Pharmacology > EXAMs > Pharmacology Exam 4 Review: Chapter 20 Anxiolytics and Hypnotic Agents! Chapter 21 Chapter 22 Chapte (All)
Pharmacology Exam 4 Review: Chapter 20 Anxiolytics and Hypnotic Agents! Chapter 21 Chapter 22 Chapter 23: Antiepileptics Chapter 24 Chapter 25 Muscle Relaxants Chapter 27 General and Local Anesthetic AgentsAnti-parkinsonism Agents Psychotherapeutic Agents Antidepressants 3Nonselective alpha/beta assessment- assess heart Comorbid disease for viagra- angina AE to noncompliance in elderly- urinary urgency Alpha adrenergic blocker (flomax) to treat sym of bph: inhibit contraction of bladder
Document Content and Description Below
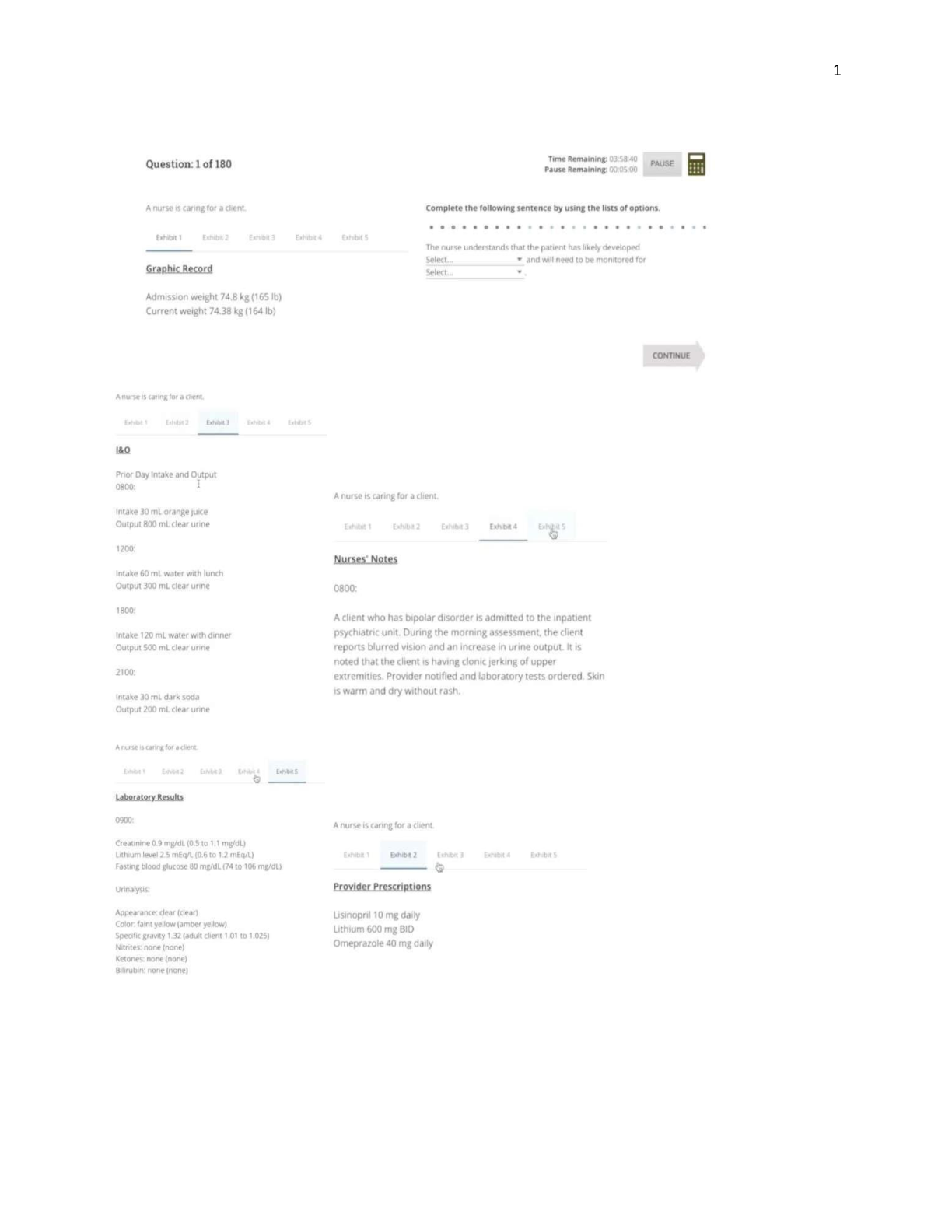
Benzodiazepines: enhance inhibitory effects of GABA in CNS. Relief from anxiety, panic disorders, stress, PTSD, absent seizures, insomnia, muscle spasm, alcohol withdrawal, preop relief of anxiety. ... Which baseline laboratory tests should a patient receive prior to starting a benzodiazepine? And why? If they have a bad liver and can't metabolize correctly does that mean the patient will have the effects of the meds longer time or less time? How will that impact the patient clinically? More awake and alert or more drowsy? So more likely or less likely to have risk for injury due to safety problems? What does all this mean to the bedside nurse? What should nurses teach patients taking anxiolytics to avoid? Why? What other drug classifications should not be stopped suddenly? Muscle relaxants Did you notice overlap with other groups? For example, what other drug classifications are indicated for patients with anxiety? **What must be monitored continuously after a patient receives versed? Phenobarbital- anxiety, insomnia, tonic-clonic seizures. Deficiency of NE, dopamine, or serotonin from rapid firing of neurons or sensitive postsynaptic receptors that increase, causing depleting neurotransaqmitter levels. Increases risk for suicide! SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors)- blocks serotonin reuptake which intensifies effects of serotonin. 1st line treatment for depression. Benefits of SSRIs takes about a month to see benefits and noting the increased risk of suicide. Please tell us more about the life threatening adverse effects of serotonin syndrome. Please explain more about the drug-drug and drug-food/drink interactions with MAO inhibitors Contraindicated with: What is particularly important to teach women who are of child-bearing age about antidepressants? Why? Do some people have depression and anxiety? How should their treatment differ from patients who report depression symptoms only without anxiety? SSRI that’s not energizing. Zoloft, Paroxetine Block dopamine, ACh, histamine, and NE receptors. Treats schizophrenia spectrum disorder, mania, bipolar, narcolepsy, ADD. Doesn’t cure, just helps them function normally (without hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior….). These meds do not cause addiction. Not for those with breast cancer, dementia, Parkinsons. Black Box: Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotics are at increased risk for death. Tell me more about Lithium. Indications, MOA, AE, Patient teaching, lab values and drug-drug interactions. Is it safe for patients who are pregnant? Tell me more about chlorpromazine - indications, MOA, contraindications, AEs, patient teaching. Chapter 23: Antiepileptics Control seizures by slowing the entrance of sodium and calcium back into the neuron. Extends the time it takes for the nerves to return to active state, slowly frequency of neuron firing. What antiseizure medication should be avoided in the Asian population? Please list all antiseizure agents that have therapeutic ranges and what they are. Why? Because you need to know these values. Which medication is often administered for patients undergoing alcohol withdrawal? Why? What should nurses teach patients with seizures and/or epilepsy to wear? Why? What should the nurse teach the patient and family regarding the administration of Levodopa-carbidopa in regards to foods and vitamins? Please explain the rationale for each interaction What about protein intake? So do we withhold protein in these patients or how long do we need to space meds from their protein meals. WE all know how important protein is to the body! Please explain why the following medications are used to treat Parkinson's disease and how they differ in mechanism of action. Levodopa and Carbidopa Why would nurses be concerned if this medication was ordered for a patient who works as a crane operator? Please tell us when the patient is most at risk for signs and symptoms of idiosyncratic adverse effects appearing and how to monitor for this AE Dantrolene is perfect. Too bad this lifesaving drug can't be used if the patient has liver failure. So what lab values must the nurse monitor? What are the signs and symptoms of malignant hyperthermia? Who is most at risk for this condition? There's a few AE's specific to Baclofen. Can you tell me what they are? So audience what are the common patient teaching guidelines for most muscle relaxants? what usual indication does bacoflen have that's unique? what AE would be especially troubling for this specific patient population? When is naloxone (Narcan) indicated? How short acting is this medication and what does that mean for the nurse administering this medication? What is antidote for Versed? Why are these different? What should the nurse be most concerned about when administering narcotics to hospitalized patients? What disorders should cause the nurse to be on high alert for adverse effects? What is a major caution/ contraindication for Ergot derivatives medications(migraine meds)? Why can Ergot derivatives and other anti-migraine medications cause heart attacks? Please compare and contrast the mechanism of action, onset and peak times, and contraindications for the antimigraine agents What other non-anti-migraine medications are used for migraine prophylaxis? What's a super important caution/contraindication for most of these drug classifications? Another problem is their vasoconstriction is not selective meaning it doesn't limit the vasoconstriction to arteries in the brain - it does it everywhere? So what does that mean for a patient's B/P after taking a antimigraine med such as ergot derivatives of triphans? The Local anesthetics decrease the permeability of the nerve cells to ions. What is the most significant ion that reduces the excitability of the cell membrane? Patients taking what drug classifications tend to have lower sodium? Why? Local anesthetics decrease the permeability of the nerve cells to ions. What is the most significant ion that reduces the excitability of the cell membrane? What are the signs and symptoms of lidocaine toxicity? Name three drugs that increase the effects of Lidocaine? What does the combination of drugs cause (drug-drug interacation)? What should a nurse be concerned about when a patient is receiving lidocaine hydrochloride via an epidural catheter? What should the nurse teach a patient who receives viscous lidocaine for pharyngeal anesthesia? What should a nurse be concerned about when a patient is receiving a marcaine block locally via a pump following a total knee replacement? • Monitor respiratory and cardiac function, sedation level, level of consciousness, pain, and any adverse effects. What are the herb interaction and dietary interactions with isoflurane and Propofol? Why do these drug-herb/fluid cause the nurse concern? What does balanced anesthesia mean? What classifications are included in this approach to anesthesia? What type of medications from previous modules be avoided in patients with epidural catheters and/or recent spinal and brain surgery? What medication(s) would the nurse anticipate anesthesia to administer to reverse the effects of neuromuscular junction blocking agents? What is recurarization? What patients are at greatest risk for this severe adverse effect? Why is Propofol white? What does that tell you and why does that tell you which co-morbidity should not receive this medication long-term (for ventilation)? What is the black box warning for succinylcholine? Why? Please tell us about ketamine Why is succinylcholine used frequently for tracheal intubation? Which of the adrenergic drugs used for hypotension and/or shock should be avoided in patients with renal failure? And why? Epinephrine or norepinephrine. Give dopamine What should the nurse do if the patient's peripheral line with norepinephrine infusing infiltrates? Why? What adrenergic drug is the first line of treatment for a patient hospitalized with decreased cardiac output due to acute exacerbation of congestive heart failure? What is the mechanism of action? Tell me about Dobutamine and Milirone. A patient arrives in the emergency department with severe hypotension with B/P of 66/34, skin tenting of 5 seconds, and dry mucous membranes. What would the nurse anticipate the provider would order? What medications have contraindications/cautions for patients with acute narrow-angle glaucoma? What medications should not be given with grapefruit juice? Are you adding this to the previous list of cholesterol and heart med list? What medication classifications cause agranulocytosis and why is this so important (risky) for patients? What medication classifications should NOT be administered in a patient who consumes alcohol? What is the goal of anti-Alzheimer medications? What is the goal of anti-Parkinson's medications? According to ATI Pharm what drug has therapeutic indications for both the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease? ATI chapter 13 What drug classifications should NOT be administered at the same time as protein? Why? What is serotonin syndrome? What drug classifications can trigger this life- threatening response and why? What are the BLACK box warning for anti-seizure agents? What are the antidotes for medications in the CNS and ANS classes? What are their half-lives? Why does the bedside nurse need to know this? How does thryotoxic crisis differ from Adrenal crisis? What are treatment priorities? What drug classifications reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives? So what do we teach the female patients? Are you keeping a running list like grapefruit juice? You should What drug classifications are teratogenic? Are you keeping a list of these? You should as these make great questions. What drug classifications are dangerous for children? Why? Are you keeping a list? What drugs increase a patient's propensity for tardive dyskinesia? Are you keeping a list? What drug classifications increase the risk of heart attacks? What's the difference between non-selective and selective alpha and beta adrenergic blocking agents? Why is it harmful to give a patient with CHF history strong alpha effects IV when having exacerbation of CHF? What drug classifications increase the risk for cancer? Breast cancer? Ovarian cancer? What do we teach a patient when a medication causes dry mucous membranes? How does this teaching differ in patients with diabetes? Which insulins can be administered IV? [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 06, 2020
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 06, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
117