APEA TEST BANK 2 QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (EXPALINED), COMPLETE GUIDE (2020)
Document Content and Description Below
APEA TEST BANK 2 QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (EXPALINED)
Question:
What is the recommendation of American Cancer Society for screening an average risk 40 year-old Caucasian male for prostate cancer?
Quest
...
ion:
Which of the following results in a clinically insignificant increase in the prostate specific antigen (PSA)?
Question:
Hesselbach’s triangle forms the landmark for:
Question:
Which of the following medications should be avoided in a 65 year-old male with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
Question:
A localized tumor in the prostate gland associated with early stage prostate cancer is likely to produce:
Question:
An elderly male patient is taking finasteride, a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor. What affect might this have on his PSA level?
Question:
Noninfectious epididymitis is common in:
Question:
The following PSA levels have been observed in a patient. What conclusion can be made following these annual readings? Year 1: 3.2 ng/mL Year 2: 3.8 ng/mL Year 3: 4.2 ng/mL
Question:
What is the recommendation of American Cancer Society for initial screening of an African-American male for prostate cancer?
Question:
What is American Cancer Society’s recommendation for prostate screening in a 70 year-old male?
He should be screened annually with PSA only.He should be screened annually with PSA and DRE.He should be screened until he has a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
Question:
A 70 year-old male presents to your clinic with a lump in his breast. How should this be evaluated?
Question:
A 22 year-old male who is otherwise healthy complains of scrotal pain. His pain has developed over the past 4 days. He is diagnosed with epididymitis. What is the most likely reason?
Question:
Digital rectal exam may be performed to assess the prostate gland. Which term does NOT describe a prostate gland that may have a tumor?
Question:
A male patient has epididymitis. His most likely complaint will be:
Question:
What is the effect of digital rectal examination (DRE) on a male’s PSA (prostate specific antigen) level if it is measured on the same day as DRE?
Question:
Hematuria is not a common clinical manifestation in:
Question:
A 25 year-old male patient is training for a marathon. He reports an acute onset of scrotal pain after a 10 mile run. He has nausea and is found to have an asymmetric, high-riding testis on the right side. What should be suspected?
Question:
A 50 year-old male comes to the nurse practitioner clinic for evaluation. He complains of fever 101F, chills, pelvic pain, and dysuria. He should be diagnosed with:
Question:
5-alpha-reductase inhibitors work by producing:
dilation of the detrusor vessels.a decrease in the size of the prostate.
Question:
A 40 year-old male has been diagnosed with acute bacterial prostatitis. His prostate specific antigen (PSA) is elevated on diagnosis. How soon should his PSA be rechecked?
Question:
A patient with testicular torsion will have a:
positive cremasteric reflex on the affected side.negative cremasteric reflex on the affected side.
and a high riding testis. There can also be profound testicular swelling and an acute onset of scrotal pain.
Question:
A common presentation of an inguinal hernia is:
groin or abdominal pain with a scrotal mass.
Question:
What class of medications can be used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia and provide immediate relief?
Alpha-1 blockers Correct5-alpha reductase inhibitorsDiureticsAnalgesics
Question:
A 65 year-old patient has a firm, non-tender, symmetrical enlarged prostate gland on examination. His PSA is 3.9 ng/mL. This probably indicates:
Question:
What symptom listed below might be seen in a male patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia?
Question:
The risk of HIV transmission is increased:
when other STDs are present.
Question:
A 25 year-old female presents with lower abdominal pain. Which finding below would likely indicate the etiology as pelvic inflammatory disease?
Question:
A male patient presents with dysuria. He states that his female partner has an STD, but he is not sure which one. Which of these should be part of the differential?
Question:
A 30 year-old male who is sexually active presents with pain during bowel movements. He is negative when checked for hemorrhoids, but has a tender prostate gland. What should be suspected?
Question:
A female patient and her male partner are diagnosed with trichomonas. She has complaints of vulval itching and discharge. He is asymptomatic. How should they be treated?
Question:
A 26 year-old male patient has been diagnosed with gonorrhea. How should he be managed?
Question:
A 24 year-old female presents with abdominal pain. On exam, she is found to have cervical motion tenderness. What finding supports a diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
Question:
A male with gonorrhea might complain of:
Question:
A patient presents with generalized lymphadenopathy. He has no other symptoms. Based on the most likely etiology, what test should be performed?
Question:
An example of primary prevention is:
Question:
The greatest risk of transmitting HIV is during:
Question:
A 21 year-old female presents with three 0.5 cm human papilloma virus (HPV) lesions on her vulva. An appropriate treatment option for this patient would be:
Question:
An adolescent male reports that he has dysuria. He admits that he is sexually active. How should this be managed?
Question:
Syphilis may present as:
Question:
Which risk factor has the greatest impact on HIV transmission?
Question:
A 35 year-old patient who is HIV positive is diagnosed with thrush. A microscopic exam of this patient’s saliva demonstrates:
Question:
In a private NP clinic, a patient presents with trichomonas. State law requires reporting of STDs to the public health department. The patient asks the NP not to report it because her husband works in the public health department. How should this be managed by the NP?
Question:
Which of the following statements regarding HIV is correct?
Question:
Which of the following symptoms is usual in a male patient with trichomonas?
Question:
A healthcare provider was exposed to the blood of a patient through a needle stick. When do the majority of patients seroconvert if they are going to do so?
Question:
A female patient has been diagnosed with chlamydia. How should this be managed?
Question:
How should a patient with suspected syphilis be screened?
Question:
A patient with newly diagnosed genital herpes would appropriately receive a prescription for:
Question:
What should be avoided in a patient being treated with metronidazole for trichomonas?
Question:
A patient being treated for trichomoniasis is given a prescription for metronidazole. What instructions should she be given?
Question:
A patient requests testing for HIV after a sexual exposure. What are CDC’s recommendations for screening for this patient?
Question:
A patient was exposed to HIV through sexual intercourse. He should be followed with screening tests to identify seroconversion for:
Question:
Chancroid is considered a co-factor for transmission of:
Question:
How long should a patient be treated with antibiotics if he has prostatitis secondary to an STD?
Question:
A patient with a past history of treatment for hyperthyroidism is most likely to exhibit:
Question:
The most appropriate time to begin screening for renal nephropathy in a patient with Type 1 diabetes is:
Question:
Which medication used to treat diabetes is associated with diarrhea and flatulence?
Question:
A patient who has been treated for hypothyroidism presents for her annual exam. Her TSH is 14.1 (normal = 0.4- 3.8). She complains of weight gain and fatigue. How should the NP proceed?
Question:
A recently diagnosed patient with type 2 diabetes presents today with fever and burning with urination. She is diagnosed with a urinary tract infection (UTI). Her urine dipstick is positive for protein. Which statement is correct?
Question:
A patient who is 73 years old was diagnosed with diabetes several years ago. His A1C has remained elevated on oral agents and a decision to use insulin has been made. What is the goal post prandial glucose for him?
Question:
A 69 year old adult with coronary artery disease is found to have hypothyroidism. Which dose of levothyroxine is considered appropriate for initial treatment?
Question:
Hyperthyroidism may affect the blood pressure:
Question:
A 45 year-old female patient has a screening TSH performed. Her TSH value is 13 mU/L. It was repeated in one week and found to be 15 mU/L. What explains this finding?
Question:
A female patient has the following characteristics. Which one represents a risk factor for development Type 2 diabetes?
Question:
Which choice best describes the most common presentation of a patient with Type 2 diabetes?
Question:
A 65 year-old diabetic has been on oral anti-hyperglycemic agents and is still having poor glycemic control. His AM fasting glucoses range from 140s-160s. You decide to add insulin. He weighs 127 kilograms. What should the NP order as an initial starting dose?
Question:
A 55-year-old female patient with diabetes has these fasting lipid values: Total cholesterol 200 mg/dL HDL 45 mg/dL LDL levels of 120 mg/dL Triglyceride 309 mg/dL According to American Diabetes Association (ADA) which patient lipid value(s) meet(s) the goal for this patient?
Question:
Metformin is a good choice for many older adults with type 2 diabetes. What should be monitored carefully?
Question:
A diabetic patient with proteinuria (approximately 1 g/d) has been placed on an ACE inhibitor. How soon can the anti-proteinuric effect of the ACE inhibitor be realized in this patient?
Question:
A 55-year-old female patient with diabetes has these fasting lipid values: Total cholesterol 200 mg/dL HDL 45 mg/dL LDL levels of 120 mg/dL Triglyceride 309 mg/dL This patient’s Hgb A1c was measured. It is 9.2%. What is the relationship between Hgb A1c and this patient’s lipid values?
Question:
A patient presents with consistently elevated blood glucose before his evening meal. What choice below represents an insulin change that would improve his evening glucose? Current regimen: AM: 22u intermediate-acting insulin, 12u short-acting insulin PM: 10u intermediate-acting insulin, 8u short-acting insulin
Question:
Undiagnosed diabetes may present as:
Question:
What is the most sensitive laboratory assay for screening and identifying the vast majority of ambulatory patients with primary hypothyroidism?
Question:
A female patient has the following characteristics. Which one represents the greatest risk factor for development of Type II diabetes?
Question:
A female patient has the following characteristics. Which one represents a risk factor for Type II diabetes?
Question:
What is the AM fasting glucose goal for a 75 year-old patient who has diabetes?
Question:
A patient has non-fasting glucose values of 110 mg/dL and 116 mg/dL. This patient:
Question:
A diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes mellitus can be made:
Question:
A 78 year-old has been diagnosed with diabetes about 10 years ago. An older adult with a hypoglycemic episode is more likely to exhibit:
Question:
A 37 year-old overweight male is diagnosed today with Type II diabetes. His fasting glucose is 159 mg/dL. He is hyperlipidemic (LDL = 210 mg/dL) and hypertensive (146/102). What medications should be initiated today?
Question:
A patient who is taking long acting insulin basal insulin has elevated blood sugars. Which blood sugars are important to review in order to increase the dose of insulin?
Question:
What is the earliest detectable glycemic abnormality in a patient with Type 2 diabetes?
Question:
The most appropriate time to begin screening for renal nephropathy in a patient with Type 2 diabetes is:
Question:
A 65 year-old patient presents to your clinic with evidence of hyperthyroidism. In assessing her cardiovascular status, what should the NP assess immediately?
Question:
A 52 year-old presents with symptoms of diabetes today. His glucose is 302 mg/dL. How should this be managed today?
Question:
A patient has been prescribed pioglitazone. The nurse practitioner must remember to:
Question:
Mr. Jones, a patient with type 2 diabetes, brings his obese 15 year old son in to see the nurse practitioner. You examine the 15 year-old son and identify acanthosis nigricans. This probably indicates:
Question:
Which drug listed below is NOT associated with weight gain?
Question:
A patient has 2 fasting glucose values of 101 mg/dL and 114 mg/dL that were measured on 2 separate days in the same week. This patient:
Question:
A patient has been diagnosed with Grave’s disease. He is likely to have:
Question:
When the serum free T4 concentration falls:
Question:
A patient with newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes asks what his target blood pressure should be. The most correct response is:
Question:
Ideally, a patient should have a fasting glucose that is:
Question:
A 38 year-old male patient, thought to be in good health, presents to a primary care clinic. On routine exam the patient’s fasting blood sugar is 242 mg/dl. A repeat value after eating is 288 mg/dL. Which of the following is least helpful in the initial evaluation of this patient?
Question:
In order to determine how much T4 replacement a patient needs to re-establish a euthyroid state, the nurse practitioner considers:
Question:
A 30 year-old female patient who complains of fatigue has a screening TSH performed. Her TSH value is 8 mU/L. What should be done next?
Question:
A patient has been diagnosed today with Type II diabetes. A criterion for diagnosis is:
Question:
An 80 year-old patient who is overweight and sedentary has developed elevated, fasting glucose levels (142, 153, and 147 mg/dL). She was diagnosed with diabetes today. Considering her age, how should the nurse practitioner proceed?
Question:
A patient who is diagnosed today with diabetes has microalbuminuria. What can be concluded about this finding?
Question:
The most appropriate screen for diabetic nephropathy is:
Question:
A patient with hypothyroidism has been in a euthyroid state for several years. On screening, her TSH is elevated. The most likely cause of this is:
Question:
A pregnant patient took L-thyroxin prior to becoming pregnant. What should be done about the L-thyroxin now that she is pregnant?
Question:
A 76 year-old patient has fasting glucose values of 151 mg/dL and 138 mg/dL on different days. This patient:
Question:
Mr. Smith, an overweight 48 year-old male with undiagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to your clinic. Which symptom is least likely associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Question:
A nurse practitioner has decided to initiate insulin in a patient who takes oral diabetic medications. How much long acting insulin should be initiated in a patient who weighs 100 kg?
Question:
Which laboratory abnormality very commonly accompanies hypothyroidism?
Question:
A patient has fatigue, weight loss, and a TSH of .05. What is his likely diagnosis?
Question:
A 19 year-old college student with anorexia is being treated as an outpatient. Today she is bradycardic and occasionally has orthostatic hypotension. What might accompany today’s findings?
Question:
The most common co-morbidity associated with depression is:
Question:
A patient has been diagnosed with anxiety. What sleep disturbance might she have?
Question:
What statement describes depression in older adults?
Question:
How should the nurse practitioner approach a patient who consumes excessive amounts of alcohol but denies that he has a problem?
Question:
What is the usual age of onset of symptoms for patients with bipolar disorder?
Question:
A 6 year-old is brought to your clinic because of behavior problems at school. DSM V criteria are used to diagnose attention deficit disorder (ADD). Which finding must be present for this diagnosis?
Question:
The nurse practitioner (NP) is treating a 22 year-old for depression with high dose fluoxetine. After several months of dosage changes, she is finally doing well and comes today for a follow up visit. She is happy and states that she might be pregnant. A urine test indicates pregnancy. The NP has referred the patient to an obstetrician who will see the patient in 4 weeks. How should the fluoxetine be handled today?
Question:
The major advantage of the CAGE questionnaire is:
Question:
A 45 year-old patient started taking paroxetine one week ago for depression. She calls to report intermittent headache and nausea. What is a likely etiology?
Question:
Which symptom listed below is typical of depression?
Question:
An adolescent female patient with anorexia nervosa must exhibit 4 criteria for diagnosis. Which criterion listed below is NOT part of the diagnostic criteria?
Question:
Serotonin is thought to play a role in the etiology of:
Exam Questions
A pregnant teenager asks if sexual activity is safe during pregnancy. The nurse practitioner responds: this can expose you to STDs. this can expose you to STDs. Correct
A 24 year-old patient presents to your clinic. She states that she has vomited for the last 5 mornings and until early afternoon. She feels better in the evenings. She denies fever. What lab tests should be monitored? Electrolytes and serum pregnancy Electrolytes and serum pregnancy Correct
Which factor below confers the lowest risk of ectopic pregnancy? Age less than 18 years Age less than 18 years Correct
The classic presentation of placenta previa is: painless vaginal bleeding after the 20th week. painless vaginal bleeding after the 20th week. Correct
In a viable pregnancy: fetal heart tones are audible at about 9-12 weeks. fetal heart tones are audible at about 9-12 weeks. Correct
In order to establish pregnancy, a pregnancy test of the urine or blood is routinely performed. How early can this be done with reliable results? 1-2 weeks after conception 1-2 weeks after conception Correct
A pregnant patient in her first trimester is found to have chlamydia. How should this be managed? Treat with azithromycin Treat with azithromycin Correct
A 17 year-old female is found to be pregnant. What is the LEAST likely risk to her fetus? Down Syndrome Down Syndrome Correct
A pregnant patient asks why she must take calcium during pregnancy. The nurse practitioner replies that: it will strengthen the bones and teeth in your fetus. it will strengthen the bones and teeth in your fetus. Correct
A pregnant patient complains of lower extremity edema and asks for a “fluid pill”. The NP explains that: this is best treated with rest and elevation of the legs. this could signify gestational hypertension. Incorrect
A patient in her first trimester of pregnancy is found to have gonorrhea. Which statement below is true? She should be treated now for gonorrhea and chlamydia. She should be treated now for gonorrhea and re-screened if symptoms re-appear. Incorrect
A 30 year-old female presents with lower abdominal pain. The nurse practitioner immediately considers an ectopic pregnancy as the cause. Which factor listed below does NOT increase her risk of an ectopic pregnancy? Age Age Correct
A 30 year-old with Type I diabetes has become pregnant. The routine diabetic screening: can be eliminated. should occur earlier. Incorrect
A 24 year-old pregnant patient has a TSH performed. The most likely reason for this is because: she has hypothyroidism. it is routinely done in pregnant women. Incorrect
The need for thyroid replacement during pregnancy: increases. increases. Correct
A patient who is found to be pregnant has asymptomatic bacteriuria. What is the likely pathogen? E. coli E. coli Correct
A mother has a negative rubella titer. She is not pregnant but is breastfeeding her 4 month-old infant. Is she able to safely receive the MMR immunization today? Yes, the immunization offers no risk to her infant. Yes, the immunization offers no risk to her infant. Correct
The classic symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are: amenorrhea, vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain. abdominal pain, nausea, vaginal bleeding. Incorrect
Ultrasounds are commonly performed during the first trimester of pregnancy because they help estimate gestational age and: identify fetal malformations. identify maternal risks. Incorrect
Immunizations are not routinely given during the first trimester of pregnancy. Which immunization(s) may be safely given during the first trimester of pregnancy? Influenza Varicella and MMR Incorrect
A pregnant patient with urinary frequency is found to have a UTI. What drug is safest to treat this? Nitrofurantoin Nitrofurantoin Correct
When should folic acid be initiated in a female patient contemplating pregnancy? Now Now Correct
A patient has a positive pregnancy test that she performed using an over the counter kit. What are the chances that a serum pregnancy test will be negative? Almost none Almost none Correct
Which factor listed below increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy? Prior history of ectopic pregnancy Prior history of ectopic pregnancy Correct
Which activity does NOT place the pregnant patient at risk of contracting toxoplasmosis? Eating sushi Poor hand washing after gardening Incorrect
In order to establish pregnancy, a pregnancy test of the urine or blood is routinely performed. This test assesses for: presence of beta hCG. quantity of beta hCG. Incorrect
A 17 year-old female is found to be pregnant. What is the most important part of her initial screening? STDs and HIV STDs and HIV Correct
A patient was diagnosed today with pregnancy. Her last pregnancy was 3 years ago. At that time she had a protective rubella titer. What should be done about evaluating a rubella titer today? She does not need one because it was protective 3 years ago. It should be evaluated to make sure it is still protective. Incorrect
The rubella vaccine is contraindicated in pregnant women because: it can cause rubella in the infant. it can cause rubella in the infant. Correct
What immunizations may be safely administered during the first trimester of pregnancy? Tdap and inactive influenza Tdap and inactive influenza Correct
You have been asked to manage thyroid disease in a pregnant patient. A pregnant patient took L-thyroxin prior to becoming pregnant. What should be done about the L-thyroxin now that she is pregnant? She should continue it and have monthly TSH levels. She should continue it and have monthly TSH levels. Correct
A patient has a positive pregnancy test that she performed from an over the counter kit. It has been 6 weeks since her last menstrual period. What are the chances that she is pregnant? > 90% > 90% Correct
An ultrasound is commonly performed during early pregnancy because it: identifies fetal malformations. identifies fetal malformations. Correct
A female who is being counseled preconceptually is found to have a negative rubella titer. If she is immunized today, for how long should she avoid pregnancy? 1 month 3 months Incorrect
The most effective way to decrease the incidence of neural tube defects in pregnant patients is to: increase folic acid. increase folic acid. Correct
Hyperemesis gravidarum is: persistent, intractable vomiting during pregnancy. persistent, intractable vomiting during pregnancy. Correct
The NP suspects that a pregnant patient may have been physically abused by a domestic partner. The NP knows that: abuse can worsen during pregnancy. this is reportable in all 50 states. Incorrect
A pregnant patient is 30 weeks gestation. She wants to travel to a higher elevation in order to go on a hiking trip. She will fly in an airplane. The nurse practitioner knows: travel to a city of high altitude can precipitate pre-term labor. there is no risk associated with this particular trip. Incorrect
Routine screening for gestational diabetes: at about 24-28 weeks. at about 24-28 weeks. Correct
A patient who is found to be pregnant has asymptomatic bacteriuria. How should this be managed? Prescribe nitrofurantoin Prescribe nitrofurantoin Correct
A pregnant patient asks if engaging in sexual activity will place her fetus at increased risk. The nurse practitioner responds: this may increase the risk of pre-term labor. this may increase the risk of pre-term labor. Correct
A pregnant patient is in her first trimester in October. How should a flu immunization be handled for her? Give the influenza immunization without regard to trimester. Give the influenza immunization without regard to trimester. Correct
Few pregnant patients actually deliver on their due dates. Why is a due date established? To determine timing of maternal/fetal screenings For evaluation of maternal uterine size Incorrect
A patient in her first trimester of pregnancy is found to be infected with chlamydia and gonorrhea. Which statement below is true? She should be treated now and re-screened later in pregnancy. She should be treated now and re-screened later in pregnancy. Correct
When do the clinical manifestations of an ectopic (fallopian tube) pregnancy typically appear? 6-8 weeks after the LMP 6-8 weeks after the LMP Correct
A pregnant patient in her second trimester will probably have a decrease in her: blood pressure. blood pressure. Correct
A pregnant patient is likely to have: a venous hum murmur and an S3. a venous hum murmur and an S3. Correct
HIV testing during pregnancy: is recommended by many learned authorities. is recommended by many learned authorities. Correct
A pregnant patient is found to have positive leukocytes and positive nitrites in her urine. What medication should be given? Nitrofurantoin Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMPS) Incorrect
Routine screening for gestational diabetes should take place: 24-28 weeks. 24-28 weeks. Correct
Question:
An x-ray report of a patient’s painful right knee indicates “joint space narrowing”. What does this mean?
Question:
A positive Tinel’s test can be used to assess carpal tunnel syndrome. What other test can be used to assess for this?
Question:
A positive Tinel’s test can be used to assess carpal tunnel syndrome. What other test can be used to assess for this?
Question:
A patient presents with right shoulder pain (7/10 on the pain scale) after an acute shoulder injury yesterday. He fell against a brick wall while working at his home. He reports pain that radiates into his upper arm. How should this be managed?
Question:
A positive Trendelenburg’s test could be used to identify a child with:
Question:
Which diagnosis is the least likely cause of extrinsic shoulder pain?
What should the nurse practitioner assess in a patient who reports a fall but does not have serious physical injury?
Question:
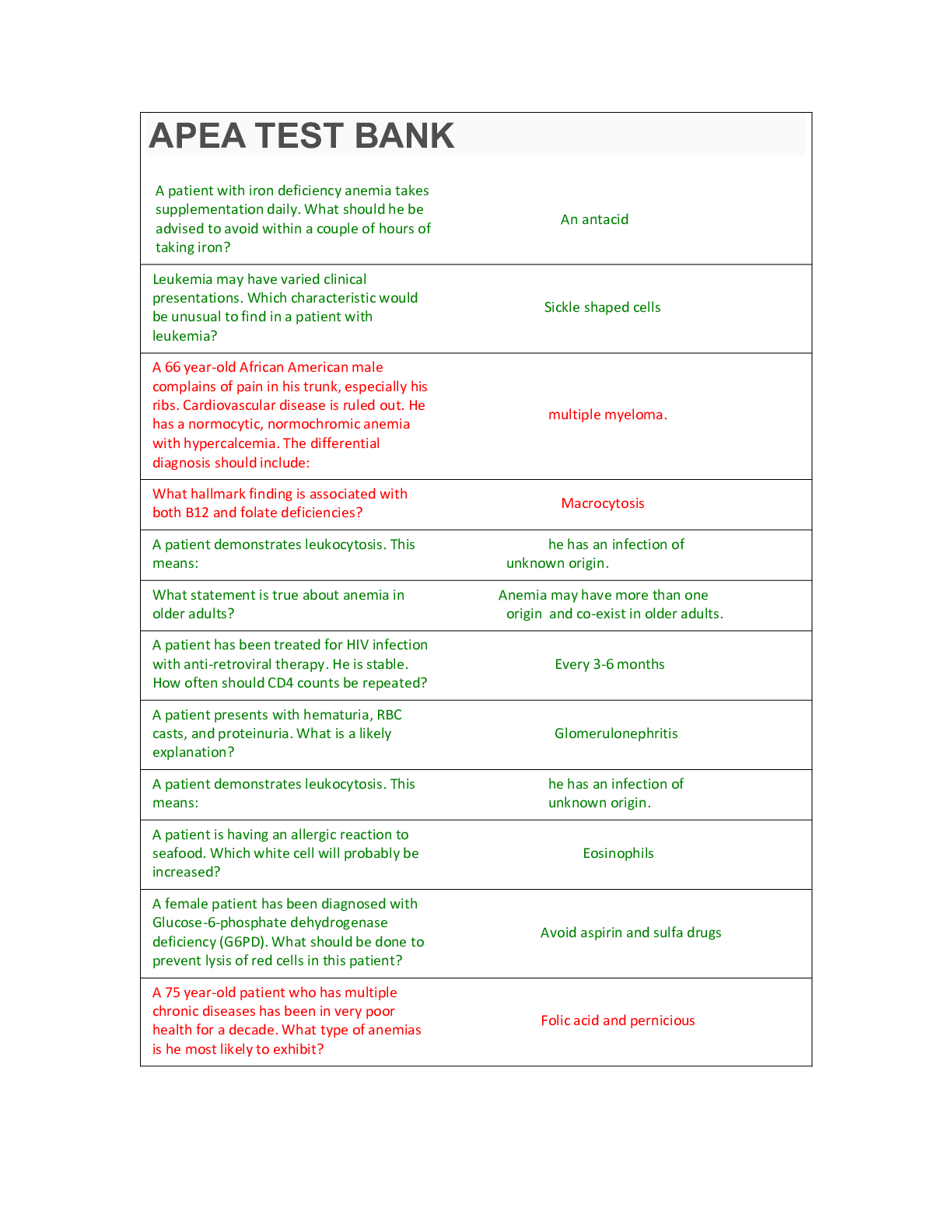
A 70 year-old African American male complains of pain in his back and trunk. Cardiovascular disease is ruled out. He has a normocytic normochromic anemia with hypercalcemia. A likely diagnosis is:
Question:
What does a positive anterior drawer test demonstrate with an injured knee?
Question:
Which symptom can be used to rule out a fracture?
Question:
A 40 year-old complains of back pain after heavy lifting. This began 2 weeks ago. He has had little improvement in his pain. Which statement is true regarding plain x-rays in this patient?
Question:
Which beverage below does not increase the risk of gout in a male who is prone to this condition?
Question:
A 60 year-old female presents with history of low back pain of recent origin. Her gait is antalgic and she reports loss of bladder function since the onset of back pain this morning. What should be done?
Question:
A 50 year-old patient reports acute pain in his lower back that started 2 weeks ago after working in his yard. The pain radiates into his right leg intermittently. He has been managing his pain with over the counter NSAIDs. There are no red flags in his history or exam. When should consideration be given to imaging studies?
Question:
A 14 year-old male client reports dull anterior knee pain, exacerbated by kneeling. What is the likely etiology?
Question:
A 55 year-old male patient describes severe pain at the base of his left first toe. He is limping and says he can’t remember hurting his toe. Which symptom below suggests something other than gout?
Question:
Which of the following is true regarding metatarsus adductus?
Question:
An elderly patient had a total knee replacement (TKR) 10 months ago. He is doing well. What information should he be given regarding the knee replacement?
A male patient takes HCTZ daily for hypertension. He developed severe pain in his great toe yesterday. He was diagnosed with gout today and started on a medication. Which medication listed below would be contraindicated at this time?
Question:
A characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis not typical in osteoarthritis is:
Question:
An adolescent complains of knee pain. He is diagnosed with Osgood-Schlatter disease. What assessment finding is typical?
Question:
An adolescent complains of knee pain. He is diagnosed with Osgood-Schlatter disease. What assessment finding is typical?
Question:
Ankle inversion is a common complaint from a patient with a:
Question:
What medication is recommended by American College of Rheumatology as a first line agent for a patient who has been unsuccessful with non-pharmacologic interventions for osteoarthritis pain?
Question:
Which of the following is NOT true regarding cervical whiplash injury?
Question:
A 65 year-old female complains of left medial knee pain. She has been told that she has arthritis in this knee. Where would the pain be located?
Question:
A 75 year-old has pain from osteoarthritis in her right knee. What intervention is considered first line to treat her pain?
Question:
The Ottawa ankle rules help the examiner determine when:
Question:
A 60 year-old adult with an antalgic gait and complaints of hip pain is examined. He has trochanteric tenderness. What is the most common cause of this?
A patient reports that her knee “locks” sometimes and feels like it will “give out”. She denies injury. She has no complaint about her other knee. What is her likely problem?
Question:
A 16 year-old complains that his knees hurt. His mother states that he has complained of knee pain for the past 2 weeks. He has a prominent tibial tubercle. What should be part of the differential diagnosis?
Question:
The drop arm test is used to assess patients with suspected:
Question:
An 80 year-old patient is very active but presents today with posterior hip pain for the past week. Which of the following is least likely part of the differential diagnosis?
Question:
A patient complains of “first step in the morning” pain in his heel. He states that it has progressed to “end of the day” heel pain. What probably has contributed to this most?
Question:
The “get up and go” test in an elderly patient is used to evaluate:
Question:
A patient has cut himself on a fence post while working outside. He has not had a tetanus shot in more than 10 years. How long can he wait before getting the immunization and still prevent tetanus?
Question:
A 60 year-old has been on NSAIDs for the past week for shoulder pain. He has complaints of blood on toilet tissue when wiping after a bowel movement. What should be suspected?
uestion:
A young athlete is found to have a depression of the longitudinal arch of both feet. He complains of heel pain bilaterally. The rest of his foot is normal and he has continued with his activities. What could be recommended for his heel pain?
Question:
A man fell off a 3-foot stepladder while working at home. He presents to your office with complaints of foot pain. He has point tenderness over the lateral malleolus, swelling, but he is able to ambulate. How should this be managed?
Question:
When should functional rehabilitation occur once a patient has had an ankle or knee sprain?
Question:
Management of a sprained ankle includes:
Question:
A 49 year-old patient has osteoarthritis in the lumbar spine and hip. His hip x-ray demonstrates bone on bone. What can be done to resolve his complaints of pain in his hip?
Question:
A 49 year-old patient has osteoarthritis in the lumbar spine and hip. His hip x-ray demonstrates bone on bone. What can be done to resolve his complaints of pain in his hip?
Question:
Which symptoms are most commonly found in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis?
Question:
A patient is at increased risk of osteopenia if she uses which form of birth control?
Question:
A 66 year-old African American female has multiple risk factors for osteoporosis. Which choice listed below is NOT a risk factor for osteoporosis?
Question:
An 8 year-old has a painful limp. He reports that his knee hurts medially. On exam he has pain with internal rotation of the hip. How should the NP manage this situation?
He should be immediately referred to orthopedics.The NP should order a hip x-ray, CBC and
Question:
What joints are least commonly involved in osteoarthritis?
Question:
A college age basketball player landed awkwardly on his foot and ankle after jumping during a game yesterday. He states that he sprained his ankle. He complains of ankle pain and foot pain but is able to limp into the exam room. How should he be managed?
Question:
A high purine diet can contribute to gouty arthritis. Which food listed below contributes most to a high purine diet?
Question:
A 75 year-old patient has osteoarthritis and pain. Which of the following medications increases the risk of a GI related ulceration?
Question:
A male patient who injured his back lifting a heavy object reports that he has low back pain. He is diagnosed with a lumbar strain. He is afraid to continue activities of daily living and especially walking because he has pain with these activities. What statement below is true?
Question:
A 65 year-old male is diagnosed with an initial episode of gout. It is likely that he:
A patient who frequently has episodes of gout should avoid which groups of food?
Question
A long distance runner is diagnosed with a tibial stress fracture. Which statement is true about the injury?
Question:
Bone mineral density screening in women over age 65 years is an example of:
Question:
A 12 year-old male with hip pain presents to the NP clinic. Hip pain has occurred with activity for the past 4-6 weeks but his pain is worse and now involves the knee. There is no history of trauma. How should the work-up be initiated?
________________________________________
Question:
Which patient below should be screened for osteoporosis?
Question:
Which factor listed below is NOT considered a risk factor for development of osteoporosis?
Question:
A 70 year old patient has had intermittent back pain for more than 3 years. In the last year, it is constant (pain scale is 2-3/10) and at times is sharp. She is not a surgical candidate. What class of medication would be a good choice for improvement of chronic pain in this patient?
Question:
The age at which a child can first walk backwards is:
Question:
A 16 year-old male plays trumpet in the school marching band. He has had marching practice every day for the last week. Today he complains of pain in his left midfoot. The foot is neither swollen nor red. What is the most likely diagnosis in the differential?
Question:
What is the most prevalent skeletal problem in the United States?
Question:
A patient with sciatica is most likely to describe relief of symptoms with:
Question:
An adolescent athlete has injured his ankle playing basketball. He has right ankle pain, ecchymosis, significant edema, and he is unable to bear weight at the time of the clinical exam. Which diagnosis is least likely?
Question:
A 79 year-old frail adult reports that she had a fall last week. She had no broken bones but is very sore. In evaluating this adult, what question is most important to ask?
Question:
Women are commonly screened for osteoporosis at age 65 years. How should screening for osteoporosis be managed in a male this age?
Question:
Which statement below is true regarding NSAIDs for low back pain?
Question:
Which of the following tests, if positive, is part of the criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Question:
A 75 year-old female, who knits daily, has a positive Finkelstein test. What is her likely diagnosis?
Question:
What is the value of Vitamin D supplementation in the diet of older adults?
Question:
A 60 year-old patient who is otherwise healthy, presents with acute onset of right knee pain. She denies injury but reports that she walked up a lot of steps yesterday. She is diagnosed with prepatellar bursitis. What is a common finding?
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 50 pages
.png)



 Questions with Answers Provided Graded A.png)