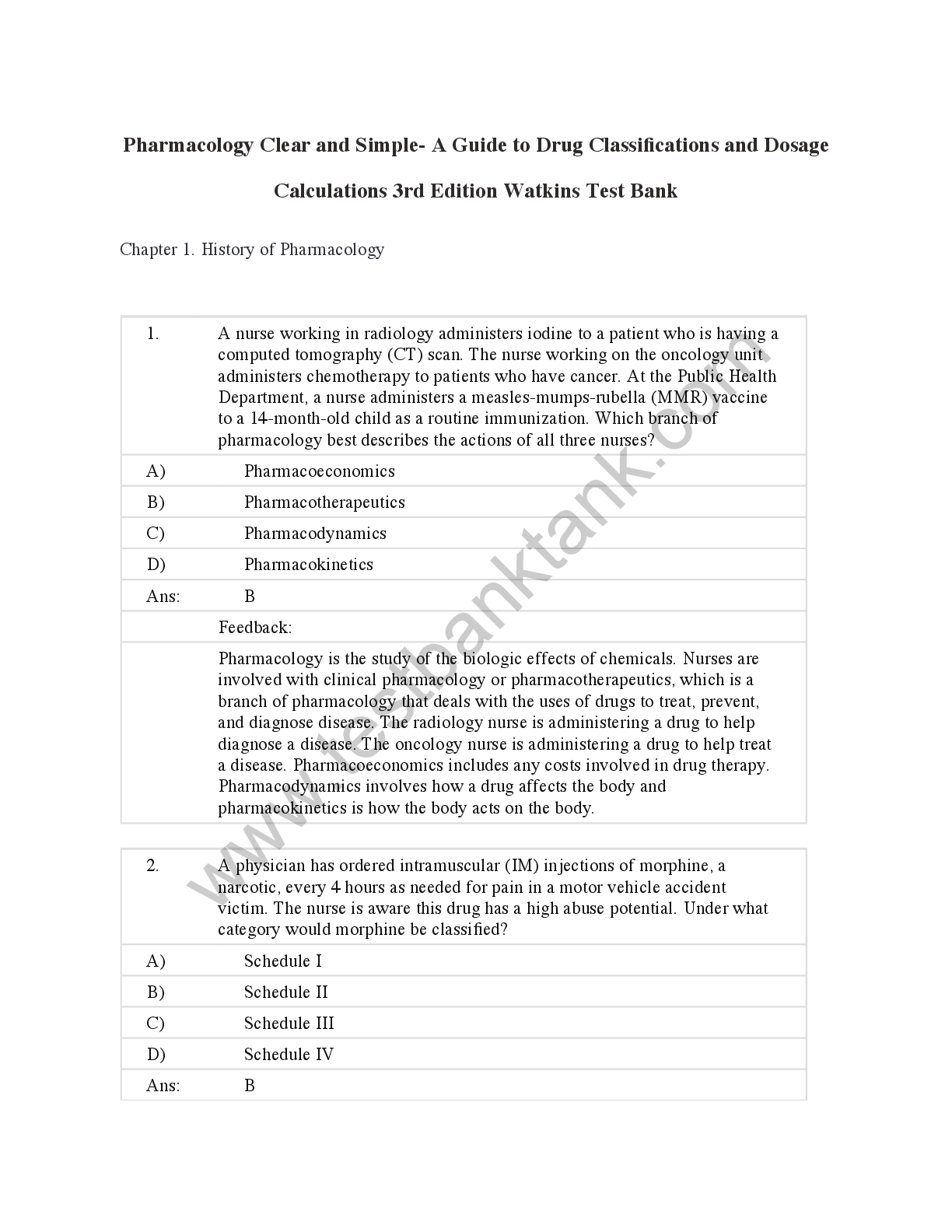
Test Bank for Macroeconomics, 10th Canadian Edition by Andrew B. Abel
$ 29
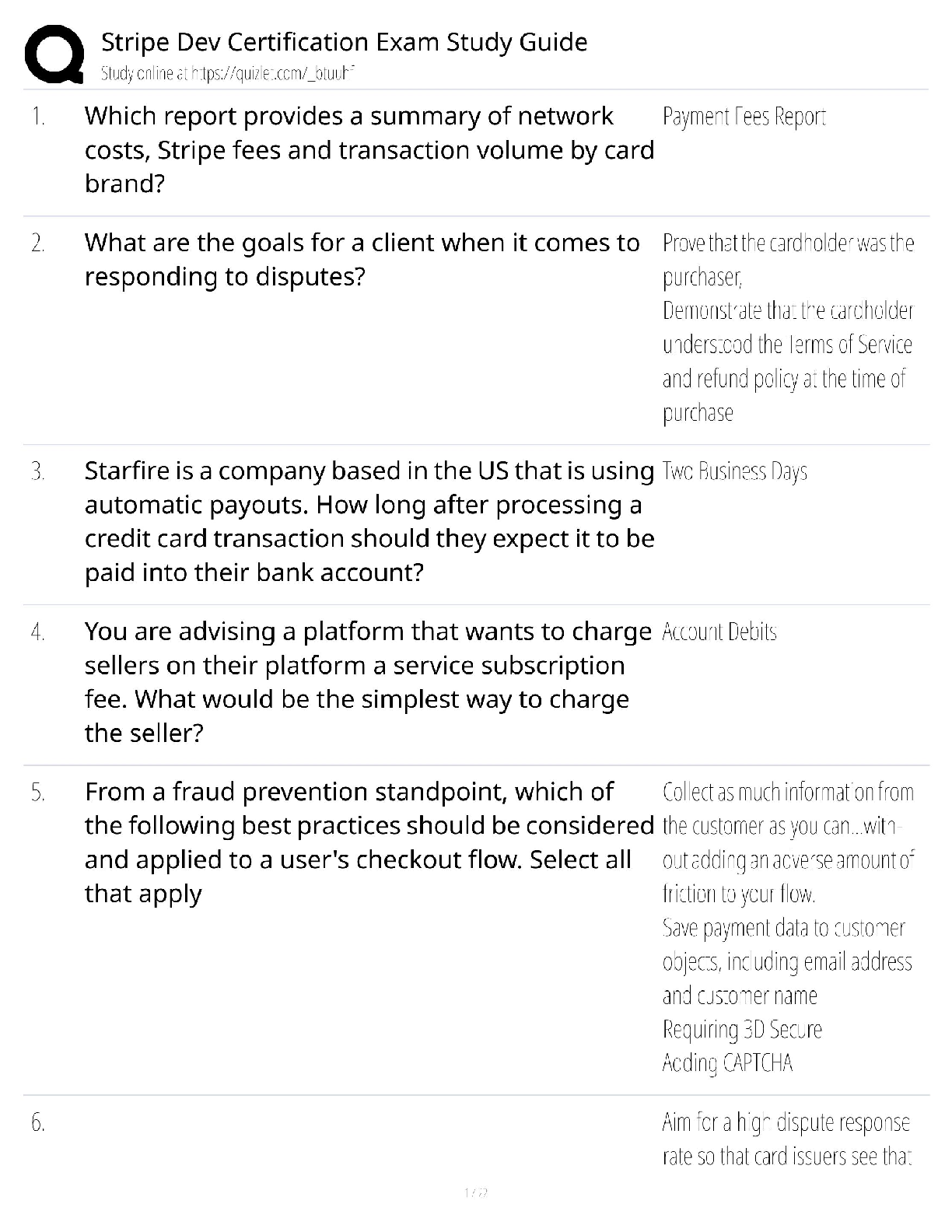
Stripe Dev Certification Exam Study Guide Test Bank / Payments API / 2025 Update / Score 100%
$ 11

Test Bank for Behavior Modification, What It Is and How To Do It, 11th Edition by Garry Martin, Joseph Pear
$ 29
CHEM101_MH_V4 Graded Exam 2 Topic 6: Quantum Theory, Grade 105.80 out of 115.00 (92%)