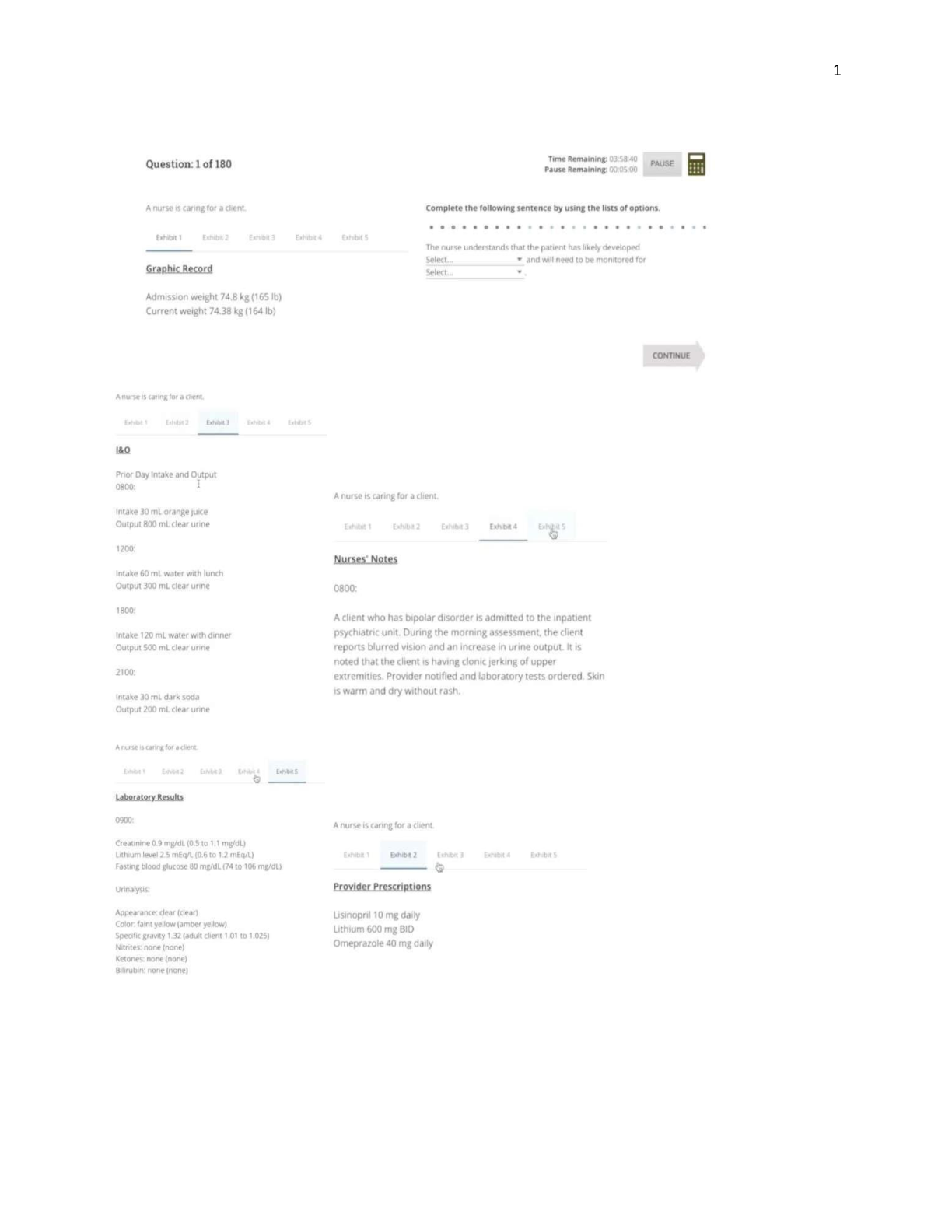
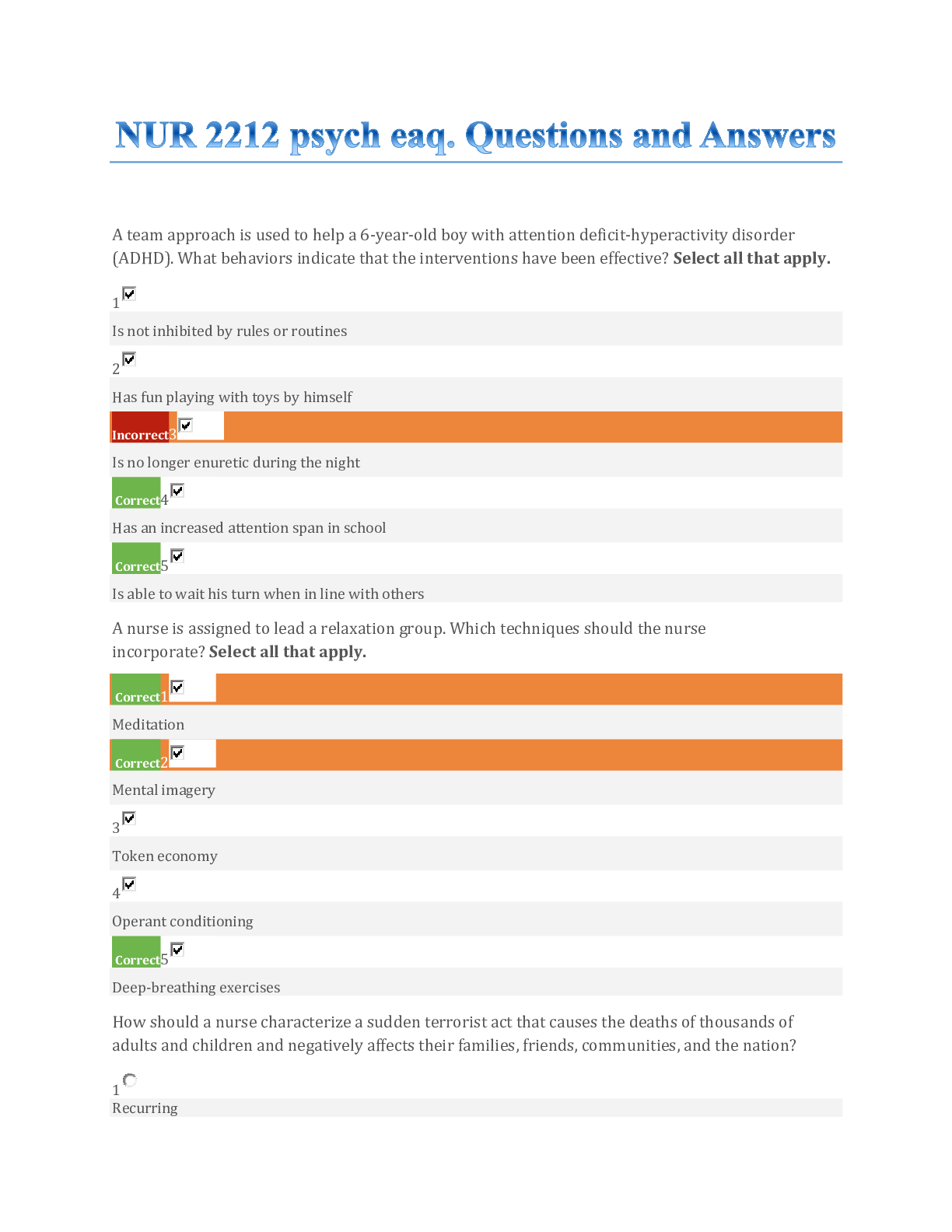
*NURSING > EXAM > NCLEX-RN Quizzes/Exam #12 to #26 Contains Over 500 Question and Answers. All Answers Provided With (All)
NCLEX-RN Quizzes/Exam #12 to #26 Contains Over 500 Question and Answers. All Answers Provided With Rationale.
Document Content and Description Below
NCLEX-RN Test Bank Quizzes/Exam #12 to #26 Contains Over 500 Question and Answers. All Answers Provided With Rationale. NCLEX Practice Exam 12 (20 Questions) 1. A patient is admitted to the hospital ... with a diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism. A nurse checking the patient’s lab results would expect which of the following changes in laboratory findings? A. Elevated serum calcium. B. Low serum parathyroid hormone (PTH). C. Elevated serum vitamin D. D. Low urine calcium. 2. A patient with Addison’s disease asks a nurse for nutrition and diet advice. Which of the following diet modifications is NOT recommended? A. A diet high in grains. B. A diet with adequate caloric intake. C. A high protein diet. D. A restricted sodium diet. 3. A patient with a history of diabetes mellitus is in the second post-operative day following cholecystectomy. She has complained of nausea and isn’t able to eat solid foods. The nurse enters the room to find the patient confused and shaky. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the patient’s symptoms? A. Anesthesia reaction. B. Hyperglycemia. C. Hypoglycemia. D. Diabetic ketoacidosis. 4. A nurse assigned to the emergency department evaluates a patient who underwent fiberoptic colonoscopy 18 hours previously. The patient reports increasing abdominal pain, fever, and chills. Which of the following conditions poses the most immediate concern? A. Bowel perforation. B. Viral gastroenteritis. C. Colon cancer. D. Diverticulitis. 5. A patient is admitted to the same day surgery unit for liver biopsy. Which of the following laboratory tests assesses coagulation? Select all that apply. A. Partial thromboplastin time. B. Prothrombin time. C. Platelet count. D. Hemoglobin E. Complete Blood Count F. White Blood Cell Count 6. A patient on the cardiac telemetry unit unexpectedly goes into ventricular fibrillation. The advanced cardiac life support team prepares to defibrillate. Which of the following choices indicates the correct placement of the conductive gel pads? A. The left clavicle and right lower sternum. B. Right of midline below the bottom rib and the left shoulder. C. The upper and lower halves of the sternum. D. The right side of the sternum just below the clavicle and left of the precordium. 7. The nurse performs an initial abdominal assessment on a patient newly admitted for abdominal pain. The nurse hears what she describes as “clicks and gurgles in all four quadrants” as well as “swishing or buzzing sound heard in one or two quadrants.” Which of the following statements is correct? A. The frequency and intensity of bowel sounds varies depending on the phase of digestion. B. In the presence of intestinal obstruction, bowel sounds will be louder and higher pitched. C. A swishing or buzzing sound may represent the turbulent blood flow of a bruit and is not normal. D. All of the above. 8. A patient arrives in the emergency department and reports splashing concentrated household cleaner in his eye. Which of the following nursing actions is a priority? A. Irrigate the eye repeatedly with normal saline solution. B. Place fluorescein drops in the eye. C. Patch the eye. D. Test visual acuity. 9. A nurse is caring for a patient who has had hip replacement. The nurse should be most concerned about which of the following findings? A. Complaints of pain during repositioning. B. Scant bloody discharge on the surgical dressing. C. Complaints of pain following physical therapy. D. Temperature of 101.8 F (38.7 C). 10. A child is admitted to the hospital with an uncontrolled seizure disorder. The admitting physician writes orders for actions to be taken in the event of a seizure. Which of the following actions would NOT be included? A. Notify the physician. B. Restrain the patient’s limbs. C. Position the patient on his/her side with the head flexed forward. D. Administer rectal diazepam. 11. A patient who has received chemotherapy for cancer treatment is given an injection of Epoetin. Which of the following should reflect the findings in a complete blood count (CBC) drawn several days later? A. An increase in neutrophil count. B. An increase in hematocrit. C. An increase in platelet count. D. An increase in serum iron. 12. A patient is admitted to the hospital with suspected polycythemia vera. Which of the following symptoms is consistent with the diagnosis? Select all that apply. A. Weight loss. B. Increased clotting time. C. Hypertension. D. Headaches. 13. A nurse is caring for a patient with a platelet count of 20,000/microliter. Which of the following is an important intervention? A. Observe for evidence of spontaneous bleeding. B. Limit visitors to family only. C. Give aspirin in case of headaches. D. Impose immune precautions. 14. A nurse in the emergency department assesses a patient who has been taking long-term corticosteroids to treat renal disease. Which of the following is a typical side effect of corticosteroid treatment? Note: More than one answer may be correct. A. Hypertension. B. Cushingoid features. C. Hyponatremia. D. Low serum albumin. 15. A nurse is caring for patients in the oncology unit. Which of the following is the most important nursing action when caring for a neutropenic patient? A. Change the disposable mask immediately after use. B. Change gloves immediately after use. C. Minimize patient contact. D. Minimize conversation with the patient. 16. A nurse is counseling patients at a health clinic on the importance of immunizations. Which of the following information is the most accurate regarding immunizations? A. All infectious diseases can be prevented with proper immunization. B. Immunizations provide natural immunity from disease. C. Immunizations are risk-free and should be universally administered. D. Immunization provides acquired immunity from some specific diseases. 17. A patient is brought to the emergency department after a bee sting. The family reports a history of severe allergic reaction, and the patient appears to have some oral swelling. Which of the following is the most urgent nursing action? A. Consult a physician. B. Maintain a patent airway. C. Administer epinephrine subcutaneously. D. Administer diphenhydramine (Benadryl) orally. 18. A mother calls the clinic to report that her son has recently started medication to treat attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The mother fears her son is experiencing side effects of the medicine. Which of the following side effects are typically related to medications used for ADHD? Note: More than one answer may be correct: A. Poor appetite. B. Insomnia. C. Sleepiness. D. Agitation. 19. A patient at a mental health clinic is taking Haldol (haloperidol) for treatment of schizophrenia. She calls the clinic to report abnormal movements of her face and tongue. The nurse concludes that the patient is experiencing which of the following symptoms: A. Co-morbid depression. B. Psychotic hallucinations. C. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia. D. Tardive dyskinesia. 20. A patient with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus is learning to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia. Which of the following symptoms is indicative of hypoglycemia? A. Polydipsia. B. Confusion. C. Blurred vision. D. Polyphagia. NCLEX Practice Exam 13 (20 Questions) 1. A child is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of Wilms tumor, stage II. Which of the following statements most accurately describes this stage? A. The tumor is less than 3 cm. in size and requires no chemotherapy. B. The tumor did not extend beyond the kidney and was completely resected. C. The tumor extended beyond the kidney but was completely resected. D. The tumor has spread into the abdominal cavity and cannot be resected. 2. A teen patient is admitted to the hospital by his physician who suspects a diagnosis of acute glomerulonephritis. Which of the following findings is consistent with this diagnosis? Note: More than one answer may be correct. A. Urine specific gravity of 1.040. B. Urine output of 350 ml in 24 hours. C. Brown (“tea-colored”) urine. D. Generalized edema. 3. Which of the following conditions most commonly causes acute glomerulonephritis? A. A congenital condition leading to renal dysfunction. B. Prior infection with group A Streptococcus within the past 10-14 days. C. Viral infection of the glomeruli. D. Nephrotic syndrome. 4. An infant with hydrocele is seen in the clinic for a follow-up visit at 1 month of age. The scrotum is smaller than it was at birth, but fluid is still visible on illumination. Which of the following actions is the physician likely to recommend? A. Massaging the groin area twice a day until the fluid is gone. B. Referral to a surgeon for repair. C. No treatment is necessary; the fluid is reabsorbing normally. D. Keeping the infant in a flat, supine position until the fluid is gone. 5. A nurse is caring for a patient with peripheral vascular disease (PVD). The patient complains of burning and tingling of the hands and feet and cannot tolerate touch of any kind. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these symptoms? A. Inadequate tissue perfusion leading to nerve damage. B. Fluid overload leading to compression of nerve tissue. C. Sensation distortion due to psychiatric disturbance. D. Inflammation of the skin on the hands and feet. 6. A nurse is assessing a clinic patient with a diagnosis of hepatitis A. Which of the following is the most likely route of transmission? A. Sexual contact with an infected partner. B. Contaminated food. C. Blood transfusion. D. Illegal drug use. 7. A leukemia patient has a relative who wants to donate blood for transfusion. Which of the following donor medical conditions would prevent this? A. A history of hepatitis C five years previously. B. Cholecystitis requiring cholecystectomy one year previously. C. Asymptomatic diverticulosis. D. Crohn’s disease in remission. 8. A physician has diagnosed acute gastritis in a clinic patient. Which of the following medications would be contraindicated for this patient? A. Naproxen sodium (Naprosyn). B. Calcium carbonate. C. Clarithromycin (Biaxin). D. Furosemide (Lasix). 9. The nurse is conducting nutrition counseling for a patient with cholecystitis. Which of the following information is important to communicate? A. The patient must maintain a low calorie diet. B. The patient must maintain a high protein/low carbohydrate diet. C. The patient should limit sweets and sugary drinks. D. The patient should limit fatty foods. 10. A patient admitted to the hospital with myocardial infarction develops severe pulmonary edema. Which of the following symptoms should the nurse expect the patient to exhibit? A. Slow, deep respirations. B. Stridor. C. Bradycardia. D. Air hunger. 11. A nurse is evaluating a postoperative patient and notes a moderate amount of serous drainage on the dressing 24 hours after surgery. Which of the following is the appropriate nursing action? A. Notify the surgeon about evidence of infection immediately. B. Leave the dressing intact to avoid disturbing the wound site. C. Remove the dressing and leave the wound site open to air. D. Change the dressing and document the clean appearance of the wound site. 12. A patient returns to the emergency department less than 24 hours after having a fiberglass cast applied for a fractured right radius. Which of the following patient complaints would cause the nurse to be concerned about impaired perfusion to the limb? A. Severe itching under the cast. B. Severe pain in the right shoulder. C. Severe pain in the right lower arm. D. Increased warmth in the fingers. 13. An older patient with osteoarthritis is preparing for discharge. Which of the following information is correct. A. Increased physical activity and daily exercise will help decrease discomfort associated with the condition. B. Joint pain will diminish after a full night of rest. C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications should be taken on an empty stomach. D. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is a more effective anti-inflammatory than ibuprofen (Motrin). 14. Which patient should NOT be prescribed alendronate (Fosamax) for osteoporosis? A. A female patient being treated for high blood pressure with an ACE inhibitor. B. A patient who is allergic to iodine/shellfish. C. A patient on a calorie restricted diet. D. A patient on bed rest who must maintain a supine position. 15. Which of the following strategies is NOT effective for prevention of Lyme disease? A. Insect repellant on the skin and clothes when in a Lyme endemic area. B. Long sleeved shirts and long pants. C. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy prior to anticipated exposure to ticks. D. Careful examination of skin and hair for ticks following anticipated exposure. 16. A nurse is performing routine assessment of an IV site in a patient receiving both IV fluids and medications through the line. Which of the following would indicate the need for discontinuation of the IV line as the next nursing action? A. The patient complains of pain on movement. B. The area proximal to the insertion site is reddened, warm, and painful. C. The IV solution is infusing too slowly, particularly when the limb is elevated. D. A hematoma is visible in the area of the IV insertion site. 17. A hospitalized patient has received transfusions of 2 units of blood over the past few hours. A nurse enters the room to find the patient sitting up in bed, dyspneic and uncomfortable. On assessment, crackles are heard in the bases of both lungs, probably indicating that the patient is experiencing a complication of transfusion. Which of the following complications is most likely the cause of the patient’s symptoms? A. Febrile non-hemolytic reaction. B. Allergic transfusion reaction. C. Acute hemolytic reaction. D. Fluid overload. 18. A patient in labor and delivery has just received an amniotomy. Which of the following is correct? Note: More than one answer may be correct. A. Frequent checks for cervical dilation will be needed after the procedure. B. Contractions may rapidly become stronger and closer together after the procedure. C. The FHR (fetal heart rate) will be followed closely after the procedure due to the possibility of cord compression. D. The procedure is usually painless and is followed by a gush of amniotic fluid. 19. A nurse is counseling the mother of a newborn infant with hyperbilirubinemia. Which of the following instructions by the nurse is NOT correct? A. Continue to breastfeed frequently, at least every 2-4 hours. B. Follow up with the infant’s physician within 72 hours of discharge for a recheck of the serum bilirubin and exam. C. Watch for signs of dehydration, including decreased urinary output and changes in skin turgor. D. Keep the baby quiet and swaddled, and place the bassinet in a dimly lit area. 20. A nurse is giving discharge instructions to the parents of a healthy newborn. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide regarding car safety and the trip home from the hospital? A. The infant should be restrained in an infant car seat, properly secured in the back seat in a rear-facing position. B. The infant should be restrained in an infant car seat, properly secured in the front passenger seat. C. The infant should be restrained in an infant car seat facing forward or rearward in the back seat. D. For the trip home from the hospital, the parent may sit in the back seat and hold the newborn. NCLEX Practice Exam 14 (20 Questions) 1. A nurse is administering IV furosemide to a patient admitted with congestive heart failure. After the infusion, which of the following symptoms is NOT expected? A. Increased urinary output. B. Decreased edema. C. Decreased pain. D. Decreased blood pressure. 2. There are a number of risk factors associated with coronary artery disease. Which of the following is a modifiable risk factor? A. Obesity. B. Heredity. C. Gender. D. Age. 3. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) is considered for treatment of a patient who arrives in the emergency department following onset of symptoms of myocardial infarction. Which of the following is a contraindication for treatment with t-PA? A. Worsening chest pain that began earlier in the evening. B. History of cerebral hemorrhage. C. History of prior myocardial infarction. D. Hypertension. 4. Following myocardial infarction, a hospitalized patient is encouraged to practice frequent leg exercises and ambulate in the hallway as directed by his physician. Which of the following choices reflects the purpose of exercise for this patient? A. Increases fitness and prevents future heart attacks. B. Prevents bedsores. C. Prevents DVT (deep vein thrombosis). D. Prevent constipations. 5. A patient arrives in the emergency department with symptoms of myocardial infarction, progressing to cardiogenic shock. Which of the following symptoms should the nurse expect the patient to exhibit with cardiogenic shock? A. Hypertension. B. Bradycardia. C. Bounding pulse. D. Confusion. 6. A patient in the cardiac unit is concerned about the risk factors associated with atherosclerosis. Which of the following are hereditary risk factors for developing atherosclerosis? A. Family history of heart disease. B. Overweight. C. Smoking. D. Age. 7. Claudication is a well-known effect of peripheral vascular disease. Which of the following facts about claudication is correct? More than one answer may be correct. A. It results when oxygen demand is greater than oxygen supply. B. It is characterized by pain that often occurs during rest. C. It is a result of tissue hypoxia. D. It is characterized by cramping and weakness. 8. A nurse is providing discharge information to a patient with peripheral vascular disease. Which of the following information should be included in instructions? A. Walk barefoot whenever possible. B. Use a heating pad to keep feet warm. C. Avoid crossing the legs. D. Use antibacterial ointment to treat skin lesions at risk of infection. 9. A patient who has been diagnosed with vasospastic disorder (Raynaud’s disease) complains of cold and stiffness in the fingers. Which of the following descriptions is most likely to fit the patient? A. An adolescent male. B. An elderly woman. C. A young woman. D. An elderly man. 10. A 23 year old patient in the 27th week of pregnancy has been hospitalized on complete bed rest for 6 days. She experiences sudden shortness of breath, accompanied by chest pain. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of her symptoms? A. Myocardial infarction due to a history of atherosclerosis. B. Pulmonary embolism due to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). C. Anxiety attack due to worries about her baby’s health. D. Congestive heart failure due to fluid overload. 11. Thrombolytic therapy is frequently used in the treatment of suspected stroke. Which of the following is a significant complication associated with thrombolytic therapy? A. Air embolus. B. Cerebral hemorrhage. C. Expansion of the clot. D. Resolution of the clot. 12. An infant is brought to the clinic by his mother, who has noticed that he holds his head in an unusual position and always faces to one side. Which of the following is the most likely explanation? A. Torticollis, with shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. B. Craniosynostosis, with premature closure of the cranial sutures. C. Plagiocephaly, with flattening of one side of the head. D. Hydrocephalus, with increased head size. 13. An adolescent brings a physician’s note to school stating that he is not to participate in sports due to a diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Which of the following statements about the disease is correct? A. The condition was caused by the student’s competitive swimming schedule. B. The student will most likely require surgical intervention. C. The student experiences pain in the inferior aspect of the knee. D. The student is trying to avoid participation in physical education. 14. The clinic nurse asks a 13-year-old female to bend forward at the waist with arms hanging freely. Which of the following assessments is the nurse most likely conducting? A. Spinal flexibility. B. Leg length disparity. C. Hypostatic blood pressure. D. Scoliosis. 15. A clinic nurse interviews a parent who is suspected of abusing her child. Which of the following characteristics is the nurse LEAST likely to find in an abusing parent? A. Low self-esteem. B. Unemployment. C. Self-blame for the injury to the child. D. Single status. 16. A nurse in the emergency department is observing a 4-year-old child for signs of increased intracranial pressure after a fall from a bicycle, resulting in head trauma. Which of the following signs or symptoms would be cause for concern? A. Bulging anterior fontanel. B. Repeated vomiting. C. Signs of sleepiness at 10 PM. D. Inability to read short words from a distance of 18 inches. 17. A nonimmunized child appears at the clinic with a visible rash. Which of the following observations indicates the child may have rubeola (measles)? A. Small blue-white spots are visible on the oral mucosa. B. The rash begins on the trunk and spreads outward. C. There is low-grade fever. D. The lesions have a “teardrop on a rose petal” appearance. 18. A child is seen in the emergency department for scarlet fever. Which of the following descriptions of scarlet fever is NOT correct? A. Scarlet fever is caused by infection with group A Streptococcus bacteria. B. “Strawberry tongue” is a characteristic sign. C. Petechiae occur on the soft palate. D. The pharynx is red and swollen. 19. A child weighing 30 kg arrives at the clinic with diffuse itching as the result of an allergic reaction to an insect bite. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 25 mg 3 times a day is prescribed. The correct pediatric dose is 5 mg/kg/day. Which of the following best describes the prescribed drug dose? A. It is the correct dose. B. The dose is too low. C. The dose is too high. D. The dose should be increased or decreased, depending on the symptoms. 20. The mother of a 2-month-old infant brings the child to the clinic for a well baby check. She is concerned because she feels only one testis in the scrotal sac. Which of the following statements about the undescended testis is the most accurate? A. Normally, the testes are descended by birth. B. The infant will likely require surgical intervention. C. The infant probably has with only one testis. D. Normally, the testes descend by one year of age. NCLEX Practice Exam 15 (50 Questions) 1. Mrs. Chua a 78-year-old client is admitted with the diagnosis of mild chronic heart failure. The nurse expects to hear when listening to client’s lungs indicative of chronic heart failure would be: A. Stridor B. Crackles C. Wheezes D. Friction rubs 2. Patrick who is hospitalized following a myocardial infarction asks the nurse why he is taking morphine. The nurse explains that morphine: A. Decrease anxiety and restlessness B. Prevents shock and relieves pain C. Dilates coronary blood vessels D. Helps prevent fibrillation of the heart 3. Which of the following should the nurse teach the client about the signs of digitalis toxicity? A. Increased appetite B. Elevated blood pressure C. Skin rash over the chest and back D. Visual disturbances such as seeing yellow spots 4. Nurse Trisha teaches a client with heart failure to take oral Furosemide in the morning. The reason for this is to help… A. Retard rapid drug absorption B. Excrete excessive fluids accumulated at night C. Prevents sleep disturbances during night D. Prevention of electrolyte imbalance 5. What would be the primary goal of therapy for a client with pulmonary edema and heart failure? A. Enhance comfort B. Increase cardiac output C. Improve respiratory status D. Peripheral edema decreased 6. Nurse Linda is caring for a client with head injury and monitoring the client with decerebrate posturing. Which of the following is a characteristic of this type of posturing? A. Upper extremity flexion with lower extremity flexion B. Upper extremity flexion with lower extremity extension C. Extension of the extremities after a stimulus D. Flexion of the extremities after stimulus 7. A female client is taking Cascara Sagrada. Nurse Betty informs the client that the following maybe experienced as side effects of this medication: A. GI bleeding B. Peptic ulcer disease C. Abdominal cramps D. Partial bowel obstruction 8. Dr. Marquez orders a continuous intravenous nitroglycerin infusion for the client suffering from myocardial infarction. Which of the following is the most essential nursing action? A. Monitoring urine output frequently B. Monitoring blood pressure every 4 hours C. Obtaining serum potassium levels daily D. Obtaining infusion pump for the medication 9. During the second day of hospitalization of the client after a Myocardial Infarction. Which of the following is an expected outcome? A. Able to perform self-care activities without pain B. Severe chest pain C. Can recognize the risk factors of Myocardial Infarction D. Can Participate in cardiac rehabilitation walking program 10. A 68-year-old client is diagnosed with a right-sided brain attack and is admitted to the hospital. In caring for this client, the nurse should plan to: A. Application of elastic stockings to prevent flaccid by muscle B. Use hand roll and extend the left upper extremity on a pillow to prevent contractions C. Use a bed cradle to prevent dorsiflexion of feet D. Do passive range of motion exercise 11. Nurse Liza is assigned to care for a client who has returned to the nursing unit after left nephrectomy. Nurse Liza’s highest priority would be… A. Hourly urine output B. Temperature C. Able to turn side to side D. Able to sips clear liquid 12. A 64-year-old male client with a long history of cardiovascular problem including hypertension and angina is to be scheduled for cardiac catheterization. During pre-cardiac catheterization teaching, Nurse Cherry should inform the client that the primary purpose of the procedure is….. A. To determine the existence of CHD B. To visualize the disease process in the coronary arteries C. To obtain the heart chambers pressure D. To measure oxygen content of different heart chambers 13. During the first several hours after a cardiac catheterization, it would be most essential for nurse Cherry to… A. Elevate clients bed at 45° B. Instruct the client to cough and deep breathe every 2 hours C. Frequently monitor client’s apical pulse and blood pressure D. Monitor clients temperature every hour 14. Kate who has undergone mitral valve replacement suddenly experiences continuous bleeding from the surgical incision during postoperative period. Which of the following pharmaceutical agents should Nurse Aiza prepare to administer to Kate? A. Protamine Sulfate B. Quinidine Sulfate C. Vitamin C D. Coumadin 15. In reducing the risk of endocarditis, good dental care is an important measure. To promote good dental care in client with mitral stenosis in teaching plan should include proper use of… A. Dental floss B. Electric toothbrush C. Manual toothbrush D. Irrigation device 16. Among the following signs and symptoms, which would most likely be present in a client with mitral regurgitation? A. Altered level of consciousness B. Exertional Dyspnea C. Increase creatine phosphokinase concentration D. Chest pain 17. Kris with a history of chronic infection of the urinary system complains of urinary frequency and burning sensation. To figure out whether the current problem is of renal origin, the nurse should assess whether the client has discomfort or pain in the… A. Urinary meatus B. Pain in the Labium C. Suprapubic area D. Right or left costovertebral angle 18. Nurse Perry is evaluating the renal function of a male client. After documenting urine volume and characteristics, Nurse Perry assesses which signs as the best indicator of renal function. A. Blood pressure B. Consciousness C. Distension of the bladder D. Pulse rate 19. John suddenly experiences a seizure, and Nurse Gina notice that John exhibits uncontrollable jerking movements. Nurse Gina documents that John experienced which type of seizure? A. Tonic seizure B. Absence seizure C. Myoclonic seizure D. Clonic seizure 20. Smoking cessation is critical strategy for the client with Buerger’s disease, Nurse Jasmin anticipates that the male client will go home with a prescription for which medication? A. Paracetamol B. Ibuprofen C. Nitroglycerin D. Nicotine (Nicotrol) 21. Nurse Lilly has been assigned to a client with Raynaud’s disease. Nurse Lilly realizes that the etiology of the disease is unknown but it is characterized by: A. Episodic vasospastic disorder of capillaries B. Episodic vasospastic disorder of small veins C. Episodic vasospastic disorder of the aorta D. Episodic vasospastic disorder of the small arteries 22. Nurse Jamie should explain to male client with diabetes that self-monitoring of blood glucose is preferred to urine glucose testing because… A. More accurate B. Can be done by the client C. It is easy to perform D. It is not influenced by drugs 23. Jessie weighed 210 pounds on admission to the hospital. After 2 days of diuretic therapy, Jessie weighs 205.5 pounds. The nurse could estimate the amount of fluid Jessie has lost… A. 0.3 L B. 1.5 L C. 2.0 L D. 3.5 L 24. Nurse Donna is aware that the shift of body fluids associated with Intravenous administration of albumin occurs in the process of: A. Osmosis B. Diffusion C. Active transport D. Filtration 25. Myrna a 52-year-old client with a fractured left tibia has a long leg cast and she is using crutches to ambulate. Nurse Joy assesses for which sign and symptom that indicates complication associated with crutch walking? A. Left leg discomfort B. Weak biceps brachii C. Triceps muscle spasm D. Forearm weakness 26. Which of the following statements should the nurse teach the neutropenic client and his family to avoid? A. Performing oral hygiene after every meal B. Using suppositories or enemas C. Performing perineal hygiene after each bowel movement D. Using a filter mask 27. A female client is experiencing painful and rigid abdomen and is diagnosed with perforated peptic ulcer. A surgery has been scheduled and a nasogastric tube is inserted. The nurse should place the client before surgery in A. Sims position B. Supine position C. Semi-fowlers position D. Dorsal recumbent position 28. Which nursing intervention ensures adequate ventilating exchange after surgery? A. Remove the airway only when client is fully conscious B. Assess for hypoventilation by auscultating the lungs C. Position client laterally with the neck extended D. Maintain humidified oxygen via nasal cannula 29. George who has undergone thoracic surgery has chest tube connected to a water-seal drainage system attached to suction. Presence of excessive bubbling is identified in water-seal chamber, the nurse should… A. “Strip” the chest tube catheter B. Check the system for air leaks C. Recognize the system is functioning correctly D. Decrease the amount of suction pressure 30. A client who has been diagnosed with hypertension is being taught to restrict intake of sodium. The nurse would know that the teachings are effective if the client states that… A. I can eat celery sticks and carrots B. I can eat broiled scallops C. I can eat shredded wheat cereal D. I can eat spaghetti on rye bread 31. A male client with a history of cirrhosis and alcoholism is admitted with severe dyspnea resulted to ascites. The nurse should be aware that the ascites is most likely the result of increased… A. Pressure in the portal vein B. Production of serum albumin C. Secretion of bile salts D. Interstitial osmotic pressure 32. A newly admitted client is diagnosed with Hodgkin’s disease undergoes an excisional cervical lymph node biopsy under local anesthesia. What does the nurse assess first after the procedure? A. Vital signs B. Incision site C. Airway D. Level of consciousness 33. A client has 15% blood loss. Which of the following nursing assessment findings indicates hypovolemic shock? A. Systolic blood pressure less than 90mm Hg B. Pupils unequally dilated C. Respiratory rate of 4 breath/min D. Pulse rate less than 60 bpm 34. Nurse Lucy is planning to give preoperative teaching to a client who will be undergoing rhinoplasty. Which of the following should be included? A. Results of the surgery will be immediately noticeable postoperatively B. Normal saline nose drops will need to be administered preoperatively C. After surgery, nasal packing will be in place 8 to 10 days D. Aspirin-containing medications should not be taken 14 days before surgery 35. Paul is admitted to the hospital due to metabolic acidosis caused by Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). The nurse prepares which of the following medications as an initial treatment for this problem? A. Regular insulin B. Potassium C. Sodium bicarbonate D. Calcium gluconate 36. Dr. Marquez tells a client that an increased intake of foods that are rich in Vitamin E and beta-carotene are important for healthier skin. The nurse teaches the client that excellent food sources of both of these substances are: A. Fish and fruit jam B. Oranges and grapefruit C. Carrots and potatoes D. Spinach and mangoes 37. A client has Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). The nurse should teach the client that after every meals, the client should… A. Rest in sitting position B. Take a short walk C. Drink plenty of water D. Lie down at least 30 minutes 38. After gastroscopy, an adaptation that indicates major complication would be: A. Nausea and vomiting B. Abdominal distention C. Increased GI motility D. Difficulty in swallowing 39. A client who has undergone a cholecystectomy asks the nurse whether there are any dietary restrictions that must be followed. Nurse Hilary would recognize that the dietary teaching was well understood when the client tells a family member that: A. “Most people need to eat a high protein diet for 12 months after surgery” B. “I should not eat those foods that upset me before the surgery” C. “I should avoid fatty foods as long as I live” D. “Most people can tolerate regular diet after this type of surgery” 40. Nurse Rachel teaches a client who has been recently diagnosed with hepatitis A about untoward signs and symptoms related to Hepatitis that may develop. The one that should be reported immediately to the physician is: A. Restlessness B. Yellow urine C. Nausea D. Clay-colored stools 41. Which of the following antituberculosis drugs can damage the 8th cranial nerve? A. Isoniazid (INH) B. Para Aminosalicylic acid (PAS) C. Ethambutol hydrochloride (Myambutol) D. Streptomycin 42. The client asks Nurse Annie the causes of peptic ulcer. Nurse Annie responds that recent research indicates that peptic ulcers are the result of which of the following: A. Genetic defect in gastric mucosa B. Stress C. Diet high in fat D. Helicobacter pylori infection 43. Ryan has undergone subtotal gastrectomy. The nurse should expect that nasogastric tube drainage will be what color for about 12 to 24 hours after surgery? A. Bile green B. Bright red C. Cloudy white D. Dark brown 44. Nurse Joan is assigned to come for client who has just undergone eye surgery. Nurse Joan plans to teach the client activities that are permitted during the postoperative period. Which of the following is best recommended for the client? A. Watching circus B. Bending over C. Watching TV D. Lifting objects 45. A client suffered from a lower leg injury and seeks treatment in the emergency room. There is a prominent deformity to the lower aspect of the leg, and the injured leg appears shorter than the other leg. The affected leg is painful, swollen and beginning to become ecchymotic. The nurse interprets that the client is experiencing: A. Fracture B. Strain C. Sprain D. Contusion 46. Nurse Jenny is instilling an otic solution into an adult male client left ear. Nurse Jenny avoids doing which of the following as part of the procedure A. Pulling the auricle backward and upward B. Warming the solution to room temperature C. Pacing the tip of the dropper on the edge of ear canal D. Placing client in side lying position 47. Nurse Bea should instruct the male client with an ileostomy to report immediately which of the following symptom? A. Absence of drainage from the ileostomy for 6 or more hours B. Passage of liquid stool in the stoma C. Occasional presence of undigested food D. A temperature of 37.6 °C 48. Jerry has diagnosed with appendicitis. He develops a fever, hypotension, and tachycardia. The nurse suspects which of the following complications? A. Intestinal obstruction B. Peritonitis C. Bowel ischemia D. Deficient fluid volume 49. Which of the following compilations should the nurse carefully monitors a client with acute pancreatitis? A. Myocardial Infarction B. Cirrhosis C. Peptic ulcer D. Pneumonia 50. Which of the following symptoms during the icteric phase of viral hepatitis should the nurse expect the client to inhibit? A. Watery stool B. Yellow sclera C. Tarry stool D. Shortness of breath NCLEX Practice Exam 16 (50 Questions) 1. Marco who was diagnosed with brain tumor was scheduled for craniotomy. In preventing the development of cerebral edema after surgery, the nurse should expect the use of: A. Diuretics B. Antihypertensive C. Steroids D. Anticonvulsants 2. Halfway through the administration of blood, the female client complains of lumbar pain. After stopping the infusion Nurse Hazel should: A. Increase the flow of normal saline B. Assess the pain further C. Notify the blood bank D. Obtain vital signs. 3. Nurse Maureen knows that the positive diagnosis of HIV infection is made based on which of the following: A. A history of high-risk sexual behaviors. B. Positive ELISA and western blot tests C. Identification of an associated opportunistic infection D. Evidence of extreme weight loss and high fever 4. Nurse Maureen is aware that a client who has been diagnosed with chronic renal failure recognizes an adequate amount of high-biologic-value protein when the food the client selected from the menu was: A. Raw carrots B. Apple juice C. Whole wheat bread D. Cottage cheese 5. Kenneth who was diagnosed with uremic syndrome has the potential to develop complications. Which among the following complications should the nurse anticipates: A. Flapping hand tremors B. An elevated hematocrit level C. Hypotension D. Hypokalemia 6. A client is admitted to the hospital with benign prostatic hyperplasia, the nurse most relevant assessment would be: A. Flank pain radiating in the groin B. Distention of the lower abdomen C. Perineal edema D. Urethral discharge 7. A client has undergone with penile implant. After 24 hrs of surgery, the client’s scrotum was edematous and painful. The nurse should: A. Assist the client with sitz bath B. Apply war soaks in the scrotum C. Elevate the scrotum using a soft support D. Prepare for a possible incision and drainage 8. Nurse Hazel receives emergency laboratory results for a client with chest pain and immediately informs the physician. An increased myoglobin level suggests which of the following? A. Liver disease B. Myocardial damage C. Hypertension D. Cancer 9. Nurse Maureen would expect a client with mitral stenosis would demonstrate symptoms associated with congestion in the: A. Right atrium B. Superior vena cava C. Aorta D. Pulmonary 10. A client has been diagnosed with hypertension. The nurse priority nursing diagnosis would be: A. Ineffective health maintenance B. Impaired skin integrity C. Deficient fluid volume D. Pain 11. Nurse Hazel teaches the client with angina about common expected side effects of nitroglycerin including: A. high blood pressure B. stomach cramps C. headache D. shortness of breath 12. The following are lipid abnormalities. Which of the following is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and PVD? A. High levels of low-density lipid (LDL) cholesterol B. High levels of high-density lipid (HDL) cholesterol C. Low concentration triglycerides D. Low levels of LDL cholesterol. 13. Which of the following represents a significant risk immediately after surgery for repair of aortic aneurysm? A. Potential wound infection B. Potential ineffective coping C. Potential electrolyte balance D. Potential alteration in renal perfusion 14. Nurse Josie should instruct the client to eat which of the following foods to obtain the best supply of Vitamin B12? A. dairy products B. vegetables C. Grains D. Broccoli 15. Karen has been diagnosed with aplastic anemia. The nurse monitors for changes in which of the following physiologic functions? A. Bowel function B. Peripheral sensation C. Bleeding tendencies D. Intake and output 16. Lydia is scheduled for elective splenectomy. Before the client goes to surgery, the nurse in charge final assessment would be: A. signed consent B. vital signs C. name band D. empty bladder 17. What is the peak age range for acquiring acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)? A. 4 to 12 years. B. 20 to 30 years C. 40 to 50 years D. 60 60 70 years 18. Marie with acute lymphocytic leukemia suffers from nausea and headache. These clinical manifestations may indicate all of the following except: A. effects of radiation B. chemotherapy side effects C. meningeal irritation D. gastric distension 19. A client has been diagnosed with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC). Which of the following is contraindicated with the client? A. Administering Heparin B. Administering Coumadin C. Treating the underlying cause D. Replacing depleted blood products 20. Which of the following findings is the best indication that fluid replacement for the client with hypovolemic shock is adequate? A. Urine output greater than 30ml/hr B. Respiratory rate of 21 breaths/minute C. Diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmHg D. Systolic blood pressure greater than 110 mmHg 21. Which of the following signs and symptoms would Nurse Maureen include in teaching plan as an early manifestation of laryngeal cancer? A. Stomatitis B. Airway obstruction C. Hoarseness D. Dysphagia 22. Karina a client with myasthenia gravis is to receive immunosuppressive therapy. The nurse understands that this therapy is effective because it: A. Promotes the removal of antibodies that impair the transmission of impulses B. Stimulates the production of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. C. Decreases the production of autoantibodies that attack the acetylcholine receptors. D. Inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. 23. A female client is receiving IV Mannitol. An assessment specific to safe administration of the said drug is: A. Vital signs q4h B. Weighing daily C. Urine output hourly D. Level of consciousness q4h 24. Patricia a 20-year-old college student with diabetes mellitus requests additional information about the advantages of using a pen-like insulin delivery devices. The nurse explains that the advantages of these devices over syringes include: A. Accurate dose delivery B. Shorter injection time C. Lower cost with reusable insulin cartridges D. Use of smaller gauge needle. 25. A male client’s left tibia was fractured in an automobile accident, and a cast is applied. To assess for damage to major blood vessels from the fracture tibia, the nurse in charge should monitor the client for: A. Swelling of the left thigh B. Increased skin temperature of the foot C. Prolonged reperfusion of the toes after blanching D. Increased blood pressure 26. After a long leg cast is removed, the male client should: A. Cleanse the leg by scrubbing with a brisk motion B. Put leg through full range of motion twice daily C. Report any discomfort or stiffness to the physician D. Elevate the leg when sitting for long periods of time. 27. While performing a physical assessment of a male client with gout of the great toe, Nurse Vivian should assess for additional tophi (urate deposits) on the: A. Buttocks B. Ears C. Face D. Abdomen 28. Nurse Katrina would recognize that the demonstration of crutch walking with tripod gait was understood when the client places weight on the: A. Palms of the hands and axillary regions B. Palms of the hand C. Axillary regions D. Feet, which are set apart 29. Mang Jose with rheumatoid arthritis states, “the only time I am without pain is when I lie in bed perfectly still”. During the convalescent stage, the nurse in charge with Mang Jose should encourage: A. Active joint flexion and extension B. Continued immobility until pain subsides C. Range of motion exercises twice daily D. Flexion exercises three times daily 30. A male client has undergone spinal surgery, the nurse should: A. Observe the client’s bowel movement and voiding patterns B. Log-roll the client to prone position C. Assess the client’s feet for sensation and circulation D. Encourage client to drink plenty of fluids 31. Marina with acute renal failure moves into the diuretic phase after one week of therapy. During this phase the client must be assessed for signs of developing: A. Hypovolemia B. renal failure C. metabolic acidosis D. hyperkalemia 32. Nurse Judith obtains a specimen of clear nasal drainage from a client with a head injury. Which of the following tests differentiates mucus from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? A. Protein B. Specific gravity C. Glucose D. Microorganism 33. A 22-year-old client suffered from his first tonic-clonic seizure. Upon awakening, the client asks the nurse, “What caused me to have a seizure? Which of the following would the nurse include in the primary cause of tonic-clonic seizures in adults more the 20 years? A. Electrolyte imbalance B. Head trauma C. Epilepsy D. Congenital defect 34. What is the priority nursing assessment in the first 24 hours after admission of the client with thrombotic CVA? A. Pupil size and pupillary response B. cholesterol level C. Echocardiogram D. Bowel sounds 35. Nurse Linda is preparing a client with multiple sclerosis for discharge from the hospital to home. Which of the following instruction is most appropriate? A. “Practice using the mechanical aids that you will need when future disabilities arise”. B. “Follow good health habits to change the course of the disease”. C. “Keep active, use stress reduction strategies, and avoid fatigue”. D. “You will need to accept the necessity for a quiet and inactive lifestyle”. 36. The nurse is aware the early indicator of hypoxia in the unconscious client is: A. Cyanosis B. Increased respirations C. Hypertension D. Restlessness 37. A client is experiencing spinal shock. Nurse Myrna should expect the function of the bladder to be which of the following? A. Normal B. Atonic C. Spastic D. Uncontrolled 38. Which of the following stage is the carcinogen irreversible? A. Progression stage B. Initiation stage C. Regression stage D. Promotion stage 39. Among the following components thorough pain assessment, which is the most significant? A. Effect B. Cause C. Causing factors D. Intensity 40. A 65 year old female is experiencing flare-up of pruritus. Which of the client’s action could aggravate the cause of flare-ups? A. Sleeping in cool and humidified environment B. Daily baths with fragrant soap C. Using clothes made from 100% cotton D. Increasing fluid intake 41. Atropine sulfate (Atropine) is indicated in all but one of the following client? A. A client with high blood B. A client with bowel obstruction C. A client with glaucoma D. A client with U.T.I. 42. Among the following clients, which among them is high risk for potential hazards from the surgical experience? A. 67-year-old client B. 49-year-old client C. 33-year-old client D. 15-year-old client 43. Nurse Jon assesses vital signs on a client undergone epidural anesthesia. Which of the following would the nurse assess next? A. Headache B. Bladder distension C. Dizziness D. Ability to move legs 44. Nurse Katrina should anticipate that all of the following drugs may be used in the attempt to control the symptoms of Ménière’s Disease except: A. Antiemetics B. Diuretics C. Antihistamines D. Glucocorticoids 45. Which of the following complications associated with tracheostomy tube? A. Increased cardiac output B. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) C. Increased blood pressure D. Damage to laryngeal nerves 46. Nurse Faith should recognize that fluid shift in an client with burn injury results from increase in the: A. Total volume of circulating whole blood B. Total volume of intravascular plasma C. Permeability of capillary walls D. Permeability of kidney tubules 47. An 83-year-old woman has several ecchymotic areas on her right arm. The bruises are probably caused by: A. increased capillary fragility and permeability B. increased blood supply to the skin C. self-inflicted injury D. elder abuse 48. Nurse Anna is aware that early adaptation of client with renal carcinoma is: A. nausea and vomiting B. flank pain C. weight gain D. intermittent hematuria 49. A male client with tuberculosis asks Nurse Brian how long the chemotherapy must be continued. Nurse Brian’s accurate reply would be: A. 1 to 3 weeks B. 6 to 12 months C. 3 to 5 months D. 3 years and more 50. A client has undergone laryngectomy. The immediate nursing priority would be: A. Keep trachea free of secretions B. Monitor for signs of infection C. Provide emotional support D. Promote means of communication 1. Marco who was diagnosed with brain tumor was scheduled for craniotomy. In preventing the development of cerebral edema after surgery, the nurse should expect the use of: A. Diuretics B. Antihypertensive C. Steroids D. Anticonvulsants 2. Halfway through the administration of blood, the female client complains of lumbar pain. After stopping the infusion Nurse Hazel should: A. Increase the flow of normal saline B. Assess the pain further C. Notify the blood bank D. Obtain vital signs. 3. Nurse Maureen knows that the positive diagnosis of HIV infection is made based on which of the following: A. A history of high-risk sexual behaviors. B. Positive ELISA and western blot tests C. Identification of an associated opportunistic infection D. Evidence of extreme weight loss and high fever 4. Nurse Maureen is aware that a client who has been diagnosed with chronic renal failure recognizes an adequate amount of high-biologic-value protein when the food the client selected from the menu was: A. Raw carrots B. Apple juice C. Whole wheat bread D. Cottage cheese 5. Kenneth who was diagnosed with uremic syndrome has the potential to develop complications. Which among the following complications should the nurse anticipates: A. Flapping hand tremors B. An elevated hematocrit level C. Hypotension D. Hypokalemia 6. A client is admitted to the hospital with benign prostatic hyperplasia, the nurse most relevant assessment would be: A. Flank pain radiating in the groin B. Distention of the lower abdomen C. Perineal edema D. Urethral discharge 7. A client has undergone with penile implant. After 24 hrs of surgery, the client’s scrotum was edematous and painful. The nurse should: A. Assist the client with sitz bath B. Apply war soaks in the scrotum C. Elevate the scrotum using a soft support D. Prepare for a possible incision and drainage 8. Nurse Hazel receives emergency laboratory results for a client with chest pain and immediately informs the physician. An increased myoglobin level suggests which of the following? A. Liver disease B. Myocardial damage C. Hypertension D. Cancer 9. Nurse Maureen would expect a client with mitral stenosis would demonstrate symptoms associated with congestion in the: A. Right atrium B. Superior vena cava C. Aorta D. Pulmonary 10. A client has been diagnosed with hypertension. The nurse priority nursing diagnosis would be: A. Ineffective health maintenance B. Impaired skin integrity C. Deficient fluid volume D. Pain 11. Nurse Hazel teaches the client with angina about common expected side effects of nitroglycerin including: A. high blood pressure B. stomach cramps C. headache D. shortness of breath 12. The following are lipid abnormalities. Which of the following is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and PVD? A. High levels of low-density lipid (LDL) cholesterol B. High levels of high-density lipid (HDL) cholesterol C. Low concentration triglycerides D. Low levels of LDL cholesterol. 13. Which of the following represents a significant risk immediately after surgery for repair of aortic aneurysm? A. Potential wound infection B. Potential ineffective coping C. Potential electrolyte balance D. Potential alteration in renal perfusion 14. Nurse Josie should instruct the client to eat which of the following foods to obtain the best supply of Vitamin B12? A. dairy products B. vegetables C. Grains D. Broccoli 15. Karen has been diagnosed with aplastic anemia. The nurse monitors for changes in which of the following physiologic functions? A. Bowel function B. Peripheral sensation C. Bleeding tendencies D. Intake and output 16. Lydia is scheduled for elective splenectomy. Before the client goes to surgery, the nurse in charge final assessment would be: A. signed consent B. vital signs C. name band D. empty bladder 17. What is the peak age range for acquiring acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)? A. 4 to 12 years. B. 20 to 30 years C. 40 to 50 years D. 60 60 70 years 18. Marie with acute lymphocytic leukemia suffers from nausea and headache. These clinical manifestations may indicate all of the following except: A. effects of radiation B. chemotherapy side effects C. meningeal irritation D. gastric distension 19. A client has been diagnosed with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC). Which of the following is contraindicated with the client? A. Administering Heparin B. Administering Coumadin C. Treating the underlying cause D. Replacing depleted blood products 20. Which of the following findings is the best indication that fluid replacement for the client with hypovolemic shock is adequate? A. Urine output greater than 30ml/hr B. Respiratory rate of 21 breaths/minute C. Diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mmHg D. Systolic blood pressure greater than 110 mmHg 21. Which of the following signs and symptoms would Nurse Maureen include in teaching plan as an early manifestation of laryngeal cancer? A. Stomatitis B. Airway obstruction C. Hoarseness D. Dysphagia 22. Karina a client with myasthenia gravis is to receive immunosuppressive therapy. The nurse understands that this therapy is effective because it: A. Promotes the removal of antibodies that impair the transmission of impulses B. Stimulates the production of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. C. Decreases the production of autoantibodies that attack the acetylcholine receptors. D. Inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. 23. A female client is receiving IV Mannitol. An assessment specific to safe administration of the said drug is: A. Vital signs q4h B. Weighing daily C. Urine output hourly D. Level of consciousness q4h 24. Patricia a 20-year-old college student with diabetes mellitus requests additional information about the advantages of using a pen-like insulin delivery devices. The nurse explains that the advantages of these devices over syringes include: A. Accurate dose delivery B. Shorter injection time C. Lower cost with reusable insulin cartridges D. Use of smaller gauge needle. 25. A male client’s left tibia was fractured in an automobile accident, and a cast is applied. To assess for damage to major blood vessels from the fracture tibia, the nurse in charge should monitor the client for: A. Swelling of the left thigh B. Increased skin temperature of the foot C. Prolonged reperfusion of the toes after blanching D. Increased blood pressure 26. After a long leg cast is removed, the male client should: A. Cleanse the leg by scrubbing with a brisk motion B. Put leg through full range of motion twice daily C. Report any discomfort or stiffness to the physician D. Elevate the leg when sitting for long periods of time. 27. While performing a physical assessment of a male client with gout of the great toe, Nurse Vivian should assess for additional tophi (urate deposits) on the: A. Buttocks B. Ears C. Face D. Abdomen 28. Nurse Katrina would recognize that the demonstration of crutch walking with tripod gait was understood when the client places weight on the: A. Palms of the hands and axillary regions B. Palms of the hand C. Axillary regions D. Feet, which are set apart 29. Mang Jose with rheumatoid arthritis states, “the only time I am without pain is when I lie in bed perfectly still”. During the convalescent stage, the nurse in charge with Mang Jose should encourage: A. Active joint flexion and extension B. Continued immobility until pain subsides C. Range of motion exercises twice daily D. Flexion exercises three times daily 30. A male client has undergone spinal surgery, the nurse should: A. Observe the client’s bowel movement and voiding patterns B. Log-roll the client to prone position C. Assess the client’s feet for sensation and circulation D. Encourage client to drink plenty of fluids 31. Marina with acute renal failure moves into the diuretic phase after one week of therapy. During this phase the client must be assessed for signs of developing: A. Hypovolemia B. renal failure C. metabolic acidosis D. hyperkalemia 32. Nurse Judith obtains a specimen of clear nasal drainage from a client with a head injury. Which of the following tests differentiates mucus from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? A. Protein B. Specific gravity C. Glucose D. Microorganism 33. A 22-year-old client suffered from his first tonic-clonic seizure. Upon awakening, the client asks the nurse, “What caused me to have a seizure? Which of the following would the nurse include in the primary cause of tonic-clonic seizures in adults more the 20 years? A. Electrolyte imbalance B. Head trauma C. Epilepsy D. Congenital defect 34. What is the priority nursing assessment in the first 24 hours after admission of the client with thrombotic CVA? A. Pupil size and pupillary response B. cholesterol level C. Echocardiogram D. Bowel sounds 35. Nurse Linda is preparing a client with multiple sclerosis for discharge from the hospital to home. Which of the following instruction is most appropriate? A. “Practice using the mechanical aids that you will need when future disabilities arise”. B. “Follow good health habits to change the course of the disease”. C. “Keep active, use stress reduction strategies, and avoid fatigue”. D. “You will need to accept the necessity for a quiet and inactive lifestyle”. 36. The nurse is aware the early indicator of hypoxia in the unconscious client is: A. Cyanosis B. Increased respirations C. Hypertension D. Restlessness 37. A client is experiencing spinal shock. Nurse Myrna should expect the function of the bladder to be which of the following? A. Normal B. Atonic C. Spastic D. Uncontrolled 38. Which of the following stage is the carcinogen irreversible? A. Progression stage B. Initiation stage C. Regression stage D. Promotion stage 39. Among the following components thorough pain assessment, which is the most significant? A. Effect B. Cause C. Causing factors D. Intensity 40. A 65 year old female is experiencing flare-up of pruritus. Which of the client’s action could aggravate the cause of flare-ups? A. Sleeping in cool and humidified environment B. Daily baths with fragrant soap C. Using clothes made from 100% cotton D. Increasing fluid intake 41. Atropine sulfate (Atropine) is indicated in all but one of the following client? A. A client with high blood B. A client with bowel obstruction C. A client with glaucoma D. A client with U.T.I. 42. Among the following clients, which among them is high risk for potential hazards from the surgical experience? A. 67-year-old client B. 49-year-old client C. 33-year-old client D. 15-year-old client 43. Nurse Jon assesses vital signs on a client undergone epidural anesthesia. Which of the following would the nurse assess next? A. Headache B. Bladder distension C. Dizziness D. Ability to move legs 44. Nurse Katrina should anticipate that all of the following drugs may be used in the attempt to control the symptoms of Ménière’s Disease except: A. Antiemetics B. Diuretics C. Antihistamines D. Glucocorticoids 45. Which of the following complications associated with tracheostomy tube? A. Increased cardiac output B. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) C. Increased blood pressure D. Damage to laryngeal nerves 46. Nurse Faith should recognize that fluid shift in an client with burn injury results from increase in the: A. Total volume of circulating whole blood B. Total volume of intravascular plasma C. Permeability of capillary walls D. Permeability of kidney tubules 47. An 83-year-old woman has several ecchymotic areas on her right arm. The bruises are probably caused by: A. increased capillary fragility and permeability B. increased blood supply to the skin C. self-inflicted injury D. elder abuse 48. Nurse Anna is aware that early adaptation of client with renal carcinoma is: A. nausea and vomiting B. flank pain C. weight gain D. intermittent hematuria 49. A male client with tuberculosis asks Nurse Brian how long the chemotherapy must be continued. Nurse Brian’s accurate reply would be: A. 1 to 3 weeks B. 6 to 12 months C. 3 to 5 months D. 3 years and more 50. A client has undergone laryngectomy. The immediate nursing priority would be: A. Keep trachea free of secretions B. Monitor for signs of infection C. Provide emotional support D. Promote means of communication NCLEX Practice Exam 17 (50 Questions) 1. A client is scheduled for insertion of an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter. Nurse Patricia consults the physician about withholding which regularly scheduled medication on the day before the surgery? A. Potassium Chloride B. Warfarin Sodium C. Furosemide D. Docusate 2. A nurse is planning to assess the corneal reflex on unconscious client. Which of the following is the safest stimulus to touch the client’s cornea? A. Cotton buds B. Sterile glove C. Sterile tongue depressor D. Wisp of cotton 3. A female client develops an infection at the catheter insertion site. The nurse in charge uses the term “iatrogenic” when describing the infection because it resulted from: A. Client’s developmental level B. Therapeutic procedure C. Poor hygiene D. Inadequate dietary patterns 4. Nurse Carol is assessing a client with Parkinson’s disease. The nurse recognizes bradykinesia when the client exhibits: A. Intentional tremor B. Paralysis of limbs C. Muscle spasm D. Lack of spontaneous movement 5. A client who suffered from automobile accident complains of seeing frequent flashes of light. The nurse should expect: A. Myopia B. Detached retina C. Glaucoma D. Scleroderma 6. Kate with severe head injury is being monitored by the nurse for increasing intracranial pressure (ICP). Which finding should be most indicative sign of increasing intracranial pressure? A. Intermittent tachycardia B. Polydipsia C. Tachypnea D. Increased restlessness 7. A hospitalized client had a tonic-clonic seizure while walking down the hall. During the seizure the nurse priority should be: A. Hold the client’s arms and leg firmly B. Place the client immediately on soft surface C. Protects the client’s head from injury D. Attempt to insert a tongue depressor between the client’s teeth 8. A client has undergone right pneumonectomy. When turning the client, the nurse should plan to position the client either: A. Right side-lying position or supine B. High Fowler’s position C. Right or left side lying position D. Low Fowler’s position 9. Nurse Jenny should caution a female client who is sexually active in taking Isoniazid (INH) because the drug has which of the following side effects? A. Prevents ovulation B. Has a mutagenic effect on ova C. Decreases the effectiveness of oral contraceptives D. Increases the risk of vaginal infection 10. A client has undergone gastrectomy. Nurse Jovy is aware that the best position for the client is: A. Left side-lying B. Low fowler’s C. Prone D. Supine 11. During the initial postoperative period of the client’s stoma. The nurse evaluates which of the following observations should be reported immediately to the physician? A. Stoma is dark red to purple B. Stoma oozes a small amount of blood C. Stoma is slightly edematous D. Stoma does not expel stool 12. Kate which has diagnosed with ulcerative colitis is following physician’s order for bed rest with bathroom privileges. What is the rationale for this activity restriction? A. Prevent injury B. Promote rest and comfort C. Reduce intestinal peristalsis D. Conserve energy 13. Nurse KC should regularly assess the client’s ability to metabolize the total parenteral nutrition (TPN) solution adequately by monitoring the client for which of the following signs: A. Hyperglycemia B. Hypoglycemia C. Hypertension D. Elevate blood urea nitrogen concentration 14. A female client has acute pancreatitis. Which of the following signs and symptoms would the nurse expect to see? A. Constipation B. Hypertension C. Ascites D. Jaundice 15. A client is suspected to develop tetany after a subtotal thyroidectomy. Which of the following symptoms might indicate tetany? A. Tingling in the fingers B. Pain in hands and feet C. Tension on the suture lines D. Bleeding on the back of the dressing 16. A 58-year-old woman has newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The nurse is aware that the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism include: A. Diarrhea B. Vomiting C. Tachycardia D. Weight gain 17. A client has undergone an ileal conduit, the nurse in charge should closely monitor the client for occurrence of which of the following complications related to pelvic surgery? A. Ascites B. Thrombophlebitis C. Inguinal hernia D. Peritonitis 18. Dr. Marquez is about to defibrillate a client in ventricular fibrillation and says in a loud voice “clear”. What should be the action of the nurse? A. Places conductive gel pads for defibrillation on the client’s chest B. Turn off the mechanical ventilator C. Shuts off the client’s IV infusion D. Steps away from the bed and make sure all others have done the same 19. A client has been diagnosed with glomerulonephritis complains of thirst. The nurse should offer: A. Juice B. Ginger ale C. Milkshake D. Hard candy 20. A client with acute renal failure is aware that the most serious complication of this condition is: A. Constipation B. Anemia C. Infection D. Platelet dysfunction 21. Nurse Karen is caring for clients in the OR. The nurse is aware that the last physiologic function that the client loss during the induction of anesthesia is: A. Consciousness B. Gag reflex C. Respiratory movement D. Corneal reflex 22. The nurse is assessing a client with pleural effusion. The nurse expects to find: A. Deviation of the trachea towards the involved side B. Reduced or absent of breath sounds at the base of the lung C. Moist crackles at the posterior of the lungs D. Increased resonance with percussion of the involved area 23. A client admitted with newly diagnosed with Hodgkin’s disease. Which of the following would the nurse expect the client to report? A. Lymph node pain B. Weight gain C. Night sweats D. Headache 24. A client has suffered from fall and sustained a leg injury. Which appropriate question would the nurse ask the client to help determine if the injury caused fracture? A. “Is the pain sharp and continuous?” B. “Is the pain dull ache?” C. “Does the discomfort feel like a cramp?” D. “Does the pain feel like the muscle was stretched?” 25. The Nurse is assessing the client’s casted extremity for signs of infection. Which of the following findings is indicative of infection? A. Edema B. Weak distal pulse C. Coolness of the skin D. Presence of “hot spot” on the cast 26. Nurse Rhia is performing an otoscopic examination on a female client with a suspected diagnosis of mastoiditis. Nurse Rhia would expect to note which of the following if this disorder is present? A. Transparent tympanic membrane B. Thick and immobile tympanic membrane C. Pearly colored tympanic membrane D. Mobile tympanic membrane 27. Nurse Jocelyn is caring for a client with nasogastric tube that is attached to low suction. Nurse Jocelyn assesses the client for symptoms of which acid-base disorder? A. Respiratory alkalosis B. Respiratory acidosis C. Metabolic acidosis D. Metabolic alkalosis 28. A male adult client has undergone a lumbar puncture to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for analysis. Which of the following values should be negative if the CSF is normal? A. Red blood cells B. White blood cells C. Insulin D. Protein 29. A client is suspected of developing diabetes insipidus. Which of the following is the most effective assessment? A. Taking vital signs every 4 hours B. Monitoring blood glucose C. Assessing ABG values every other day D. Measuring urine output hourly 30. A 58-year-old client is suffering from acute phase of rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following would the nurse in charge identify as the lowest priority of the plan of care? A. Prevent joint deformity B. Maintaining usual ways of accomplishing task C. Relieving pain D. Preserving joint function 31. Among the following, which client is autotransfusion possible? A. Client with AIDS B. Client with ruptured bowel C. Client who is in danger of cardiac arrest D. Client with wound infection 32. Which of the following is not a sign of thromboembolism? A. Edema B. Swelling C. Redness D. Coolness 33. Nurse Becky is caring for client who begins to experience seizure while in bed. Which action should the nurse implement to prevent aspiration? A. Position the client on the side with head flexed forward B. Elevate the head C. Use tongue depressor between teeth D. Loosen restrictive clothing 34. A client has undergone bone biopsy. Which nursing action should the nurse provide after the procedure? A. Administer analgesics via IM B. Monitor vital signs C. Monitor the site for bleeding, swelling and hematoma formation D. Keep area in neutral position 35. A client is suffering from low back pain. Which of the following exercises will strengthen the lower back muscle of the client? A. Tennis B. Basketball C. Diving D. Swimming 36. A client with peptic ulcer is being assessed by the nurse for gastrointestinal perforation. The nurse should monitor for: A. (+) guaiac stool test B. Slow, strong pulse C. Sudden, severe abdominal pain D. Increased bowel sounds 37. A client has undergone surgery for retinal detachment. Which of the following goal should be prioritized? A. Prevent an increase intraocular pressure B. Alleviate pain C. Maintain darkened room D. Promote low-sodium diet 38. A Client with glaucoma has been prescribed with miotics. The nurse is aware that miotics is for: A. Constricting pupil B. Relaxing ciliary muscle C. Constricting intraocular vessel D. Paralyzing ciliary muscle 39. When suctioning an unconscious client, which nursing intervention should the nurse prioritize in maintaining cerebral perfusion? A. Administer diuretics B. Administer analgesics C. Provide hygiene D. Hyperoxygenate before and after suctioning 40. When discussing breathing exercises with a postoperative client, Nurse Hazel should include which of the following teaching? A. Short frequent breaths B. Exhale with mouth open C. Exercise twice a day D. Place hand on the abdomen and feel it rise 41. Louie, with burns over 35% of the body, complains of chilling. In promoting the client’s comfort, the nurse should: A. Maintain room humidity below 40% B. Place top sheet on the client C. Limit the occurrence of drafts D. Keep room temperature at 80 degrees 42. Nurse Trish is aware that temporary heterograft (pig skin) is used to treat burns because this graft will: A. Relieve pain and promote rapid epithelialization B. Be sutured in place for better adherence C. Debride necrotic epithelium D. Concurrently used with topical antimicrobials 43. Mark has multiple abrasions and a laceration to the trunk and all four extremities says, “I can’t eat all this food”. The food that the nurse should suggest to be eaten first should be: A. Meatloaf and coffee B. Meatloaf and strawberries C. Tomato soup and apple pie D. Tomato soup and buttered bread 44. Tony returns from surgery with permanent colostomy. During the first 24 hours, the colostomy does not drain. The nurse should be aware that: A. Proper functioning of nasogastric suction B. Presurgical decrease in fluid intake C. Absence of gastrointestinal motility D. Intestinal edema following surgery 45. When teaching a client about the signs of colorectal cancer, Nurse Trish stresses that the most common complaint of persons with colorectal cancer is: A. Abdominal pain B. Hemorrhoids C. Change in caliber of stools D. Change in bowel habits 46. Louis develops peritonitis and sepsis after surgical repair of ruptured diverticulum. The nurse in charge should expect an assessment of the client to reveal: A. Tachycardia B. Abdominal rigidity C. Bradycardia D. Increased bowel sounds 47. Immediately after liver biopsy, the client is placed on the right side, the nurse is aware that this position should be maintained because it will: A. Help stop bleeding if any occurs B. Reduce the fluid trapped in the biliary ducts C. Position with greatest comfort D. Promote circulating blood volume 48. Tony was diagnosed with hepatitis A. The information from the health history that is most likely linked to hepatitis A is: A. Exposed with arsenic compounds at work B. Working as local plumber C. Working at hemodialysis clinic D. Dishwasher in restaurants 49. Nurse Trish is aware that the laboratory test result that most likely would indicate acute pancreatitis is an elevated: A. Serum bilirubin level B. Serum amylase level C. Potassium level D. Sodium level 50. Dr. Marquez orders serum electrolytes. To determine the effect of persistent vomiting, Nurse Trish should be most concerned with monitoring the: A. Chloride and sodium levels B. Phosphate and calcium levels C. Protein and magnesium levels D. Sulfate and bicarbonate levels NCLEX Practice Exam 18 (50 Questions) Mr. Duffy is admitted to the CCU with a diagnosis of R/O MI. He presented in the ER with a typical description of pain associated with an MI, and is now cold and clammy, pale and dyspneic. He has an IV of D5W running, and is complaining of chest pain. Oxygen therapy has not been started, and he is not on the monitor. He is frightened. 1. The nurse is aware of several important tasks that should all be done immediately in order to give Mr. Duffy the care he needs. Which of the following nursing interventions will relieve his current myocardial ischemia? A. Stool softeners, rest B. O2 therapy, analgesia C. Reassurance, cardiac monitoring D. Adequate fluid intake, low-fat diet 2. During the first three days that Mr. Duffy is in the CCU, a number of diagnostic blood tests are obtained. Which of the following patterns of cardiac enzyme elevation are most common following an MI? A. SGOT, CK, and LDH are all elevated immediately. B. SGOT rises 4-6 hours after infarction with CK and LDH rising slowly 24 hours later. C. CK peaks first (12-24 hours), followed by the SGOT (peaks in 24-36 hours) and then the LDH (peaks 3-4 days). D. CK peaks first and remains elevated for 1 to 2 weeks. 3. On his second day in CCU, Mr. Duffy suffers a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Considering his diagnosis, which is the most probable arrhythmia? A. atrial tachycardia B. ventricular fibrillation C. atrial fibrillation D. heart block 4. Mr. Duffy is placed on digitalis on discharge from the hospital. The nurse planning with him for his discharge should educate him as to the purpose and actions of his new medication. What should she or he teach Mr. Duffy to do at home to monitor his reaction to this medication? A. take his blood pressure B. take his radial pulse for one minute C. check his serum potassium (K) level D. weigh himself every day 5. You decide to discuss glaucoma prevention. Which of the following diagnostic tests should these clients request from their care provider? A. fluorescein stain B. Snellen’s test C. tonometry D. slit lamp 6. You also explain common eye changes associated with aging. One of these is presbyopia, which is: A. Refractive error that prevents light rays from coming to a single focus on the retina. B. Poor distant vision C. Poor near vision D. A gradual lessening of the power of accommodation 7. Some of the diabetic clients are interested in understanding what is visualized during funduscopic examination. During your discussion, you describe the macular area as: A. Head of the optic nerve, seen on the nasal side of the field, lighter in color than the retina. B. The area of central vision, seen on the temporal side of the optic disc, which is quite avascular. C. Area where the central retinal artery and vein appear on the retina. D. Reddish orange in color, sometimes stippled. 8. One of the clients has noted a raised yellow plaque on the nasal side of the conjunctiva. You explain that this is called: A. A pinguecula, which is normal slightly raised fatty structure under the conjunctiva that may gradually increase with age. B. Icterus, which may be due to liver disease. C. A pterygium, which will interfere with vision. D. Ciliary flush caused by congestion of the ciliary artery. 9. You know that all but one of the following may eventually result in uremia. Which option is not implicated? A. glomerular disease B. uncontrolled hypertension C. renal disease secondary to drugs, toxins, infections, or radiations D. all of the above 10. You did the initial assessment on Mr. Kaplan when he came to your unit. What classical signs and symptoms did you note? A. fruity-smelling breath. B. Weakness, anorexia, pruritus C. Polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia D. Ruddy complexion 11. Numerous drugs have been used on Mr. Kaplan in an attempt to stabilize him. Regarding his diagnosis and management of his drugs, you know that: A. The half-life of many drugs is decreased in uremia; thus dosage may have to be increased to be effective. B. Drug toxicity is a major concern in uremia; individualization of therapy and often a decrease in dose is essential. C. Drug therapy is not usually affected by this diagnosis D. Precautions should be taken with prescription drugs, but most OTC medications are safe for him to use. 12. The point of maximal impulse (PMI) is an important landmark in the cardiac exam. Which statement best describes the location of the PMI in the healthy adult? A. Base of the heart, 5th intercostal space, 7-9 cm to the left of the midsternal line. B. Base of the heart, 7th intercostal space, 7-9 cm to the left of the midsternal line. C. Apex of the heart, intercostal space, 7-9 cm to the left of the midsternal line. D. Apex of the heart, intercostal space, 7-9 cm to the left of the midsternal line. 13. During the physical examination of the well adult client, the health care provider auscultates the heart. When the stethoscope is placed on the 5th intercostal space along the left sternal border, which valve closure is best evaluated? A. Tricuspid B. Pulmonic C. Aortic D. Mitral 14. The pulmonic component of which heart sound is best heard at the 2nd LICS at the LSB? A. S1 B. S2 C. S3 D. S4 15. The coronary arteries furnish blood supply to the myocardium. Which of the following is a true statement relative to the coronary circulation? A. the right and left coronary arteries are the first of many branches off the ascending aorta B. blood enters the right and left coronary arteries during systole only C. the right coronary artery forms almost a complete circle around the heart, yet supplies only the right ventricle D. the left coronary artery has two main branches, the left anterior descending and left circumflex: both supply the left ventricle Sally Baker, a 40-year-old woman, is admitted to the hospital with an established diagnosis of mitral stenosis. She is scheduled for surgery to repair her mitral valve. 16. Ms. Baker has decided to have surgical correction of her stenosed valve at this time because her subjective complaints of dyspnea, hemoptysis, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea have become unmanageable. These complaints are probably due to: A. thickening of the pericardium B. right heart failure C. pulmonary hypertension D. left ventricular hypertrophy 17. On physical exam of Ms. Baker, several abnormal findings can be observed. Which of the following is not one of the usual objective findings associated with mitral stenosis? A. low-pitched rumbling diastolic murmur, precordial thrill, and parasternal lift B. small crepitant rales at the bases of the lungs C. weak, irregular pulse, and peripheral and facial cyanosis in severe disease D. chest x-ray shows left ventricular hypertrophy 18. You are seeing more clients with diagnoses of mitral valve prolapse. You know those mitral valve prolapse is usually a benign cardiac condition, but may be associated with atypical chest pain. This chest pain is probably caused by: A. ventricular ischemia B. dysfunction of the left ventricle C. papillary muscle ischemia and dysfunction D. cardiac arrhythmias 19. The most common lethal cancer in males between their fifth and seventh decades is: A. cancer of the prostate B. cancer of the lung C. cancer of the pancreas D. cancer of the bowel 20. Of the four basic cell types of lung cancer listed below, which is always associated with smoking? A. adenocarcinoma B. squamous cell carcinoma (epidermoid) C. undifferentiated carcinoma D. bronchoalveolar carcinoma 21. Chemotherapy may be used in combination with surgery in the treatment of lung cancer. Special nursing considerations with chemotherapy include all but which of the following? A. Helping the client deal with depression secondary to the diagnosis and its treatment B. Explaining that the reactions to chemotherapy are minimal C. Careful observation of the IV site of the administration of the drugs D. Careful attention to blood count results 22. Which of the following operative procedures of the thorax is paired with the correct definition? A. Pneumonectomy: removal of the entire lung B. Wedge resection: removal of one or more lobes of a lung C. Decortication: removal of the ribs or sections of ribs D. Thoracoplasty: removal of fibrous membrane that develops over visceral pleura as a result of emphysema Mr. Liberatore, age 76, is admitted to your unit. He has a past medical history of hypertension, DM, hyperlipidemia. Recently he has had several episodes where he stops talking mid-sentence and stares into space. Today the episode lasted for 15 minutes. The admission diagnosis is impending CVA. 23. The episodes Mr. Liberatore has been experiencing are probably: A. small cerebral hemorrhages B. TIA’s or transient ischemic attacks C. Secondary to hypoglycemia D. Secondary to hyperglycemia 24. Mr. Liberatore suffers a left-sided CVA. He is right-handed. The nurse should expect: A. left-sided paralysis B. visual loss C. no alterations in speech D. no impairment of bladder function 25. Upper motor neuron disease may be manifested in which of the following clinical signs? A. spastic paralysis, hyperreflexia, presence of Babinski reflex B. flaccid paralysis, hyporeflexia C. muscle atrophy, fasciculations D. decreased or absent voluntary movement 26. During your assessment of Julie, she tells you all visual symptoms are gone but that she now has a severe pounding headache over her left eye. You suspect Julie may have: A. a tension headache B. the aura and headache of migraine C. a brain tumor D. a conversion reaction 27. You explain to Julie and her mother that migraine headaches are caused by: A. an allergic response triggered by stress B. dilation of cerebral arteries C. persistent contraction of the muscles of the head, neck, and face D. increased intracranial pressure 28. A thorough history reveals that hormonal changes associated with menstruation may have triggered Julie’s migraine attack. In investigating Julie’s history what factors would be least significant in migraine? A. seasonal allergies B. trigger foods such as alcohol, MSG, chocolate C. family history of migraine D. warning sign of onset, or aura 29. A client with muscle contraction headache will exhibit a pattern different for Julie’s. Which of the following is more compatible with tension headache? A. severe aching pain behind both eyes B. headache worse when bending over C. a bandlike burning around the neck D. feeling of tightness bitemporally, occipitally, or in the neck Mr. Snyder is admitted to your unit with a brain tumor. The type of tumor he has is currently unknown. You begin to think about the way brain tumors are classified. 30. Glioma is an intracranial tumor. Which of the following statements about gliomas do you know to be false? A. 50% of all intracranial tumors are gliomas B. gliomas are usually benign C. they grow rapidly and often cannot be totally excised from the surrounding tissue D. most glioma victims die within a year after diagnosis 31. Acoustic neuromas produce symptoms of progressive nerve deafness, tinnitus, and vertigo due to pressure and eventual destruction of: A. CN5 B. CN7 C. CN8 D. The ossicles 32. Whether Mr. Snyder’s tumor is benign or malignant, it will eventually cause increased intracranial pressure. Signs and symptoms of increasing intracranial pressure may include all of the following except: A. headache, nausea, and vomiting B. papilledema, dizziness, mental status changes C. obvious motor deficits D. increased pulse rate, drop in blood pressure 33. Mr. Snyder is scheduled for surgery in the morning, and you are surprised to find out that there is no order for an enema. You assess the situation and conclude that the reason for this is: A. Mr. Snyder has had some mental changes due to the tumor and would find an enema terribly traumatic B. Straining to evacuate the enema might increase the intracranial pressure C. Mr. Snyder had been on clear liquids and then was NPO for several days, so an enema is not necessary D. An oversight and you call the physician to obtain the order 34. Postoperatively Mr. Snyder needs vigilant nursing care including all of the following except: A. Keeping his head flat B. Assessments q ½ hour of LOC, VS, pupillary responses, and mental status C. Helping him avoid straining at stool, vomiting, or coughing D. Providing a caring, supportive atmosphere for him and his family 35. Potential post intracranial surgery problems include all but which of the following? A. increased ICP B. extracranial hemorrhage C. seizures D. leakage of cerebrospinal fluid Mrs. Hogan, a 43-year-old woman, is admitted to your unit for cholecystectomy. 36. You are responsible for teaching Mrs. Hogan deep breathing and coughing exercises. Why are these exercises especially important for Mrs. Hogan? A. they prevent postoperative atelectasis and pneumonia B. the incision in gallbladder surgery is in the subcostal area, which makes the client reluctant to take a deep breath and cough C. because she is probably overweight and will be less willing to breathe, cough, and move postoperatively 37. On the morning of Mrs. Hogan’s planned cholecystectomy, she awakens with a pain in her right scapular area and thinks she slept in poor position. While doing the pre-op checklist, you note that on her routine CB report, her WBC is 15,000. Your responsibility at this point is: A. to notify the surgeon at once; this is an elevated WBC indicating an inflammatory reaction B. to record this finding in a prominent place on the pre-op checklist and in your preop notes C. to call the laboratory for a STAT repeat WBC D. None. This is not an unusual finding 38. Mrs. Hogan is scheduled for surgery 2 days later and is to be given atropine 0.3 mg IM and Demerol 50 mg IM one hour preoperatively. Which nursing actions follow the giving of the pre op medication? A. have her void soon after receiving the medication B. allow her family to be with her before the medication takes effect C. bring her valuables to the nursing station D. reinforce pre op teaching 39. Mrs. Hogan is transported to the recovery room following her cholecystectomy. As you continue to check her vital signs you note a continuing trend in Mrs. Hogan’s status: her BP is gradually dropping and her pulse rate is increasing. Your most appropriate nursing action is to: A. order whole blood for Mrs. Hogan from the lab B. increase IV fluid rate of infusion and place in trendelenburg position C. immediately report signs of shock to the head nurse and/or surgeon and monitor VS closely D. place in lateral sims position to facilitate breathing 40. Mrs. Hogan returns to your clinical unit following discharge from the recovery room. Her vital signs are stable and her family is with her. Postoperative leg exercises should be initiated: A. after the physician writes the order B. after the family leaves C. if Mrs. Hogan will not be ambulated early D. stat 41. An oropharyngeal airway may: A. Not be used in a conscious patient. B. Cause airway obstruction. C. Prevent a patient from biting and occluding an ET tube. D. Be inserted “upside down” into the mouth opening and then rotated into the proper orientation as it is advanced into the mouth. E. All of the above. 42. Endotracheal intubation: A. Can be attempted for up to 2 minutes before you need to stop and ventilate the patient. B. Reduces the risk of aspiration of gastric contents. C. Should be performed with the neck flexed forward making the chin touch the chest. D. Should be performed after a patient is found to be not breathing and two breaths have been given but before checking for a pulse. 43. When giving bag-valve mask ventilations: A. Rapid and forceful ventilations are desirable so that adequate ventilation will be assured B. Effective ventilations can always be given by one person. C. Cricoid pressure may prevent gastric inflation during ventilations. D. Tidal volumes will always be larger than when giving mouth to pocket mask ventilations. 44. If breath sounds are only heard on the right side after intubation: A. Extubate, ventilate for 30 seconds then try again. B. The patient probably only has one lung, the right. C. You have intubated the stomach. D. Pull the tube back and listen again. 45. An esophageal obturator airway (EOA): A. Can be inserted by any person trained in ACLS. B. Requires visualization of the trachea before insertion. C. Never causes regurgitation. D. Should not be used with a conscious person, pediatric patients, or patients who have swallowed caustic substances. 46. During an acute myocardial infarct (MI): A. A patient may have a normal appearing ECG. B. Chest pain will always be present. C. A targeted history is rarely useful in making the diagnosis of MI. D. The chest pain is rarely described as crushing, pressing, or heavy. 47. The most common lethal arrhythmia in the first hour of an MI is: A. Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia B. Asystole C. Ventricular fibrillation D. First-degree heart block. 48. Which of the following is true about verapamil? A. It is used for wide-complex tachycardia. B. It may cause a drop in blood pressure. C. It is a first line drug for Pulseless Electrical Activity. D. It is useful for treatment of severe hypotension. 49. Atropine: A. Is always given for a heart rate less than 60 bpm. B. Cannot be given via ET tube. C. Has a maximum total dosage of 0.03-0.04 mg/kg IV in the setting of cardiac arrest. D. When given IV, should always be given slowly. 50. Asystole should not be “defibrillated.” A. True B. False C. Partially False D. Partially True NCLEX Practice Exam 19 (50 Questions) 1. The nursing care plan for a toddler diagnosed with Kawasaki Disease (mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome) should be based on the high risk for development of which problem? A. Chronic vessel plaque formation B. Pulmonary embolism C. Occlusions at the vessel bifurcations D. Coronary artery aneurysms 2. A nurse has just received a medication order which is not legible. Which statement best reflects assertive communication? A. “I cannot give this medication as it is written. I have no idea of what you mean.” B. “Would you please clarify what you have written so I am sure I am reading it correctly?” C. “I am having difficulty reading your handwriting. It would save me time if you would be more careful.” D. “Please print in the future so I do not have to spend extra time attempting to read your writing.” 3. The nurse is discussing negativism with the parents of a 30 month-old child. How should the nurse tell the parents to best respond to this behavior? A. Reprimand the child and give a 15-minute “time out” B. Maintain a permissive attitude for this behavior C. Use patience and a sense of humor to deal with this behavior D. Assert authority over the child through limit setting 4. An ambulatory client reports edema during the day in his feet and an ankle that disappears while sleeping at night. What is the most appropriate follow-up question for the nurse to ask? A. “Have you had a recent heart attack?” B. “Do you become short of breath during your normal daily activities?” C. “How many pillows do you use at night to sleep comfortably?” D. “Do you smoke?” 5. The nurse is planning care for a client during the acute phase of a sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis. Which of the following actions would be most appropriate? A. Fluid restriction 1000cc per day B. Ambulate in hallway 4 times a day C. Administer analgesic therapy as ordered D. Encourage increased caloric intake 6. While working with an obese adolescent, it is important for the nurse to recognize that obesity in adolescents is most often associated with what other behavior? A. Sexual promiscuity B. Poor body image C. Dropping out of school D. Drug experimentation 7. A nurse and client are talking about the client’s progress toward understanding his behavior under stress. This is typical of which phase in the therapeutic relationship? A. Pre-interaction B. Orientation C. Working D. Termination 8. A nurse is eating in the hospital cafeteria when a toddler at a nearby table chokes on a piece of food and appears slightly blue. The appropriate initial action should be to A. Begin mouth to mouth resuscitation B. Give the child water to help in swallowing C. Perform 5 abdominal thrusts D. Call for the emergency response team 9. The emergency room nurse admits a child who experienced a seizure at school. The father comments that this is the first occurrence, and denies any family history of epilepsy. What is the best response by the nurse? A. “Do not worry. Epilepsy can be treated with medications.” B. “The seizure may or may not mean your child has epilepsy.” C. “Since this was the first convulsion, it may not happen again.” D. “Long-term treatment will prevent future seizures.” 10. A nurse admits a 3 week-old infant to the special care nursery with a diagnosis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. As the nurse reviews the birth history, which data would be most consistent with this diagnosis? A. Gestational age assessment suggested growth retardation B. Meconium was cleared from the airway at delivery C. Phototherapy was used to treat Rh incompatibility D. The infant received mechanical ventilation for 2 weeks 11. Parents of a 6 month-old breastfed baby ask the nurse about increasing the baby’s diet. Which of the following should be added first? A. Cereal B. Eggs C. Meat D. Juice 12. A victim of domestic violence states, “If I were better, I would not have been beaten.” Which feeling best describes what the victim may be experiencing? A. Fear B. Helplessness C. Self-blame D. Rejection 13. The nurse is assessing the mental status of a client admitted with possible organic brain disorder. Which of these questions will best assess the function of the client’s recent memory? A. “Name the year.” “What season is this?” (pause for answer after each question) B. “Subtract 7 from 100 and then subtract 7 from that.” (pause for answer) “Now continue to subtract 7 from the new number.” C. “I am going to say the names of three things and I want you to repeat them after me: blue, ball, pen.” D. “What is this on my wrist?” (point to your watch) Then ask, “What is the purpose of it?” 14. Which oxygen delivery system would the nurse apply that would provide the highest concentrations of oxygen to the client? A. Venturi mask B. Partial rebreather mask C. Non-rebreather mask D. Simple face mask 15. A nurse is caring for a client who had a closed reduction of a fractured right wrist followed by the application of a fiberglass cast 12 hours ago. Which finding requires the nurse’s immediate attention? A. Capillary refill of fingers on right hand is 3 seconds B. Skin warm to touch and normally colored C. Client reports prickling sensation in the right hand D. Slight swelling of fingers of right hand 16. Included in teaching the client with tuberculosis taking INH about follow-up home care, the nurse should emphasize that a laboratory appointment for which of the following lab tests is critical? A. Liver function B. Kidney function C. Blood sugar D. Cardiac enzymes 17. Which client is at highest risk of developing a pressure ulcer? A. 23-year-old in traction for fractured femur B. 72-year-old with peripheral vascular disease, who is unable to walk without assistance C. 75-year-old with left-sided paresthesia and is incontinent of urine and stool D. 30-year-old who is comatose following a ruptured aneurysm 18. Which contraindication should the nurse assess for prior to giving a child immunization? A. Mild cold symptoms B. Chronic asthma C. Depressed immune system D. Allergy to eggs 19. The nurse is caring for a 2-year-old who is being treated with chelation therapy, calcium disodium edetate, for lead poisoning. The nurse should be alert for which of the following side effects? A. Neurotoxicity B. Hepatomegaly C. Nephrotoxicity D. Ototoxicity 20. A newborn is having difficulty maintaining a temperature above 98 degrees Fahrenheit and has been placed in a warming isolette. Which action is a nursing priority? A. Protect the eyes of the neonate from the heat lamp B. Monitor the neonate’s temperature C. Warm all medications and liquids before giving D. Avoid touching the neonate with cold hands 21. At a senior citizens meeting a nurse talks with a client who has diabetes mellitus Type 1. Which statement by the client during the conversation is most predictive of a potential for impaired skin integrity? A. “I give my insulin to myself in my thighs.” B. “Sometimes when I put my shoes on I don’t know where my toes are.” C. “Here are my up and down glucose readings that I wrote on my calendar.” D. “If I bathe more than once a week my skin feels too dry.” 22. A 4-year-old hospitalized child begins to have a seizure while playing with hard plastic toys in the hallway. Of the following nursing actions, which one should the nurse do first? A. Place the child in the nearest bed B. Administer IV medication to slow down the seizure C. Place a padded tongue blade in the child’s mouth D. Remove the child’s toys from the immediate area 23. The nurse is at the community center speaking with retired people. To which comment by one of the retirees during a discussion about glaucoma would the nurse give a supportive comment to reinforce correct information? A. “I usually avoid driving at night since lights sometimes seem to make things blur.” B. “I take half of the usual dose for my sinuses to maintain my blood pressure.” C. “I have to sit at the side of the pool with the grandchildren since I can’t swim with this eye problem.” D. “I take extra fiber and drink lots of water to avoid getting constipated.” 24. The nurse is teaching a parent about side effects of routine immunizations. Which of the following must be reported immediately? A. Irritability B. Slight edema at site C. Local tenderness D. Temperature of 102.5 F 25. A client is admitted with the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. While taking a history, the client tells the nurse he was admitted for the same thing twice before, the last time just 3 months ago. The nurse would anticipate the health care provider ordering A. Pulmonary embolectomy B. Vena caval interruption C. Increasing the coumadin therapy to an INR of 3-4 D. Thrombolytic therapy 26. A woman in her third trimester complains of severe heartburn. What is appropriate teaching by the nurse to help the woman alleviate these symptoms? A. Drink small amounts of liquids frequently B. Eat the evening meal just before retiring C. Take sodium bicarbonate after each meal D. Sleep with head propped on several pillows 27. The nurse is teaching the mother of a 5 month-old about nutrition for her baby. Which statement by the mother indicates the need for further teaching? A. “I’m going to try feeding my baby some rice cereal.” B. “When he wakes at night for a bottle, I feed him.” C. “I dip his pacifier in honey so he’ll take it.” D. “I keep formula in the refrigerator for 24 hours.” 28. For a 6-year-old child hospitalized with moderate edema and mild hypertension associated with acute glomerulonephritis (AGN), which one of the following nursing interventions would be appropriate? A. Institute seizure precautions B. Weigh the child twice per shift C. Encourage the child to eat protein-rich foods D. Relieve boredom through physical activity 29. Which statement by the client with chronic obstructive lung disease indicates an understanding of the major reason for the use of occasional pursed-lip breathing? A. “This action of my lips helps to keep my airway open.” B. “I can expel more when I pucker up my lips to breathe out.” C. “My mouth doesn’t get as dry when I breathe with pursed lips.” D. “By prolonging breathing out with pursed lips the little areas in my lungs don’t collapse.” 30. A 57-year-old male client has hemoglobin of 10 mg/dl and a hematocrit of 32%. What would be the most appropriate follow-up by the home care nurse? A. Ask the client if he has noticed any bleeding or dark stools B. Tell the client to call 911 and go to the emergency department immediately C. Schedule a repeat Hemoglobin and Hematocrit in 1 month D. Tell the client to schedule an appointment with a hematologist 31. Which response by the nurse would best assist the chemically impaired client to deal with issues of guilt? A. “Addiction usually causes people to feel guilty. Don’t worry, it is a typical response due to your drinking behavior.” B. “What have you done that you feel most guilty about and what steps can you begin to take to help you lessen this guilt?” C. “Don’t focus on your guilty feelings. These feelings will only lead you to drinking and taking drugs.” D. “You’ve caused a great deal of pain to your family and close friends, so it will take time to undo all the things you’ve done.” 32. An adolescent client comes to the clinic 3 weeks after the birth of her first baby. She tells the nurse she is concerned because she has not returned to her pre-pregnant weight. Which action should the nurse perform first? A. Review the client’s weight pattern over the year B. Ask the mother to record her diet for the last 24 hours C. Encourage her to talk about her view of herself D. Give her several pamphlets on postpartum nutrition 33. Which of the following measures would be appropriate for the nurse to teach the parent of a nine-month-old infant about diaper dermatitis? A. Use only cloth diapers that are rinsed with bleach B. Do not use occlusive ointments on the rash C. Use commercial baby wipes with each diaper change D. Discontinue a new food that was added to the infant’s diet just prior to the rash 34. A 16-year-old client is admitted to a psychiatric unit with a diagnosis of attempted suicide. The nurse is aware that the most frequent cause of suicide in adolescents is A. Progressive failure to adapt B. Feelings of anger or hostility C. Reunion wish or fantasy D. Feelings of alienation or isolation 35. A mother brings her 26-month-old to the well-child clinic. She expresses frustration and anger due to her child’s constantly saying “no” and his refusal to follow her directions. The nurse explains this is normal for his age, as negativism is attempting to meet which developmental need? A. Trust B. Initiative C. Independence D. Self-esteem 36. Following mitral valve replacement surgery, a client develops PVC’s. The health care provider orders a bolus of Lidocaine followed by a continuous Lidocaine infusion at a rate of 2 mgm/minute. The IV solution contains 2 grams of Lidocaine in 500 cc’s of D5W. The infusion pump delivers 60 microdrops/cc. What rate would deliver 4 mgm of Lidocaine/minute? A. 60 microdrops/minute B. 20 microdrops/minute C. 30 microdrops/minute D. 40 microdrops/minute 37. A couple asks the nurse about risks of several birth control methods. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse? A. Norplant is safe and may be removed easily B. Oral contraceptives should not be used by smokers C. Depo-Provera is convenient with few side effects D. The IUD gives protection from pregnancy and infection 38. The nurse is caring for a client in the late stages of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (A.L.S.). Which finding would the nurse expect? A. Confusion B. Loss of half of visual field C. Shallow respirations D. Tonic-clonic seizures 39. A client experiences postpartum hemorrhage eight hours after the birth of twins. Following administration of IV fluids and 500 ml of whole blood, her hemoglobin and hematocrit are within normal limits. She asks the nurse whether she should continue to breastfeed the infants. Which of the following is based on sound rationale? A. “Nursing will help contract the uterus and reduce your risk of bleeding.” B. “Breastfeeding twins will take too much energy after the hemorrhage.” C. “The blood transfusion may increase the risks to you and the babies.” D. “Lactation should be delayed until the “real milk” is secreted.” 40. A client complained of nausea, a metallic taste in her mouth, and fine hand tremors 2 hours after her first dose of lithium carbonate (Lithane). What is the nurse’s best explanation of these findings? A. These side effects are common and should subside in a few days B. The client is probably having an allergic reaction and should discontinue the drug C. Taking the lithium on an empty stomach should decrease these symptoms D. Decreasing dietary intake of sodium and fluids should minimize the side effects 41. The nurse is caring for a post-surgical client at risk for developing deep vein thrombosis. Which intervention is an effective preventive measure? A. Place pillows under the knees B. Use elastic stockings continuously C. Encourage range of motion and ambulation D. Massage the legs twice daily 42. The parents of a newborn male with hypospadias want their child circumcised. The best response by the nurse is to inform them that A. Circumcision is delayed so the foreskin can be used for the surgical repair B. This procedure is contraindicated because of the permanent defect C. There is no medical indication for performing a circumcision on any child D. The procedure should be performed as soon as the infant is stable 43. The nurse is teaching parents about the treatment plan for a 2-week-old infant with Tetralogy of Fallot. While awaiting future surgery, the nurse instructs the parents to immediately report A. Loss of consciousness B. Feeding problems C. Poor weight gain D. Fatigue with crying 44. An infant weighed 7 pounds 8 ounces at birth. If growth occurs at a normal rate, what would be the expected weight at 6 months of age? A. Double the birth weight B. Triple the birth weight C. Gain 6 ounces each week D. Add 2 pounds each month 45. The nurse is caring for a 13-year-old following spinal fusion for scoliosis. Which of the following interventions is appropriate in the immediate post-operative period? A. Raise the head of the bed at least 30 degrees B. Encourage ambulation within 24 hours C. Maintain in a flat position, logrolling as needed D. Encourage leg contraction and relaxation after 48 hours 46. A client asks the nurse about including her 2 and 12-year-old sons in the care of their newborn sister. Which of the following is an appropriate initial statement by the nurse? A. “Focus on your son’s’ needs during the first days at home.” B. “Tell each child what he can do to help with the baby.” C. “Suggest that your husband spend more time with the boys.” D. “Ask the children what they would like to do for the newborn.” 47. A nurse is caring for a 2-year-old child after corrective surgery for Tetralogy of Fallot. The mother reports that the child has suddenly begun seizing. The nurse recognizes this problem is probably due to A. A cerebral vascular accident B. Postoperative meningitis C. Medication reaction D. Metabolic alkalosis 48. A client with schizophrenia is receiving Haloperidol (Haldol) 5 mg t.i.d.. The client’s family is alarmed and calls the clinic when “his eyes rolled upward.” The nurse recognizes this as what type of side effect? A. Oculogyric crisis B. Tardive dyskinesia C. Nystagmus D. Dysphagia 49. A home health nurse is at the home of a client with diabetes and arthritis. The client has difficulty drawing up insulin. It would be most appropriate for the nurse to refer the client to A. A social worker from the local hospital B. An occupational therapist from the community center C. A physical therapist from the rehabilitation agency D. Another client with diabetes mellitus and takes insulin 50. A client was admitted to the psychiatric unit after complaining to her friends and family that neighbors have bugged her home in order to hear all of her business. She remains aloof from other clients, paces the floor and believes that the hospital is a house of torture. Nursing interventions for the client should appropriately focus on efforts to A. Convince the client that the hospital staff is trying to help B. Help the client to enter into group recreational activities C. Provide interactions to help the client learn to trust staff D. Arrange the environment to limit the client’s contact with other clients NCLEX Practice Exam 20 (25 Questions) 1. A client is scheduled for a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). The nurse knows that a PTCA is the A. Surgical repair of a diseased coronary artery B. Placement of an automatic internal cardiac defibrillator C. Procedure that compresses plaque against the wall of the diseased coronary artery to improve blood flow D. Non-invasive radiographic examination of the heart 2. A newborn has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism. In discussing the condition and treatment with the family, the nurse should emphasize A. They can expect the child will be mentally retarded B. Administration of thyroid hormone will prevent problems C. This rare problem is always hereditary D. Physical growth/development will be delayed 3. A priority goal of involuntary hospitalization of the severely mentally ill client is A. Re-orientation to reality B. Elimination of symptoms C. Protection from harm to self or others D. Return to independent functioning 4. A 19-year-old client is paralyzed in a car accident. Which statement used by the client would indicate to the nurse that the client was using the mechanism of “suppression”? A. “I don’t remember anything about what happened to me.” B. “I’d rather not talk about it right now.” C. “It’s the other entire guy’s fault! He was going too fast.” D. “My mother is heartbroken about this.” 5. The nurse is caring for a woman 2 hours after a vaginal delivery. Documentation indicates that the membranes were ruptured for 36 hours prior to delivery. What are the priority nursing diagnoses at this time? A. Altered tissue perfusion B. Risk for fluid volume deficit C. High risk for hemorrhage D. Risk for infection 6. A 3-year-old had a hip spica cast applied 2 hours ago. In order to facilitate drying, the nurse should A. Expose the cast to air and turn the child frequently B. Use a heat lamp to reduce the drying time C. Handle the cast with the abductor bar D. Turn the child as little as possible 7. A client is scheduled for an Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP). In order to prepare the client for this test, the nurse would: A. Instruct the client to maintain a regular diet the day prior to the examination B. Restrict the client’s fluid intake 4 hours prior to the examination C. Administer a laxative to the client the evening before the examination D. Inform the client that only 1 x-ray of his abdomen is necessary 8. Following a diagnosis of acute glomerulonephritis (AGN) in their 6-year-old child, the parent’s remark: “We just don’t know how he caught the disease!” The nurse’s response is based on an understanding that A. AGN is a streptococcal infection that involves the kidney tubules B. The disease is easily transmissible in schools and camps C. The illness is usually associated with chronic respiratory infections D. It is not “caught” but is a response to a previous B-hemolytic strep infection 9. The nurse is caring for a 20 lbs (9 kg) 6 month-old with a 3-day history of diarrhea, occasional vomiting and fever. Peripheral intravenous therapy has been initiated, with 5% dextrose in 0.33% normal saline with 20 mEq of potassium per liter infusing at 35 ml/hr. Which finding should be reported to the healthcare provider immediately? A. 3 episodes of vomiting in 1 hour B. Periodic crying and irritability C. Vigorous sucking on a pacifier D. No measurable voiding in 4 hours 10. While caring for the client during the first hour after delivery, the nurse determines that the uterus is boggy and there is vaginal bleeding. What should be the nurse’s first action? A. Check vital signs B. Massage the fundus C. Offer a bedpan D. Check for perineal lacerations 11. The nurse is assessing an infant with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Which finding would the nurse anticipate? A. Unequal leg length B. Limited adduction C. Diminished femoral pulses D. Symmetrical gluteal folds 12. To prevent a Valsalva maneuver in a client recovering from an acute myocardial infarction, the nurse would A. Assist the client to use the bedside commode B. Administer stool softeners every day as ordered C. Administer antidysrhythmics prn as ordered D. Maintain the client on strict bed rest 13. On admission to the psychiatric unit, the client is trembling and appears fearful. The nurse’s initial response should be to A. Give the client orientation materials and review the unit rules and regulations B. Introduce him/her and accompany the client to the client’s room C. Take the client to the day room and introduce her to the other clients D. Ask the nursing assistant to get the client’s vital signs and complete the admission search 14. During the admission assessment on a client with chronic bilateral glaucoma, which statement by the client would the nurse anticipate since it is associated with this problem? A. “I have constant blurred vision.” B. “I can’t see on my left side.” C. “I have to turn my head to see my room.” D. “I have specks floating in my eyes.” 15. A client with asthma has low pitched wheezes present in the final half of exhalation. One hour later the client has high pitched wheezes extending throughout exhalation. This change in assessment indicates to the nurse that the client A. Has increased airway obstruction B. Has improved airway obstruction C. Needs to be suctioned D. Exhibits hyperventilation 16. Which behavioral characteristic describes the domestic abuser? A. Alcoholic B. Overconfident C. High tolerance for frustrations D. Low self-esteem 17. The nurse is caring for a client with a long leg cast. During discharge teaching about appropriate exercises for the affected extremity, the nurse should recommend A. Isometric B. Range of motion C. Aerobic D. Isotonic 18. A client is in her third month of her first pregnancy. During the interview, she tells the nurse that she has several sex partners and is unsure of the identity of the baby’s father. Which of the following nursing interventions is a priority? A. Counsel the woman to consent to HIV screening B. Perform tests for sexually transmitted diseases C. Discuss her high risk for cervical cancer D. Refer the client to a family planning clinic 19. A 16-month-old child has just been admitted to the hospital. As the nurse assigned to this child enters the hospital room for the first time, the toddler runs to the mother, clings to her and begins to cry. What would be the initial action by the nurse? A. Arrange to change client care assignments B. Explain that this behavior is expected C. Discuss the appropriate use of “time-out” D. Explain that the child needs extra attention 20. While planning care for a 2-year-old hospitalized child, which situation would the nurse expect to most likely affect the behavior? A. Strange bed and surroundings B. Separation from parents C. Presence of other toddlers D. Unfamiliar toys and games 21. While explaining an illness to a 10-year-old, what should the nurse keep in mind about the cognitive development at this age? A. They are able to make simple association of ideas B. They are able to think logically in organizing facts C. Interpretation of events originate from their own perspective D. Conclusions are based on previous experiences 22. The nurse has just admitted a client with severe depression. From which focus should the nurse identify a priority nursing diagnosis? A. Nutrition B. Elimination C. Activity D. Safety 23. Which playroom activities should the nurse organize for a small group of 7-year-old hospitalized children? A. Sports and games with rules B. Finger paints and water play C. “Dress-up” clothes and props D. Chess and television programs 24. A client is discharged following hospitalization for congestive heart failure. The nurse teaching the family suggests they encourage the client to rest frequently in which of the following positions? A. High Fowler’s B. Supine C. Left lateral D. Low Fowler’s 25. The nurse is caring for a 10-year-old on admission to the burn unit. One assessment parameter that will indicate that the child has adequate fluid replacement is A. Urinary output of 30 ml per hour B. No complaints of thirst C. Increased hematocrit D. Good skin turgor around burn NCLEX Practice Exam 22 (34 Questions) 1. What is the priority nursing diagnosis for a patient experiencing a migraine headache dd? A. Acute pain related to biologic and chemical factors B. Anxiety related to change in or threat to health status C. Hopelessness related to deteriorating physiological condition D. Risk for Side effects related to medical therapy 2. You are creating a teaching plan for a patient with newly diagnosed migraine headaches. Which key items should be included in the teaching plan? (Choose all that apply). A. Avoid foods that contain tyramine, such as alcohol and aged cheese. B. Avoid drugs such as Tagamet, nitroglycerin and Nifedipine. C. Abortive therapy is aimed at eliminating the pain during the aura. D. A potential side effect of medications is rebound headache. E. Complementary therapies such as relaxation may be helpful. F. Continue taking estrogen as prescribed by your physician. 3. The patient with migraine headaches has a seizure. After the seizure, which action can you delegate to the nursing assistant? A. Document the seizure. B. Perform neurologic checks. C. Take the patient’s vital signs. D. Restrain the patient for protection. 4. You are preparing to admit a patient with a seizure disorder. Which of the following actions can you delegate to LPN/LVN? A. Complete admission assessment. B. Set up oxygen and suction equipment. C. Place a padded tongue blade at bedside. D. Pad the side rails before patient arrives. 5. A nursing student is teaching a patient and family about epilepsy prior to the patient’s discharge. For which statement should you intervene? A. “You should avoid consumption of all forms of alcohol.” B. “Wear your medical alert bracelet at all times.” C. “Protect your loved one’s airway during a seizure.” D. “It’s OK to take over-the-counter medications.” 6. A patient with Parkinson’s disease has a nursing diagnosis of Impaired Physical Mobility related to neuromuscular impairment. You observe a nursing assistant performing all of these actions. For which action must you intervene? A. The NA assists the patient to ambulate to the bathroom and back to bed. B. The NA reminds the patient not to look at his feet when he is walking. C. The NA performs the patient’s complete bath and oral care. D. The NA sets up the patient’s tray and encourages patient to feed himself. 7. The nurse is preparing to discharge a patient with chronic low back pain. Which statement by the patient indicates that additional teaching is necessary? A. “I will avoid exercise because the pain gets worse.” B. “I will use heat or ice to help control the pain.” C. “I will not wear high-heeled shoes at home or work.” D. “I will purchase a firm mattress to replace my old one.” 8. A patient with a spinal cord injury (SCI) complains about a severe throbbing headache that suddenly started a short time ago. Assessment of the patient reveals increased blood pressure (168/94) and decreased heart rate (48/minute), diaphoresis, and flushing of the face and neck. What action should you take first? A. Administer the ordered acetaminophen (Tylenol). B. Check the Foley tubing for kinks or obstruction. C. Adjust the temperature in the patient’s room. D. Notify the physician about the change in status. 9. Which patient should you, as charge nurse, assign to a new graduate RN who is orienting to the neurologic unit? A. A 28-year-old newly admitted patient with spinal cord injury B. A 67-year-old patient with stroke 3 days ago and left-sided weakness C. An 85-year-old dementia patient to be transferred to long-term care today D. A 54-year-old patient with Parkinson’s who needs assistance with bathing 10. A patient with a spinal cord injury at level C3-4 is being cared for in the ED. What is the priority assessment? A. Determine the level at which the patient has intact sensation. B. Assess the level at which the patient has retained mobility. C. Check blood pressure and pulse for signs of spinal shock. D. Monitor respiratory effort and oxygen saturation level. 11. You are pulled from the ED to the neurologic floor. Which action should you delegate to the nursing assistant when providing nursing care for a patient with SCI? A. Assess patient’s respiratory status every 4 hours. B. Take patient’s vital signs and record every 4 hours. C. Monitor nutritional status including calorie counts. D. Have patient turn, cough, and deep breathe every 3 hours. 12. You are helping the patient with an SCI to establish a bladder-retraining program. What strategies may stimulate the patient to void? (Choose all that apply). A. Stroke the patient’s inner thigh. B. Pull on the patient’s pubic hair. C. Initiate intermittent straight catheterization. D. Pour warm water over the perineum. E. Tap the bladder to stimulate detrusor muscle. 13. The patient with a cervical SCI has been placed in fixed skeletal traction with a halo fixation device. When caring for this patient the nurse may delegate which action (s) to the LPN/LVN? (Choose all that apply). A. Check the patient’s skin for pressure form device. B. Assess the patient’s neurologic status for changes. C. Observe the halo insertion sites for signs of infection. D. Clean the halo insertion sites with hydrogen peroxide. 14. You are preparing a nursing care plan for the patient with SCI including the nursing diagnosis Impaired Physical Mobility and Self-Care Deficit. The patient tells you, “I don’t know why we’re doing all this. My life’s over.” What additional nursing diagnosis takes priority based on this statement? A. Risk for Injury related to altered mobility B. Imbalanced Nutrition, Less Than Body Requirements C. Impaired Adjustment to Spinal Cord Injury D. Poor Body Image related to immobilization 15. Which patient should be assigned to the traveling nurse, new to neurologic nursing care, who has been on the neurologic unit for 1 week? A. A 34-year-old patient newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis (MS) B. A 68-year-old patient with chronic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) C. A 56-year-old patient with Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) in respiratory distress D. A 25-year-old patient admitted with CA level spinal cord injury (SCI) 16. The patient with multiple sclerosis tells the nursing assistant that after physical therapy she is too tired to take a bath. What is your priority nursing diagnosis at this time? A. Fatigue related to disease state B. Activity Intolerance due to generalized weakness C. Impaired Physical Mobility related to neuromuscular impairment D. Self-care Deficit related to fatigue and neuromuscular weakness 17. The LPN/LVN, under your supervision, is providing nursing care for a patient with GBS. What observation would you instruct the LPN/LVN to report immediately? A. Complaints of numbness and tingling B. Facial weakness and difficulty speaking C. Rapid heart rate of 102 beats per minute D. Shallow respirations and decreased breath sounds 18. The nursing assistant reports to you, the RN, that the patient with myasthenia gravis (MG) has an elevated temperature (102.20 F), heart rate of 120/minute, rise in blood pressure (158/94), and was incontinent off urine and stool. What is your best first action at this time? A. Administer an acetaminophen suppository. B. Notify the physician immediately. C. Recheck vital signs in 1 hour. D. Reschedule patient’s physical therapy. 19. You are providing care for a patient with an acute hemorrhage stroke. The patient’s husband has been reading a lot about strokes and asks why his wife did not receive alteplase. What is your best response? A. “Your wife was not admitted within the time frame that alteplase is usually given.” B. “This drug is used primarily for patients who experience an acute heart attack.” C. “Alteplase dissolves clots and may cause more bleeding into your wife’s brain.” D. “Your wife had gallbladder surgery just 6 months ago and this prevents the use of alteplase.” 20. You are supervising a senior nursing student who is caring for a patient with a right hemisphere stroke. Which action by the student nurse requires that you intervene? A. The student instructs the patient to sit up straight, resulting in the patient’s puzzled expression. B. The student moves the patient’s tray to the right side of her over-bed tray. C. The student assists the patient with passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises. D. The student combs the left side of the patient’s hair when the patient combs only the right side. 21. Which action (s) should you delegate to the experienced nursing assistant when caring for a patient with a thrombotic stroke with residual left-sided weakness? (Choose all that apply). A. Assist patient to reposition every 2 hours. B. Reapply pneumatic compression boots. C. Remind patient to perform active ROM. D. Check extremities for redness and edema. 22. The patient who had a stroke needs to be fed. What instruction should you give to the nursing assistant who will feed the patient? A. Position the patient sitting up in bed before you feed her. B. Check the patient’s gag and swallowing reflexes. C. Feed the patient quickly because there are three more waiting. D. Suction the patient’s secretions between bites of food. 23. You have just admitted a patient with bacterial meningitis to the medical-surgical unit. The patient complains of a severe headache with photophobia and has a temperature of 102.60 F orally. Which collaborative intervention must be accomplished first? A. Administer codeine 15 mg orally for the patient’s headache. B. Infuse ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 2000 mg IV to treat the infection. C. Give acetaminophen (Tylenol) 650 mg orally to reduce the fever. D. Give furosemide (Lasix) 40 mg IV to decrease intracranial pressure. 24. You are mentoring a student nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) while caring for a patient with meningococcal meningitis. Which action by the student requires that you intervene immediately? A. The student enters the room without putting on a mask and gown. B. The student instructs the family that visits are restricted to 10 minutes. C. The student gives the patient a warm blanket when he says he feels cold. D. The student checks the patient’s pupil response to light every 30 minutes. 25. A 23-year-old patient with a recent history of encephalitis is admitted to the medical unit with new onset generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Which nursing activities included in the patient’s care will be best to delegate to an LPN/LVN whom you are supervising? (Choose all that apply). A. Document the onset time, nature of seizure activity, and postictal behaviors for all seizures. B. Administer phenytoin (Dilantin) 200 mg PO daily. C. Teach patient about the need for good oral hygiene. D. Develop a discharge plan, including physician visits and referral to the Epilepsy Foundation. 26. While working in the ICU, you are assigned to care for a patient with a seizure disorder. Which of these nursing actions will you implement first if the patient has a seizure? A. Place the patient on a non-rebreather mask will the oxygen at 15 L/minute. B. Administer lorazepam (Ativan) 1 mg IV. C. Turn the patient to the side and protect airway. D. Assess level of consciousness during and immediately after the seizure. 27. A patient recently started on phenytoin (Dilantin) to control simple complex seizures is seen in the outpatient clinic. Which information obtained during his chart review and assessment will be of greatest concern? A. The gums appear enlarged and inflamed. B. The white blood cell count is 2300/mm3. C. Patient occasionally forgets to take the phenytoin until after lunch. D. Patient wants to renew his driver’s license in the next month. 28. After receiving a change-of-shift report at 7:00 AM, which of these patients will you assess first? A. A 23-year-old with a migraine headache who is complaining of severe nausea associated with retching B. A 45-year-old who is scheduled for a craniotomy in 30 minutes and needs preoperative teaching C. A 59-year-old with Parkinson’s disease who will need a swallowing assessment before breakfast D. A 63-year-old with multiple sclerosis who has an oral temperature of 101.80 F and flank pain 29. All of these nursing activities are included in the care plan for a 78-year-old man with Parkinson’s disease who has been referred to your home health agency. Which ones will you delegate to a nursing assistant (NA)? (Choose all that apply). A. Check for orthostatic changes in pulse and blood pressure. B. Monitor for improvement in tremor after levodopa (L-dopa) is given. C. Remind the patient to allow adequate time for meals. D. Monitor for abnormal involuntary jerky movements of extremities. E. Assist the patient with prescribed strengthening exercises. F. Adapt the patient’s preferred activities to his level of function. 30. As the manager in a long-term-care (LTC) facility, you are in charge of developing a standard plan of care for residents with Alzheimer’s disease. Which of these nursing tasks is best to delegate to the LPN team leaders working in the facility? A. Check for improvement in resident memory after medication therapy is initiated. B. Use the Mini-Mental State Examination to assess residents every 6 months. C. Assist residents to toilet every 2 hours to decrease risk for urinary intolerance. D. Develop individualized activity plans after consulting with residents and family. 31. A patient who has been admitted to the medical unit with new-onset angina also has a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Her husband tells you that he rarely gets a good night’s sleep because he needs to be sure she does not wander during the night. He insists on checking each of the medications you give her to be sure they are the same as the ones she takes at home. Based on this information, which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate for this patient? A. Decreased Cardiac Output related to poor myocardial contractility B. Caregiver Role Strain related to continuous need for providing care C. Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management related to poor patient memory D. Risk for Falls related to patient wandering behavior during the night 32. You are caring for a patient with a recurrent glioblastoma who is receiving dexamethasone (Decadron) 4 mg IV every 6 hours to relieve symptoms of right arm weakness and headache. Which assessment information concerns you the most? A. The patient does not recognize family members. B. The blood glucose level is 234 mg/dL. C. The patient complains of a continued headache. D. The daily weight has increased 1 kg. 33. A 70-year-old alcoholic patient with acute lethargy, confusion, and incontinence is admitted to the hospital ED. His wife tells you that he fell down the stairs about a month ago, but “he didn’t have a scratch afterward.” She feels that he has become gradually less active and sleepier over the last 10 days or so. Which of the following collaborative interventions will you implement first? A. Place on the hospital alcohol withdrawal protocol. B. Transfer to radiology for a CT scan. C. Insert a retention catheter to straight drainage. D. Give phenytoin (Dilantin) 100 mg PO. 34. Which of these patients in the neurologic ICU will be best to assign to an RN who has floated from the medical unit? A. A 26-year-old patient with a basilar skull structure who has clear drainage coming out of the nose B. A 42-year-old patient admitted several hours ago with a headache and diagnosed with a ruptured berry aneurysm. C. A 46-year-old patient who was admitted 48 hours ago with bacterial meningitis and has an antibiotic dose due D. A 65-year-old patient with an astrocytoma who has just returned to the unit after having a craniotomy NCLEX Practice Exam 23 (50 Questions) 1. Nurse Michelle should know that the drainage is normal four (4) days after a sigmoid colostomy when the stool is: A. Green liquid B. Solid formed C. Loose, bloody D. Semiformed 2. Where would nurse Kristine place the call light for a male client with a right-sided brain attack and left homonymous hemianopsia? A. On the client’s right side B. On the client’s left side C. Directly in front of the client D. Where the client like 3. A male client is admitted to the emergency department following an accident. What are the first nursing actions of the nurse? A. Check respiration, circulation, neurological response. B. Align the spine, check pupils, and check for hemorrhage. C. Check respirations, stabilize spine, and check circulation. D. Assess level of consciousness and circulation. 4. In evaluating the effect of nitroglycerin, Nurse Arthur should know that it reduces preload and relieves angina by: A. Increasing contractility and slowing heart rate. B. Increasing AV conduction and heart rate. C. Decreasing contractility and oxygen consumption. D. Decreasing venous return through vasodilation. 5. Nurse Patricia finds a female client who is post-myocardial infarction (MI) slumped on the side rails of the bed and unresponsive to shaking or shouting. Which is the nurse next action? A. Call for help and note the time. B. Clear the airway C. Give two sharp thumps to the precordium, and check the pulse. D. Administer two quick blows. 6. Nurse Monett is caring for a client recovering from gastrointestinal bleeding. The nurse should: A. Plan care so the client can receive 8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. B. Monitor vital signs every 2 hours. C. Make sure that the client takes food and medications at prescribed intervals. D. Provide milk every 2 to 3 hours. 7. A male client was on warfarin (Coumadin) before admission and has been receiving heparin I.V. for 2 days. The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is 68 seconds. What should Nurse Carla do? A. Stop the I.V. infusion of heparin and notify the physician. B. Continue treatment as ordered. C. Expect the warfarin to increase the PTT. D. Increase the dosage, because the level is lower than normal. 8. A client underwent ileostomy, when should the drainage appliance be applied to the stoma? A. 24 hours later, when edema has subsided. B. In the operating room. C. After the ileostomy begins to function. D. When the client is able to begin self-care procedures. 9. A client has undergone spinal anesthetic, it will be important that the nurse immediately position the client in: A. On the side, to prevent obstruction of airway by tongue. B. Flat on back. C. On the back, with knees flexed 15 degrees. D. Flat on the stomach, with the head turned to the side. 10. While monitoring a male client several hours after a motor vehicle accident, which assessment data suggest increasing intracranial pressure? A. Blood pressure is decreased from 160/90 to 110/70. B. Pulse is increased from 87 to 95, with an occasional skipped beat. C. The client is oriented when aroused from sleep and goes back to sleep immediately. D. The client refuses dinner because of anorexia. 11. Mrs. Cruz, 80 years old is diagnosed with pneumonia. Which of the following symptoms may appear first? A. Altered mental status and dehydration B. Fever and chills C. Hemoptysis and Dyspnea D. Pleuritic chest pain and cough 12. A male client has active tuberculosis (TB). Which of the following symptoms will be exhibited? A. Chest and lower back pain B. Chills, fever, night sweats, and hemoptysis C. Fever of more than 104°F (40°C) and nausea D. Headache and photophobia 13. Mark, a 7-year-old client is brought to the emergency department. He’s tachypneic and afebrile and has a respiratory rate of 36 breaths/minute and has a nonproductive cough. He recently had a cold. Form this history; the client may have which of the following conditions? A. Acute asthma B. Bronchial pneumonia C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) D. Emphysema 14. Marichu was given morphine sulfate for pain. She is sleeping and her respiratory rate is 4 breaths/minute. If action isn’t taken quickly, she might have which of the following reactions? A. Asthma attack B. Respiratory arrest C. Seizure D. Wake up on his own 15. A 77-year-old male client is admitted for elective knee surgery. Physical examination reveals shallow respirations but no sign of respiratory distress. Which of the following is a normal physiologic change related to aging? A. Increased elastic recoil of the lungs B. Increased number of functional capillaries in the alveoli C. Decreased residual volume D. Decreased vital capacity 16. Nurse John is caring for a male client receiving lidocaine I.V. Which factor is the most relevant to administration of this medication? A. Decrease in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) when measured with a pulse oximeter. B. Increase in systemic blood pressure. C. Presence of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) on a cardiac monitor. D. Increase in intracranial pressure (ICP). 17. Nurse Ron is caring for a male client taking an anticoagulant. The nurse should teach the client to: A. Report incidents of diarrhea. B. Avoid foods high in vitamin K C. Use a straight razor when shaving. D. Take aspirin for pain relief. 18. Nurse Lynette is preparing a site for the insertion of an I.V. catheter. The nurse should treat excess hair at the site by: A. Leaving the hair intact B. Shaving the area C. Clipping the hair in the area D. Removing the hair with a depilatory. 19. Nurse Michelle is caring for an elderly female with osteoporosis. When teaching the client, the nurse should include information about which major complication: A. Bone fracture B. Loss of estrogen C. Negative calcium balance D. Dowager’s hump 20. Nurse Len is teaching a group of women to perform BSE. The nurse should explain that the purpose of performing the examination is to discover: A. Cancerous lumps B. Areas of thickness or fullness C. Changes from previous examinations. D. Fibrocystic masses 21. When caring for a female client who is being treated for hyperthyroidism, it is important to: A. Provide extra blankets and clothing to keep the client warm. B. Monitor the client for signs of restlessness, sweating, and excessive weight loss during thyroid replacement therapy. C. Balance the client’s periods of activity and rest. D. Encourage the client to be active to prevent constipation. 22. Nurse Kris is teaching a client with history of atherosclerosis. To decrease the risk of atherosclerosis, the nurse should encourage the client to: A. Avoid focusing on his weight. B. Increase his activity level. C. Follow a regular diet. D. Continue leading a high-stress lifestyle. 23. Nurse Greta is working on a surgical floor. Nurse Greta must logroll a client following a: A. Laminectomy B. Thoracotomy C. Hemorrhoidectomy D. Cystectomy 24. A 55-year old client underwent cataract removal with intraocular lens implant. Nurse Oliver is giving the client discharge instructions. These instructions should include which of the following? A. Avoid lifting objects weighing more than 5 lb (2.25 kg). B. Lie on your abdomen when in bed. C. Keep rooms brightly lit. D. Avoiding straining during bowel movement or bending at the waist. 25. George should be taught about testicular examinations during: A. when sexual activity starts B. After age 69 C. After age 40 D. Before age 20 26. A male client has undergone a colon resection. While turning him, wound dehiscence with evisceration occurs. Nurse Trish first response is to: A. Call the physician. B. Place a saline-soaked sterile dressing on the wound. C. Take a blood pressure and pulse. D. Pull the dehiscence closed. 27. Nurse Audrey is caring for a client who has suffered a severe cerebrovascular accident. During routine assessment, the nurse notices Cheyne- Stokes respirations. Cheyne-stokes respirations are: A. A progressively deeper breath followed by shallower breaths with apneic periods. B. Rapid, deep breathing with abrupt pauses between each breath. C. Rapid, deep breathing and irregular breathing without pauses. D. Shallow breathing with an increased respiratory rate. 28. Nurse Bea is assessing a male client with heart failure. The breath sounds commonly auscultated in clients with heart failure are: A. Tracheal B. Fine crackles C. Coarse crackles D. Friction rubs 29. The nurse is caring for Kenneth experiencing an acute asthma attack. The client stops wheezing and breath sounds aren’t audible. The reason for this change is that: A. The attack is over. B. The airways are so swollen that no air cannot get through. C. The swelling has decreased. D. Crackles have replaced wheezes. 30. Mike with epilepsy is having a seizure. During the active seizure phase, the nurse should: A. Place the client on his back remove dangerous objects, and insert a bite block. B. Place the client on his side, remove dangerous objects, and insert a bite block. C. Place the client o his back, remove dangerous objects, and hold down his arms. D. Place the client on his side, remove dangerous objects, and protect his head. 31. After insertion of a chest tube for a pneumothorax, a client becomes hypotensive with neck vein distention, tracheal shift, absent breath sounds, and diaphoresis. Nurse Amanda suspects a tension pneumothorax has occurred. What cause of tension pneumothorax should the nurse check for? A. Infection of the lung B. Kinked or obstructed chest tube C. Excessive water in the water-seal chamber D. Excessive chest tube drainage 32. Nurse Maureen is talking to a male client, the client begins choking on his lunch. He’s coughing forcefully. The nurse should: A. Stand him up and perform the abdominal thrust maneuver from behind. B. Lay him down, straddle him, and perform the abdominal thrust maneuver. C. Leave him to get assistance. D. Stay with him but not intervene at this time. 33. Nurse Ron is taking a health history of an 84-year-old client. Which information will be most useful to the nurse for planning care? A. General health for the last 10 years. B. Current health promotion activities. C. Family history of diseases. D. Marital status. 34. When performing oral care on a comatose client, Nurse Krina should: A. Apply lemon glycerin to the client’s lips at least every 2 hours. B. Brush the teeth with client lying supine. C. Place the client in a side-lying position, with the head of the bed lowered. D. Clean the client’s mouth with hydrogen peroxide. 35. A 77-year-old male client is admitted with a diagnosis of dehydration and change in mental status. He’s being hydrated with L.V. fluids. When the nurse takes his vital signs, she notes he has a fever of 103°F (39.4°C) a cough producing yellow sputum and pleuritic chest pain. The nurse suspects this client may have which of the following conditions? A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) B. Myocardial infarction (MI) C. Pneumonia D. Tuberculosis 36. Nurse Oliver is working in a outpatient clinic. He has been alerted that there is an outbreak of tuberculosis (TB). Which of the following clients entering the clinic today most likely to have TB? A. A 16-year-old female high school student B. A 33-year-old daycare worker C. A 43-year-old homeless man with a history of alcoholism D. A 54-year-old businessman 37. Virgie with a positive Mantoux test result will be sent for a chest X-ray. The nurse is aware that which of the following reasons this is done? A. To confirm the diagnosis B. To determine if a repeat skin test is needed C. To determine the extent of lesions D. To determine if this is a primary or secondary infection 38. Kennedy with acute asthma showing inspiratory and expiratory wheezes and a decreased forced expiratory volume should be treated with which of the following classes of medication right away? A. Beta-adrenergic blockers B. Bronchodilators C. Inhaled steroids D. Oral steroids 39. Mr. Vasquez 56-year-old client with a 40-year history of smoking one to two packs of cigarettes per day has a chronic cough producing thick sputum, peripheral edema, and cyanotic nail beds. Based on this information, he most likely has which of the following conditions? A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) B. Asthma C. Chronic obstructive bronchitis D. Emphysema Situation: Francis, age 46 is admitted to the hospital with diagnosis of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. 40. The treatment for patients with leukemia is bone marrow transplantation. Which statement about bone marrow transplantation is not correct? A. The patient is under local anesthesia during the procedure B. The aspirated bone marrow is mixed with heparin. C. The aspiration site is the posterior or anterior iliac crest. D. The recipient receives cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) for 4 consecutive days before the procedure. 41. After several days of admission, Francis becomes disoriented and complains of frequent headaches. The nurse in-charge first action would be: A. Call the physician. B. Document the patient’s status in his charts. C. Prepare oxygen treatment. D. Raise the side rails. 42. During routine care, Francis asks the nurse, “How can I be anemic if this disease causes increased my white blood cell production?” The nurse in-charge best response would be that the increased number of white blood cells (WBC) is: A. crowded red blood cells B. is not responsible for the anemia. C. uses nutrients from other cells D. have an abnormally short lifespan of cells. 43. Diagnostic assessment of Francis would probably not reveal: A. Predominance of lymphoblasts B. Leukocytosis C. Abnormal blast cells in the bone marrow D. Elevated thrombocyte counts 44. Robert, a 57-year-old client with acute arterial occlusion of the left leg undergoes an emergency embolectomy. Six hours later, the nurse isn’t able to obtain pulses in his left foot using Doppler ultrasound. The nurse immediately notifies the physician and asks her to prepare the client for surgery. As the nurse enters the client’s room to prepare him, he states that he won’t have any more surgery. Which of the following is the best initial response by the nurse? A. Explain the risks of not having the surgery B. Notifying the physician immediately C. Notifying the nursing supervisor D. Recording the client’s refusal in the nurses’ notes 45. During the endorsement, which of the following clients should the on-duty nurse assess first? A. The 58-year-old client who was admitted 2 days ago with heart failure, blood pressure of 126/76 mm Hg, and a respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute B. The 89-year-old client with end-stage right-sided heart failure, blood pressure of 78/50 mm Hg, and a “do not resuscitate” order C. The 62-year-old client who was admitted 1 day ago with thrombophlebitis and is receiving L.V. heparin D. The 75-year-old client who was admitted 1 hour ago with new-onset atrial fibrillation and is receiving L.V. diltiazem (Cardizem) 46. Honey, a 23-year old client complains of substernal chest pain and states that her heart feels like “it’s racing out of the chest”. She reports no history of cardiac disorders. The nurse attaches her to a cardiac monitor and notes sinus tachycardia with a rate of 136beats/minutes. Breath sounds are clear and the respiratory rate is 26 breaths/minutes. Which of the following drugs should the nurse question the client about using? A. Barbiturates B. Opioids C. Cocaine D. Benzodiazepines 47. A 51-year-old female client tells the nurse-in-charge that she has found a painless lump in her right breast during her monthly self-examination. Which assessment finding would strongly suggest that this client’s lump is cancerous? A. Eversion of the right nipple and mobile mass B. Nonmobile mass with irregular edges C. Mobile mass that is soft and easily delineated D. Nonpalpable right axillary lymph nodes 48. A 35-year-old client with vaginal cancer asks the nurse, “What is the usual treatment for this type of cancer?” Which treatment should the nurse name? A. Surgery B. Chemotherapy C. Radiation D. Immunotherapy 49. Cristina undergoes a biopsy of a suspicious lesion. The biopsy report classifies the lesion according to the TNM staging system as follows: TIS, N0, M0. What does this classification mean? A. No evidence of primary tumor, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis B. Carcinoma in situ, no abnormal regional lymph nodes, and no evidence of distant metastasis C. Can’t assess tumor or regional lymph nodes and no evidence of metastasis D. Carcinoma in situ, no demonstrable metastasis of the regional lymph nodes, and ascending degrees of distant metastasis 50. Lydia undergoes a laryngectomy to treat laryngeal cancer. When teaching the client how to care for the neck stoma, the nurse should include which instruction? A. “Keep the stoma uncovered.” B. “Keep the stoma dry.” C. “Have a family member perform stoma care initially until you get used to the procedure.” D. “Keep the stoma moist.” NCLEX Practice Exam 24 (50 Questions) 1. A 37-year-old client with uterine cancer asks the nurse, “Which is the most common type of cancer in women?” The nurse replies that it’s breast cancer. Which type of cancer causes the most deaths in women? A. Breast cancer B. Lung cancer C. Brain cancer D. Colon and rectal cancer 2. Antonio with lung cancer develops Horner’s syndrome when the tumor invades the ribs and affects the sympathetic nerve ganglia. When assessing for signs and symptoms of this syndrome, the nurse should note: A. miosis, partial eyelid ptosis, and anhidrosis on the affected side of the face. B. chest pain, dyspnea, cough, weight loss, and fever. C. arm and shoulder pain and atrophy of arm and hand muscles, both on the affected side. D. hoarseness and dysphagia. 3. Vic asks the nurse what PSA is. The nurse should reply that it stands for: A. prostate-specific antigen, which is used to screen for prostate cancer. B. protein serum antigen, which is used to determine protein levels. C. pneumococcal strep antigen, which is a bacteria that causes pneumonia. D. Papanicolaou-specific antigen, which is used to screen for cervical cancer. 4. What is the most important postoperative instruction that nurse Kate must give a client who has just returned from the operating room after receiving a subarachnoid block? A. “Avoid drinking liquids until the gag reflex returns.” B. “Avoid eating milk products for 24 hours.” C. “Notify a nurse if you experience blood in your urine.” D. “Remain supine for the time specified by the physician.” 5. A male client suspected of having colorectal cancer will require which diagnostic study to confirm the diagnosis? A. Stool Hematest B. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) C. Sigmoidoscopy D. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan 6. During a breast examination, which finding most strongly suggests that the Luz has breast cancer? A. Slight asymmetry of the breasts. B. A fixed nodular mass with dimpling of the overlying skin C. Bloody discharge from the nipple D. Multiple firm, round, freely movable masses that change with the menstrual cycle 7. A female client with cancer is being evaluated for possible metastasis. Which of the following is one of the most common metastasis sites for cancer cells? A. Liver B. Colon C. Reproductive tract D. White blood cells (WBCs) 8. Nurse Mandy is preparing a client for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to confirm or rule out a spinal cord lesion. During the MRI scan, which of the following would pose a threat to the client? A. The client lies still. B. The client asks questions. C. The client hears thumping sounds. D. The client wears a watch and wedding band. 9. Nurse Cecile is teaching a female client about preventing osteoporosis. Which of the following teaching points is correct? A. Obtaining an X-ray of the bones every 3 years is recommended to detect bone loss. B. To avoid fractures, the client should avoid strenuous exercise. C. The recommended daily allowance of calcium may be found in a wide variety of foods. D. Obtaining the recommended daily allowance of calcium requires taking a calcium supplement. 10. Before Jacob undergoes arthroscopy, the nurse reviews the assessment findings for contraindications for this procedure. Which finding is a contraindication? A. Joint pain B. Joint deformity C. Joint flexion of less than 50% D. Joint stiffness 11. Mr. Rodriguez is admitted with severe pain in the knees. Which form of arthritis is characterized by urate deposits and joint pain, usually in the feet and legs, and occurs primarily in men over age 30? A. Septic arthritis B. Traumatic arthritis C. Intermittent arthritis D. Gouty arthritis 12. A heparin infusion at 1,500 unit/hour is ordered for a 64-year-old client with stroke in evolution. The infusion contains 25,000 units of heparin in 500 ml of saline solution. How many milliliters per hour should be given? A. 15 ml/hour B. 30 ml/hour C. 45 ml/hour D. 50 ml/hour 13. A 76-year-old male client had a thromboembolic right stroke; his left arm is swollen. Which of the following conditions may cause swelling after a stroke? A. Elbow contracture secondary to spasticity B. Loss of muscle contraction decreasing venous return C. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) due to immobility of the ipsilateral side D. Hypoalbuminemia due to protein escaping from an inflamed glomerulus 14. Heberden’s nodes are a common sign of osteoarthritis. Which of the following statement is correct about this deformity? A. It appears only in men B. It appears on the distal interphalangeal joint C. It appears on the proximal interphalangeal joint D. It appears on the dorsolateral aspect of the interphalangeal joint. 15. Which of the following statements explains the main difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis? A. Osteoarthritis is gender-specific, rheumatoid arthritis isn’t B. Osteoarthritis is a localized disease rheumatoid arthritis is systemic C. Osteoarthritis is a systemic disease, rheumatoid arthritis is localized D. Osteoarthritis has dislocations and subluxations, rheumatoid arthritis doesn’t 16. Mrs. Cruz uses a cane for assistance in walking. Which of the following statements is true about a cane or other assistive devices? A. A walker is a better choice than a cane. B. The cane should be used on the affected side C. The cane should be used on the unaffected side D. A client with osteoarthritis should be encouraged to ambulate without the cane 17. A male client with type 1 diabetes is scheduled to receive 30 U of 70/30 insulin. There is no 70/30 insulin available. As a substitution, the nurse may give the client: A. 9 U regular insulin and 21 U neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH). B. 21 U regular insulin and 9 U NPH. C. 10 U regular insulin and 20 U NPH. D. 20 U regular insulin and 10 U NPH. 18. Nurse Len should expect to administer which medication to a client with gout? A. aspirin B. furosemide (Lasix) C. colchicines D. calcium gluconate (Kalcinate) 19. Mr. Domingo with a history of hypertension is diagnosed with primary hyperaldosteronism. This diagnosis indicates that the client’s hypertension is caused by excessive hormone secretion from which of the following glands? A. Adrenal cortex B. Pancreas C. Adrenal medulla D. Parathyroid 20. For a diabetic male client with a foot ulcer, the doctor orders bed rest, a wetto- dry dressing change every shift, and blood glucose monitoring before meals and bedtime. Why are wet-to-dry dressings used for this client? A. They contain exudate and provide a moist wound environment. B. They protect the wound from mechanical trauma and promote healing. C. They debride the wound and promote healing by secondary intention. D. They prevent the entrance of microorganisms and minimize wound discomfort. 21. Nurse Zeny is caring for a client in acute addisonian crisis. Which laboratory data would the nurse expect to find? A. Hyperkalemia B. Reduced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) C. Hypernatremia D. Hyperglycemia 22. A client is admitted for treatment of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Which nursing intervention is appropriate? A. Infusing I.V. fluids rapidly as ordered B. Encouraging increased oral intake C. Restricting fluids D. Administering glucose-containing I.V. fluids as ordered 23. A female client tells nurse Nikki that she has been working hard for the last 3 months to control her type 2 diabetes mellitus with diet and exercise. To determine the effectiveness of the client’s efforts, the nurse should check: A. urine glucose level. B. fasting blood glucose level. C. serum fructosamine level. D. glycosylated hemoglobin level. 24. Nurse Trinity administered neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin to a diabetic client at 7 a.m. At what time would the nurse expect the client to be most at risk for a hypoglycemic reaction? A. 10:00 am B. Noon C. 4:00 pm D. 10:00 pm 25. The adrenal cortex is responsible for producing which substances? A. Glucocorticoids and androgens B. Catecholamines and epinephrine C. Mineralocorticoids and catecholamines D. Norepinephrine and epinephrine 26. On the third day after a partial thyroidectomy, Proserfina exhibits muscle twitching and hyperirritability of the nervous system. When questioned, the client reports numbness and tingling of the mouth and fingertips. Suspecting a life-threatening electrolyte disturbance, the nurse notifies the surgeon immediately. Which electrolyte disturbance most commonly follows thyroid surgery? A. Hypocalcemia B. Hyponatremia C. Hyperkalemia D. Hypermagnesemia 27. Which laboratory test value is elevated in clients who smoke and can’t be used as a general indicator of cancer? A. Acid phosphatase level B. Serum calcitonin level C. Alkaline phosphatase level D. Carcinoembryonic antigen level 28. Francis with anemia has been admitted to the medical-surgical unit. Which assessment findings are characteristic of iron-deficiency anemia? A. Nights sweats, weight loss, and diarrhea B. Dyspnea, tachycardia, and pallor C. Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia D. Itching, rash, and jaundice 29. In teaching a female client who is HIV-positive about pregnancy, the nurse would know more teaching is necessary when the client says: A. The baby can get the virus from my placenta.” B. “I’m planning on starting on birth control pills.” C. “Not everyone who has the virus gives birth to a baby who has the virus.” D. “I’ll need to have a C-section if I become pregnant and have a baby.” 30. When preparing Judy with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) for discharge to the home, the nurse should be sure to include which instruction? A. “Put on disposable gloves before bathing.” B. “Sterilize all plates and utensils in boiling water.” C. “Avoid sharing such articles as toothbrushes and razors.” D. “Avoid eating foods from serving dishes shared by other family members.” 31. Nurse Marie is caring for a 32-year-old client admitted with pernicious anemia. Which set of findings should the nurse expect when assessing the client? A. Pallor, bradycardia, and reduced pulse pressure B. Pallor, tachycardia, and a sore tongue C. Sore tongue, dyspnea, and weight gain D. Angina, double vision, and anorexia 32. After receiving a dose of penicillin, a client develops dyspnea and hypotension. Nurse Celestina suspects the client is experiencing anaphylactic shock. What should the nurse do first? A. Page an anesthesiologist immediately and prepare to intubate the client. B. Administer epinephrine, as prescribed, and prepare to intubate the client if necessary. C. Administer the antidote for penicillin, as prescribed, and continue to monitor the client’s vital signs. D. Insert an indwelling urinary catheter and begin to infuse I.V. fluids as ordered. 33. Mr. Marquez with rheumatoid arthritis is about to begin aspirin therapy to reduce inflammation. When teaching the client about aspirin, the nurse discusses adverse reactions to prolonged aspirin therapy. These include: A. weight gain. B. fine motor tremors. C. respiratory acidosis. D. bilateral hearing loss. 34. A 23-year-old client is diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). After recovering from the initial shock of the diagnosis, the client expresses a desire to learn as much as possible about HIV and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When teaching the client about the immune system, the nurse states that adaptive immunity is provided by which type of white blood cell? A. Neutrophil B. Basophil C. Monocyte D. Lymphocyte 35. In an individual with Sjögren’s syndrome, nursing care should focus on: A. moisture replacement. B. electrolyte balance. C. nutritional supplementation. D. arrhythmia management. 36. During chemotherapy for lymphocytic leukemia, Mathew develops abdominal pain, fever, and “horse barn” smelling diarrhea. It would be most important for the nurse to advise the physician to order: A. enzyme-linked immunosuppressant assay (ELISA) test. B. electrolyte panel and hemogram. C. stool for Clostridium difficile test. D. flat plate X-ray of the abdomen. 37. A male client seeks medical evaluation for fatigue, night sweats, and a 20-lb weight loss in 6 weeks. To confirm that the client has been infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the nurse expects the physician to order: A. E-rosette immunofluorescence. B. Quantification of T-lymphocytes. C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). D. Western blot test with ELISA. 38. A complete blood count is commonly performed before a Joe goes into surgery. What does this test seek to identify? A. Potential hepatic dysfunction indicated by decreased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels B. Low levels of urine constituents normally excreted in the urine C. Abnormally low hematocrit (HCT) and hemoglobin (Hb) levels D. Electrolyte imbalance that could affect the blood’s ability to coagulate properly 39. While monitoring a client for the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), the nurse should take note of what assessment parameters? A. Platelet count, prothrombin time, and partial thromboplastin time B. Platelet count, blood glucose levels, and white blood cell (WBC) count C. Thrombin time, calcium levels, and potassium levels D. Fibrinogen level, WBC, and platelet count 40. When taking a dietary history from a newly admitted female client, Nurse Len should remember that which of the following foods is a common allergen? A. Bread B. Carrots C. Orange D. Strawberries 41. Nurse John is caring for clients in the outpatient clinic. Which of the following phone calls should the nurse return first? A. A client with hepatitis A who states, “My arms and legs are itching.” B. A client with cast on the right leg who states, “I have a funny feeling in my right leg.” C. A client with osteomyelitis of the spine who states, “I am so nauseous that I can’t eat.” D. A client with rheumatoid arthritis who states, “I am having trouble sleeping.” 42. Nurse Sarah is caring for clients on the surgical floor and has just received report from the previous shift. Which of the following clients should the nurse see first? A. A 35-year-old admitted three hours ago with a gunshot wound; 1.5 cm area of dark drainage noted on the dressing. B. A 43-year-old who had a mastectomy two days ago; 23 ml of serosanguinous fluid noted in the Jackson-Pratt drain. C. A 59-year-old with a collapsed lung due to an accident; no drainage noted in the previous eight hours. D. A 62-year-old who had an abdominal-perineal resection three days ago; client complaints of chills. 43. Nurse Eve is caring for a client who had a thyroidectomy 12 hours ago for treatment of Grave’s disease. The nurse would be most concerned if which of the following was observed? A. Blood pressure 138/82, respirations 16, oral temperature 99 degrees Fahrenheit. B. The client supports his head and neck when turning his head to the right. C. The client spontaneously flexes his wrist when the blood pressure is obtained. D. The client is drowsy and complains of sore throat. 44. Julius is admitted with complaints of severe pain in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. To assist with pain relief, the nurse should take which of the following actions? A. Encourage the client to change positions frequently in bed. B. Administer Demerol 50 mg IM q 4 hours and PRN. C. Apply warmth to the abdomen with a heating pad. D. Use comfort measures and pillows to position the client. 45. Nurse Tina prepares a client for peritoneal dialysis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? A. Assess for a bruit and a thrill. B. Warm the dialysate solution. C. Position the client on the left side. D. Insert a Foley catheter 46. Nurse Jannah teaches an elderly client with right-sided weakness how to use cane. Which of the following behaviors, if demonstrated by the client to the nurse, indicates that the teaching was effective? A. The client holds the cane with his right hand, moves the can forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg. B. The client holds the cane with his right hand, moves the cane forward followed by his left leg, and then moves the right leg. C. The client holds the cane with his left hand, moves the cane forward followed by the right leg, and then moves the left leg. D. The client holds the cane with his left hand, moves the cane forward followed by his left leg, and then moves the right leg. 47. An elderly client is admitted to the nursing home setting. The client is occasionally confused and her gait is often unsteady. Which of the following actions, if taken by the nurse, is most appropriate? A. Ask the woman’s family to provide personal items such as photos or mementos. B. Select a room with a bed by the door so the woman can look down the hall. C. Suggest the woman eat her meals in the room with her roommate. D. Encourage the woman to ambulate in the halls twice a day. 48. Nurse Evangeline teaches an elderly client how to use a standard aluminum walker. Which of the following behaviors, if demonstrated by the client, indicates that the nurse’s teaching was effective? A. The client slowly pushes the walker forward 12 inches, then takes small steps forward while leaning on the walker. B. The client lifts the walker, moves it forward 10 inches, and then takes several small steps forward. C. The client supports his weight on the walker while advancing it forward, then takes small steps while balancing on the walker. D. The client slides the walker 18 inches forward, then takes small steps while holding onto the walker for balance. 49. Nurse Derek is supervising a group of elderly clients in a residential home setting. The nurse knows that the elderly are at greater risk of developing sensory deprivation for what reason? A. Increased sensitivity to the side effects of medications. B. Decreased visual, auditory, and gustatory abilities. C. Isolation from their families and familiar surroundings. D. Decrease musculoskeletal function and mobility. 50. A male client with emphysema becomes restless and confused. What step should nurse Jasmine take next? A. Encourage the client to perform pursed-lip breathing. B. Check the client’s temperature. C. Assess the client’s potassium level. D. Increase the client’s oxygen flow rate. NCLEX Practice Exam 25 (50 Questions) 1. Randy has undergone kidney transplant, what assessment would prompt Nurse Katrina to suspect organ rejection? A. Sudden weight loss B. Polyuria C. Hypertension D. Shock 2. The immediate objective of nursing care for an overweight, mildly hypertensive male client with ureteral colic and hematuria is to decrease: A. Pain B. Weight C. Hematuria D. Hypertension 3. Matilda, with hyperthyroidism, is to receive Lugol’s iodine solution before a subtotal thyroidectomy is performed. The nurse is aware that this medication is given to: A. Decrease the total basal metabolic rate. B. Maintain the function of the parathyroid glands. C. Block the formation of thyroxine by the thyroid gland. D. Decrease the size and vascularity of the thyroid gland. 4. Ricardo was diagnosed with type I diabetes. The nurse is aware that acute hypoglycemia also can develop in the client who is diagnosed with: A. Liver disease B. Hypertension C. Type 2 diabetes D. Hyperthyroidism 5. Tracy is receiving combination chemotherapy for treatment of metastatic carcinoma. Nurse Ruby should monitor the client for the systemic side effect of: A. Ascites B. Nystagmus C. Leukopenia D. Polycythemia 6. Norma, with recent colostomy, expresses concern about the inability to control the passage of gas. Nurse Oliver should suggest that the client plan to: A. Eliminate foods high in cellulose. B. Decrease fluid intake at meal times. C. Avoid foods that in the past caused flatus. D. Adhere to a bland diet prior to social events. 7. Nurse Ron begins to teach a male client how to perform colostomy irrigations. The nurse would evaluate that the instructions were understood when the client states, “I should: A. Lie on my left side while instilling the irrigating solution.” B. Keep the irrigating container less than 18 inches above the stoma.” C. Instill a minimum of 1200 ml of irrigating solution to stimulate evacuation of the bowel.” D. Insert the irrigating catheter deeper into the stoma if cramping occurs during the procedure.” 8. Patrick is in the oliguric phase of acute tubular necrosis and is experiencing fluid and electrolyte imbalances. The client is somewhat confused and complains of nausea and muscle weakness. As part of the prescribed therapy to correct this electrolyte imbalance, the nurse would expect to: A. Administer Kayexalate B. Restrict foods high in protein C. Increase oral intake of cheese and milk. D. Administer large amounts of normal saline via I.V. 9. Mario has burn injury. After 48 hours, the physician orders for Mario 2 liters of IV fluid to be administered q12 h. The drop factor of the tubing is 10 gtt/ml. The nurse should set the flow to provide: A. 18 gtt/min B. 28 gtt/min C. 32 gtt/min D. 36 gtt/min 10. Terence suffered from burn injury. Using the rule of nines, which has the largest percent of burns? A. Face and neck B. Right upper arm and penis C. Right thigh and penis D. Upper trunk 11. Herbert, a 45-year-old construction engineer is brought to the hospital unconscious after falling from a 2-story building. When assessing the client, the nurse would be most concerned if the assessment revealed: A. Reactive pupils B. A depressed fontanel C. Bleeding from ears D. An elevated temperature 12. Nurse Sherry is teaching male client regarding his permanent artificial pacemaker. Which information given by the nurse shows her knowledge deficit about the artificial cardiac pacemaker? A. Take the pulse rate once a day, in the morning upon awakening B. May be allowed to use electrical appliances C. Have regular follow up care D. May engage in contact sports 13. The nurse is aware that the most relevant knowledge about oxygen administration to a male client with COPD is A. Oxygen at 1-2L/min is given to maintain the hypoxic stimulus for breathing. B. Hypoxia stimulates the central chemoreceptors in the medulla that makes the client breath. C. Oxygen is administered best using a non-rebreathing mask D. Blood gases are monitored using a pulse oximeter. 14. Tonny has undergoes a left thoracotomy and a partial pneumonectomy. Chest tubes are inserted, and one-bottle water-seal drainage is instituted in the operating room. In the postanesthesia care unit, Tonny is placed in Fowler’s position on either his right side or on his back. The nurse is aware that this position: A. Reduce incisional pain. B. Facilitate ventilation of the left lung. C. Equalize pressure in the pleural space. D. Increase venous return 15. Kristine is scheduled for a bronchoscopy. When teaching Kristine what to expect afterward, the nurse’s highest priority of information would be: A. Food and fluids will be withheld for at least 2 hours. B. Warm saline gargles will be done q 2h. C. Coughing and deep-breathing exercises will be done q2h. D. Only ice chips and cold liquids will be allowed initially. 16. Nurse Tristan is caring for a male client in acute renal failure. The nurse should expect hypertonic glucose, insulin infusions, and sodium bicarbonate to be used to treat: A. hypernatremia. B. hypokalemia. C. hyperkalemia. D. hypercalcemia. 17. Ms. X has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? A. This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually. B. The most common treatment is metronidazole (Flagyl), which should eradicate the problem within 7 to 10 days. C. The potential for transmission to her sexual partner will be eliminated if condoms are used every time they have sexual intercourse. D. The human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes condylomata acuminata, can’t be transmitted during oral sex. 18. Maritess was recently diagnosed with a genitourinary problem and is being examined in the emergency department. When palpating her kidneys, the nurse should keep which anatomical fact in mind? A. The left kidney usually is slightly higher than the right one. B. The kidneys are situated just above the adrenal glands. C. The average kidney is approximately 5 cm (2″) long and 2 to 3 cm (¾” to 1-1/8″) wide. D. The kidneys lie between the 10th and 12th thoracic vertebrae. 19. Jestoni with chronic renal failure (CRF) is admitted to the urology unit. The nurse is aware that the diagnostic test is consistent with CRF if the result is: A. Increased pH with decreased hydrogen ions. B. Increased serum levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium. C. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 100 mg/dl and serum creatinine 6.5 mg/ dl. D. Uric acid analysis 3.5 mg/dl and phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP) excretion 75%. 20. Katrina has an abnormal result on a Papanicolaou test. After admitting that she read her chart while the nurse was out of the room, Katrina asks what dysplasia means. Which definition should the nurse provide? A. Presence of completely undifferentiated tumor cells that don’t resemble cells of the tissues of their origin. B. Increase in the number of normal cells in a normal arrangement in a tissue or an organ. C. Replacement of one type of fully differentiated cell by another in tissues where the second type normally isn’t found. D. Alteration in the size, shape, and organization of differentiated cells. 21. During a routine checkup, Nurse Marianne assesses a male client with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) for signs and symptoms of cancer. What is the most common AIDS-related cancer? A. Squamous cell carcinoma B. Multiple myeloma C. Leukemia D. Kaposi’s sarcoma 22. Ricardo is scheduled for a prostatectomy, and the anesthesiologist plans to use a spinal (subarachnoid) block during surgery. In the operating room, the nurse positions the client according to the anesthesiologist’s instructions. Why does the client require special positioning for this type of anesthesia? A. To prevent confusion B. To prevent seizures C. To prevent cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage D. To prevent cardiac arrhythmias 23. A male client had a nephrectomy 2 days ago and is now complaining of abdominal pressure and nausea. The first nursing action should be to: A. Auscultate bowel sounds. B. Palpate the abdomen. C. Change the client’s position. D. Insert a rectal tube. 24. Wilfredo with a recent history of rectal bleeding is being prepared for a colonoscopy. How should the nurse Patricia position the client for this test initially? A. Lying on the right side with legs straight B. Lying on the left side with knees bent C. Prone with the torso elevated D. Bent over with hands touching the floor 25. A male client with inflammatory bowel disease undergoes an ileostomy. On the first day after surgery, Nurse Oliver notes that the client’s stoma appears dusky. How should the nurse interpret this finding? A. Blood supply to the stoma has been interrupted. B. This is a normal finding 1 day after surgery. C. The ostomy bag should be adjusted. D. An intestinal obstruction has occurred. 26. Anthony suffers burns on the legs, which nursing intervention helps prevent contractures? A. Applying knee splints B. Elevating the foot of the bed C. Hyperextending the client’s palms D. Performing shoulder range-of-motion exercises 27. Nurse Ron is assessing a client admitted with second- and third-degree burns on the face, arms, and chest. Which finding indicates a potential problem? A. Partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) value of 80 mm Hg. B. Urine output of 20 ml/hour. C. White pulmonary secretions. D. Rectal temperature of 100.6° F (38° C). 28. Mr. Mendoza who has suffered a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is too weak to move on his own. To help the client avoid pressure ulcers, Nurse Celia should: A. Turn him frequently. B. Perform passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises. C. Reduce the client’s fluid intake. D. Encourage the client to use a footboard. 29. Nurse Maria plans to administer dexamethasone cream to a female client who has dermatitis over the anterior chest. How should the nurse apply this topical agent? A. With a circular motion, to enhance absorption. B. With an upward motion, to increase blood supply to the affected area C. In long, even, outward, and downward strokes in the direction of hair growth D. In long, even, outward, and upward strokes in the direction opposite hair growth 30. Nurse Kate is aware that one of the following classes of medication protect the ischemic myocardium by blocking catecholamines and sympathetic nerve stimulation is: A. Beta-adrenergic blockers B. Calcium channel blocker C. Narcotics D. Nitrates 31. A male client has jugular distention. On what position should the nurse place the head of the bed to obtain the most accurate reading of jugular vein distention? A. High Fowler’s B. Raised 10 degrees C. Raised 30 degrees D. Supine position 32. The nurse is aware that one of the following classes of medications maximizes cardiac performance in clients with heart failure by increasing ventricular contractility? A. Beta-adrenergic blockers B. Calcium channel blocker C. Diuretics D. Inotropic agents 33. A male client has a reduced serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level and an elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) level. Which of the following dietary modifications is not appropriate for this client? A. Fiber intake of 25 to 30 g daily B. Less than 30% of calories from fat C. Cholesterol intake of less than 300 mg daily D. Less than 10% of calories from saturated fat 34. A 37-year-old male client was admitted to the coronary care unit (CCU) 2 days ago with an acute myocardial infarction. Which of the following actions would breach the client confidentiality? A. The CCU nurse gives a verbal report to the nurse on the telemetry unit before transferring the client to that unit B. The CCU nurse notifies the on-call physician about a change in the client’s condition C. The emergency department nurse calls up the latest electrocardiogram results to check the client’s progress. D. At the client’s request, the CCU nurse updates the client’s wife on his condition 35. A male client arriving in the emergency department is receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation from paramedics who are giving ventilations through an endotracheal (ET) tube that they placed in the client’s home. During a pause in compressions, the cardiac monitor shows narrow QRS complexes and a heart rate of beats/minute with a palpable pulse. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? A. Start an L.V. line and administer amiodarone (Cordarone), 300 mg L.V. over 10 minutes. B. Check endotracheal tube placement. C. Obtain an arterial blood gas (ABG) sample. D. Administer atropine, 1 mg L.V. 36. After cardiac surgery, a client’s blood pressure measures 126/80 mm Hg. Nurse Katrina determines that mean arterial pressure (MAP) is which of the following? A. 46 mm Hg B. 80 mm Hg C. 95 mm Hg D. 90 mm Hg 37. A female client arrives at the emergency department with chest and stomach pain and a report of black tarry stool for several months. Which of the following order should the nurse Oliver anticipate? A. Cardiac monitor, oxygen, creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase levels B. Prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen and fibrin split product values C. Electrocardiogram, complete blood count, testing for occult blood, comprehensive serum metabolic panel D. Electroencephalogram, alkaline phosphatase, and aspartate aminotransferase levels, basic serum metabolic panel 38. Macario had coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery 3 days ago. Which of the following conditions is suspected by the nurse when a decrease in platelet count from 230,000 ul to 5,000 ul is noted? A. Pancytopenia B. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) C. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) D. Heparin-associated thrombosis and thrombocytopenia (HATT) 39. Which of the following drugs would be ordered by the physician to improve the platelet count in a male client with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)? A. Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) B. Corticosteroids C. Methotrexate D. Vitamin K 40. A female client is scheduled to receive a heart valve replacement with a porcine valve. Which of the following types of transplant is this? A. Allogeneic B. Autologous C. Syngeneic D. Xenogeneic 41. Marco falls off his bicycle and injures his ankle. Which of the following actions shows the initial response to the injury in the extrinsic pathway? A. Release of Calcium B. Release of tissue thromboplastin C. Conversion of factors XII to factor XIIa D. Conversion of factor VIII to factor VIIIa 42. Instructions for a client with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) would include information about which of the following blood dyscrasias? A. Dressler’s syndrome B. Polycythemia C. Essential thrombocytopenia D. Von Willebrand’s disease 43. The nurse is aware that the following symptom is most commonly an early indication of stage 1 Hodgkin’s disease? A. Pericarditis B. Night sweat C. Splenomegaly D. Persistent hypothermia 44. Francis with leukemia has neutropenia. Which of the following functions must be frequently assessed? A. Blood pressure B. Bowel sounds C. Heart sounds D. Breath sounds 45. The nurse knows that neurologic complications of multiple myeloma (MM) usually involve which of the following body system? A. Brain B. Muscle spasm C. Renal dysfunction D. Myocardial irritability 46. Nurse Patricia is aware that the average length of time from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection to the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)? A. Less than 5 years B. 5 to 7 years C. 10 years D. More than 10 years 47. An 18-year-old male client admitted with heat stroke begins to show signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following laboratory findings is most consistent with DIC? A. Low platelet count B. Elevated fibrinogen levels C. Low levels of fibrin degradation products D. Reduced prothrombin time 48. Mario comes to the clinic complaining of fever, drenching night sweats, and unexplained weight loss over the past 3 months. Physical examination reveals a single enlarged supraclavicular lymph node. Which of the following is the most probable diagnosis? A. Influenza B. Sickle cell anemia C. Leukemia D. Hodgkin’s disease 49. A male client with a gunshot wound requires an emergency blood transfusion. His blood type is AB negative. Which blood type would be the safest for him to receive? A. AB Rh-positive B. A Rh-positive C. A Rh-negative D. O Rh-positive Situation: Stacy is diagnosed with acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL) and beginning chemotherapy. 50. Stacy is discharged from the hospital following her chemotherapy treatments. Which statement of Stacy’s mother indicated that she understands when she will contact the physician? A. “I should contact the physician if Stacy has difficulty in sleeping”. B. “I will call my doctor if Stacy has persistent vomiting and diarrhea”. C. “My physician should be called if Stacy is irritable and unhappy”. D. “Should Stacy have continued hair loss, I need to call the doctor”. NCLEX Practice Exam 26 (50 Questions) 1. Stacy’s mother states to the nurse that it is hard to see Stacy with no hair. The best response for the nurse is: A. “Stacy looks very nice wearing a hat”. B. “You should not worry about her hair, just be glad that she is alive”. C. “Yes, it is upsetting. But try to cover up your feelings when you are with her or else she may be upset”. D. “This is only temporary; Stacy will re-grow new hair in 3-6 months but may be different in texture”. 2. Stacy has beginning stomatitis. To promote oral hygiene and comfort, the nurse-in-charge should: A. Provide frequent mouthwash with normal saline. B. Apply viscous Lidocaine to oral ulcers as needed. C. Use lemon glycerine swabs every 2 hours. D. Rinse mouth with Hydrogen Peroxide. 3. During the administration of chemotherapy agents, Nurse Oliver observed that the IV site is red and swollen when the IV is touched Stacy shouts in pain. The first nursing action to take is: A. Notify the physician B. Flush the IV line with saline solution C. Immediately discontinue the infusion D. Apply an ice pack to the site, followed by warm compress. 4. The term “blue bloater” refers to a male client which of the following conditions? A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) B. Asthma C. Chronic obstructive bronchitis D. Emphysema 5. The term “pink puffer” refers to the female client with which of the following conditions? A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) B. Asthma C. Chronic obstructive bronchitis D. Emphysema 6. Jose is in danger of respiratory arrest following the administration of a narcotic analgesic. An arterial blood gas value is obtained. Nurse Oliver would expect the paco2 to be which of the following values? A. 15 mm Hg B. 30 mm Hg C. 40 mm Hg D. 80 mm Hg 7. Timothy’s arterial blood gas (ABG) results are as follows; pH 7.16; Paco2 80 mm Hg; Pao2 46 mm Hg; HCO3- 24 mEq/L; Sao2 81%. This ABG result represents which of the following conditions? A. Metabolic acidosis B. Metabolic alkalosis C. Respiratory acidosis D. Respiratory alkalosis 8. Norma has started a new drug for hypertension. Thirty minutes after she takes the drug, she develops chest tightness and becomes short of breath and tachypneic. She has a decreased level of consciousness. These signs indicate which of the following conditions? A. Asthma attack B. Pulmonary embolism C. Respiratory failure D. Rheumatoid arthritis Situation: Mr. Gonzales was admitted to the hospital with ascites and jaundice. To rule out cirrhosis of the liver: 9. Which laboratory test indicates liver cirrhosis? A. Decreased red blood cell count B. Decreased serum acid phosphatase level C. Elevated white blood cell count D. Elevated serum aminotransferase 10. The biopsy of Mr. Gonzales confirms the diagnosis of cirrhosis. Mr. Gonzales is at increased risk for excessive bleeding primarily because of: A. Impaired clotting mechanism B. Varix formation C. Inadequate nutrition D. Trauma of invasive procedure 11. Mr. Gonzales develops hepatic encephalopathy. Which clinical manifestation is most common with this condition? A. Increased urine output B. Altered level of consciousness C. Decreased tendon reflex D. Hypotension 12. When Mr. Gonzales regained consciousness, the physician orders 50 ml of Lactulose p.o. every 2 hours. Mr. Gonzales develops diarrhea. The nurse best action would be: A. “I’ll see if your physician is in the hospital”. B. “Maybe you’re reacting to the drug; I will withhold the next dose”. C. “I’ll lower the dosage as ordered so the drug causes only 2 to 4 stools a day”. D. “Frequently, bowel movements are needed to reduce sodium level”. 13. Which of the following groups of symptoms indicates a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm? A. Lower back pain, increased blood pressure, decreased red blood cell (RBC) count, increased white blood (WBC) count. B. Severe lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, increased WBC count. C. Severe lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, decreased RBC count, decreased WBC count. D. Intermittent lower back pain, decreased blood pressure, decreased RBC count, increased WBC count. 14. After undergoing a cardiac catheterization, Tracy has a large puddle of blood under his buttocks. Which of the following steps should the nurse take first? A. Call for help. B. Obtain vital signs C. Ask the client to “lift up” D. Apply gloves and assess the groin site 15. Which of the following treatment is a suitable surgical intervention for a client with unstable angina? A. Cardiac catheterization B. Echocardiogram C. Nitroglycerin D. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) 16. The nurse is aware that the following terms used to describe reduced cardiac output and perfusion impairment due to ineffective pumping of the heart is: A. Anaphylactic shock B. Cardiogenic shock C. Distributive shock D. Myocardial infarction (MI) 17. A client with hypertension ask the nurse which factors can cause blood pressure to drop to normal levels? A. Kidneys’ excretion to sodium only. B. Kidneys’ retention of sodium and water C. Kidneys’ excretion of sodium and water D. Kidneys’ retention of sodium and excretion of water 18. Nurse Rose is aware that the statement that best explains why furosemide (Lasix) is administered to treat hypertension is: A. It dilates peripheral blood vessels. B. It decreases sympathetic cardioacceleration. C. It inhibits the angiotensin-converting enzymes D. It inhibits reabsorption of sodium and water in the loop of Henle. 19. Nurse Nikki knows that laboratory results supports the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is: A. Elevated serum complement level B. Thrombocytosis, elevated sedimentation rate C. Pancytopenia, elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer D. Leukocytosis, elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels 20. Arnold, a 19-year-old client with a mild concussion is discharged from the emergency department. Before discharge, he complains of a headache. When offered acetaminophen, his mother tells the nurse the headache is severe and she would like her son to have something stronger. Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate? A. “Your son had a mild concussion, acetaminophen is strong enough.” B. “Aspirin is avoided because of the danger of Reye’s syndrome in children or young adults.” C. “Narcotics are avoided after a head injury because they may hide a worsening condition.” D. Stronger medications may lead to vomiting, which increases the intracranial pressure (ICP).” 21. When evaluating an arterial blood gas from a male client with a subdural hematoma, the nurse notes the Paco2 is 30 mm Hg. Which of the following responses best describes the result? A. Appropriate; lowering carbon dioxide (CO2) reduces intracranial pressure (ICP) B. Emergent; the client is poorly oxygenated C. Normal D. Significant; the client has alveolar hypoventilation 22. When prioritizing care, which of the following clients should the nurse Olivia assess first? A. A 17-year-old client 24-hours post appendectomy B. A 33-year-old client with a recent diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome C. A 50-year-old client 3 days post myocardial infarction D. A 50-year-old client with diverticulitis 23. JP has been diagnosed with gout and wants to know why colchicine is used in the treatment of gout. Which of the following actions of colchicines explains why it’s effective for gout? A. Replaces estrogen B. Decreases infection C. Decreases inflammation D. Decreases bone demineralization 24. Norma asks for information about osteoarthritis. Which of the following statements about osteoarthritis is correct? A. Osteoarthritis is rarely debilitating B. Osteoarthritis is a rare form of arthritis C. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis D. Osteoarthritis affects people over 60 25. Ruby is receiving thyroid replacement therapy develops the flu and forgets to take her thyroid replacement medicine. The nurse understands that skipping this medication will put the client at risk for developing which of the following life threatening complications? A. Exophthalmos B. Thyroid storm C. Myxedema coma D. Tibial myxedema 26. Nurse Sugar is assessing a client with Cushing’s syndrome. Which observation should the nurse report to the physician immediately? A. Pitting edema of the legs B. An irregular apical pulse C. Dry mucous membranes D. Frequent urination 27. Cyrill with severe head trauma sustained in a car accident is admitted to the intensive care unit. Thirty-six hours later, the client’s urine output suddenly rises above 200 ml/hour, leading the nurse to suspect diabetes insipidus. Which laboratory findings support the nurse’s suspicion of diabetes insipidus? A. Above-normal urine and serum osmolality levels B. Below-normal urine and serum osmolality levels C. Above-normal urine osmolality level, below-normal serum osmolality level D. Below-normal urine osmolality level, above-normal serum osmolality level 28. Jomari is diagnosed with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) is stabilized and prepared for discharge. When preparing the client for discharge and home management, which of the following statements indicates that the client understands her condition and how to control it? A. “I can avoid getting sick by not becoming dehydrated and by paying attention to my need to urinate, drink, or eat more than usual.” B. “If I experience trembling, weakness, and headache, I should drink a glass of soda that contains sugar.” C. “I will have to monitor my blood glucose level closely and notify the physician if it’s constantly elevated.” D. “If I begin to feel especially hungry and thirsty, I’ll eat a snack high in carbohydrates.” 29. A 66-year-old client has been complaining of sleeping more, increased urination, anorexia, weakness, irritability, depression, and bone pain that interferes with her going outdoors. Based on these assessment findings, the nurse would suspect which of the following disorders? A. Diabetes mellitus B. Diabetes insipidus C. Hypoparathyroidism D. Hyperparathyroidism 30. Nurse Lourdes is teaching a client recovering from Addisonian crisis about the need to take fludrocortisone acetate and hydrocortisone at home. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? A. “I’ll take my hydrocortisone in the late afternoon, before dinner.” B. “I’ll take all of my hydrocortisone in the morning, right after I wake up.” C. “I’ll take two-thirds of the dose when I wake up and one-third in the late afternoon.” D. “I’ll take the entire dose at bedtime.” 31. Which of the following laboratory test results would suggest to the nurse Len that a client has a corticotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma? A. High corticotropin and low cortisol levels B. Low corticotropin and high cortisol levels C. High corticotropin and high cortisol levels D. Low corticotropin and low cortisol levels 32. A male client is scheduled for a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy to remove a pituitary tumor. Preoperatively, the nurse should assess for potential complications by doing which of the following? A. Testing for ketones in the urine B. Testing urine specific gravity C. Checking temperature every 4 hours D. Performing capillary glucose testing every 4 hours 33. Capillary glucose monitoring is being performed every 4 hours for a client diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis. Insulin is administered using a scale of regular insulin according to glucose results. At 2 p.m., the client has a capillary glucose level of 250 mg/dl for which he receives 8 U of regular insulin. Nurse Mariner should expect the dose’s: A. onset to be at 2 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 p.m. B. onset to be at 2:15 p.m. and its peak to be at 3 p.m. C. onset to be at 2:30 p.m. and its peak to be at 4 p.m. D. onset to be at 4 p.m. and its peak to be at 6 p.m. 34. The physician orders laboratory tests to confirm hyperthyroidism in a female client with classic signs and symptoms of this disorder. Which test result would confirm the diagnosis? A. No increase in the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level after 30 minutes during the TSH stimulation test B. A decreased TSH level C. An increase in the TSH level after 30 minutes during the TSH stimulation test D. Below-normal levels of serum triiodothyronine (T3) and serum thyroxine (T4) as detected by radioimmunoassay 35. Rico with diabetes mellitus must learn how to self-administer insulin. The physician has prescribed 10 U of U-100 regular insulin and 35 U of U-100 isophane insulin suspension (NPH) to be taken before breakfast. When teaching the client how to select and rotate insulin injection sites, the nurse should provide which instruction? A. “Inject insulin into healthy tissue with large blood vessels and nerves.” B. “Rotate injection sites within the same anatomic region, not among different regions.” C. “Administer insulin into areas of scar tissue or hypotrophy whenever possible.” D. “Administer insulin into sites above muscles that you plan to exercise heavily later that day.” 36. Nurse Sarah expects to note an elevated serum glucose level in a client with hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). Which other laboratory finding should the nurse anticipate? A. Elevated serum acetone level B. Serum ketone bodies C. Serum alkalosis D. Below-normal serum potassium level 37. For a client with Graves’ disease, which nursing intervention promotes comfort? A. Restricting intake of oral fluids B. Placing extra blankets on the client’s bed C. Limiting intake of high-carbohydrate foods D. Maintaining room temperature in the low-normal range 38. Patrick is treated in the emergency department for a Colles’ fracture sustained during a fall. What is a Colles’ fracture? A. Fracture of the distal radius B. Fracture of the olecranon C. Fracture of the humerus D. Fracture of the carpal scaphoid 39. Cleo is diagnosed with osteoporosis. Which electrolytes are involved in the development of this disorder? A. Calcium and sodium B. Calcium and phosphorous C. Phosphorous and potassium D. Potassium and sodium 40. Johnny a firefighter was involved in extinguishing a house fire and is being treated to smoke inhalation. He develops severe hypoxia 48 hours after the incident, requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. He most likely has developed which of the following conditions? A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) B. Atelectasis C. Bronchitis D. Pneumonia 41. A 67-year-old client develops acute shortness of breath and progressive hypoxia requiring right femur. The hypoxia was probably caused by which of the following conditions? A. Asthma attack B. Atelectasis C. Bronchitis D. Fat embolism 42. A client with shortness of breath has decreased to absent breath sounds on the right side, from the apex to the base. Which of the following conditions would best explain this? A. Acute asthma B. Chronic bronchitis C. Pneumonia D. Spontaneous pneumothorax 43. A 62-year-old male client was in a motor vehicle accident as an unrestrained driver. He’s now in the emergency department complaining of difficulty of breathing and chest pain. On auscultation of his lung field, no breath sounds are present in the upper lobe. This client may have which of the following conditions? A. Bronchitis B. Pneumonia C. Pneumothorax D. Tuberculosis (TB) 44. If a client requires a pneumonectomy, what fills the area of the thoracic cavity? A. The space remains filled with air only B. The surgeon fills the space with a gel C. Serous fluids fills the space and consolidates the region D. The tissue from the other lung grows over to the other side 45. Hemoptysis may be present in the client with a pulmonary embolism because of which of the following reasons? A. Alveolar damage in the infarcted area B. Involvement of major blood vessels in the occluded area C. Loss of lung parenchyma D. Loss of lung tissue 46. Alvin with a massive pulmonary embolism will have an arterial blood gas analysis performed to determine the extent of hypoxia. The acid-base disorder that may be present is? A. Metabolic acidosis B. Metabolic alkalosis C. Respiratory acidosis D. Respiratory alkalosis 47. After a motor vehicle accident, Armand a 22-year-old client is admitted with a pneumothorax. The surgeon inserts a chest tube and attaches it to a chest drainage system. Bubbling soon appears in the water seal chamber. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the bubbling? A. Air leak B. Adequate suction C. Inadequate suction D. Kinked chest tube 48. Nurse Michelle calculates the IV flow rate for a postoperative client. The client receives 3,000 ml of Ringer’s lactate solution IV to run over 24 hours. The IV infusion set has a drop factor of 10 drops per milliliter. The nurse should regulate the client’s IV to deliver how many drops per minute? A. 18 B. 21 C. 35 D. 40 49. Mickey, a 6-year-old child with a congenital heart disorder is admitted with congestive heart failure. Digoxin (lanoxin) 0.12 mg is ordered for the child. The bottle of Lanoxin contains .05 mg of Lanoxin in 1 ml of solution. What amount should the nurse administer to the child? A. 1.2 ml B. 2.4 ml C. 3.5 ml D. 4.2 ml 50. Nurse Alexandra teaches a client about elastic stockings. Which of the following statements, if made by the client, indicates to the nurse that the teaching was successful? A. “I will wear the stockings until the physician tells me to remove them.” B. “I should wear the stockings even when I am asleep.” C. “Every four hours I should remove the stockings for a half hour.” D. “I should put on the stockings before getting out of bed in the morning.” • [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 230 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 2 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 05, 2020
Number of pages
230
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 05, 2020
Downloads
3
Views
1134