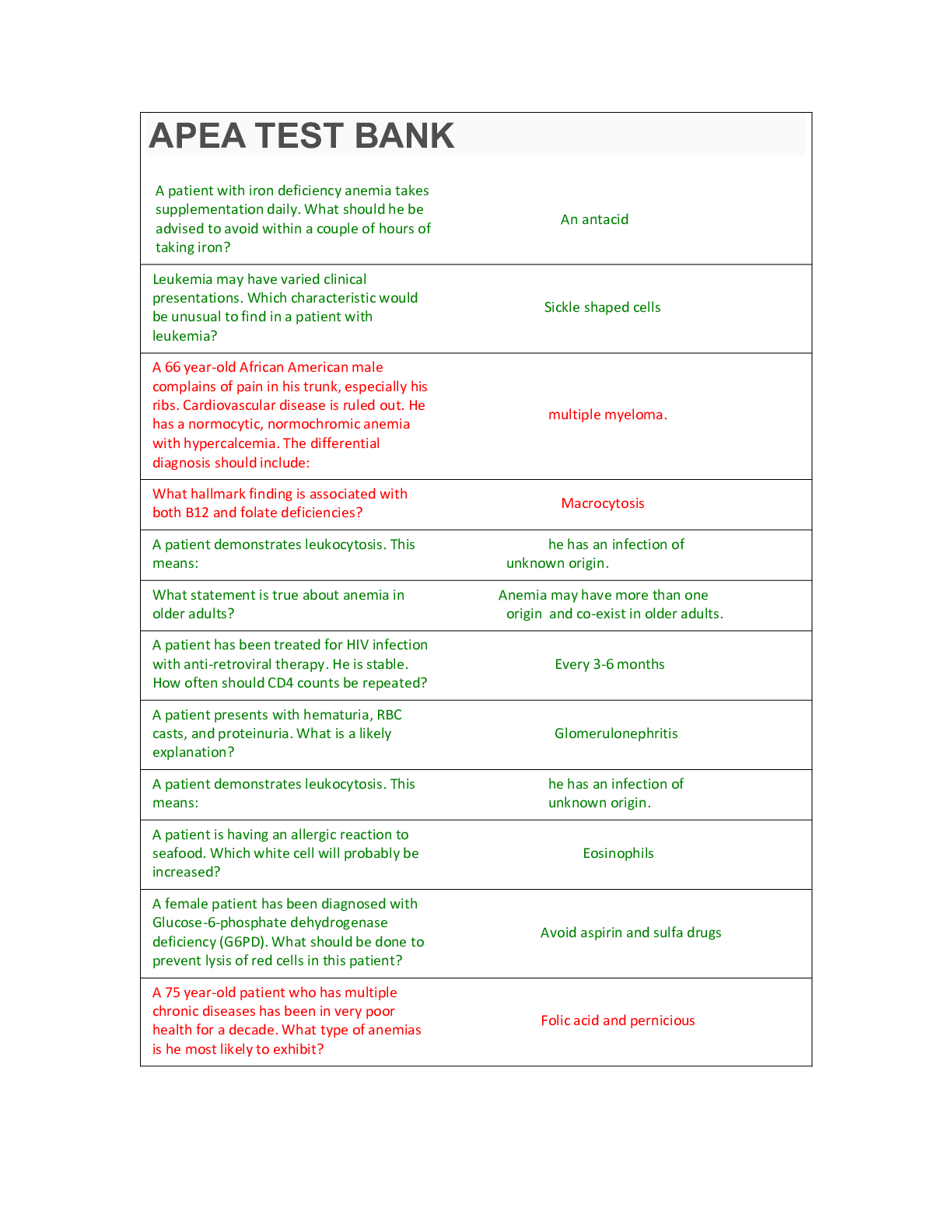
Pharm 530 Exam 1 Study Guide Objectives: Module 1: Intro to Pharmacology and Pathophysiology 1 Discuss the four main processes that make up pharmacokinetics. 2. Discuss the advantages/disadvantag... es of the various techniques of drug administration as they relate to pharmacokinetics. 3. Describe blood flow to tissues; the ability of a drug to exit the vascular system, and the ability of a drug to enter cells, and then discuss the characteristics of drug molecules that can alter these processes. Your description should include protein binding and factors that influence protein binding. 4. Describe the ultimate “goal” of drug metabolism. Discuss the general processes involved in drug metabolism and identify the major or vital organs in which most drug metabolism occurs. 5. Discuss the importance of understanding the time course of drug responses (plasma drug levels, single-dose time course, drug half-life, and drug levels produced with repeated doses). 6. Discuss the consequences of drug blood levels that fluctuate considerably or erratically between doses and describe how to identify such fluctuations. 7. Define pharmacodynamics and its relationship to the action of drugs on the body. 8. Discuss dose-response relationships, the effects drugs can produce, and the amount of drug needed to elicit an effect. 9. Discuss properties of drug-receptor interactions. 10. Describe how receptors function in the responses to many drugs and physiologic processes. 11. Differentiate drugs that are agonists, partial agonists, or antagonists. 12. Discuss inter-patient variability in drug responses. 13. Discuss the concept of a drug’s therapeutic index and its application and benefits to clinical practice. 14. Discuss the consequences of drug-drug interactions, the basic mechanisms of drug-drug interactions, and the critical steps in minimizing adverse drug-drug interactions. 15. Focus on the liver as an example of a drug-metabolizing system and explain why it is such a crucial organ in many drug-drug interactions. 16. Discuss the effect of food on drug absorption, on drug metabolism (e.g., grapefruit juice), and on drug toxicity and action, as well as the timing of drug administration with respect to meals. 17. Discuss side effect, toxicity, allergic reaction, idiosyncratic effect, iatrogenic disease, physical dependence, carcinogenic effect, and teratogenic effects of drugs. 18. Discuss organ-specific toxicity. (Focus on the liver as a drug-metabolizing system.) 19. Discuss the significance of body weight/composition. 20. Discuss age as a factor in medication administration. 21. Discuss the effects of kidney disease, liver disease, acid-base imbalance, and altered electrolyte status on drug responses. 22. Discuss bioavailability and other causes of variable absorption. Explain why differences in bioavailability are a significant concern with drugs that have a narrow therapeutic index. 23. Discuss the effects of diet (especially protein) on drug responses. High protein diets can accelerate drug metabolism by stimulating enzymes within the liver. 24. Explain the differences in drug therapy and changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in extreme age groups (the very young and the very old.) Module 1B: Fluids, Electrolytes, IV Fluids and intro to Renal Disease 1. Explain the factors that influence variation in drug responses 2. Describe considerations that affect drug therapy in pregnancy 3. Explain a teratogen and describe the most critical time that exposure can cause fetal problems 4. Broadly explain significance of the different categories of drugs in pregnancy. 5. Describe the significant differences in ADME in children 6. Describe the significant differences in ADME in older adults 7. Describe normal fluid distribution within the body 8. Explain concentration gradient and the difference in diffusion, osmosis, filtration, and active transport 9. Describe the makeup and differences in isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions and the effect each has on human cells 10. Explain the importance of fluid intake and fluid loss as it relates to nursing care 11. Describe the effect of thirst on fluid maintenance 12. Explain in broad terms, the effect of the kidney on fluid and electrolyte balance 13. Describe the normal ranges of electrolyte values for adults Normal Electrolyte Values for Adults Sodium Potassium Chloride Calcium (total) Calcium (ionized) Magnesium 14. Describe the major causes of water imbalance in the human 15. Describe different types of fluid losses and their causes 16. Explain "third spacing" 17. Describe different types of fluid excess and their causes 18. Describe the causes of edema and explain how edema is classified 19. Describe the major function of sodium and potassium in the human body 20. Describe the signs and symptoms of sodium, potassium, and calcium imbalance 21. Describe the uses of IV therapy 22. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of IV fluid therapy 23. Describe the potential complications of IV therapy 24. Explain why POTASSIUM is NEVER GIVEN AS A BOLUS 25. Explain when and why dextrose and water solutions are administered 26. Explain when and why saline solutions are administered 27. Describe the characteristics of normal urine 28. Describe the tests for renal functions 29. Explain the difference between acute and chronic renal failure 30. Describe the differences in PRErenal, INTRArenal and POSTrenal causes of kidney injury and give examples of their causes 31. Describe the phases of acute tubular injury 32. Define chronic renal failure 33. Explain how glomerular filtration is related to severity of renal failure 34. Describe the clinical symptoms and manifestations of early and late renal failure 35. Describe the effects of kidney disease on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics 36. Describe the methods of renal replacement in chronic renal disease 37. Describe the role of diet in the management of chronic renal disease 38. Describe the effects of chronic kidney disease in children 39. Describe normal changes in the kidney of older adults Module 2: Cell regulation, anemia, and blood and blood products will be introduced. 40. Describe the anatomy of a human cell and the function of the organelles 41. Name the phases of the cell cycle 42. Explain the phases of mitosis 43. Define hyperplasia, hypertrophy, atrophy, anaplasia, metaplasia, and dysplasia 44. Explains the differences between benign and malignant cells Describe the characteristics of malignant cells 45. Describe three causes of cancer 46. Explain the role of viruses as a cause of cancer 47. Describe the tests used to diagnose cancer 48. Describe, in broad terms, four treatment modalities for cancer 49. Define anemia 50. Describe three nutritional causes of anemia 51. Describe the genetic and non-genetic causes of hemolytic anemia 52. Describe the causes of aplastic anemia. 53. Describe tests used for diagnosing anemia. 54. Describe the cellular components of blood. Look at chart-great description 55. Describe two functions of plasma 56. Describe the protein components of plasma and their function. 57. Explain the function of red cells, neutrophils, and granulocytes 58. Explain the purpose of blood transfusion The purpose of blood transfusion is to: 59. Explain the differences in whole blood, packed red cells, platelets, fresh frozen plasma, and albumin transfusions and describe their purposes Red cell components 60. Describe the potential complications of blood transfusion 61. Describe mechanisms to prevent transfusion complication 62. Describe tests used for diagnosing anemia 63. Describe in general terms the function of vitamins 64. List the fat soluble and water soluble vitamins 65. List at least two conditions caused by deficiency of Vitamin A and one condition caused by deficiency of each of the following: Vitamin D and Vitamin K 66. Describe food sources of Vitamin C and the B vitamins and describe what distinguishes Vitamin B12 from the rest of the B vitamins 67. Describe the major complication(s) caused by deficiencies of each of the B vitamins including folic acid 68. Define enteral nutrition 69. Describe the indications for total parenteral nutrition(TPN) 70. Explain the most common method for administering total parenteral nutrition 71. List three complications associated with total parenteral nutrition 72. Explain the emergent management when total parenteral nutrition is suddenly discontinued (for whatever reason) [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 36 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 29, 2020
Number of pages
36
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 29, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
288













.png)





