Computer Science > EXAM > CS 221 exam-2014 Stanford University (All)
CS 221 exam-2014 Stanford University
Document Content and Description Below
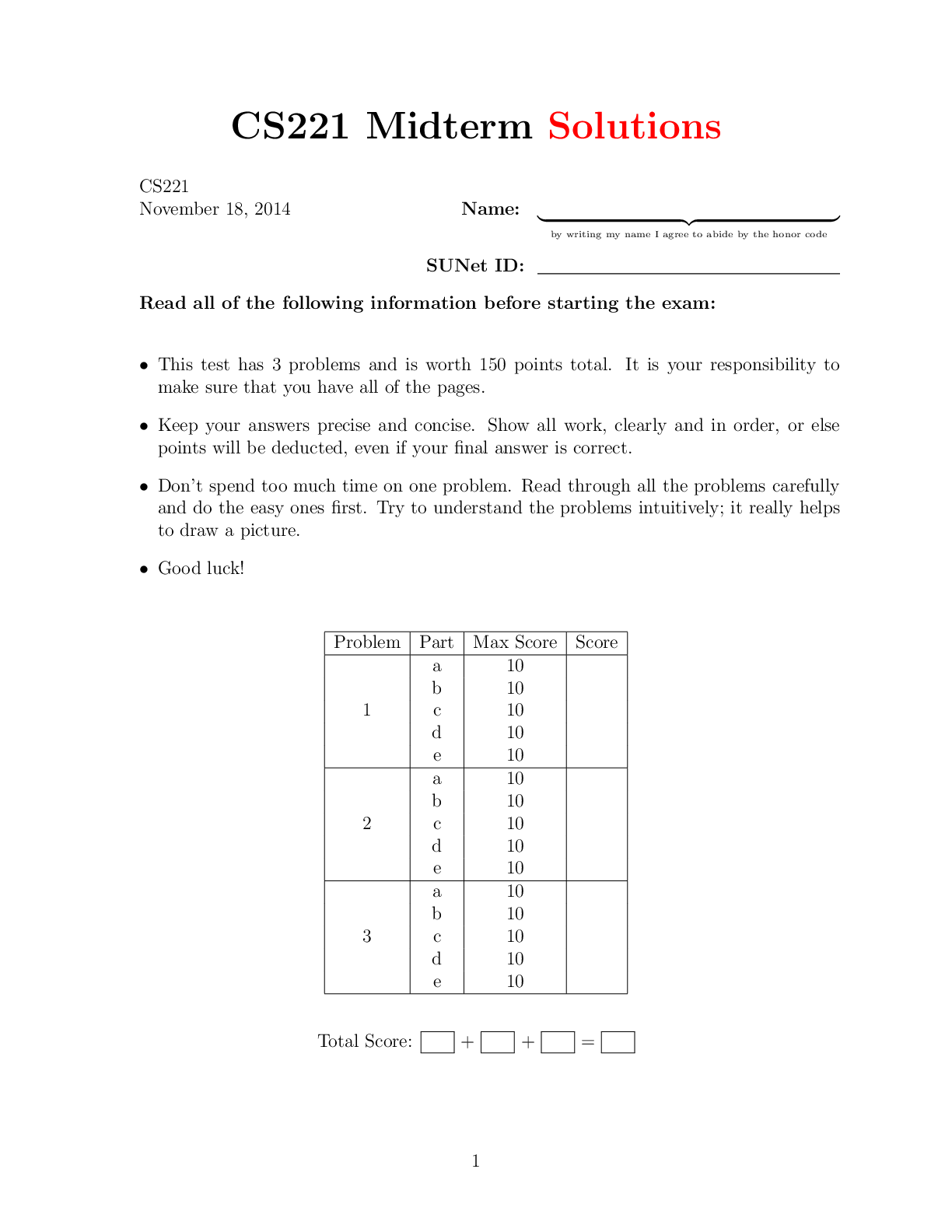
CS221 Midterm Solutions CS221 November 18, 2014 Name: | {z } by writing my name I agree to abide by the honor code SUNet ID: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: • ... This test has 3 problems and is worth 150 points total. It is your responsibility to make sure that you have all of the pages. • Keep your answers precise and concise. Show all work, clearly and in order, or else points will be deducted, even if your final answer is correct. • Don’t spend too much time on one problem. Read through all the problems carefully and do the easy ones first. Try to understand the problems intuitively; it really helps to draw a picture. • Good luck! Problem Part Max Score Score 1 a 10 b 10 c 10 d 10 e 10 2 a 10 b 10 c 10 d 10 e 10 3 a 10 b 10 c 10 d 10 e 10 Total Score: + + = 11. Enchaining Realm (50 points) This problem is about machine learning. a. (10 points) Suppose we want to predict a real-valued output y 2 R given an input x = (x1; x2) 2 R2, which is represented by a feature vector φ(x) = (x1; jx1 − x2j). Consider the following training set of (x; y) pairs: Dtrain = f((1; 2); 2); ((1; 1); 1); ((2; 1); 3)g: (1) We use a modified squared loss function, which penalizes overshooting twice as much as undershooting: Loss(x; y; w) = ((12w(w· φ· φ(x(x) )−−y)y2)2 if otherwise w · φ(x) < y (2) Using a fixed learning rate of η = 1, apply the stochastic gradient descent algorithm on this training set starting from w = [0; 0] after looping through each example (x; y) in order and performing the following update: w w − η rwLoss(x; y; w): (3) For each example in the training set, calculate the loss on that example and update the weight vector w to fill in the table below: x φ(x) Loss(x; y; w) rwLoss(x; y; w) weights w Initialization n/a n/a n/a n/a [0; 0] After example 1 (1,2) After example 2 (1,1) After example 3 (2,1) Solution x φ(x) Loss(x; y; w) rwLoss(x; y; w) weights w Initialization n/a n/a n/a n/a [0; 0] After example 1 (1,2) (1,1) 2 [−2; −2] [2; 2] After example 2 (1,1) (1,0) 1 [2; 0] [0; 2] After example 3 (2,1) (2,1) 0.5 [−2; −1] [2; 3] 2b. (10 points) Consider the following set of 6 points in the plane: fA = (0; 0); B = (1; 0); C = (0; 3); D = (1; 3); E = (5; 7); F = (8; 12)g (4) You’d like to partition the points into two clusters, where each cluster is represented by a centroid µk that is constrained to lie on the diagonal line; formally, µk = [ck; ck] for k 2 f1; 2g. Recall that the reconstruction loss is the sum of squared distances from each point to the centroid it is assigned to. Modify the K-means algorithm to minimize this loss while respecting the diagonal constraint. Suppose we have K = 2 clusters which are initialized with c1 = 3 and c2 = 11. Break ties, if any, by assigning a point to the centroid farther away from the origin. Run two iterations of K-means, filling out the values below: Iteration Task Value 1. Assignment zi = 1: (i) 1. Assignment zi = 2: (ii) 1. New c1: (iii) 1. New c2: (iv) 1. Reconstruction loss after updating centroids: (v) 2. Assignment zi = 1: (vi) 2. Assignment zi = 2: (vii) 2. New c1: (viii) 2. New c2: (ix) 2. Reconstruction loss after updating centroids: (x) 3Solution Iteration Task Value 1. Assignment zi = 1: (i) A, B, C, D, E 1. Assignment zi = 2: (ii) F 1. New c1: (iii) 2 1. New c2: (iv) 10 1. Reconstruction loss: (v) 62 2. Assignment zi = 1: (vi) A, B, C, D 2. Assignment zi = 2: (vii) E, F 2. New c1: (viii) 1 2. New c2: (ix) 8 2. Reconstruction loss: (x) 38 4c. (10 points) Given two images x1 and x2, our goal is to predict whether they are of the same person (y = 1) or not (y = −1). We build the following model: We have a feature extractor that maps an image x to a feature vector φ(x) 2 Rd. For each j = 1; : : : ; K, define hj(x) = vj · φ(x). Intuitively, each parameter vj 2 Rd corresponds to a direction; hj(x) corresponds to the projection of φ(x) along that direction. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 28 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

Stanford University CS 221 exams (2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018) , aut2018-exam, midterm2015, Midterm Spring 2019
Stanford University CS 221 exams (2014, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018) , aut2018-exam, midterm2015, Midterm Spring 2019
By Muchiri 4 years ago
$25
8
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 15, 2021
Number of pages
28
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
122