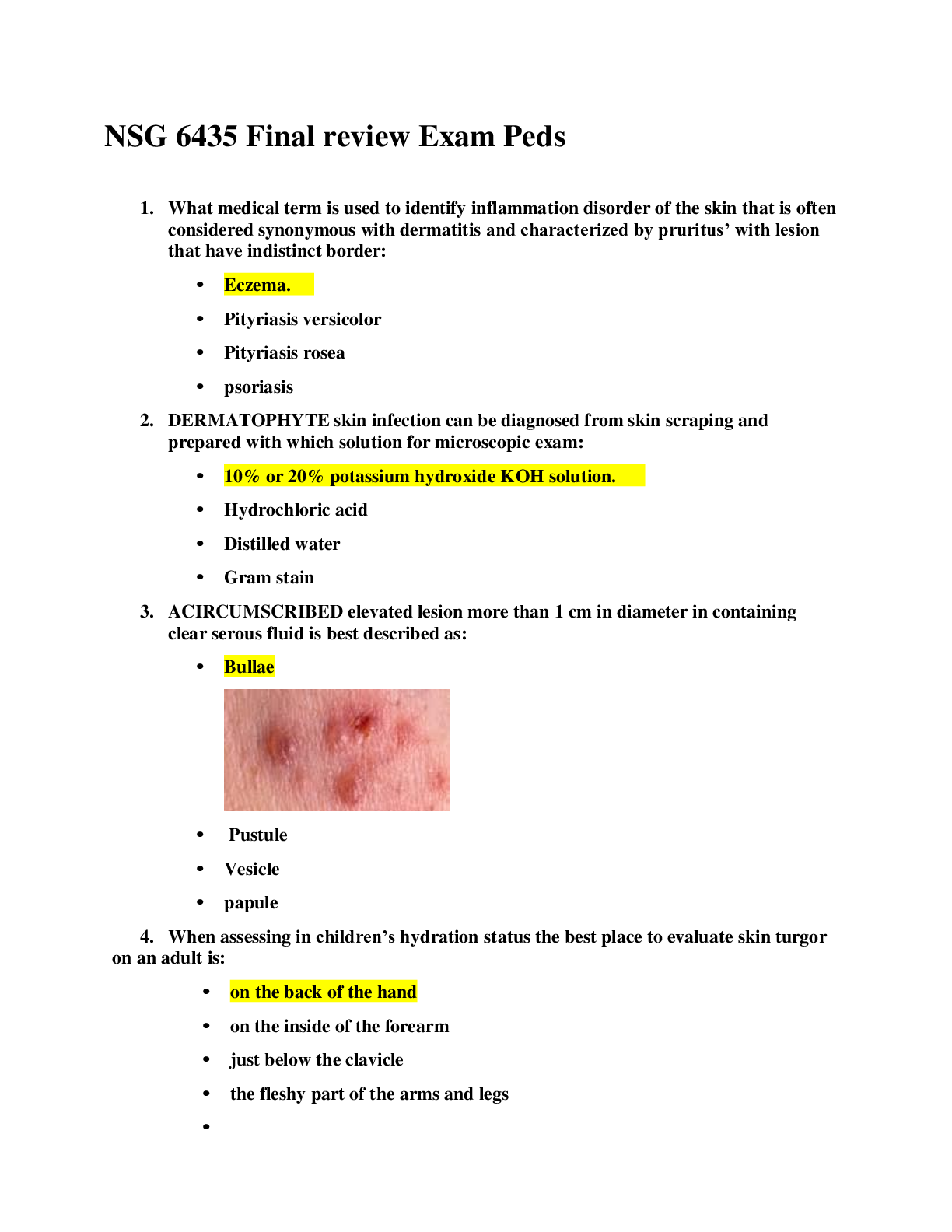
1. (TCO 1) Which best explains the differences between historians and political scientists? (Points : 2)
Historians look for generalizations, and political scientists are reluctant to generalize. Historians are reluctan
...
1. (TCO 1) Which best explains the differences between historians and political scientists? (Points : 2)
Historians look for generalizations, and political scientists are reluctant to generalize. Historians are reluctant to generalize, and political scientists look for generalizations. Historians are more likely to look for comparisons than political scientists.
Historians tend to focus on nature-based explanations, and political scientists focus on nurture- based explanations.
Question 2. 2. (TCO 1) The notion that politicians think practically and political scientists think abstractly is indicative of which of the following? (Points : 2)
Political scientists often train politicians. Politicians often train political scientists.
Political scientists and politicians are different in that the former studies the latter. Political scientists and politicians are often indistinguishable.
Question 3. 3. (TCO 1) When people base their views on beliefs that may not be based in reality, they are behaving . (Points : 2)
irrationally rationally politically legitimately
Question 4. 4. (TCO 1) A political leader’s ability to command respect and exercise power is known as
. (Points : 2)
sovereignty corruption authority
legitimacy
Question 5. 5. (TCO 1) Despite a disputed 2000 presidential election, once President George W. Bush took office, few people doubted his . (Points : 2)
charisma control legitimacy sovereignty
Question 6. 6. (TCO 1) Relating concepts in a way that connects them in an empirical manner is the basis of building. (Points : 2)
scholarship theory power culture
Question 7. 7. (TCO 1) A(n) is an initial theory a researcher starts with to be proved with evidence. (Points : 2)
quantification hypothesis qualification empirical
Question 8. 8. (TCO 4) Unlike natural law, positive law uses . (Points : 2)
the spirit of the law to make determinations
books to reach conclusions
judicial sentencing to determine case outcomes jury selection to manipulate judgment
Question 9. 9. (TCO 4) Under which of the following circumstances might a case be pursued as both a criminal and a civil case? (Points : 2)
The federal government accuses investment houses of wrongdoing and investors who lost
money sue them.
Drug traffickers violate property and federal law by moving drugs across state borders. Burglars violate federal property and the state sues them for damages.
A state accuses banks of mortgage fraud in mortgages sold to investors elsewhere in the nation.
Question 10. 10. (TCO 4) Describe the significance of Marbury v. Madison. (Points : 2)
The ruling laid precedent for judicial review.
The ruling stated that the president is subject to the court’s decisions.
The ruling decreed that current administrations must honor the appointments of previous administrations.
The ruling claimed that federal taxes could not be levied on the states.
Question 11. 11. (TCO 4) What legal agency in the United States generates reputation-based ratings of prospective federal judges? (Points : 2)
Judicial Ratings Bureau
Federal Bureau of Judicial Review American Bar Association
Office of Legal Assessment
Question 12. 12. (TCO 4) When was judicial review granted to the Supreme Court within the United States? (Points : 2)
It was granted during the Constitution Convention of 1787. It was granted in the Bill of Rights.
It was the result of the Marbury v. Madison decision of 1803. It was never officially adopted but is an unofficial practice.
Question 13. 13. (TCO 4) Which of the following best articulates the stance of judicial restraint advocates? (Points : 2)
Judicial review is the best and only true method of checking legislative power.
The court should practice restraint in cases in which legislative acts are presented for interpretation.
Only the executive branch can restrain the court, keeping the power of judicial review in balance
with the other governing branches.
Only Congress should make public policy and, unless a legislative act clearly violates the Constitution, the law should stand.
Question 14. 14. (TCO 4) The Supreme Court’s decision in (1954) triggered a revolution in American race relations, an area Congress had been unwilling to touch. (Points : 2)
Miranda v. Arizona Dred Scott v. Sandford
Brown v. Board of Education Gibbons v. Ogden
Question 15. 15. (TCO 5) Which systems demonstrate the clearest separation of power between the executive and legislative branches? (Points : 2)
Parliamentary
[Show More]
Chamberlain School of Nursing POLI 330 Final Exam.png)