BIOL 251 Exam 3
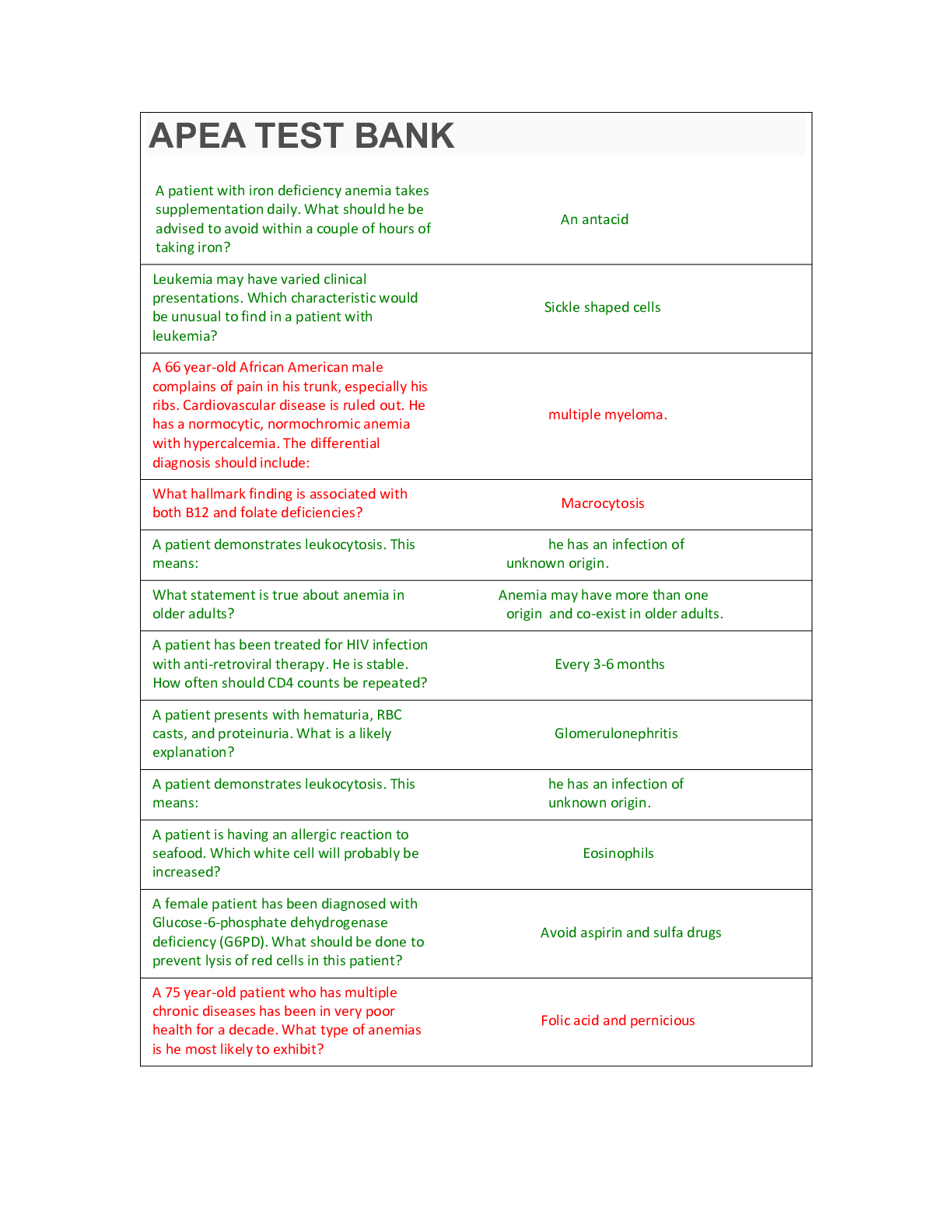
1. What is the function of antidiuretic hormone?
It stimulates angiotensin II secretion.
It promotes water conservation.
It stimulates hypothalamic osmoreceptors.
It inhibits salivation and thirst.
...
BIOL 251 Exam 3
1. What is the function of antidiuretic hormone?
It stimulates angiotensin II secretion.
It promotes water conservation.
It stimulates hypothalamic osmoreceptors.
It inhibits salivation and thirst.
It targets the cerebral cortex.
2. Fluid intake is governed mainly by hypothalamic neurons called __________.
baroreceptors
proprioceptors
nociceptors
osmoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
3. What is the total body water (TBW) content of a 70 kg young male?
10 L
20 L
40 L
60 L
70 L
4. What is the greatest determinant of the intracellular water volume?
K+
Na+
Ca2+
Cl-
PO43-
5. Where are cells with aldosterone receptors found?
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Posterior pituitary
Proximal convoluted tubule
Distal convoluted tubule
6. How is calcium concentration in the body regulated?
By hormones
By sodium and calcium concentrations in the plasma
By chloride and phosphate concentrations in the plasma
By the parasympathetic nervous system
By the sympathetic nervous system
7. Breathing into and out of a paper bag for a long period of time will lead to __________.
metabolic alkalosis
metabolic acidosis
urinary alkalosis
urinary acidosis
respiratory acidosis
8. The bicarbonate buffer system would not work very well in the human body if not for the action of the respiratory system, which ___________.
supplies the buffer system with CO2
supplies the buffer system with O2
expels HCO3- produced by the buffer system
expels H+ produced by the buffer system
expels CO2 produced by the buffer system
9. Place the following descriptions in order to represent the effects of profuse sweating.
1. Water loss (sweating)
2. Sweat glands produce perspiration by capillary filtration
3. Blood volume and pressure drop; osmolarity rises
4. Blood absorbs tissue fluid to replace loss
5. Intracellular fluid diffuses out of cells to replace lost tissue fluid
10. Dehydration
Reduced plasma volume and blood pressure
Renin release
Angiotensinogen conversion to angiotensin I
Angiotensin I conversion to angiotensin II
Angiotensin II stimulation of hypothalamus
Sense of thirst
Ingestion of water
Moistens mouth and distends stomach
Plasma volume elevates
11. Place a single word into each sentence to make it correct.
Antidiuretic hormone provides a means of controlling water output .
The increased osmolarity of the blood stimulates the hypothalamus to stimulate the posterior pituitary to release ADH.
ADH will work on the kidneys to reabsorb water into the blood stream.
A negative feedback system is used until the blood volume and osmolarity return to normal levels.
12. Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the appropriate position.
A buffer is any mechanism that resists changes in pH.
A physiological buffer uses direct elimination of acids, bases, or carbon dioxide from the body in order to adjust systemic acidity.
A substance that binds H+ during times of acidity and releases H+ during time of alkalinity is referred to as a chemical buffer .
Carbon dioxide, when present in sufficient amounts, will bind with water to form carbonic acid which is capable of dissociating into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions.
The phosphate buffer system plays a significant role in the ICF because phosphates are capable of binding and unbinding H+ depending on current conditions of acidity or alkalinity.
The carboxyl ends of protein chains are capable of buffering H+ as part of the protein buffer system .
13. Which of the following is not an accessory organ of digestion?
Tongue
Liver
Pancreas
Salivary glands
Spleen
14. __________ is a hormone, whereas __________ is an enzyme.
Enterokinase; pepsin
Gastrin; secretin
Gastrin; cholecystokinin (CCK)
Gastric lipase; histamine
Secretin; pepsin
15. The small intestine is suspended from the abdominal wall by the ___________.
falciform ligament
mesentery
greater omentum
lesser omentum
esophageal hiatus
16. The oral phase of swallowing is under __________ control and the pharyngo-esophageal phase is __________.
central nervous system; also controlled by the central nervous system
central nervous system; controlled by autonomic reflexes
autonomic nervous system; controlled by autonomic reflexes
voluntary; also voluntary
involuntary; also involuntary
17. The swallowing center is located in the __________.
mouth
oropharynx
esophagus
medulla oblongata
enteric nervous system
18. The __________ regulates the flow of contents from the stomach to the duodenum.
gastric rugae
antrum
pyloric sphincter
fundic region
cardiac region
19. The enzyme that catalyzes the first step reaction in HCl production by gastric parietal cells is called __________.
carbonic acid
carbonic anhydrase
dipeptidase
protease
ATPase
20. Which of the following enzymes functions at the lowest pH?
Salivary amylase
Pancreatic amylase
Pepsin
Trypsin
Dipeptidase
21. The __________ stores excess glucose and releases it into the blood when needed.
pancreas
stomach
liver
spleen
small intestine
22.
Which of the following is not a component of the pancreatic juice?
Trypsinogen
Chymotrypsinogen
Deoxyribonuclease
Sodium bicarbonate
Enterokinase
23. Which of the following is not associated with the large absorptive surface of the small intestine?0-2013
Circular folds (plicae circulares)
Intestinal length
Microvilli
Villi
Rugae
24. The __________ of the small intestine is/are similar to the __________ of the stomach.
villi; pyloric glands
rugae; Peyer patches
intestinal crypts; gastric pits
goblet cells; parietal cells
pyloric sphincter; ileocecal valve
25. Which of the following statements regarding the migrating motor complex is true?
It milks the chyme toward the colon.
It allows a bolus to move down the esophagus.
It churns and mixes residue in the descending colon.
It churns and mixes a bolus with gastric juices.
It propels pancreatic juice down the pancreatic duct.
26. Which of the following statements is true regarding the sodium-glucose transport protein (SGLP)?
It is a uniport carrier.
It is an antiport carrier.
It uses solvent drag to transport glucose and sodium.
It transports glucose and sodium from the intestinal lumen into the epithelial cells.
It transports glucose from the intestinal lumen into the epithelial cells, and sodium in the opposite direction.
27. Lecithin prepares fats for hydrolysis by forming __________.
triglycerides, fatty acids, and glycerol
low density lipoproteins (LDL)
chylomicrons
emulsification droplets
micelles
28. The muscle tone of the __________ along the colon contracts it lengthwise, causing its walls to bulge and form pouches called __________.
circular folds; ceca
taeniae coli; haustra
haustra; taeniae coli
internal sphincters; omental (epiploic) appendages
internal sphincters; ceca
29.
The movement of colonic contents from one puckered section to another is called __________.
the gastrocolic reflex
the duodenocolic reflex
mass movement
haustral contraction
defecation
30. Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify whether the region is part of the large or small intestine.
Large Intestine
Rectum
Cecum
Ascending Colon
Transverse Colon
Descending Colon
Sigmoid Colon
Small Intestine
Jejunum
Ileum
Duodenum
31. Identify each organ pictured below. Then click and drag each characteristic listed into the appropriate category to identify the organ to which it pertains.
Rugae Plicae
Gastric Pits Villi
Oblique Layer of Muscularis Brush border
Maximized size for storage and mixing Maximized surface area for absorption
Microvilli
Pryers Patches
\
32. Read each function of gastric juice below. Then click and drag each to the specific secretion to which it applies.
Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Gastric Lipase Instrinsic Factor
Activated Pepsin and Active form of a Digests fat in the Dysfunction could
Lingual Lipase Zymogen Stomach pernicious anemia
Breaks up connective Digests proteins Essential to absorption
tissue and cell wall of plants of vitamin B12
Destroys most ingested Autocatalytic
Pathogens
Converts iron to an
Absorbable form
33. Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify whether the structure is an actual part of the digestive tract or an accessory structure.
Accessory Organ Digestive Tract
Teeth Buccal cavity
Salivary glands Duodenum
Liver Jejunum
Gallbladder Ileum
Colon
Retctum
34. Place the appropriate words and descriptions with the picture with the correct highlighted peritoneal structure.
Words can be used more than once.
Attached
T
35. . Fill-in the sentences with the correct word and place the sentences in order to describe the flow of bile in the biliary ducts.
Bile is made in the and released into
the
This duct then merges with the from the
galldladder to make the bile duct.
The bile duct merges with the from
the pancreas to form the
This short tube opens up and releases bile into the
at the major duodenal papilla.
[Show More]