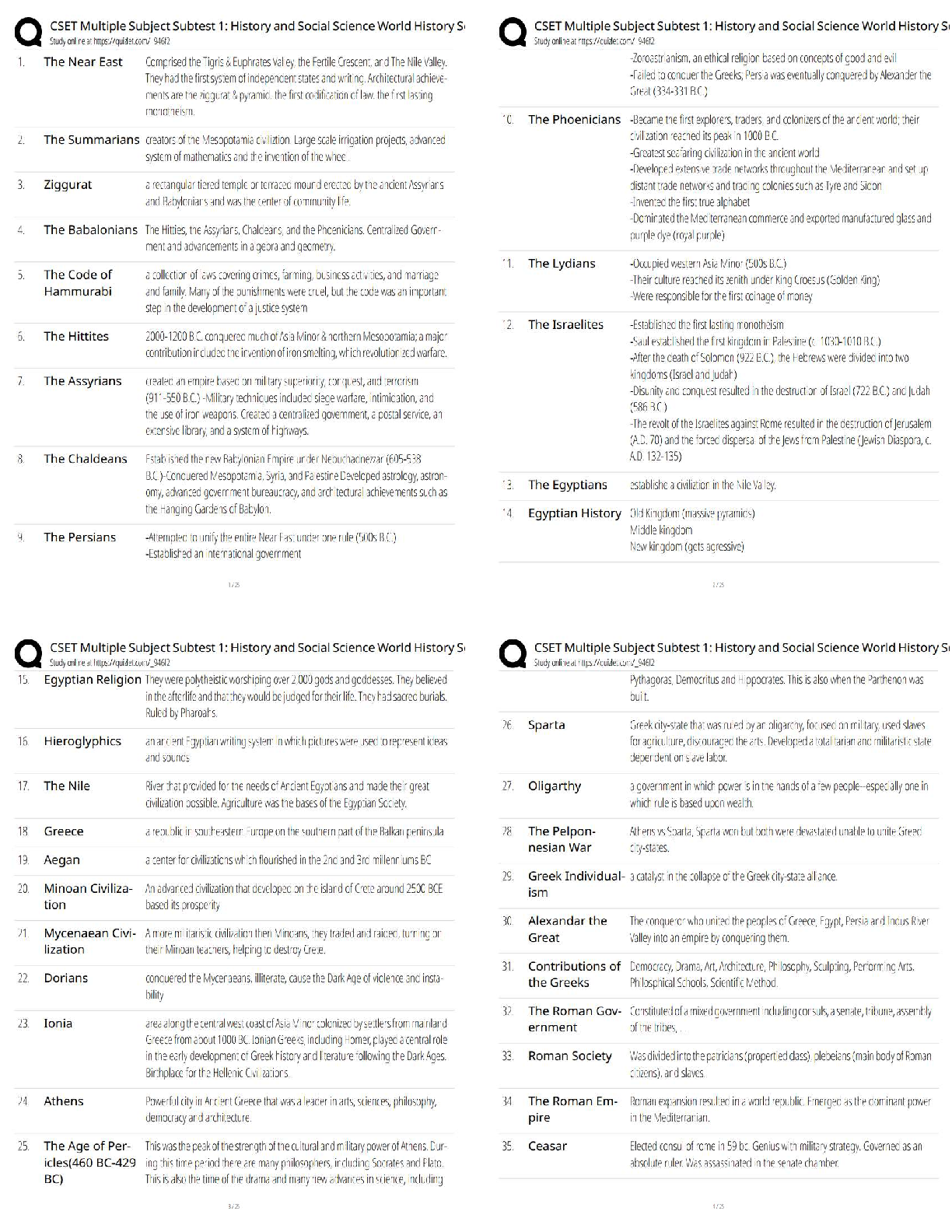
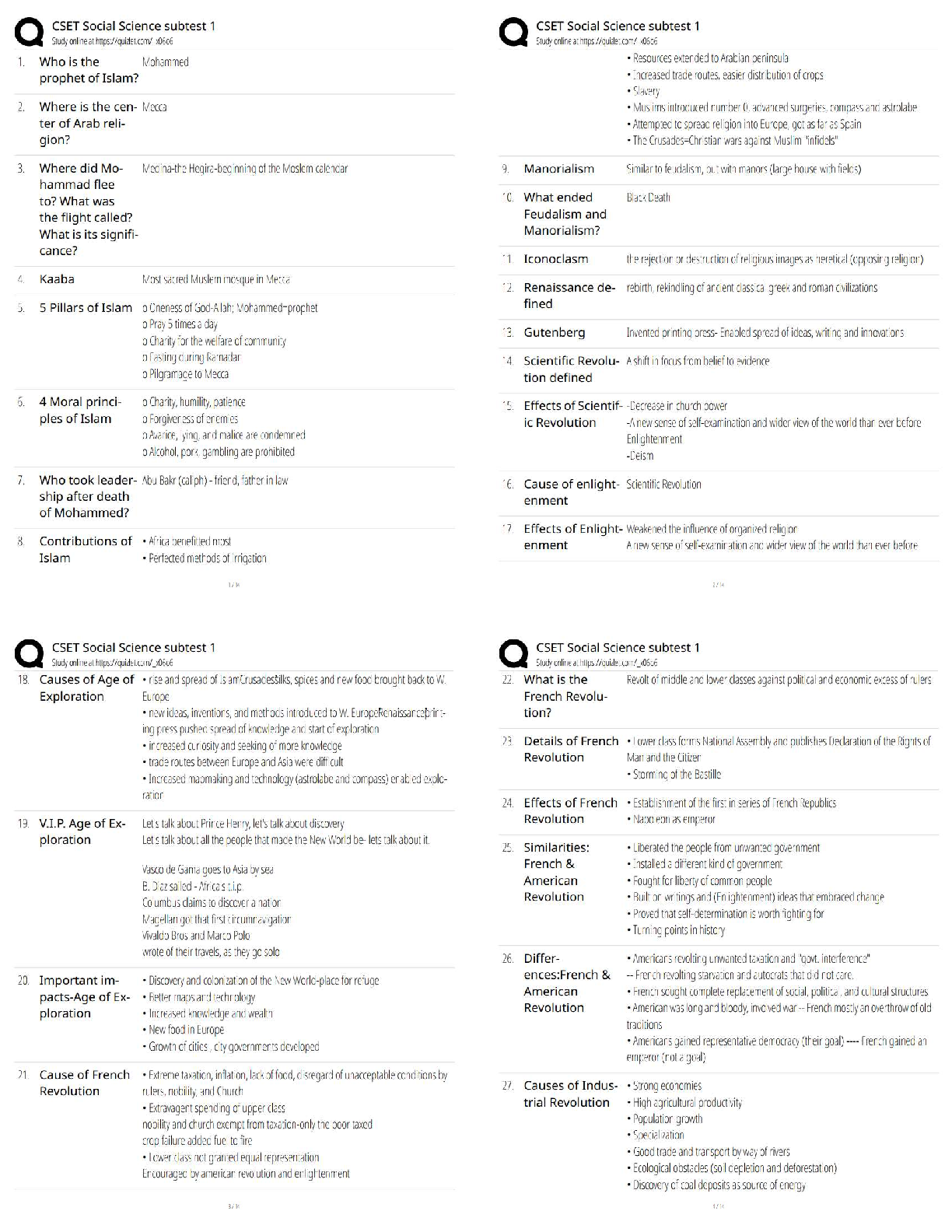
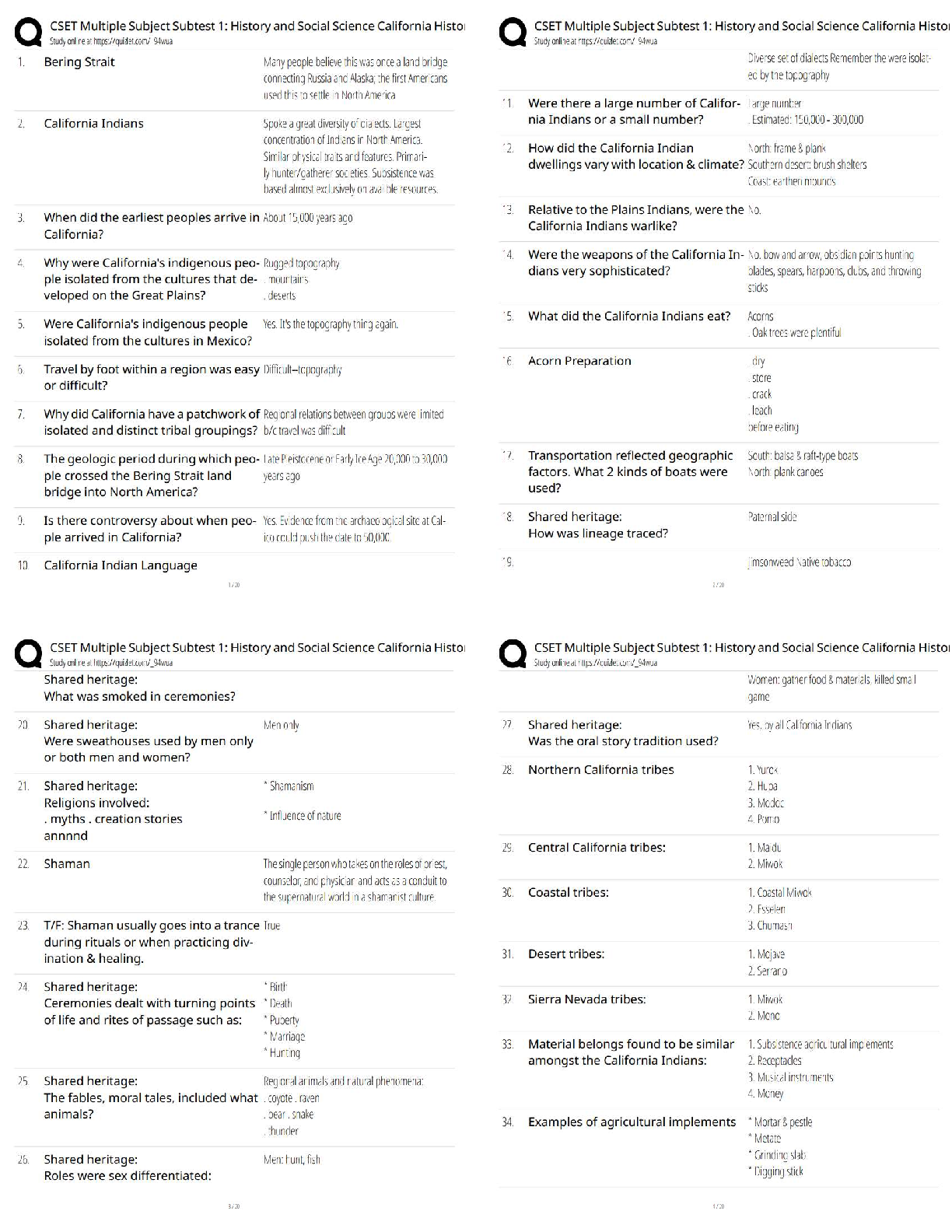
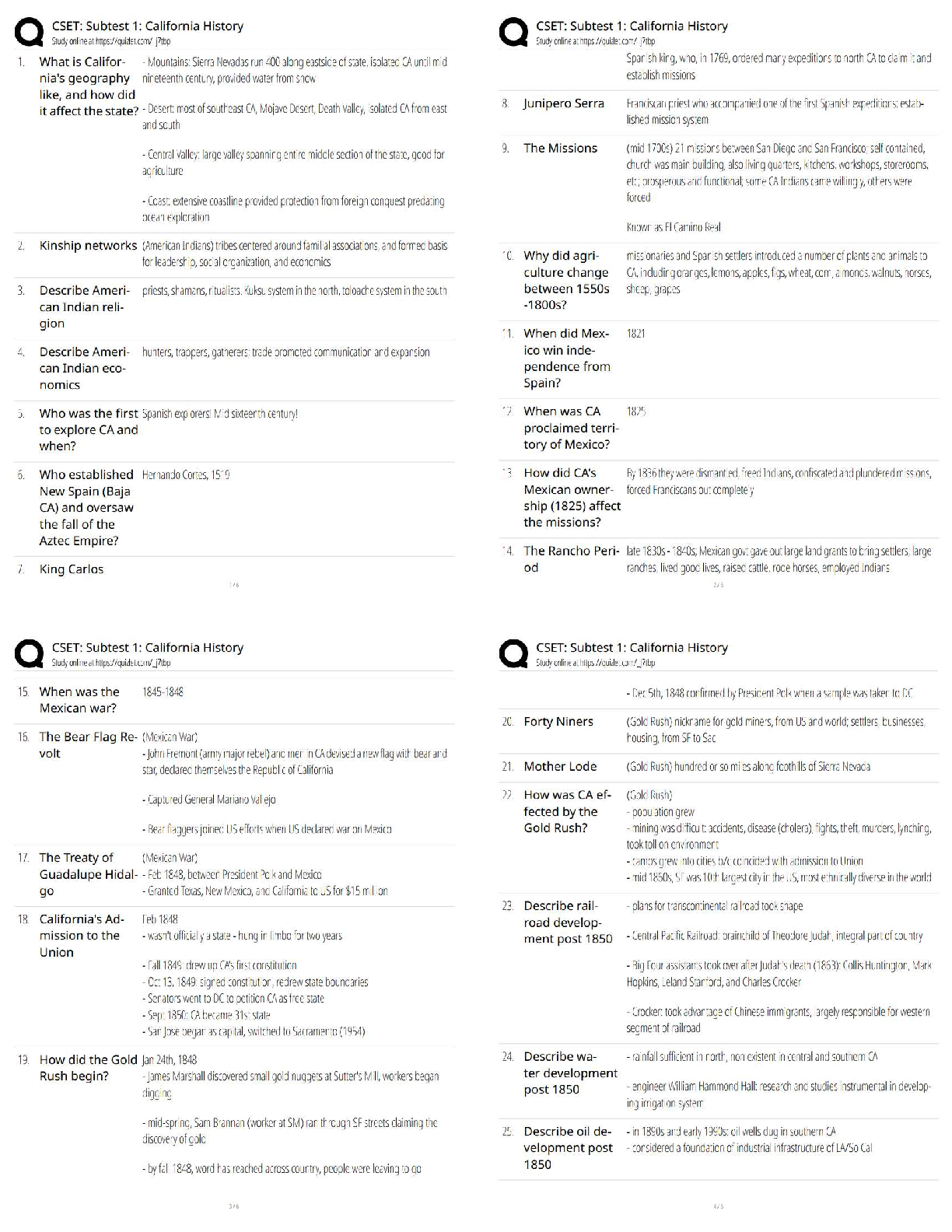
Physics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PHYS 202].Electric Field 1-solutions complete solutions to pursue grade A+ (All)
PHYS 202].Electric Field 1-solutions complete solutions to pursue grade A+
Document Content and Description Below
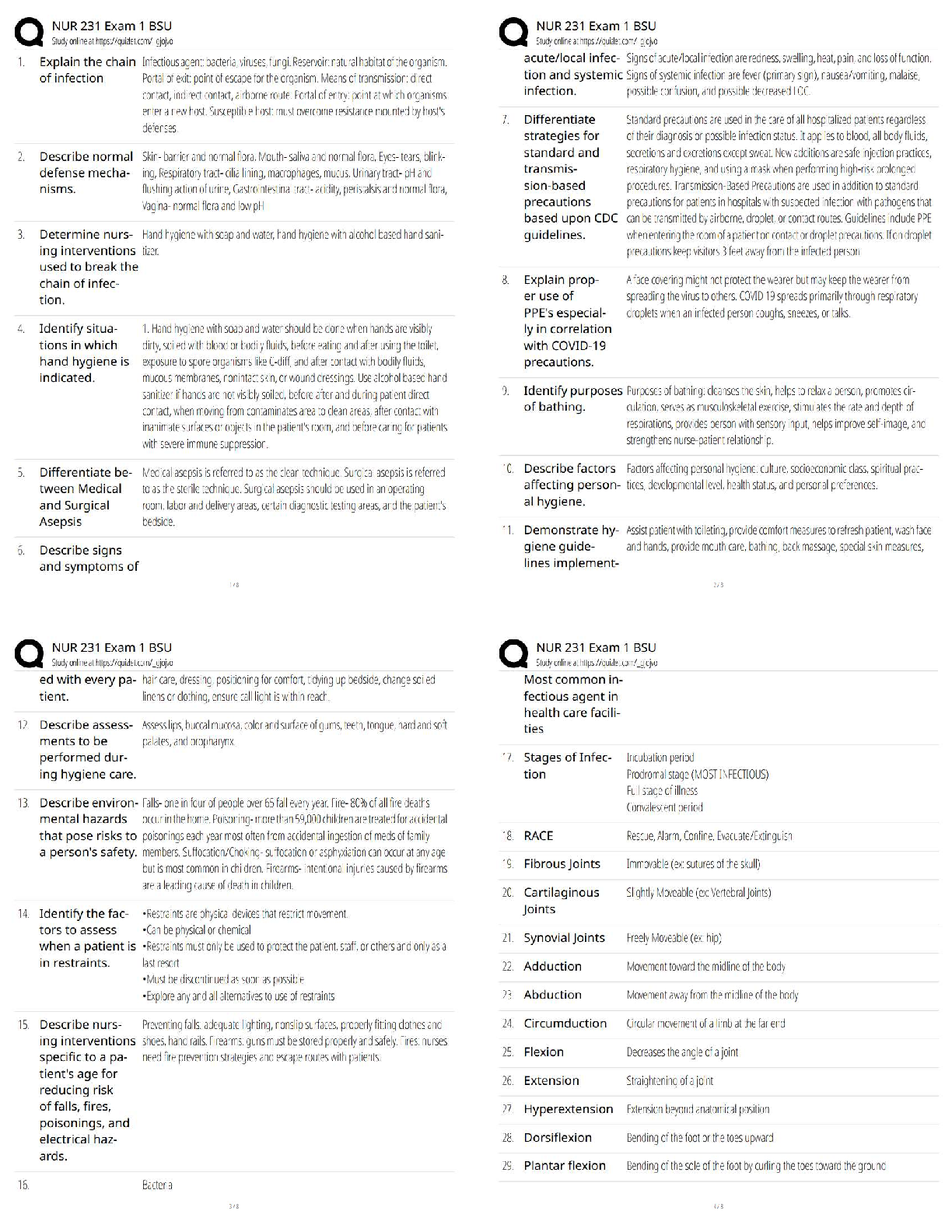
gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 1 This print-out should have 26 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on + − the next column or page - find all choices befo ... re answering. This homework is due Tuesday, February 1, at midnight Tucson time. 001 10.0 points Two small spheres carry equal amounts of electric charge. There are equally spaced points (a , b , and c) which lie along the same a 9. a 10. a b c + − b c + − b c line. + − a b c What is the direction of the net electric field at each point due to these charges? Explanation: Since the field originates from positive charges and terminates on the negative charges, + − 1. a 2. a 3. a 4. a + − b c + − b c + − b c + − b c a b c 002 10.0 points A droplet of ink in an industrial ink-jet printer carries a charge of 2 × 10−10 C and is deflected onto paper by a force of 0.0003 N. Find the strength of the electric field to produce this force. Correct answer: 1.5 × 106 V/m. Explanation: Let : Fe = 0.0003 N and q = 2 × 10−10 C . The electrical force is Fe = E q 0.0003 N 5. a correct 6. a 7. a 8. + − b c + − b c + − b c E = Fe = q 2 × 10−10 C = 1.5 × 106 V/m . 003 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points In 1909 Robert Millikan was the first to find the charge of an electron in his now-famous oil drop experiment. In the experiment tiny oil drops are sprayed into a uniform electric field between a horizontal pair of oppositely charged plates. The drops are observed with a magnifying eyepiece, and the electric field is adjusted so that the upward force q E on some negatively charged oil drops is just sufficient to balance the downward force m g of gravity. Millikan accurately measured the charges on many oil drops and found the values to be E = (4.99592 * 10? 13 kg) (9.8 m/s2 ) e = 5.44 * 10? 18 C ? gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 2 whole-number multiples of 1.6 × 10−19 C — Explanation: the charge of the electron. For this he won the Nobel Prize. Let : F = 0.227 N and If a drop of mass 4.99592×10−13 kg remains E = 4.27 × 105 N/C . stationary in an electric field of 9 × 105 N/C, what is the charge on this drop? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . Correct answer: 5.44 × 10−18 C. Explanation: The electric field is E = F q q = F E = 0.227 N 4.27 × 105 N/C = 5.31616 × 10−7 . Let : m = 4.99592 × 10−13 kg , E = 9 × 105 N/C , and g = 9.8 m/s2 . When suspended, m g = E q q = m g 006 (part 1 of 3) 10.0 points A charge of 7 µC is at the origin. What is the magnitude of the electric field on the x axis at x = 6 m? The Coulomb constant is 8.98755 × 109 N m2 /C2 . Correct answer: 1747.58 N/C. 9 × 105 N/C = 5.44 × 10−18 C . 004 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points How many extra electrons are on this particular oil drop (given the presently known charge of the electron)? Correct answer: 34. Explanation: Explanation: Let : k = 8.98755 × 109 N m2 /C2 , q = 7 µC = 7 × 10−6 C , and x = 6 m . The electric field at a point P located a distance x from a charge q is E (x) = k q (1) x 2 rp,o . Let : e = 1.6 × 10−19 C . E (6 m) = (8.98755 × 109 N m2 /C2 ) × 7 × 10− 6 C ı The number of electrons can be calculated from the charges on the oil drop: N = q (6 m)2 = (1747.58 N/C) ˆı 1.6 × 10−19 C = 34 . 005 10.0 points A test charge has a force of 0.227 N on it when it is placed in an electric field intensity of 4.27 × 105 N/C. What is the magnitude of the charge? Correct answer: 5.31616 × 10−7 C. The electric field is directed along the positive x-axis. 007 (part 2 of 3) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the electric field on the x axis at x = −9 m? Correct answer: 776.702 N/C. Explanation: (?? gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 3 Let : x = −9 m . 500 250 E 4. 0 (x) = k q (1) E x 2 rp,o . (−9 m) = (8.98755 × 109 N m2 /C2 ) × 7 × 10− 6 C ı) −250 −500 −2 −1 0 1 2 (−9 m)2 = − (776.702 N/C) ˆı ∥ ∥ E (−9 m) = (776.702 N/C) ˆı The electric field is directed along the negative x-axis. 008 (part 3 of 3) 10.0 points Sketch the function Ex versus x for both positive and negative values of x. (Remember that Ex is negative when E points in the negative x direction.) 500 250 1. 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 0 1 2 x (m) 500 250 2. 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 0 1 2 x (m) 500 250 3. 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 0 1 2 500 250 5. 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 500 250 6. 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 Explanation: The function E (x) = low. 500 250 0 −250 −500 −2 −1 x (m) 0 1 2 x (m) 0 1 2 x (m) k q rp,o is shown bex 2 0 1 2 x (m) x (m) 009 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points correct Consider three charges arranged as shown. gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 4 is directed toward the charge since q3 is nega8.8 µC 3.6 µC −3.1 µC + + − tive. Thus Enet = E1 − E2 + E3 ( ) 3.3 cm 1.6 cm = ke ( q1 2 2 r 1 − r 2 + |q2 | r3 What is the magnitude of the electric field = 8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 ) [ strength at a point 2.8 cm to the left of the middle charge? The value of the Coulomb × (8.8 × 10−6 C) (0.005 m)2 constant is 8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . Correct answer: 3.13674 × 109 N/C. Explanation: Let : q1 = 8.8 µC = 8.8 × 10−6 C , q2 = 3.6 µC = 3.6 × 10−6 C , q3 = −3.1 µC = −3.1 × 10−6 C , r 1,2 = 3.3 cm = 0.033 m , r 2,3 = 1.6 cm = 0.016 m , x = 2.8 cm = 0.028 m , and ke = 8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . r 1 = r1,2 − x = 0.033 m − 0.028 m = 0.005 m r 2 = x = 0.028 m r 3 = r2,3 + x = 0.016 m + 0.028 m = 0.044 m E net = E 1 + E 2 + E 3 E = ke q r 2 Considering the magnitudes of the electric fields at a point 2.8 cm to the left of the middle charge, − (3.6 × 10− 6 C) (0.028 m)2 ] + (3.1 × 10− 6 C) (0.044 m)2 = (8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 ) × [(0.352 N/C) −(0.00459184 N/C) +(0.00160124 N/C)] = 3.13674 × 109 N/C , directed along the positive x-axis. 010 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the force on a −3.1 µC charge placed at this point? Correct answer: 9723.89 N. Explanation: Let : q = −3.1 µC = −3.1 × 10−6 C . The electric force is Felectric = q Enet E1 = ke q2 r 1 is directed away from the charge since q1 is positive, = −3.1 × 10−6 C × (3.13674 × 109 N/C) = −9723.89 N , ∥Felectric∥ = 9723.89 N . E2 = ke q2 r 2 is directed away from the charge since q2 is positive, and E3 = ke |q2 | r3 Felectric has a magnitude of 9723.89 N and is directed along the negative x axis. 011 10.0 points A charge of −4.87 µC is located at the origin, y 2 = ke ( d q2 gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 5 and a charge of −5.52 µC is located along the y axis at 1.03917 m. Correct answer: 1.51219 g. At what point along the y-axis is the electric field zero? The value of the Coulomb constant is 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . Correct answer: 0.503316 m. Explanation: Let : q1 = −4.87 µC , q2 = −5.52 µC , and d = 1.03917 m . Call the point where the fields cancel y. Since the charges are of equal sign, the only place y can be is somewhere between them. The field from the particle q1 at the origin is Explanation: Let : Q = 27.7 µC = 2.77 × 10−5 C , E = 535 N/C , and g = 9.8 m/s2 . Call the vertical direction the y-direction, so the the unit vector ĵ points up. Then force equilibrium in the vertical direction for a charge Q of mass m yields ∑ F = Q E ĵ + m g (−ĵ) = 0 For this to hold, Q E − m g = 0 E1 = ke q1 y 2 pointing down (since q1 is negative). The field from the charge q2 at a point d along the y-axis is m = Q E g = (2.77 × 10− 5 C) (535 N/C) 9.8 m/s2 × 1000 g 1 kg E2 = ke q2 (d − y)2 pointing up (since q2 is negative). Thus we have cancellation at d provided E1 equals E2 , or ke q1 = 1.51219 g . 013 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the electric field that will balance the weight of an electron? − y)2 q2 y2 = q1 (d − y)2 √ The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2 . 1. Unable to determine q2 q1 y = d − y y = d √ = 2.5.13158 × 10−8 N/C downward 1.03917 m √ 1 + q2 q1 −5.52 µC 3. None of these 1 + −4.87 µC = 0.503316 m . 012 10.0 points An object having a net charge of 27.7 µC is placed in a uniform electric field of 535 N/C directed vertically up. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . What is the mass of this object if it “floats” in the field? 4.5.13158 × 10−8 N/C upward 5.5.58496 × 10−11 N/C downward correct 6.1.02576 × 10−7 N/C upward 7.5.58496 × 10−11 N/C upward 8.1.02576 × 10−7 N/C downward Explanation: ? ? gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 6 For the proton Let : me = 9.109 × 10−31 kg , qe = −1.60 × 10−19 C , and g = 9.81 m/s2 . Felectric − Fg = 0 q E − m g = 0 For the electron, qe E = me g E = me g qe = (9.109 × 10− 31 kg) (9.81 m/s2 ) −1.6 × 10−19 C = −5.58496 × 10−11 N/C , a field of 5.58496 × 10−11 N/C directed downward. 014 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the electric field that will balance the weight of a proton? 1. None of these 2.5.58496 × 10−11 N/C downward 3.5.13158 × 10−8 N/C upward 4. Unable to determine 5.1.02576 × 10−7 N/C upward correct 6.5.58496 × 10−11 N/C upward 7.1.02576 × 10−7 N/C downward 8.5.13158 × 10−8 N/C downward Explanation: Let : mp = 1.673 × 10−27 kg and qp = 1.60 × 10−19 C . qp E = mp g E = mp g qp = (1.673 × 10− 27 kg)(9.81 m/s2 ) 1.6 × 10−19 C = 1.02576 × 10−7 N/C , directed upward. 015 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points Three point charges are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. −4.1 C ĵ ı 60◦ −4.1 C P −4.1 C Find the magnitude of the electric field vector E at P . The value of the Coulomb ∥ ∥ constant is 8.9875 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . Correct answer: 5.01292 × 108 N/C. Explanation: Let : a = 9.9 m , q = −4.1 C , and k = 8.9875 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . q ĵ ı q P q Electric field vectors due to bottom two charges cancel out each other. The magnitude 2. ?? 5. ? gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 7 of the field vector due to charge at to top of the origin. The Coulomb constant is 8.99 × the triangle, which gives 109 N · m2 /C2 . k q k q Correct answer: 92597 N/C. ∥ ∥ E = ( √ 3 2 ) 2 = 4 3 a 2 a Explanation: = 4 3 (8.9875 × 109 N · m2 /C2 ) (−4.1 C) (9.9 m)2 Let : q1 = 3.23 µC at the origin , q2 = −1.13 µC , = 5.01292 × 108 N/C , √ 3 (x1 , y1 ) = (0 m, 0 m) , (x2 , y2 ) = (0.810 m, 0 m) , (xP , yp ) = (0 m, 0.544 m) , and where h = a cos(30◦ ) = the triangle. 2 a is the height of kC = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . r 1 = yP − y1 = yP = 0.544 m 016 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points E r 2 = (xP − x2 ) 2 + (yP − y2 ) 2 Find the direction of the field vector at P . 1 = (0 − x2 ) 2 + (yP − 0)2 = x2 + yP = (0.81 m)2 + (0.544 m)2 1. 3. √ (ˆı − ĵ) 2 ı 1 √ (ˆı + ĵ) 2 = 0.952036 m2 The magnitude of E1 is E1 = kC q2 r 1 4. − ı 6. k 1 √ (ˆı − ĵ) = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 2 × 3.23 × 10− 6 C (0.544 m)2 = 98121.6 N/C . 7. ĵ correct 8. −k 1 Enet = E 1 + E 2 √ Enet = Enet,x + Enet,y The electric field produced by the charge q1 9. − √ (ˆı + ĵ) 2 10. −ĵ Explanation: By inspection, E at P due to q = −4.1 C is along ĵ direction (see figure above). 017 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A charge of 3.23 µC is at the origin and a second charge of −1.13 µC is on the positive x-axis 0.810 m from the origin. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point P on the y-axis 0.544 m from is along the y-axis and is directed away from the charge, since q1 is positive, so E1,x = 0 N/C and E1,y = E1 . The magnitude of E2 is E2 = kC |q2 | r2 = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 × 1.13 × 10− 6 C 0.952036 m2 = 10670.5 N/C . gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) ( ) 8 The electric field produced by the charge q2 is along the line connecting q2 and point P , and is directed to the right and downward toward the charge since q2 is negative. The direction of E2 is θ = tan−1 ( = tan−1 Enet,y Enet,x 92172.4 N/C 8858.15 N/C ) tan = x ϕ y ϕ = tan−1 ( x y ) ( ) 0.81 m = tan−1 0.544 m = 84.5105◦ . The electric field at point P(x = 0.0 m, y = 0.544 m) is 92597 N/C, directed 84.5105 ◦ = 56.1145◦ . The components of E2 are E2,x = E2 sin = (10670.5 N/C) sin 56.1145 ϕ ◦ = 8858.15 N/C , E2,y = E2 cos = (10670.5 N/C) cos 56.1145 ϕ ◦ = 5949.18 N/C . The components of Enet are Enet,x = E1,x + E2,x = 0 N/C + 8858.15 N/C = 8858.15 N/C , Enet,y = E1,y − E2,y = 98121.6 N/C − 5949.18 N/C = 92172.4 N/C . Thus the net force is √ Enet = Enet,x + Enet,y [ above the positive x-axis. 019 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points Two charges are located on a horizontal axis. p 1.8 m 1.2 µC 1.2 µC 3 m 3 m Determine the electric field at p on a vertical axis as shown in the figure above. Up is the positive direction. The Coulomb constant is 8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . Correct answer: 906.678 V/m. Explanation: Let : x = 3 m , = (8858.15 N/C)2 + (92172.4 N/C)2 ] 1/2 = 92597 N/C . 018 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Determine the direction of this electric field (as an angle between −180◦ and 180◦ measured from the positive x-axis, with counterclockwise positive). Correct answer: 84.5105◦ . Explanation: The direction of Enet is tan θ = Enet,y Enet,x y = 1.8 m , q = 1.2 µC , and ke = 8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . θ y q q −x x The distance from each point charge to the point of interest on the y-axis is √ √ r = x 2 + y2 = (3 m)2 + (1.8 m)2 = 3.49857 m . gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) Therefore, the electric field due to one of the y point charges is E = ke q 9 r 2 = (8.98755 × 109 N · m2 /C2 )(1.2 × 10− 6 C) (3.49857 m)2 = 881.132 V/m . Now, we need to vector add the contributions from each charge. By symmetry, the x-components cancel, and we only have twice the y-components left. To find the y compo5.5 nC 0.765 m + 0.448 m - −3.0 nC x + 1.5 nC nents, we note that the angle θ is ( ) What is the net electric force on the charge at the origin? The Coulomb constant is 8.99 × θ = arcsin 1.8 m 3.49857 m 109 N · m2 /C2 . = 30.9638◦ , Correct answer: 7.49861 × 10−7 N. so the total electric field is Etot = 2 (881.132 V/m) sin 30.9638◦ = 906.678 V/m , where Etot points upward. 020 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Calculate the vertical component of the electric force on a −3 µC charge placed at point p. Correct answer: −0.00272003 N. Explanation: Let : q = −3 µC . The force is F = q E = (−3 × 10−6 C) (906.678 V/m) = −0.00272003 N , where the force F points downward. 021 (part 1 of 4) 10.0 points Consider three charges arranged in a triangle as shown. Explanation: Let : q1 = 5.5 nC at the origin , q2 = 1.5 nC , q3 = −3.0 nC , r 1,2 = 0.765 m , r 1,3 = 0.448 cm , and kC = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 . Consider the magnitudes of the forces, given by Felectric = kC q1 22 r The repulsive force F1,2 = kC q12q 2 r 1,2 = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 × (5.5 × 10− 9 C)(1.5 × 10− 9 C) (0.765 m)2 = 1.26733 × 10−7 N acts along the negative x-axis, and the attractive force F1,3 = kC q1 |q3 | r 1,3 F 21,2 + F 2 gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 10 = 8.99 × 109 N · m2 /C2 024 (part 4 of 4) 10.0 points × (5.5 × 10− 9 C)(3 × 10− 9 C) (0.448 m)2 = 7.39073 × 10−7 N acts along the negative y-axis. Thus √ F1,net = 1,3 [ What is the direction of the net electric field (as an angle between −180◦ and +180◦ measured from the positive x-axis, with counterclockwise positive). Correct answer: −99.7302◦ . = (1.26733 × 10−7 N)2 +(7.39073 × 10−7 N)2 ] 1/2 = 7.49861 × 10−7 N . Explanation: E and F are in the same direction, so the 022 (part 2 of 4) 10.0 points What is the direction of this force (as an angle between −180◦ and +180◦ measured from the positive x-axis, with counterclockwise positive)? Correct answer: −99.7302◦ . Explanation: tan θ = F1,3 F1,3 direction is −99.7302◦ . 025 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A small 6.42 g plastic ball is suspended by a 23.8 cm long string in a uniform electric field of 4220 N/C, as shown. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 , and the Coulomb constant is 8.99×109 N · m2 /C2 4220 N/C ( θ = tan−1 F1,3 F1,2 ) 23.4◦ 23.8 cm ( = tan−1 −7.39073 × 10−7 N −1.26733 × 10−7 N ) = 80.2698◦ below the negative x-axis. From the positive x-axis, the angle is −180◦ + 80.2698◦ = −99.7302◦ . 023 (part 3 of 4) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the net electric field at the position of the charge at the origin? Correct answer: 136.338 N/C. Explanation: Felectric = q E E = Felectric = 7.49861 × 10− 7 N 6.42 g Is the ball’s charge positive or negative? 1. positive correct 2. negative 3. Unable to determine Explanation: The charge is positive, since the electrical force exerted on it has the same direction as the electric field. q 5.5 × 10−9 C = 136.338 N/C . 026 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points If the ball is in equilibrium when the string gilvin (jg47854) - 3. Electric Field 1 - meyers - (21235) 11 makes a 23.4◦ angle with the vertical as indicated, what is the net charge on the ball? Correct answer: 6.4517 µC. Explanation: Let : m = 6.42 g = 0.00642 kg , L = 23.8 cm , E = 4220 N/C , and θ = 23.4◦ . T θ F = qE mg The ball is in equilibrium horizontally, Felectric − T sin θ = 0 q E − T sin θ = 0 T sin θ = q E and vertically, T cos θ − Fg = 0 T cos θ − m g = 0 T cos θ = m g . Dividing, tan θ = FT sin θ FT cos θ = m Eg q = m g tan θ E = (0.00642 kg)(9.8 m/s2 ) tan 23.4◦ 4220 N/C × 106 µC C = 6.4517 µC . [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages
![Preview image of PHYS 202].Electric Field 1-solutions complete solutions to pursue grade A+ document](https://scholarfriends.com/storage/Electric_Field_1_solutions.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 05, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 05, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
74






.png)
.png)
.png)