Linguistics > EXAMs > ASLP 5825 Pediatric SSD Midterm Exam | Complete Solutions (Verified Answers) (All)
ASLP 5825 Pediatric SSD Midterm Exam | Complete Solutions (Verified Answers)
Document Content and Description Below
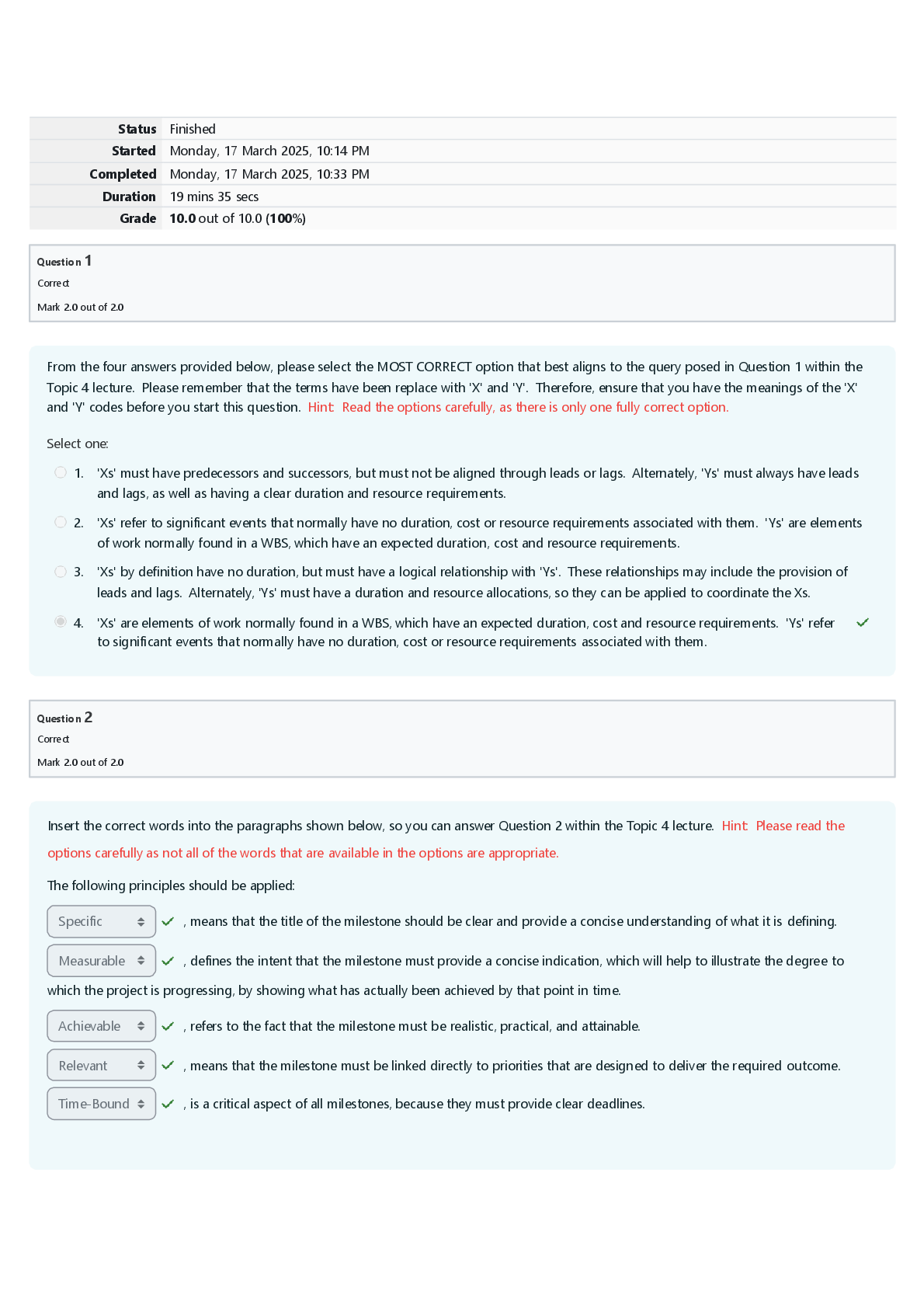
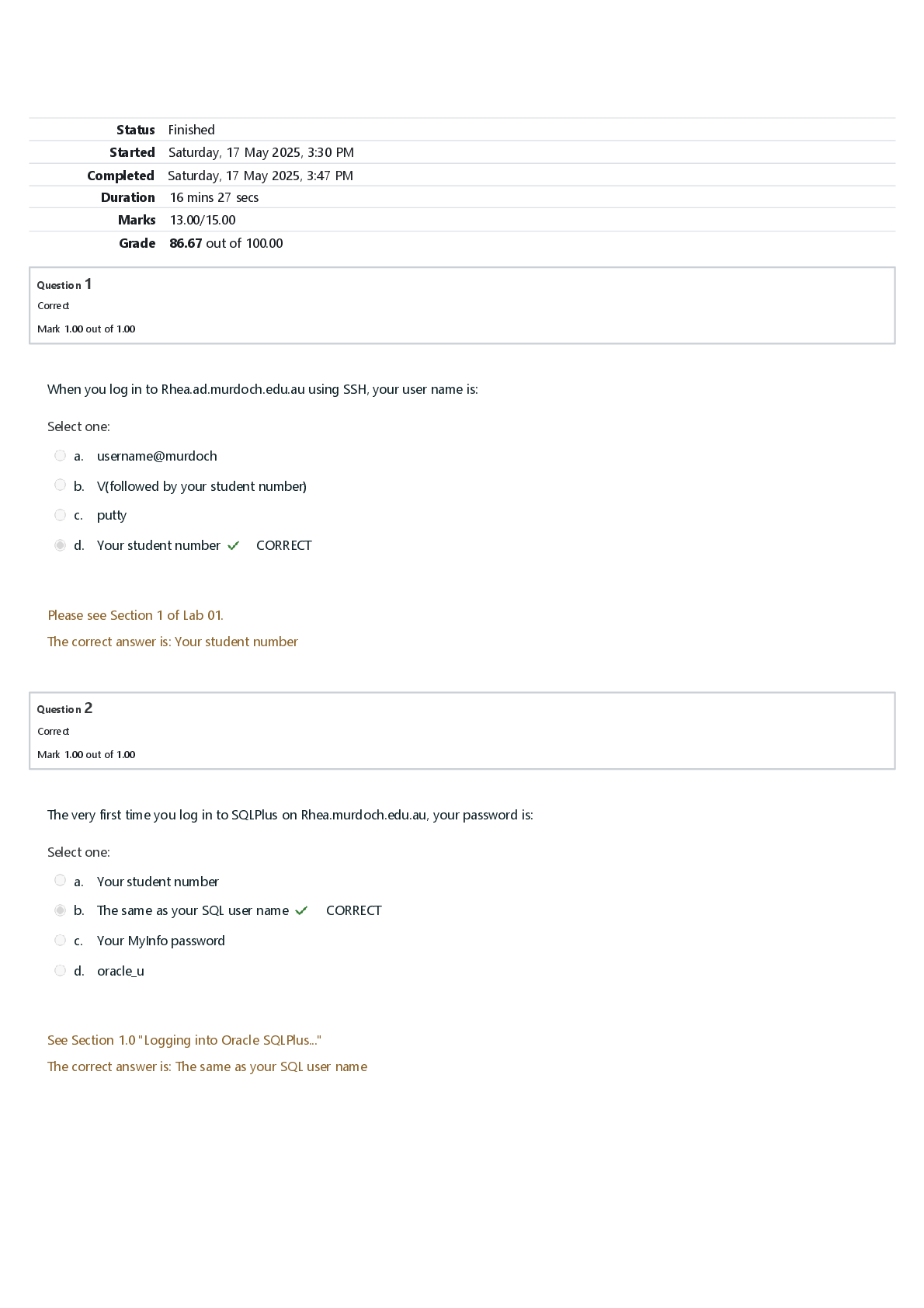
ASLP 5825 Pediatric SSD Midterm Exam | Complete Solutions (Verified Answers) When do you expect your child to reach 100% intelligibility? 4yo Rules governing the sound system of a language Phonolog ... y Words that only have one phoneme that is different than the other minimal pairs Possible sequencing of phonemes in a language Phonotactics Study of sounds of human speech Phonetics variants of the same phoneme (same sound, but different production-aspirated, dark, light) Allophones Motor movements in speech sounds Articulation The collection of possible sounds within a language (includes all allophones) Phonetic inventory How many phonemes in the phonemic inventory 44 phonemes Which one is larger: Phonetic inventory vs phonemic inventory phonetic inventory ________ inventory is any sound you can produce with your articulators, where ___________ inventory is the sounds you can use to create meaning phonetic, phonemic phonology (cognitive linguistic or motor) cognitive linguistic phonetics (cognitive-linguistic or motor) motor movement comparing phonological impairments with no neurological disorders vs apraxia vs dysarthria, which has better intelligibility? FIX IT apraxia and dysarthria Why are those with phonological impairments with no neurological impairments highly intelligible? They have no issues with production, but there are issues in connecting meaning to the phonemes. Neurological impairments are inconsistent. To differentiate the consonants /b, /m/, /p/, & /d/, how many dimensions would you need? 3 (voice, place, manner) How many consonants are there in English 24 In English, there are a a max of _____ consonants at the beginning of the words, but there are a max of ______ consonants at the end of the word 3, 4 T/F all languages have consonant clusters F: some don't have consonant clusters There are _____total vowels, _____ monophthongs, and _______ diphthongs in English 20, 12, 8 How many dimensions are there to differentiate vowels, and what are they? 4: Tongue position, lip roundness, tense/lax, nasalization Tense sounds are typically ______ in duration, which lax sounds are typically ________ in duration longer, shorter There are _____ vowel letters in English, and they are _____________ 5, A E I O U vowel letters are for __________ and ______, while vowels are _________ for ________ processing and production reading, literacy, phonemes, speech T/F vowels and vowel letters are the same F: they are different and have different purposes A strategy the brain uses to process speech sounds and minimize cognitive load categorical perception when allophones are presented and manipulate the voice onset time. You can tell how many phonemes there are, but the actual production shows variants (allophones) and differences in voicing. categorical perception NEED to know where definitions come from (ASHA, International Expert Panel on Multilingual Children's speech, DSM-5, ICD 11-WHO) Definition and source: impact all forms of speech sounds or the function of speech sounds within a language. Speech Sound Disorders, ASHA Definition and source: Disorders that impact the form of speech sounds and are associated with structural (e.g., cleft palate) and motor-based difficulties (e.g., apraxia). Articulation Disorders, ASHA Definition and source: Disorders that impact the way speech sounds (phonemes) function within a language Phonological disorders, ASHA T/F the DSM-V includes speech perception in their definition of SSD False T/F the DSM-V states that SSD is attributable to congenital or acquired conditions (cerebral palsy, cleft palate, deafness or hearing loss, TBI, or other medical or neurological conditions) False how the brain selects, organizes, and interprets sensory information Perception T/F the International expert panel on multilingual children's speech's definition for SSD includes speech perception, articulation, and phonological delay/disorder, and speech impairment True "The speech errors are not directly attributable to a hearing impairment or to a structural or neurological abnormality" (________________) WHO T/F Of students that require additional support, communicative disorders are the #1 ranked reason F, #2. #1 Specific learning difficulty The presence of a ______________ disorder is the most important predictor that a student will require a high level of support at school Communication Parents show concern for_________________, while educators show more concern for _________________________ in children 4-5yo social-emotional skills, receptive language skills T/F Expressive speech and language skills, such as talking and speech sounds is the #1 concern among parents and educators True Among all children with disabilities aged 3 to 21, ___________ of them received services in public schools for primary speech or language disorders 21.1% 74.7% (3/4) of pre-k students enrolled in SLP services received services for ____________________ articulation/intelligibility As children get __________, the __________ they receive speech therapy. older, less What are the 5 reasons that there is a huge variation in prevalence across studies for SSD? 1. Age range 2. How data is collected 3. Differences in definitions in SSD 4. Sampling Method 5. Cut-off point on a standardized Would prevalence be higher or lower in younger children Higher Direct assessments show a____________ prevalence, while Parents'/Teachers' report shows a ___________ prevalence higher, lower ___________ sampling method is more representative of a population, but it is ________ Nation-wide, expensive There is __________ prevalence when sampling a school High T/F cutoff points on standardized studies can show variation of prevalence in determining the presence of SSD True When one study is using 1 SD below the mean for the cutoff as opposed to 2 SD below the mean, which has a higher prevalence? 1 standard deviation below the mean When a study has the cut-off as 2 standard deviations below the mean, is this a high or low prevalence low prevalence. They are only taking Severe cases Paths for children according to Gruber, 1999: When children grow out of their disorders Path A "the normalizers" Paths for children according to Gruber, 1999: "deletion, substitutions, and omission declined" Path A Paths for children according to Gruber, 1999: When children make progress, but shift and compensate for changes Path B "The non-normalizers" Paths for children according to Gruber, 1999: "common clinical distortions increased as deletions and substitutions decreased" Path B T/F In the Templin longitudinal study, Adults with SSD have shown emotional adjustment, introversion/anxiety, likeliness to get employment, satisfaction with educational/occupational outcomes False, Adults with SSD are equally likely for employment (different kinds of jobs) and are satisfied with their education and jobs. They are resilient and have adjusted their expectations. Not more introverted/anxious Adults with SSD have ______ years of education and _______ skilled jobs fewer, lower T/F Adults with SSD are more introverted and anxious and are more likely to be unemployed False! What is a weakness of the Goldman Fristo? Doesn’t use multisyllabic words Not affective for apraxia The Cleveland Family Speech and Language study is for... SSD Teens with persistent SSD The Cleveland test shows difficulties in _________words errors in _________ speech Speech errors include distortion on /________/, substitution errors, and ____________ processes weakness in __________ poorer ___________ repetition, vocabulary reading, spelling Polysyllabic conversational /r, l, s, z/, phonological prosody nonword what does the nonword repetition test do? the short-term memory for sounds T/F Educational status and socioeconomic status, high school completion, and undergraduate are more likely for LD vs SSD False: SSD and typical individuals are greater in these areas than those with Language Difficulty T/F Typical, SSD, language difficulties show differences in marriage/permanent relationship, number of children, % of employment, subjective quality of life False no differences Would younger or older children hold a more negative view towards people with communicative disabilities? Older. More different Negative attitudes towards males with speech problems have a perception of ________ speech ability, intelligence, education, and masculinity Lower some cultures see speech difficulties as ________________ Emotionally disturbed Are they risk factors or not for SSD? Male, Family history of SSD, Hearing status (e.g., hearing loss), education of mother and/or father Yes, more evidence for maternal education than paternal education Are they risk factors or not for SSD? Hearing status (e.g., hearing loss) Yes There is _________ evidence for maternal education than paternal education as a risk factor for SSD More Which is NOT a risk factor for SSD? A. Male B. Maternal Education C. Bilingualism D. race, minority status, and language spoken E. Both C and D Are they risk factors or not for SSD? Temperament of the individuals, socioeconomic status, birth order/family size Evidence is UNCLEAR Temperament (which came first?) Socioeconomic status (measured by household income, but does not correlate to education) Birth order/family size (dependent on size of family when the child is learning foundational language) Clients with ______________ _____________have consistent/predictable errors Phonological impairment Motor or phonological based: phonological impairment is __________ based Phonological Motor or phonological based: Inconsistent Speech Disorder (ISD) is ____________-based Phonological Which is not motor-based? A. Dysarthria B. Inconsistent Speech Disorder (ISD) C. Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS) D. Phonological Impairment E. Both B and D How many possible templates for phoneme insertion are there in English 20 Difficulty learning the phonological system of the native language and affects the phonemic organization Phonological impairment T/F children with only phonological impairment will have problems with the articulation of individual speech sounds and show difficulties with peripheral motor processes False they do NOT have articulation difficulties Children need to learn these things about the phonological system of a language: 1. How many __________ 2. ___________ and distributions phonemes, phonotactics What does this describe: the probability of /ŋ/ at word-initial position is 0; some phonemes occur more frequently than others Distributions of phonemes What does this describe: some sound sequences occur more frequently than others Probability of sound sequences Can phonological impairment clients imitate speech sounds Yes Does successful imitation imply the ability to perceive and use target sounds contrastively for meanings in words for phonological impairment? it does not rule out problems perceiving speech sounds contrastively in words. Does successful imitation imply the ability to use sounds in accordance with phonotactic rules for phonological impairment? no, abilities to imitate do not rule out problems with phonotactic rules Features of Phonological Impairment: •Difficulty learning how speech sounds are used __________________ to express meanings •Difficulty ______________ and __________speech sounds according to rules specific to the native languages contrastively, perceiving and producing T/F Phonological impairment shows consistent errors True T/F Phonological impairment shows oro-motor signs of childhood apraxia FALSE. No issues in motor planning because errors are consistent _____________ ___________ _________ is useful in revealing pattern-based errors Phonological process analyses T/F ISD shows predictable errors False, errors are not predictable When multiple phonemes are lumped together phonemic collapse T/F client with phonological impairment can show oro-motor signs of childhood apraxia False: there should be NO oro-motor signs of childhood apraxia of speech Difficulty in learning the sound system of language Phonological impairment Phonological ___________: systematic errors that are typical in younger children and should have resolved at the age of your clients Delay Phonological __________: systematic errors that are not typical in younger children Disorder Non-developmental phonological errors 1. backing 2. use of _____________ language phonemes 3. ___________ sound preference non-native, systematic Phonological Delay and disorder fall under phonological __________ Impairment Phonological impairment have difficulty in learning the sound system of a language or _________________ Phonotactics ISD accounts for ______% of children with SSD 10% Children with ISD have lexical __________ errors Inconsistency What does this sample describe? Target bat: /tæt/, /dæt/, /fæt/ Inconsistent speech disorder (ISD): unpredictable pronunciations of the same word (lexical inconsistency) Inconsistent speech disorder (ISD) shows difficulty in phonological _________ Planning Features of inconsistent speech disorders: 1. Clients (can/cannot) articulate a range of speech sounds 2. Clients (can/cannot) imitate words 3. Absences of __________ signs of childhood apraxia Can, can, oromotor T/F Intelligibility improves in word imitation compared to spontaneous speech in ISD True What strategy is useful for ISD? Core vocabulary What kind of assessment to determine ISD or apraxia imitation and conversational speech T/F The Diagnostic Evaluation of Articulation and Phonology (DEAP) is a test of accuracy. False, measures consistency Articulation is a motor speech _______ Difficulty T/F DEAP is a good test to differentiate between apraxia, dysarthria, and ISD and is what you should do first in assessment. False, All will perform poorly articulation errors are typically _______ and/or ________ sibilants /s, z/, rhotic /r/ T/F one can have articulation impairment and show oromotor signs of CAS False, there should not be any oromoror signs How can you tell if a client has only articulation impairment without concurrent difficulty with phonology (i.e., speech difficulties are strictly motor-based)? 1. Picture Identification tasks of minimal pairs 2. error detection in your speech What is the prevalence of apraxia? 0.1% RARE Dysarthria is a motor speech _________ Disorder Difficulty controlling and executing speech movements caused by a neurological impairment Dysarthria Places stress of syllables correctly, but had irregular breathing and uncoordination of musculature Dysarthria Difficulty placing stress on the right syllable apraxia A neurological childhood SSD in which the precision and consistency of movements underlying speech are impaired in the absence of neuromuscular deficits Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) Features of CAS •_______________ consonantal and vowel errors in repeated productions of syllables or words •___________ and disrupted coarticulatory transitions between sounds and syllables •Sometimes you will see _________ behaviors •Inappropriate __________ Inconsistent, Lengthened, groping, prosody Stress can occur at the word level (__________) or the sentence level lexical stress Stress is at the word level (disyllabic words) lexical stress T/F We can talk about lexical stress with monosyllabic words. False Both apraxia and dysarthria have difficulty with prosody. Can perform in lexical stress or at the sentence level. Which population has difficulty with both? Apraxia T/F client's with dysarthria find imitation difficult True Apraxia clients are better at ___________ than _______________ speech spontaneous speech, imitation ISD clients are better at ___________ than _______________ speech imitation, spontaneous T/F Dysarthria clients are better at spontaneous speech. False, both imitation and spontaneous speech are difficult for clients with dysarthria because they have difficulty with motor weakness Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) is a motor speech _________ Disorder dysarthria is related to muscle _________, where apraxia have difficulty with motor _________ weakness, planning Which classifications have inconsistent speech errors? [Show More]
Last updated: 2 months ago
Preview 5 out of 23 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$18.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 28, 2025
Number of pages
23
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 28, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
11