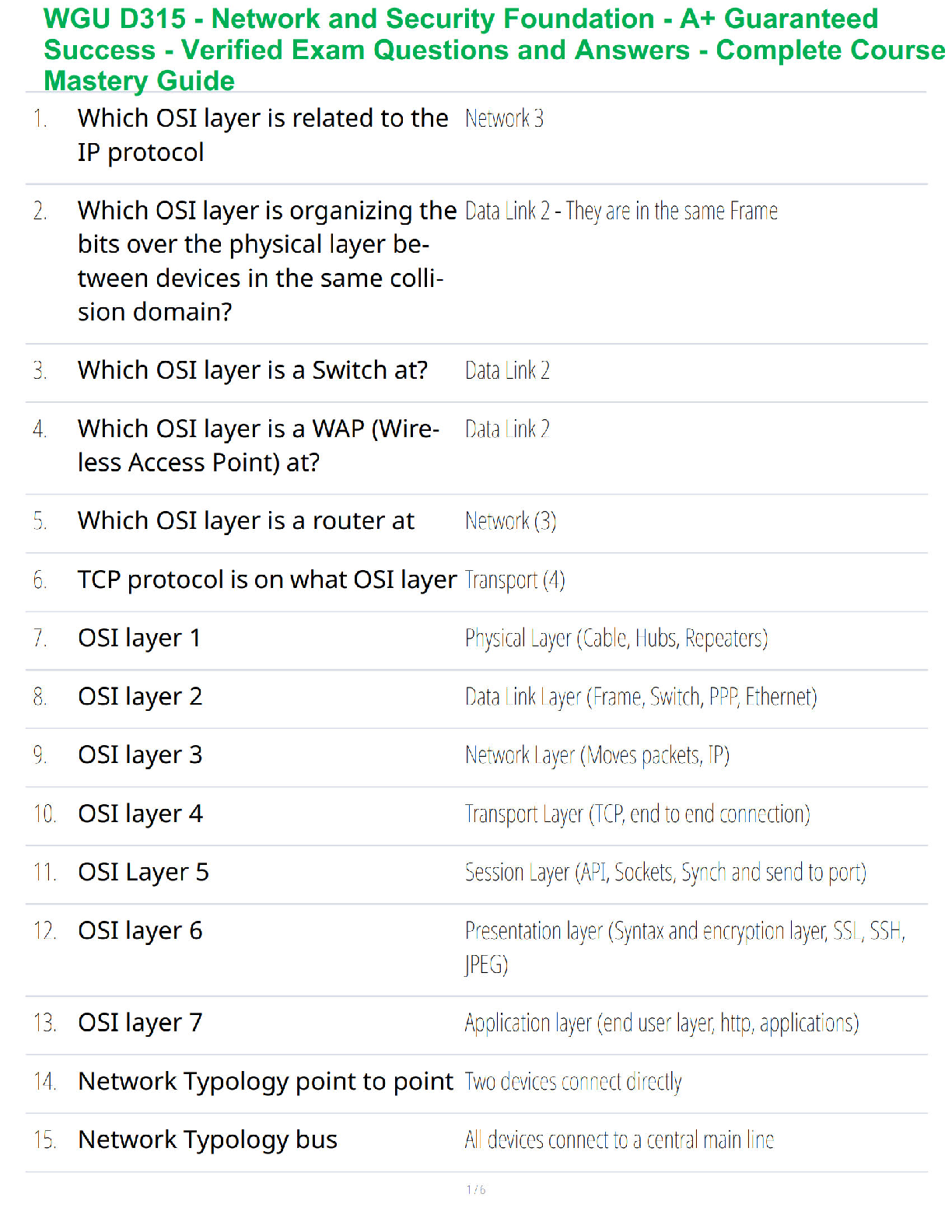
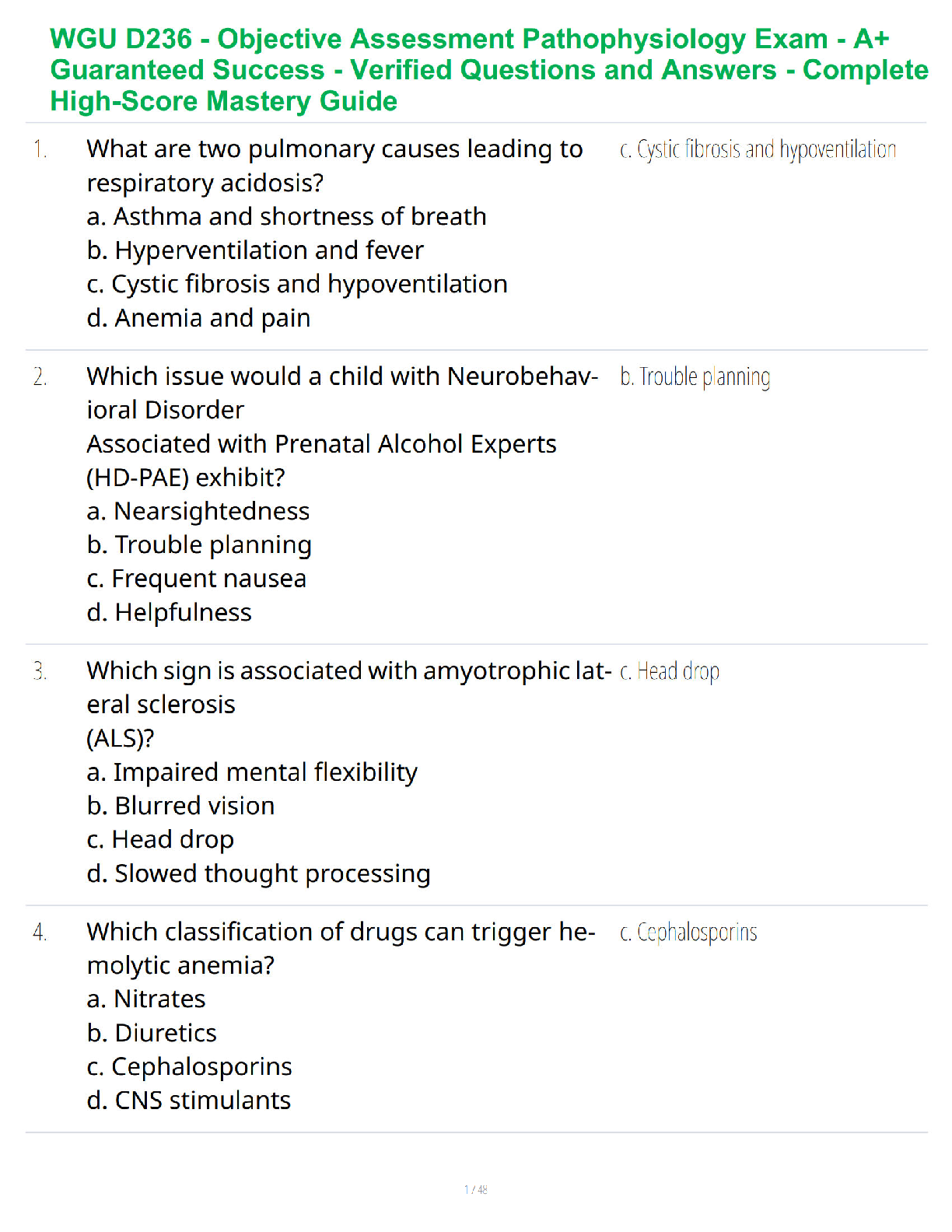
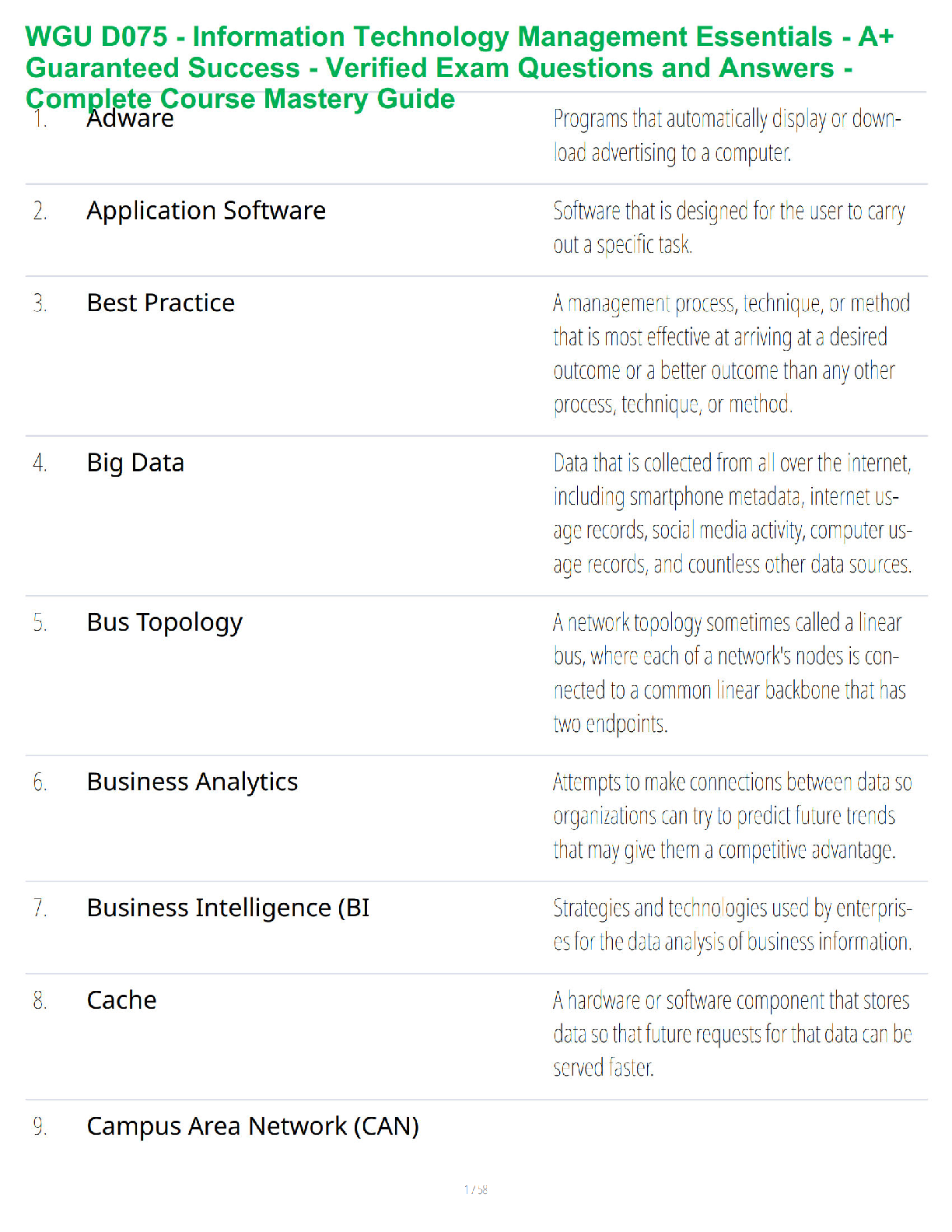
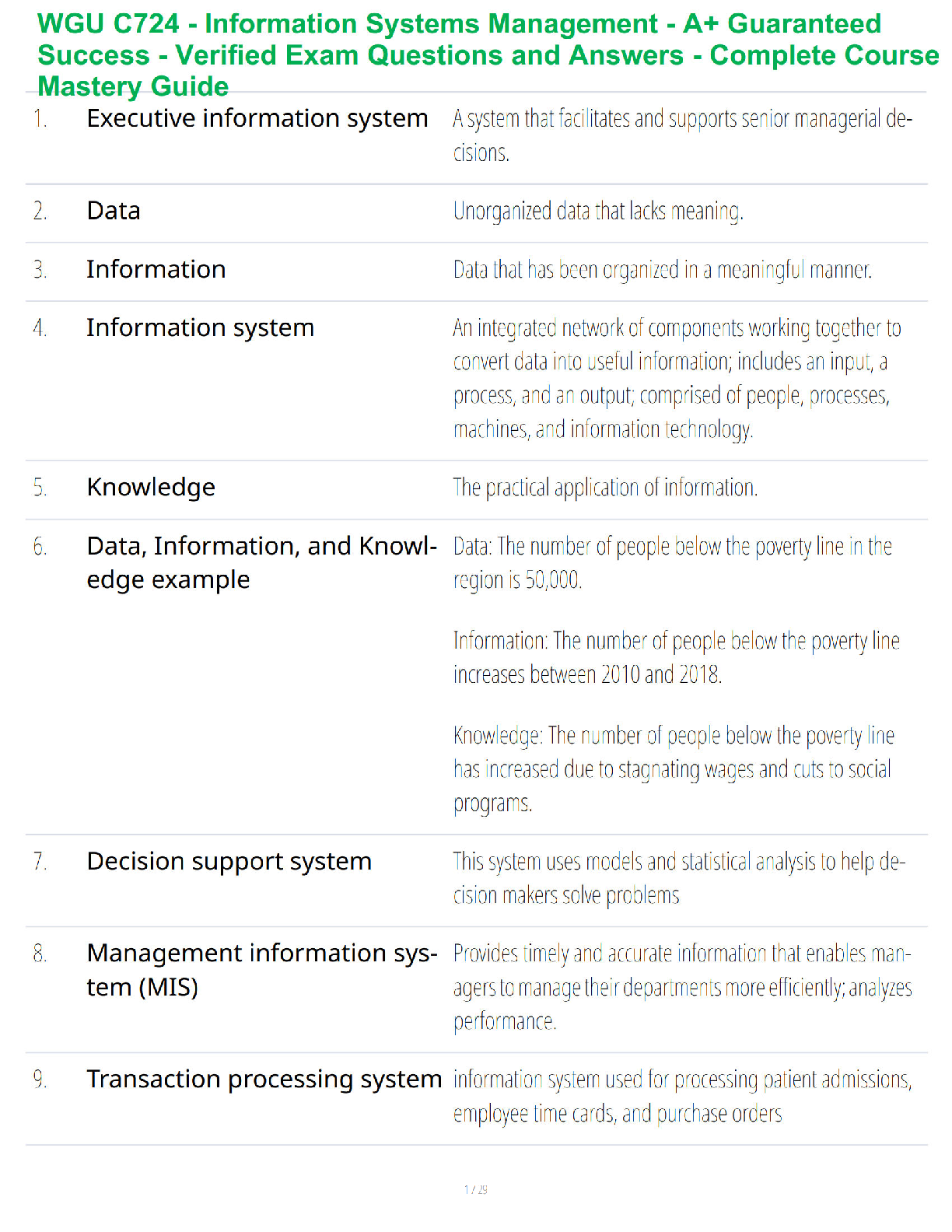
A Level Business H431/01 Question Paper 2021
$ 6.5

SOPHIA UNIT 1 Philosophy_Milestone 2 Exam | DeVry University | Correct Answers Higlighted
$ 10

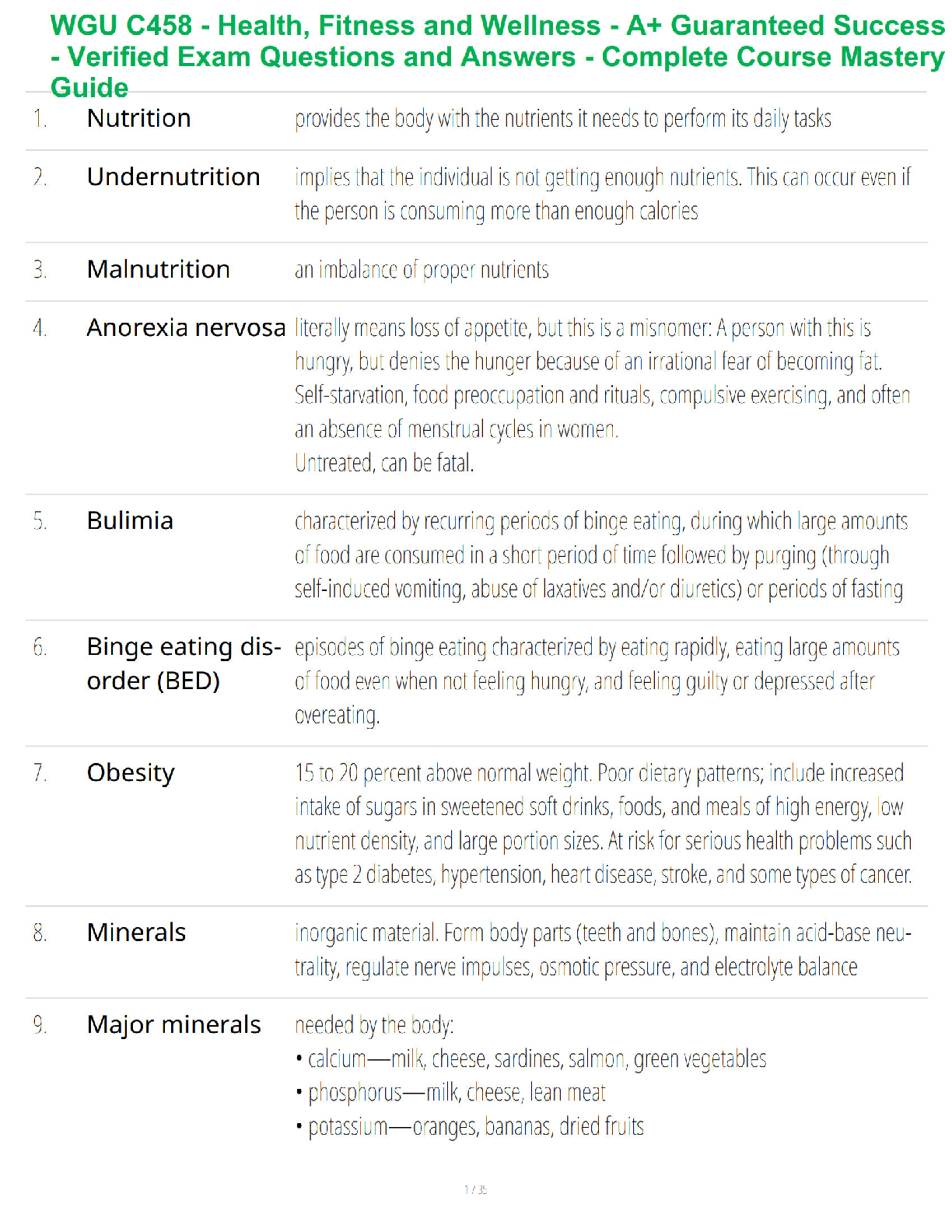
NSG 6006 Study Guide | COMPLETE GUIDE
$ 11
.png)
BIO 101 TEAS Science Study Guide 2022/2023
$ 7

BIOS 252 UNIT 8 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE | LATEST GUIDE
$ 13

NURS 6501 Week 8 Quiz Advanced Pathophysiology
$ 13.5

HUMN 303N Week 1 Discussion 1: The Value of the Humanities – Download To Score An A+
$ 10

ATI PEDS ATI 2024 B WITH NGNRATIONALES EXAM FULLY SOLVED & UPDATED
$ 35.5

HESI A2 Health Information Systems Complete Test Preparation Test Bank
$ 17.5

NR 507 Week 4 Test Winter 2020 Chamberlain University
$ 14

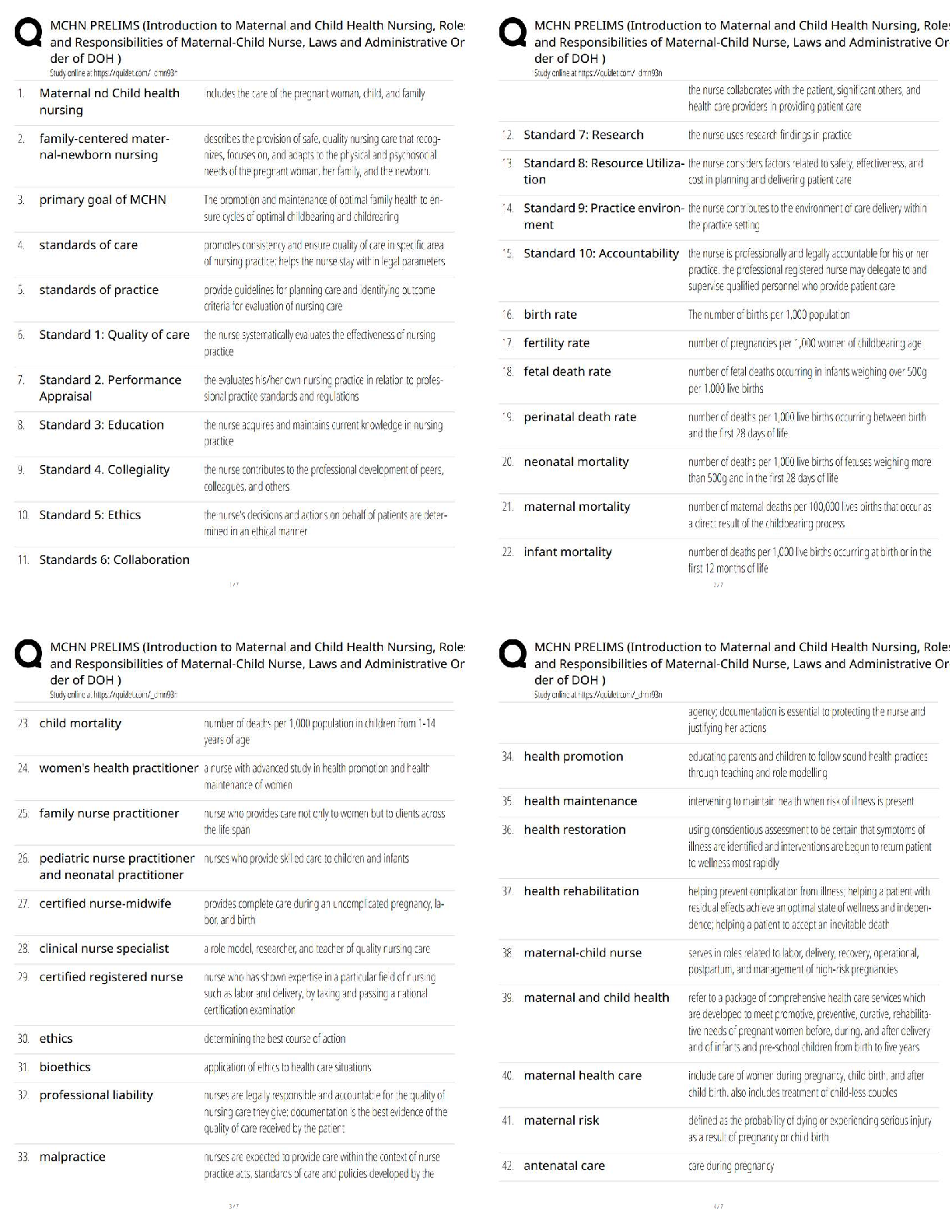
Maternal-Newborn-Nursing
$ 20

PAN Anatomy — Class Notes, Study Guide & Test Bank (High-Yield Anatomy Exam Prep)
$ 19

Principles of Pediatric Nursing: Caring for Children, 7e (Ball et al.) Chapter 1 Nurse's Role in Care of the Child: Hospital, Community, and Home
$ 14.5

Test Bank For Elementary Statistics, 4th Edition by William Navidi, Barry Monk Chapter 1-15. KEY ANSWERS AT THE END OF EVERY CHAPTER.
$ 20

MATH 221 Week 7: Quiz: Statistics for Decision-Making With Answers.
$ 12
.png)
Building Pangaea (A+ Assured)
$ 10

Concepts of Biology - study notes
$ 12

Carbon cycle Gizmo.-2020
$ 12.5
 – 100% CORRECT.png)
SOPHIA _US HISTORY UNIT 1 CHALLENGE 3 (2020) – 100% CORRECT | SOPHIA _US HISTORY UNIT 1 CHALLENGE 3 (2020) – 100% CORRECT
$ 12.5

NUR 114 Partial Focus Notes Final Fall 2019
$ 12

BIOL 214 Genes and Evolution Final Exam 4 (MULTIPLE CHOICE).
$ 7
.png)
STAT 200 Week 2 Homework Help study Guide With ALL the information needed 100%
$ 10

Comprehensive Predictor ATI 1ST Retake (2022 – 2023) With Complete Solution
$ 4

NCC EFM EXAMS AND TEST|QUESTIONS ANSWERED 100% CORRECT |2023-2024
$ 26

UNIT 3 — MILESTONE 3,100% CORRECT
$ 12

ATI MED SURG VIDEO CASE STUDIES RN 3.0 HEART FAILURE
$ 5

World Religions
$ 7
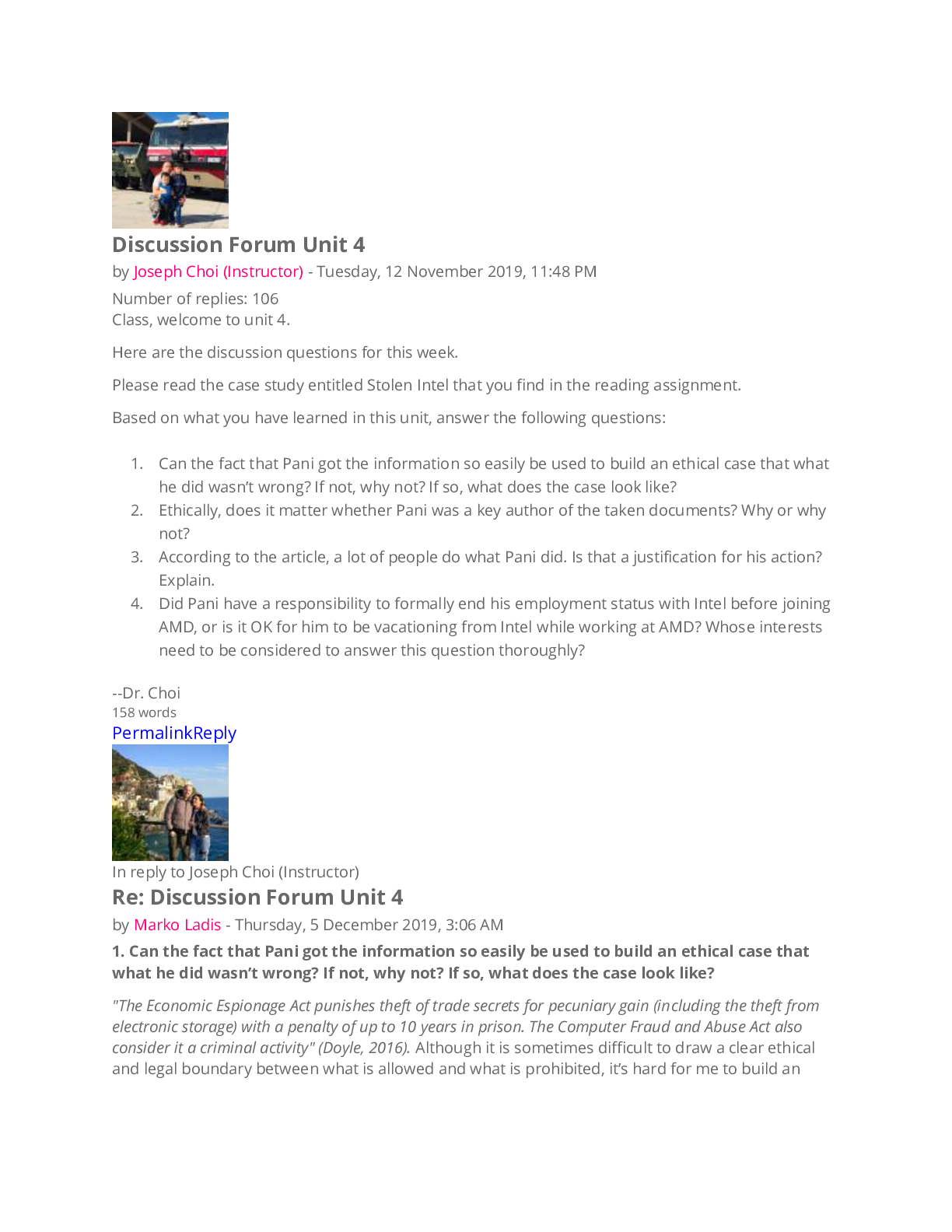
University of the People - PHIL 1404PHIL 1404 Discussion Forum Unit 4
$ 7

River Erosion GIZMO MAY 2020
$ 9

Theo 104 Quiz #2 | 50 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Updated & Verified
$ 6

ATI PEDIATRIC NURSING NCLEX TEST EXAM 2025 QUIZ 7 WITH 40 Q&A’S WITH RATIONALES (GUARANTEED PASS) | RATED A+
$ 18

Cambridge IGCSE™ (9–1) BIOLOGY 0970/01 Paper 1 Multiple Choice (Core) For examination from 2023 + MARK SCHEME
$ 12
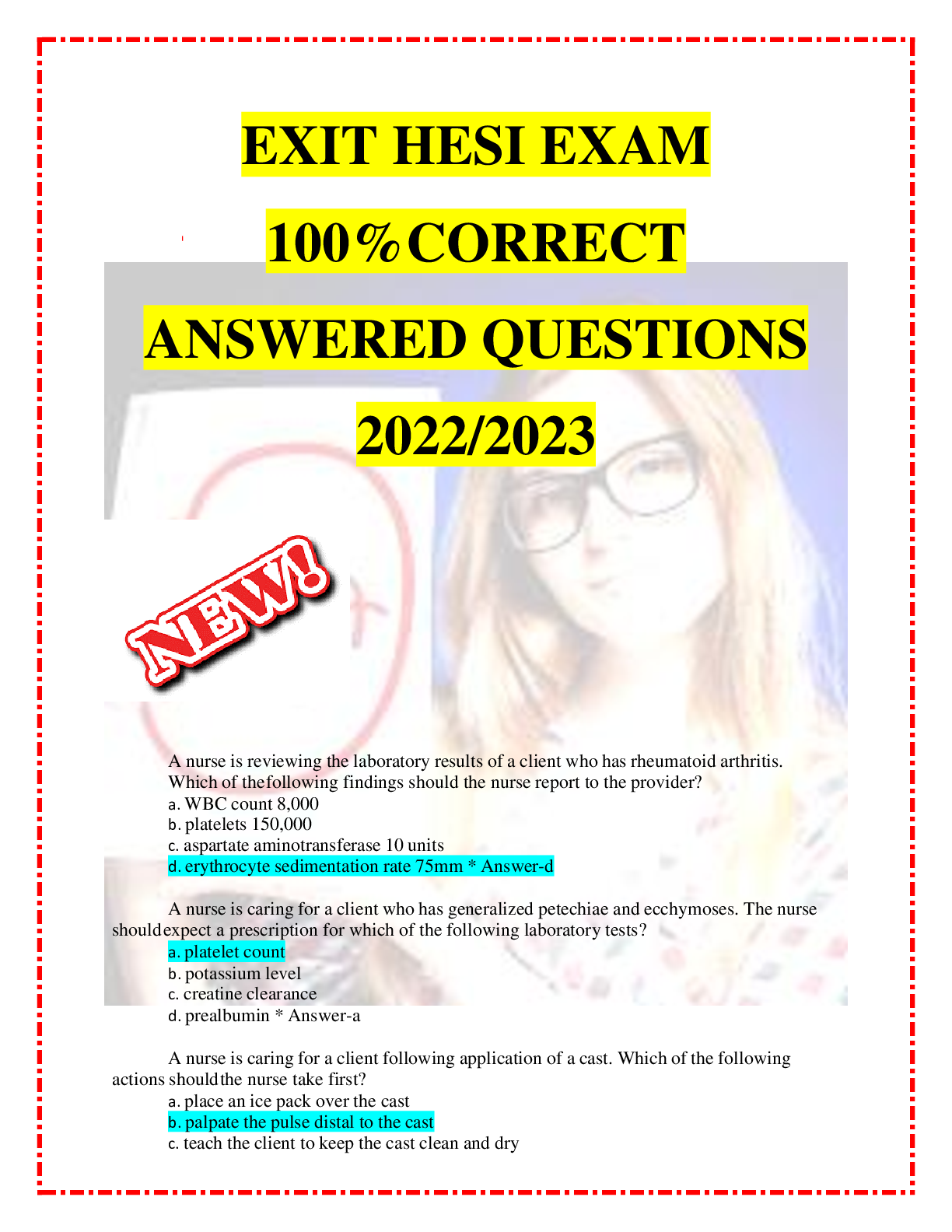
EXIT HESI EXAM 100%CORRECT ANSWERED QUESTIONS 2022/2023
$ 15

AS Systems, Programing & Algorithms 7516/2 Paper 2 Mark scheme June 2020 Version: 1.1 Final
$ 5

TEST BANK RICCI MATERNITY PEDIATRIC NURSING 3RD EDITION 2016 100% CORRECT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADED A+
$ 13.5

TLI4801 Assignment 1 & 2 2021
$ 9
.png)
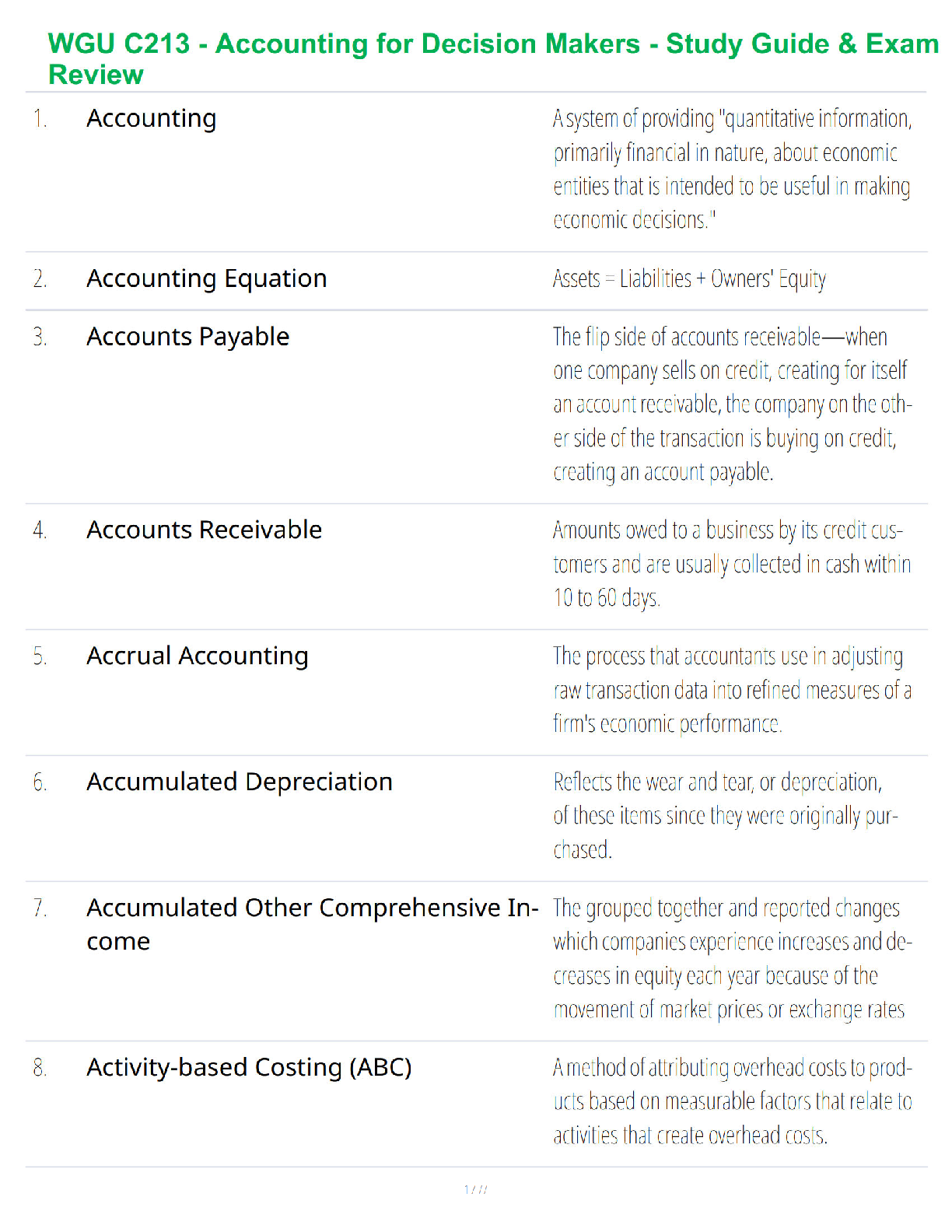
AQA A-level ACCOUNTING 7127/2 Paper 2 Accounting for analysis and decision-making Mark scheme June 2021 Version 1.0 Final Mark Scheme
$ 10

WGU C963 Quizzes 1–23 with Verified Answers (2025/2026 Update) – American Politics & U.S. Constitution, 100% Correct
$ 30
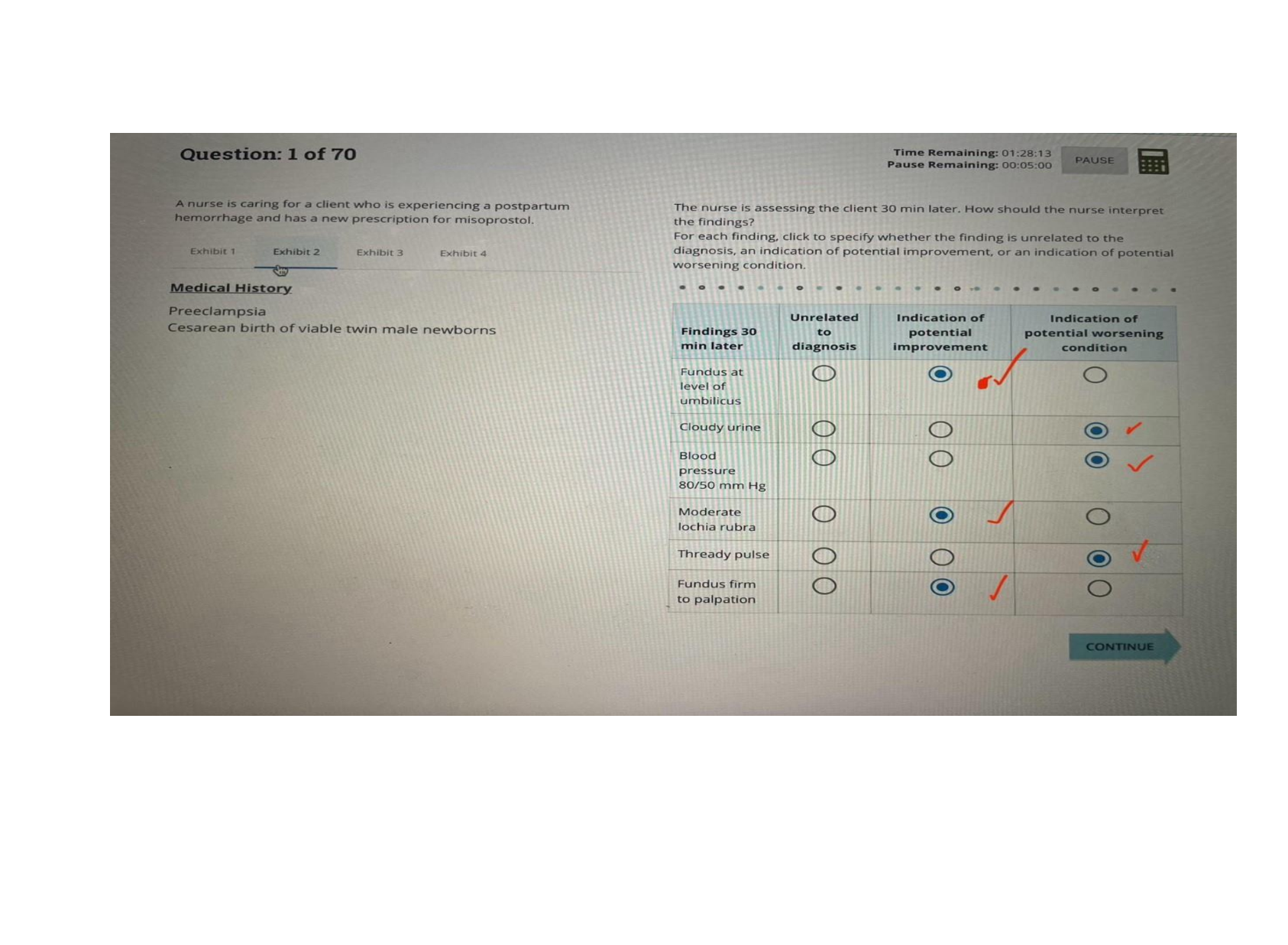
RN MATERNAL NEWBORN PROCTORED ACTUAL EXAM 100% WITH NGN 2024 (70 QUESTION & ANSWERS).pdf
$ 27

[eBook] [PDF] Aircraft Performance An Engineering Approach 2nd Edition By Mohammad H. Sadraey
$ 25

Karen Floyd Abdominal Pain
$ 12

TEST BANK Exploring Anatomy & Physiology In The Laboratory 4th Edition By Erin C. Amerman, All Chapters 1-29
$ 19

CNA Chapter 9 exam with Certified Answers
$ 1

Forensics Lab Who killed Barry?
$ 12

Biochemistry Final Exam Notes.[COMPLETELY AND 100% VERIFIED]
$ 12.5

NURS 5315 : Pathophysiology 4th EDITION STUDY GUIDE
$ 15

Brigham Young University, IdahoFDREL 225Week_01_reflection
$ 4

ATI PEDIATRICS PROCTORED LATEST 2023 TEST BANK 100 REAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND DETAILED ANSWERS|AGRADE
$ 10.5

HUMAN BIOLOGY UNIT 5 MILESTONE {30 out of 30} | Southern New Hampshire University | Already Graded A.
$ 10

Update MedSurg Final Practice Questions 2023
$ 10

NHA CCMA Certification Exam Review With Complete Solution
$ 6

Plant Research: Artichoke part 3
$ 8

AQA A-Level GEOGRAPHY Paper 2 Human Geography MS June 2020
$ 8

University of the West Indies at St. Augustine HUMANITIES HUMANITIES FOUN 1101 Caribbean identity?' How has the response of Caribbean nations to the Covid-19 pandemic challenged or supported the idea of 'a single Caribbean identity?...
$ 7
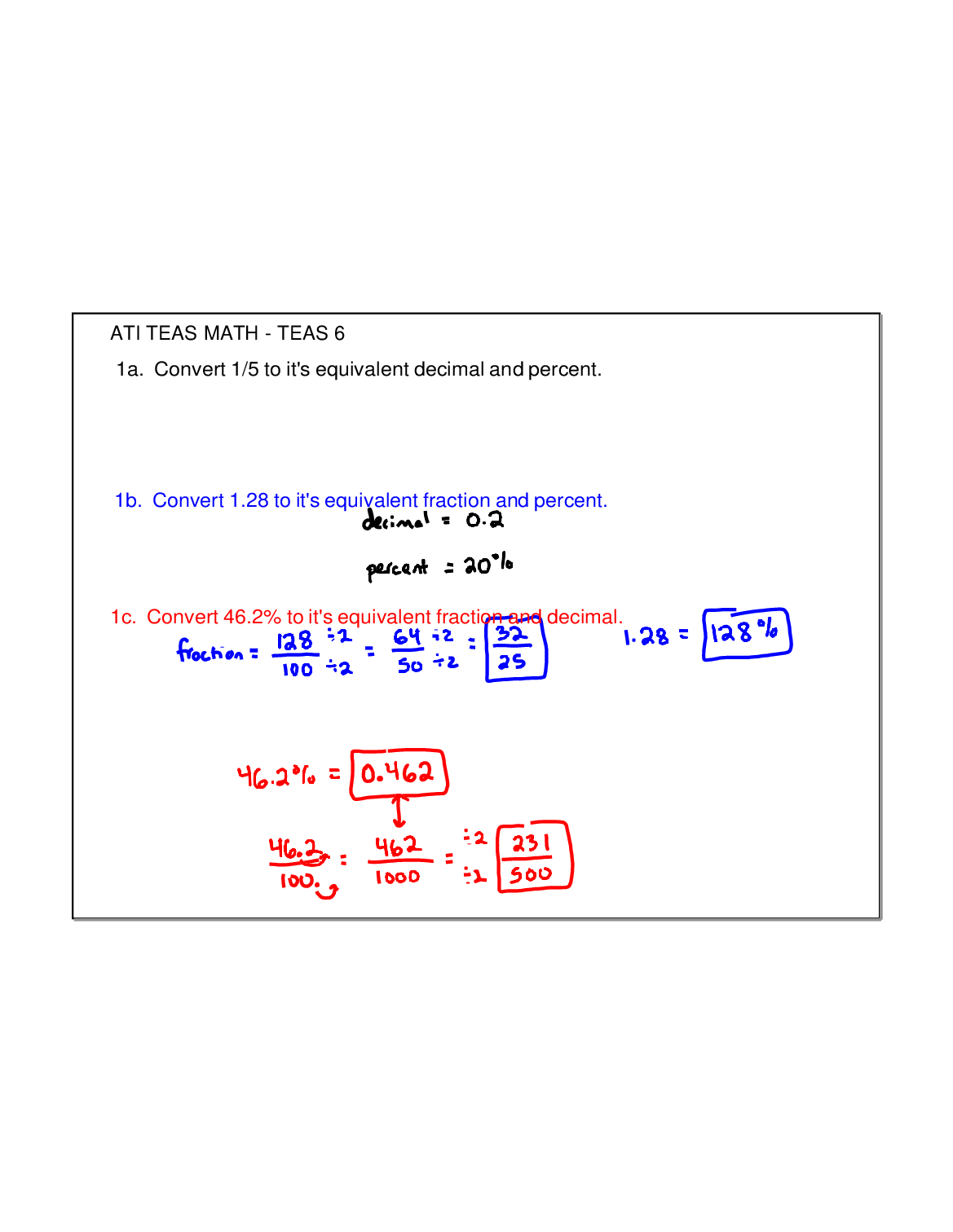
ATI TEAS MATH Section
$ 30
.png)
NR443_ CARING FOR THE POPULATION Milestone 1 Community Windshield Survey Form.
$ 8

BC OWNER BUILDER AUTHORIZATION EXAM 2026/2027
$ 25

Loyola University Chicago - HIST 102Why We Are Militant Review Thi Tran
$ 7

University of the West Indies at Cave Hill FOUN FOUN 1101 How has the response of Caribbean nations to the COVID-19 pandemic challenged or supported the idea of 'a single Caribbean identity'? Share Question
$ 7
.png)
NURS 6541 Week 7 Quiz
$ 5

University of British Columbia - EOSC 114EOSC 114 Reading Assignment. Fall 2018
$ 7

[eBook] [PDF] Essentials of Organizational Behavior 15th Global Edition By Stephen Robbins, Timothy Judge
$ 30

2023 PEDS ATI PROCTORED EXAM QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 32

[eBook][PDF] The Basic Practice of Statistics, 8th Edition By David Moore, William Notz, Michael Fligner
$ 14.5

eBook Standard method of detailing structural concrete 4th Edition By The Institution of Structural Engineers
$ 29

MOPAR EXAM22 - Mopar History and Heritage Latest 2023
$ 7
i-Human Case Analysis (Week 4, 2025) – 20-YearOld Male With Eye Complaint | Class 6512 | Walden University | Full Screenshots
$ 1

Lifeguard Test Red Cross (20222023) NEWEST- 100% CORRECT)
$ 15

PN EXIT HESI Exam Questions And Answers Best Rated A+ Guaranteed Success New Update 2023
$ 30

Tina Jones Health History Shadow Health- Review Systems
$ 11

MNG3701: LATEST (Notes, Memos and Assignment 2 (Answers) 2021
$ 13.5

CCRP CERTIFICATION PRACTICE EXAM 2 Q & A FEB 2024 UPDATE
$ 14

Early Childhood Development Exam 80 Questions with Answers,100% CORRECT
$ 8.5
2023 AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY 8464/P/2H Physics Paper 2H Question Paper & Mark scheme (Merged) June 2023 [VERIFIED]
$ 7

AS Level Mathematics A H230/01 Question Paper 2021
$ 6
.png)
WGU C207 STUDY GUIDE MODULE 3 & 4 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALREADY PASSED
$ 8

MOPAR EXAM22 - Customizing Essentials (2022/2023) Graded A+
$ 10
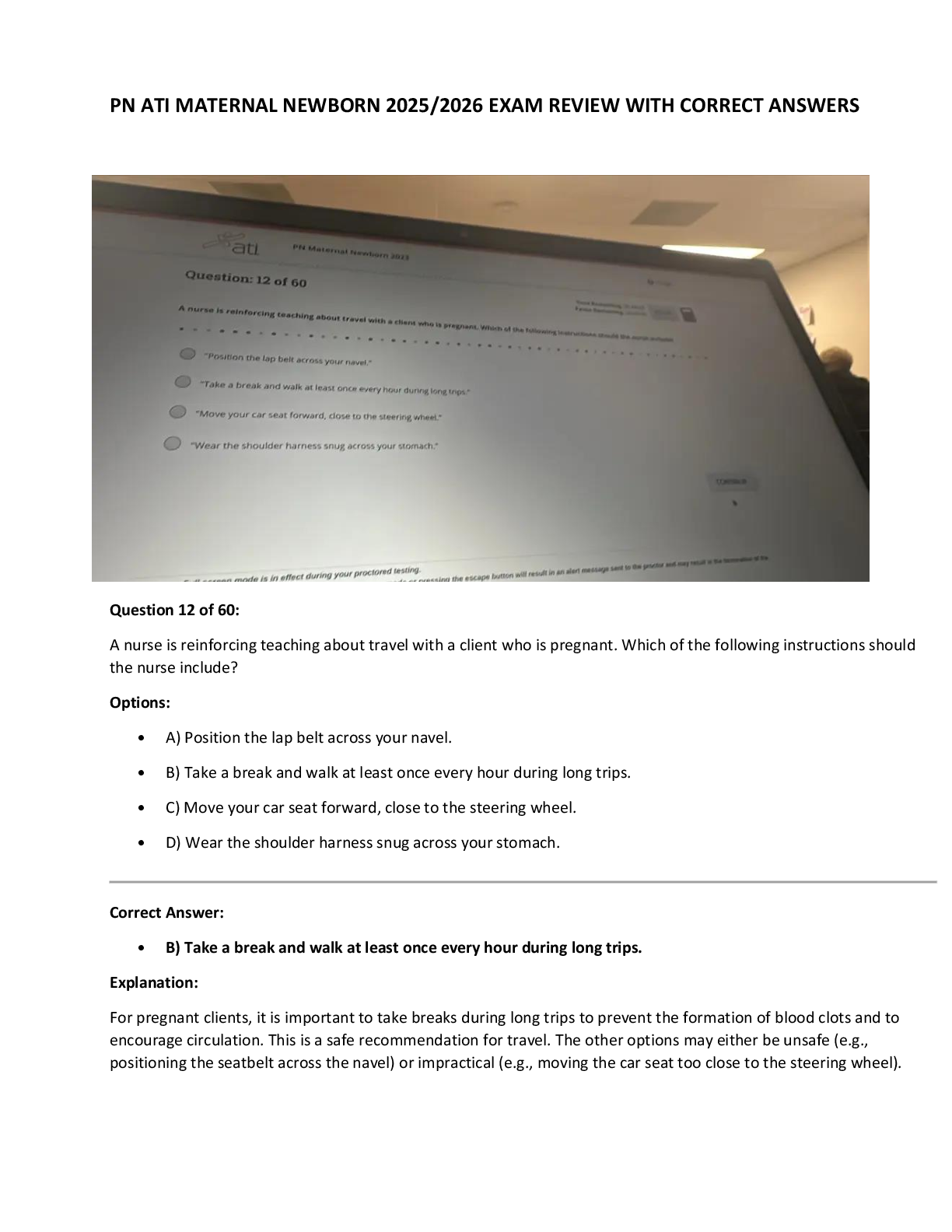
PN ATI MATERNAL NEWBORN 2025 EXAM REVIEW WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 18

BM 102 Comprehensive Exam 2022 2023
$ 14

WEEK 2 Midweek Comprehension Quiz with Complete Solutions - 2023
$ 11

Thibodeau & Patton: Structure & Function of the Body, 16th Edition TESTBANK
$ 21.5
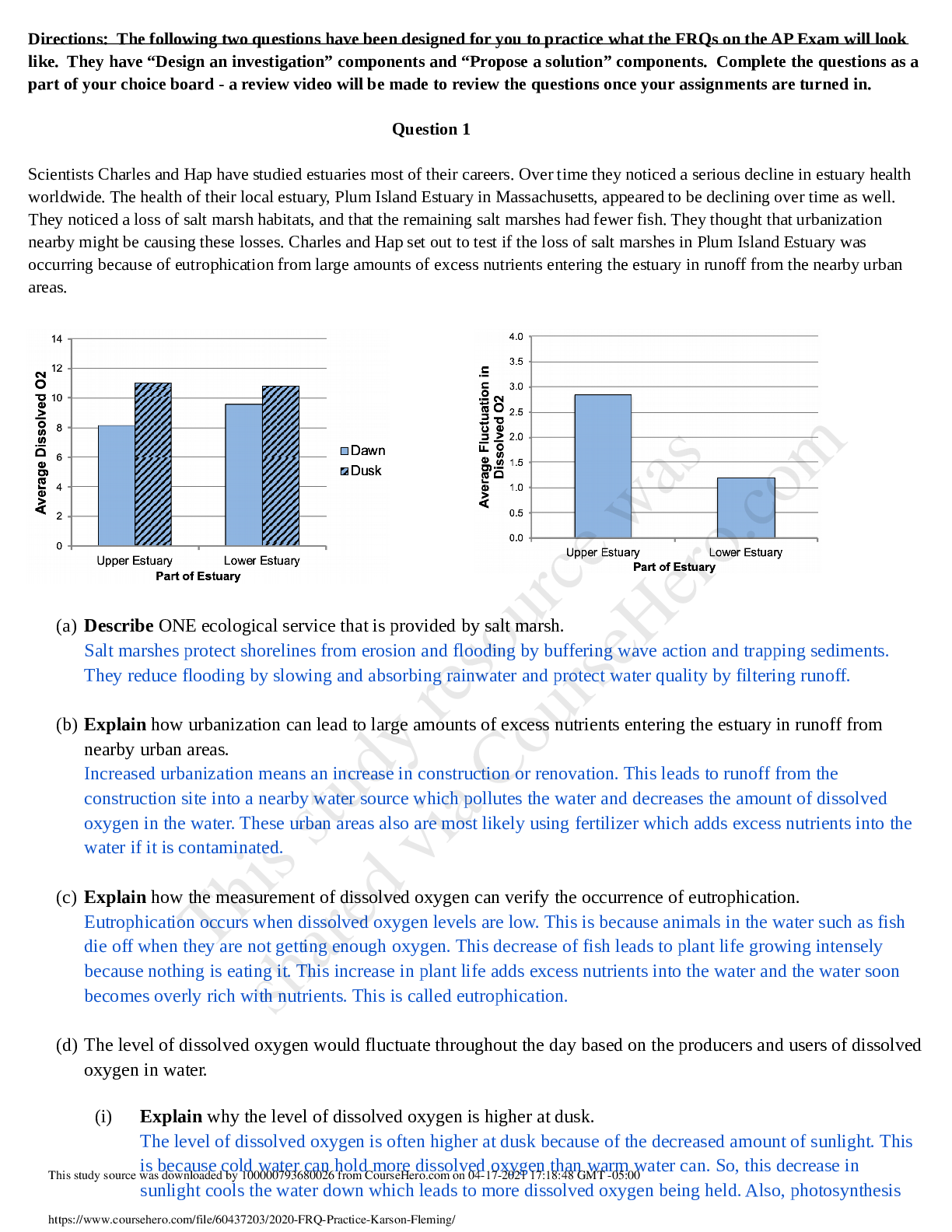
2020_FRQ_Practice-_Karson_Fleming
$ 9
.png)
Commack High School - SCIENCE PHYSICSPhysics IA
$ 7
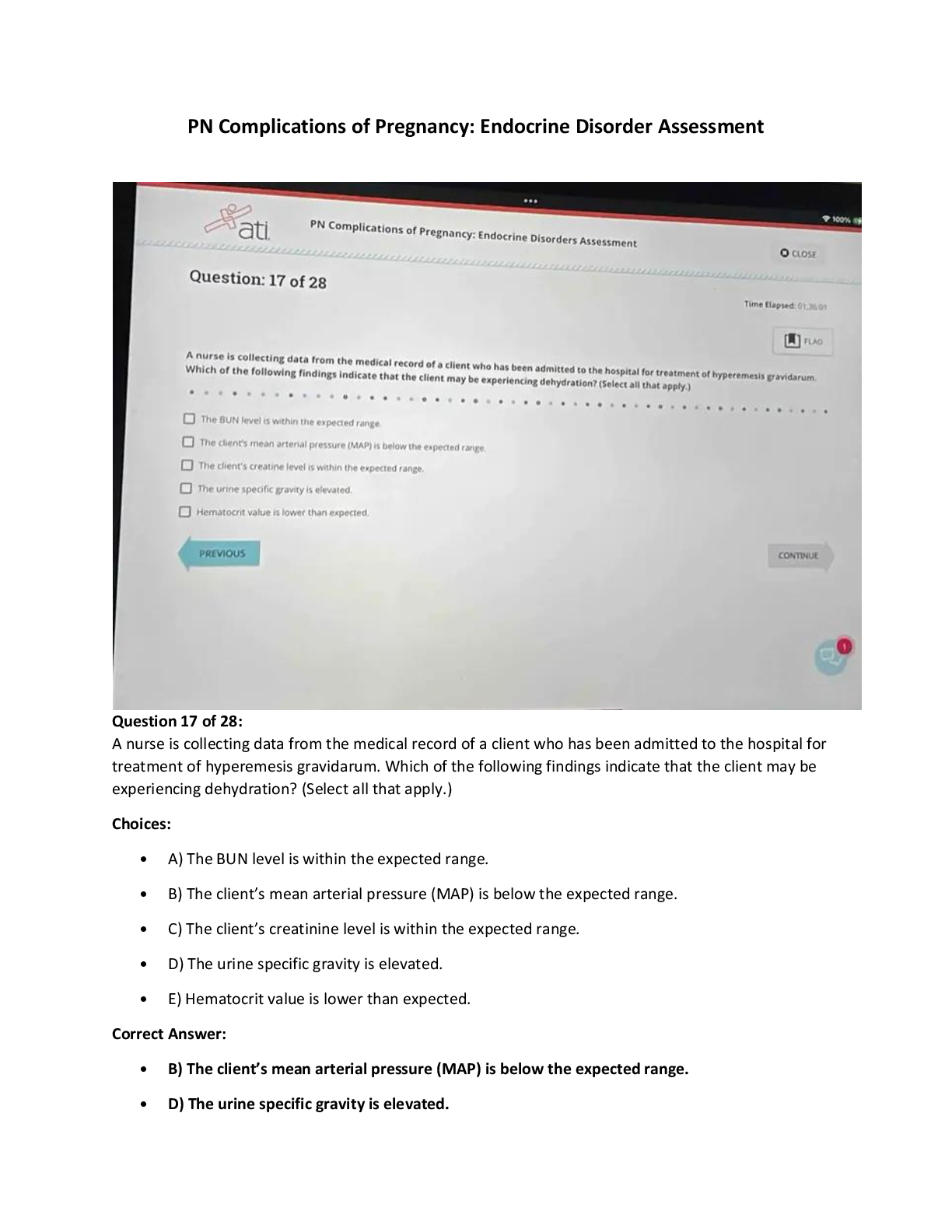
PN Complications of Pregnancy Endocrine Disorder Assessment.pdf
$ 65

Coral Reef Key GIZMOS
$ 9

COMPUTER CONCEPTS MODULE 10 EXAM 100% CORRECT
$ 11.5

Gizmos Student Exploration: Weathering
$ 10

Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1
$ 12.5

Global Marketing: Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. The Presentation