Biology > EXAM REVIEW > Newest Bios 256 Midterm Exam Review Packet-1 (All)
Newest Bios 256 Midterm Exam Review Packet-1
Document Content and Description Below
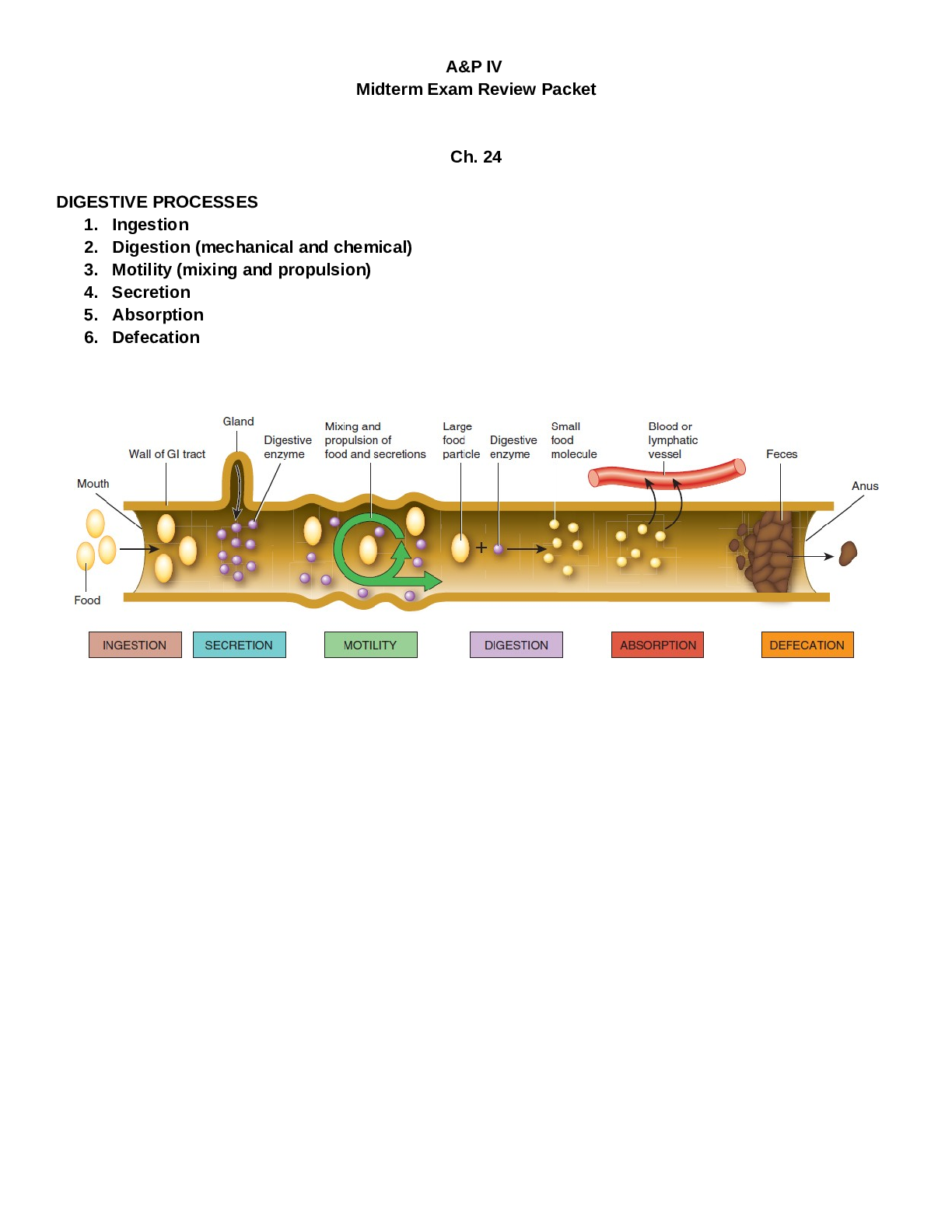
A&P IV Midterm Exam Review Packet Ch. 24 DIGESTIVE PROCESSES 1. Ingestion 2. Digestion (mechanical and chemical) 3. Motility (mixing and propulsion) 4. Secretion 5. Absorption 6. Defeca... tion GI TRACT AND ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE STRUCTURES BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY EACH ORGAN ON THE IMAGE ABOVE. GI TRACT INNERVATION • Autonomic NS o Parasympathetic NV (enhances digestion) o Sympathetic NV (inhibits or slows down digestion) • Enteric Nervous System o Submucosal plexus o Myenteric plexus Be able to identify all parts of the GI tract What are the histological significances of the GI tract? The GI tract consist of 4 layers: Mucosa- Divides into 3 layers Epithelium – Surface Epithelium Lamina Propria – Connective Tissue Muscularis Mucosae – Smooth Muscle Submucosa- Areolar Connective Tissue Muscularis- In all GI tract organs except the stomach Serosa ENZYMES originating in the oral cavity What are the functions of the oral cavity? Salivary glands Parotid glands (under the cheek bones) Submandibular glands (under the mandible) Sublingual glands (under the tongue) • All secrete SALIVA, which contains: o Mostly water o Ions o Buffers o Lysosyme o Salivary amylase Salivary Amylase (made by the salivary glands) - Break down carbohydrates - Converts Polysaccharides to monosaccharides, maltose, maltotriose and alpha-dextrins - Deactivated by stomach acid Lingual Lipase (made by the lingual glands of the tongue) - From lingual glands of the tongue - Break down lipids - Activated by HCl of stomach - Converts triglycerides to fatty acids and monoglycerides - What are the components of saliva? Among these polynucleotides, what is digested in the oral cavity? (proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates) THE SIGNIFICANT CELLS OF THE STOMACH AND THEIR SECRETIONS (GASTRIC JUICE) Parietal Cells - Secrete HCl - makes the chyme acidic - kills bacteria - denaturing (unfolding) proteins - activates pepsin along with lingual lipase. - Secrete intrinsic factor, which allows for absorption of vitamin B12 Chief Cells - The major stomach cells - Secrete pepsinogen, which is activated (by stomach acid) and becomes pepsin, a peptidase - Pepsin breaks down proteins - Secrete gastric lipase - breaks down triglycerides into monoglycerides and fatty acids G Cells - Secrete Gastrin (hormone): contracts cardiac sphincter; loosens pyloric sphincter; promotes stomach motility; promotes secretion of pepsinogen from chief cells and HCl from parietal cells Mucous Cells - THEY SECRETE MUCOUS - Mucous forms a protective barrier against acidic chyme What is the function of stomach acid? ...................................................................CONTINUED...................................................................... [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 08, 2021
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
62