BTN 533 Final Exam | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions)
Document Content and Description Below
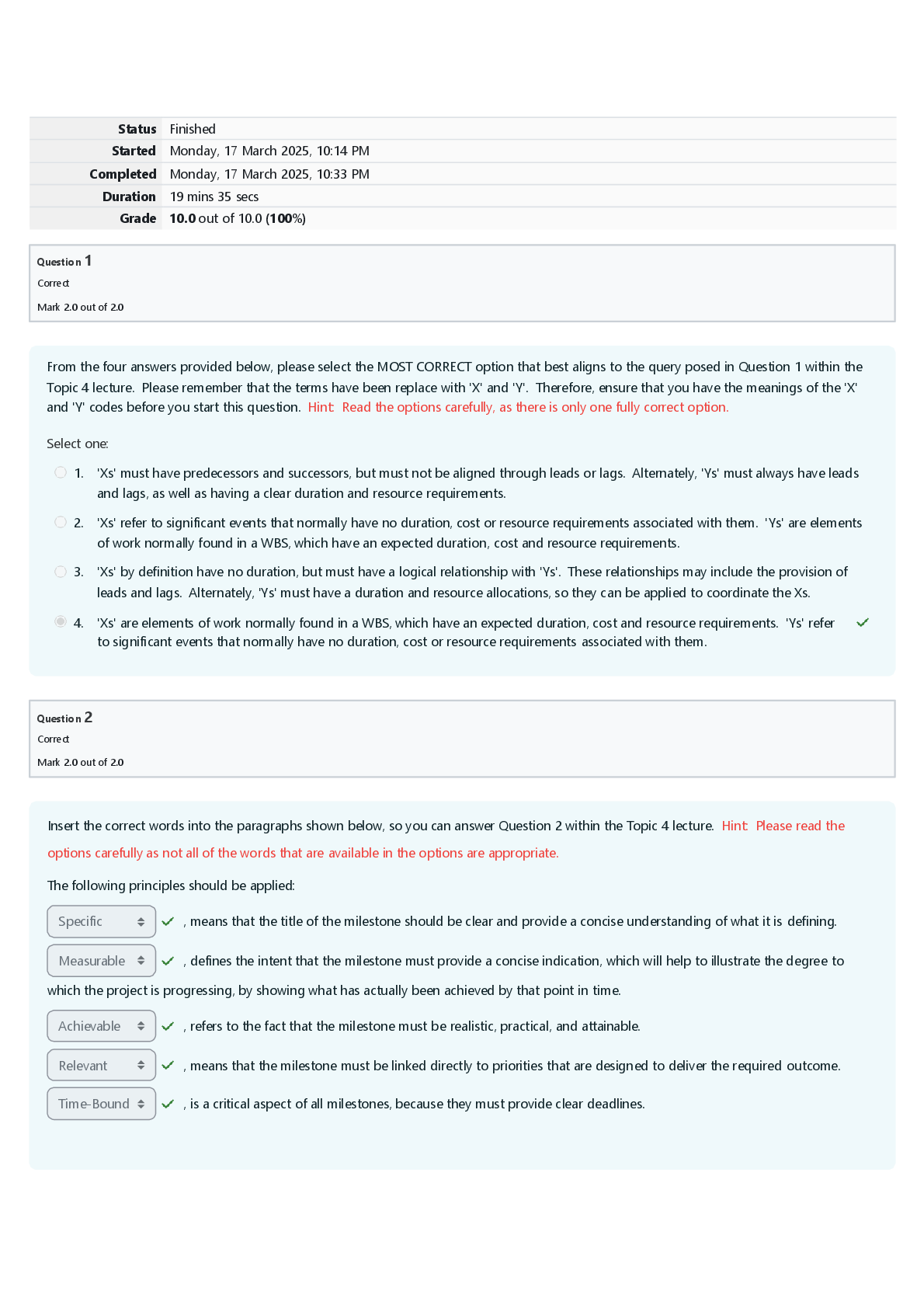
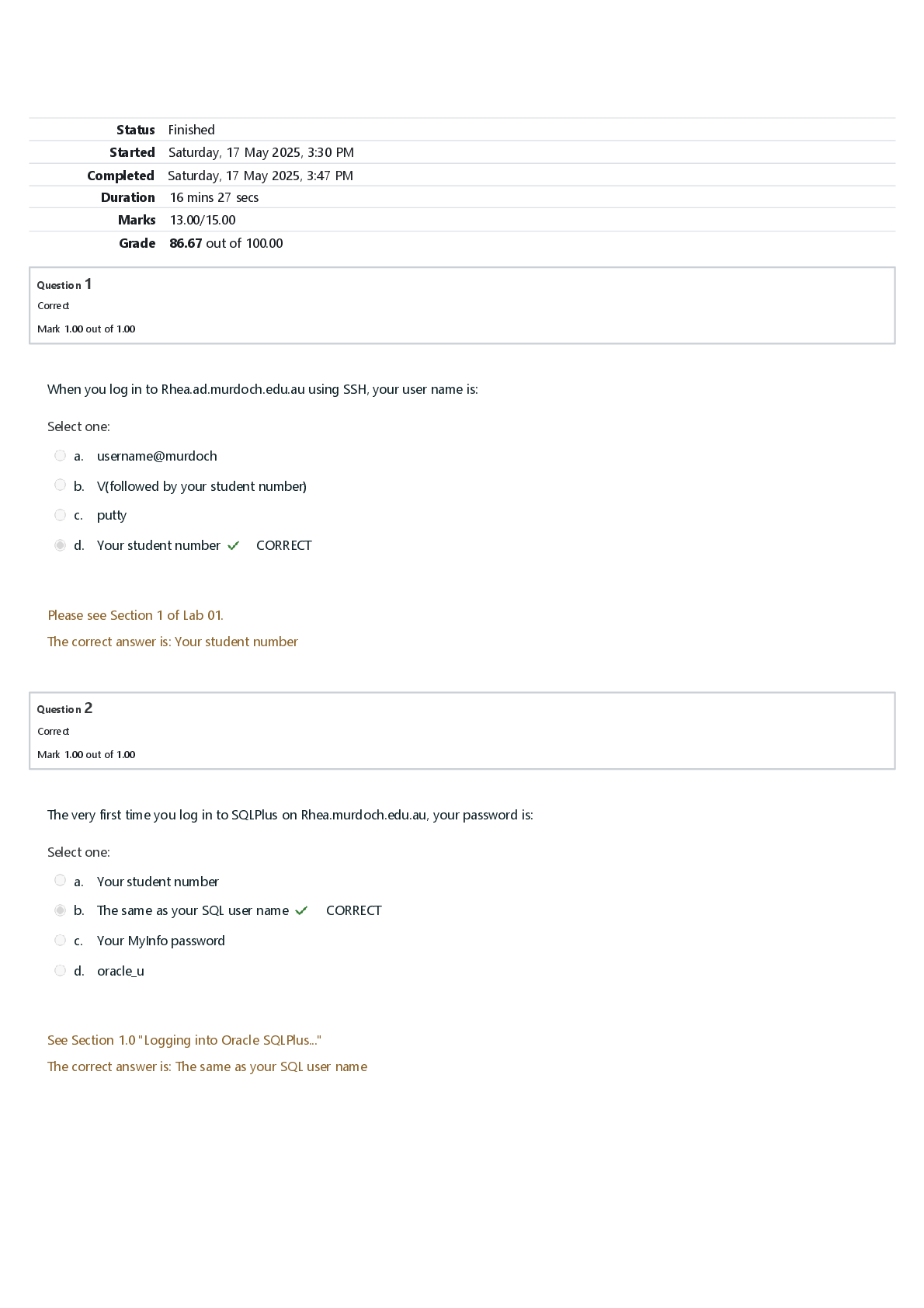
BTN 533 Final Exam | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions) Which of the following is NOT a healthy work habit when pipetting? A. Pipetting by mouth to avoid thumb strain. B. Alternating activi ... ties to avoid prolonged periods of continuous pipetting. C. Taking 1-2 minute breaks every 20 minutes. D. Rotating pipetting activities with other qualified lab staff. E. Alternating the workload between right and left hands. This type of pipette allows a technician to set and dispense a specific volume into multiple receptacles without having to aspirate between dispenses. A. Multichannel Pipette B. Repeating Pipette C. Transfer Pipette D. Vacuum Pipette E. Multidrop Pipette When transferring liquid using a pipette, the tip of the pipette should A. be in the center of the test tube B. should touch the side of the test tube C. never touch the side of the test tube D. remain in the air above the tube and never enter the tube. When transferring liquid aseptically from one tube to another, you should A. remove the cap of the tube with the little finger of the hand holding the pipette B. remove the cap of the tube with the little finger of the hand holding the tube C. place the cap on the bench top with the inside up D. place the cap on the bench top with the inside down. A typical can of Diet Coke contains 355 ml. A. Express this volume in microliters. B. Express this volume in liters. A. 355,000 𝜇l B. 0.355 L A pound of M&M's weighs 453 g. A. Express this weight in milligrams. B. Express this weight in micrograms. A. 453,000 mg B. 453,000,000 μg What pipette would you use to measure out... 15 μl 100 μl 750 μl 1400 μl A) use the 20 μl, B) 200 μl, c) 1000 μl, d) there are a few different ways, 1000 μl + 200 μl + 200 μl; 1000 μl + 400 μl , or use the 1000 μl to measure out 700 μl, twice. The purpose of streaking a plate is to obtain A. large quantities of bacteria B. bacteria in pure culture Plates should be incubated A. agar side up B. agar side down C. it doesn't matter. When streaking a plate, the lid should be A. placed on the bench top, top side up B. placed on the bench top, inside surface up C. should be held in the same hand as the plate D. should be held in the opposite hand from the plate. An organism is completely dependent on atmospheric O2 for growth. This organism is a(n) A) osmotolerant. B) acidophile. C) facultative anaerobe. D) aero-tolerant anaerobe. E) obligate aerobe. The organism which grows best above 45°C are called A. psychrophilic B. mesosphilic C. thermophilic D. any of these. Lag phase is also known as A. period of initial adjustment B. transitional period C. generation time D. none of these The central dogma of molecular biology states: A. Humans were intelligently designed B. RNA --> DNA --> polypeptide C. Life only exists on earth D. DNA --> RNA --> polypeptide E. Proteins are pseudo-genetic agents Cytologists can use which of the following to describe locations of a gene at a specific place on the chromosome? A) DNA sequence of a chromosomal region. B) Protein expression from a chromosomal region. C) Banding pattern of stained chromosomes D) Comparison to markers located within a few thousand bp. The set of all genes necessary to specify an organism's complete list of characteristics is known as the A) Mendelian factor. B) Genome. C) Linkage group. D) None of the above. An organism is homozygous dominant for trait "Q." Which statement is correct? A) The genotype is QQ; the phenotype is the expression of trait Q. B) The genotype is qq; the phenotype is the expression of trait Q. C) The phenotype is QQ; the genotype is the expression of trait Q. D) The phenotype is qq; the genotype is the expression of trait Q Polygenic inheritance is very common in determining characteristics that are A) Qualitative in nature. B) Quantitative in nature. C) Primarily hidden. D) Not in keeping with Mendelian genetics. If a dominant gene is present but not expressed in a population, this situation is referred to as A) Variable expressivity. B) Lack of penetrance. C) Environmental interference. D) Either a single- or double-factor cross, depending on the traits involved. The following image represents the agarose gel electrophoresis results from a restriction digest experiment. Lane 1 is a DNA ladder and Lane 2 is the DNA sample cut by a single restriction enzyme. What is the MINIMUM size of the uncut DNA fragment? Circle the right answer. A) 10kb B) 13kb C) 5kb D) 7.5kb E) 11kb A scientist wishes to verify that a restriction digestion has successfully cut a linear DNA fragment. She decides to compare the cut and uncut DNA samples using agarose gel electrophoresis. Which of the following agarose gel results is a result that would indicate the linear piece of DNA was digested? I. One band in the uncut DNA lane and two smaller bands in the digested DNA lane II. One band in the uncut DNA lane and a single smaller band in the digested DNA lane III. One band in the uncut DNA lane and three smaller bands in the digested DNA lane A. I B. II C. III D. Two of the answers are correct E. All of the answers are correct. Which of the following statements is true? A. DNA fragments move through agarose at a rate inversely proportional to their length. B. DNA moves toward the negative electrode. C. Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of amplifying DNA. D. Two of the statements are true. E. None of the statements are true. In gel electrophoresis, what does the gel act like? A. A barrier B. A gate C. A filter D. An open window. What do we use to cut the DNA before gel electrophoresis? A. Restriction enzymes B. DNA polymerase C. Lipase D. Helicase. Which is a false statement about an mRNA molecule? A. It contains anticodons B. It contains the nitrogenous base adenine C. It contains the nitrogenous base uracil D. It is complementary to the DNA template strand In gel electrophoresis, how do we make the DNA migrate through the gel? A. Gravity B. We place a negative electrode away from the wells C. We place a positive electrode away from the wells D. Large fragments drift to the end of the gel. The rate of migration of DNA within an agarose gel in the gel electrophoresis technique is primarily based on what factor? A) The size of the DNA fragments B) The number of DNA fragments C) The size of the wells of the gel D) The negative charge of the DNA E) The volume of the DNA sample loaded. In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA is moved towards the A. cathode B. anode C. DNA doesn't move D. none of above. After electrophoresis the gel is illuminated with a _____ lamp (usually by placing it on a light box, while using protective gear to limit exposure to ultraviolet radiation) to view the DNA bands. A. Electromagnetic spectrum B. X-ray C. Visible spectrum D. Ultraviolet In Bacterial transformation the bacteria takes up and express foreign DNA usually in the form of a ___? A. Plasmid B. Enzyme C. Cofactor D. RNA The purpose of calcium chloride is to allow the plasmid to pass through the bacterial cell wall? A. True B. False DNA transformation involves the transfer of DNA via A) pili B) naked DNA in solution C) a restriction endonuclease D) a bacteriophage. In transformation, both strands of donor DNA enter the recipient cell. A) True B) False Donor DNA is combined with recipient DNA by homologous recombination. A) True B) False DNA transformation involves the transfer of naked DNA into a recipient cell. A. True B. False In order to persist and be stably maintained in the cell, a plasmid DNA molecule must contain what? A. DNA B. RNA C. proteins D. origin of replication The plasmids can be eliminated from a cell by the process known as A. curing B. breaking C. fixing D. expulsion Which of the following statement describes plasmids? A. Another name for a protoplast B. A complex membrane structure that covers the chromosome of bacteria C. Small, circular DNA molecules that can exist independently of chromosomes commonly found in bacteria D. None of the above In nature, the purpose of restriction enzymes is to A. Protect the bacterium from virus attack by not allowing the virus to attach to the cell wall. B. Protect the bacterium from the DNA of other organisms the bacterium infects. C. Protect the bacterium from replicating its DNA at the wrong time. D. Protect the bacterium from virus attack by cutting up foreign DNA. Restriction enzymes A. Bind together strands of DNA. B. Bind RNA fragments together. C. Cut DNA at specific sites. D. Stop transcription. All restriction enzyme recognition sites A. Are never read the same forward and backward. B. End with CGT. C. Begin with CGT. D. Are read the same forward and backward. A vector is A. Used to carry foreign genes or DNA fragments. B. Divided by the charge of the DNA. C. Carries restriction enzymes to their restriction sites. D. Only used in matching DNA samples. A restriction enzyme digestion reaction consists of which particular ingredients in the list below? water ethyl alcohol DNA buffer alcohol dehydrogenase restriction enzyme a.1, 2, 3 and 4 b.1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 c. 2, 3, 4, and 5 d. 1, 3, 4, and 6 e. 1, 3, 4, and 5 f. 2, 3, 4, and 6 g. all ingredients listed. In recombinant DNA technology, a selected gene is removed from an animal, plant, or microorganism, and is inserted into what? A) A primer B) An oligonucleotide C) A palindrome D) A vector E) A cloning host. Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use? A. DNA polymerase—polymerase chain reaction to amplify sections of DNA B. electrophoresis—separation of DNA fragments C. reverse transcriptase—production of cDNA from mRNA D. restriction enzyme—analysis of RFLPs E. DNA ligase—cutting DNA, creating sticky ends of restriction fragments. There are three basic steps in DNA cloning: 1) "cut" the DNA, 2) "paste" the DNA into a plasmid (a circular section of DNA), 3) "copy" the DNA by introducing it to a bacteria, which will replicate the plasmid when it replicates itself. What are these three processes called? A. 1) Transfection, 2) Ligation, 3) Fragmentation B. 1) Ligation, 2) Transfection, 3) Fragmentation C. 1) Ligation, 2) Fragmentation, 3) Transfection D. 1) Fragmentation, 2) Ligation, 3) Transfection. What enzyme is used during the process of ligation? A. DNA Polymerase B. None of these C. Reverse Transcriptase D. DNA Ligase. Is human cloning illegal in the United States? A. No, both therapeutic and reproductive cloning are legal in all cases B. Yes, both therapeutic and reproductive cloning are illegal in all cases C. Reproductive cloning is illegal in some states but therapeutic cloning is legal everywhere D. Therapeutic cloning is illegal in some states but reproductive cloning is legal everywhere What enzyme is used during the process of transfection? A. Transferase B. DNA Polymerase C. Reverse Transcriptase D. None of these. Which of the following scientific breakthroughs did NOT develop from DNA cloning? A. The development of a gene therapy that allows for an embryo to have three biological parents in 2010 B. The creation of Dolly the Sheep in 1997 C. The creation of herbicide resistant tobacco plants in 1986 D. The development of synthetic human insulin in 1978. Western blotting would be a useful technique to determine expression of a gene in a particular tissue. A) True B) False What type of probe would you use for a Western blot experiment? A) A known DNA sequence. B) An RNA molecule. C) A purified protein. D) An antibody. One end of a polynucleotide has a (n) _____ terminus, and the other end has a(n) _____ terminus. A. amino group; 3′-OH B. amino group, carboxyl group C. 5′-P; 3′-OH D. Ester linkage; ester linkage E. Carboxyl group; 5′-P. In SDS electrophoresis, proteins are separated on basis of A. charge B. mass C. both A and B D. structure The term "blotting" refers to: A. Running the gel in the presence of SDS B. Digesting the DNA with restriction enzyme C. Transfer of biomolecules to an immobilizing membrane D. Disrupting the disulfide bonds of proteins in the presence of β-mercaptoethanol. Proteins that are to be separated in SDS-PAGE are subjected to treat with all of the following reagents except: A. Heat B. SDS C. β-mercaptoethanol D. Ammonium persulfate. Which tracking dye did you use in SDS-PAGE? A. Coomassie blue B. Bromophenol blue C. Bromothymol blue D. DTT Structural and functional unit of life is called A. cell B. tissues [Show More]
Last updated: 3 months ago
Preview 5 out of 21 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$18.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 01, 2025
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 01, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
9