*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Maternal Newborn ATI Comprehensive Test Bank, Questions, correct answers (Verified & explained) (All)
Maternal Newborn ATI Comprehensive Test Bank, Questions, correct answers (Verified & explained)
Document Content and Description Below
Maternal Newborn ATI Comprehensive Test Bank Chapter 2: Contemporary Issues in Women’s, Families, and Children’s Health Care Nursing School Test Banks MULTIPLE CHOICE The clinic nurse is... working with a mother and her 3-year-old child who have arrived for the childs routine checkup. The nurse encourages the mother to return for her childs measles-mumps-rubella immunization prior to the childs entering school. This intervention is an example of what type of care? A. Mandatory health care B. Primary health prevention C. Secondary health prevention D. Tertiary health prevention A nurse wishing to be an advocate for access to health care would most likely choose to participate in which of the following activities? A. Lobby for improved insurance access for all individuals, whether or not they are employed. B. Help establish fast-track or minor illness areas in local emergency rooms. C. Partner with medical centers to provide free services for low-income patients. D. Work with visiting nurses associations to create on-site clinics at day-care centers. A nurse working with an after-school program is concerned about the lack of health literacy in the students parents. What action would best address this need? A. Conduct a monthly health-related seminar for parents. B. Investigate grants or other funding for a computer bank. C. Invite parents to healthy cooking demonstrations. D. Provide brochures on a variety of health problems. 4. A nurse is caring for a patient near the end of life whose wishes regarding care are not known. The two sons disagreed with the two daughters about future medical plans for the patient during a recent family conference, and now the sons and daughters are not talking to one another. What action by the nurse would be best to help resolve this dilemma? A. Call the facilitys ethics committee and request a formal consultation. B. Have social work coordinate another family meeting to discuss the issue. C. Meet with the sons and daughters separately to discuss their wishes. D. Request that the physician tell the family what is in the patients best interests. 5. A mother and her 12-year-old daughter visit the clinic often because of the daughters asthma. The clinic nurse recognizes that one of the most important nursing actions in this situation is which of the following? A. Continue to schedule regular clinic visits for the child to follow her condition. B. Give the mother time to talk about her daughters illness while she is present. C. Listen patiently to the child as she talks about her illness, letting her tell her story. D. Regulate and modify the childs medications in response to her asthma symptoms. 6. The nurse managing a pediatric clinic often sees single mothers with children. What action by the nurse would best help this population of women access health care? A. Arrange to have evening and weekend hours. B. Offer sample medications instead of prescriptions. C. Provide a play center for waiting children. D. Provide bus tokens for transportation to the clinic. 7. A community health nurse explains to the nursing student that the best health-related programming includes which of the following elements? A. Has both individual and societal components B. Is directed toward individual responsibility C. Provides incentives to compensate healthy choices D. Requires legislation to truly be effective 8. A nursing student wishes to investigate national health goals. Where should the student research this information? A. Cochrane Database B. Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature C. Government websites D. Healthy People initiative 9. A nurse is interested in primary prevention programs. Which of the following activities would this nurse choose to do? A. Assist with blood pressure screening at the local mall. B. Collect and distribute used eyeglasses for poor people. C. Staff a mobile mammogram unit for underserved groups. D. Teach teenagers about the dangers of texting and driving. 10. A nurse wants to work in the community providing secondary prevention activities. Which action would this nurse choose to do? A. Educate teenage girls about birth control options. B. Provide STD/STI testing at the local youth center. C. Staff the county health department flu shot clinic. D. Volunteer to drive cancer patients to receive their treatments. 11. A nurse is interested in providing tertiary prevention activities. Which of the following activities would this nurse choose to do? A. Assist with low-cost swimming lessons at the YMCA. B. Conduct monthly educational seminars at a church. C. Join the county pandemic outbreak response team. D. Provide glucose and cholesterol screening at the mall. 12. A practicing nurse tells a student nurse that beyond the World Health Organizations definition of health, providers must also consider which of the following factors when determining the health of a community? A. The definition of health as described by the community B. The incidence of preventable health problems in the group C. The morbidity caused by genetically related health problems D. The mortality rates that could be lowered with primary prevention 13. A nurse wants to know the trend concerning death due to cardiovascular disease. What source should the nurse consult? A. Epidemiology data B. Morbidity data C. Mortality data D. Primary prevention data 14. A nurse enjoys working with patients who have chronic illnesses. What group of people would this nurse enjoy working with most? A. Ethnic minorities B. Men and boys C. Older adults D. Women and girls 15. A nurse would like to improve the health of the community. Which action by the nurse would have the greatest impact? A. Blood glucose screening at the local Korean church B. Blood pressure screening at a predominantly black church C. Teaching immigrants heart-healthy cooking for traditional foods D. Teaching men the signs and symptoms of heart attacks 16. A nurse is working with a parent teacher association to combat school bullying. What action can the nurse suggest that would best help to decrease this form of interpersonal violence? A. Advise that victims parents call law enforcement and press charges. B. Begin offering martial arts classes in the school for bullied children. C. Encourage the school to adopt no-tolerance policies for bullying. D. Suggest limiting television viewing, especially for younger children. 17. A school nurse is increasingly concerned with a growing absentee problem. To best address this issue, which of the following actions should the nurse take? A. Begin a structured follow-up program for asthmatic children. B. Hold informational meetings on the importance of childhood vaccines. C. Partner with providers on continuity plans for kids with chronic illness. D. Work with law enforcement to develop a truancy response team. 18. A nurse is working with a patient who misses appointments frequently and doesn’t always fill prescriptions for herself or her children. On reviewing the patients chart, the nurse sees that the patient has insurance. What action by the nurse would be the most helpful? A. Ask the patient to describe her health insurance coverage. B. Educate the patient about the consequences of skipping medicines. C. Find out if the patient is seeing other health-care providers. D. Remind the patient that she is responsible for her children’s health. 19. A nurse reads in the paper that the death rate for women overall has declined substantially. To what does the nurse correlate this finding? A. Abundant new choices in contraception B. Better detection and treatment of breast cancer C. Greater access to sources of fresh produce D. Improved diagnosis of heart disease in women 20. A nurse working with the elderly population is distressed that in order to obtain public funding for long-term care, the elderly must expend nearly all of their resources. When considering bioethical principles, which principle should the nurse choose to act from to make the biggest difference in this situation? A. Autonomy B. Fidelity C. Justice D. Veracity 21. A nurse considers beneficence as the guiding ethical principle for nursing practice. Working within that framework, which action by the nurse best demonstrates that concept? A. Administering a pain medication before therapy so that the patient can participate B. Allowing the patient to make informed choices as to his or her plan of care C. Promising a pain medication in 1 hour and returning with it on time D. Turning patients to prevent pressure sores, despite causing temporary discomfort 22. A nurse ensures that a patient does not have questions regarding the upcoming surgical procedure and verifies that the signature on the consent form is the patients signature. Which ethical principle is this nurse demonstrating? A. Autonomy B. Beneficence C. Fidelity D. Justice 23. A 45-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of chest pain and feeling anxious. She asks to have an electrocardiogram (EKG) but is told that heart disease is a mans disease and is given a prescription for lorazepam (Ativan). What can the nurse conclude? A. If the woman were older, she may have received an EKG. B. Sex hormones play a powerful role in determining heart disease. C. Stereotyping seriously impacted the care the woman received. D. Women under the age of 45 are at low risk of having heart disease. 24. A nurse has heard of the digital divide between people who have access to technology and those who dont. The nurse asks a mentor how this can affect health care. What response by the mentor is most accurate? A. Its just easier and faster to make appointments online. B. Much health-care information is available only digitally. C. The so-called digital divide really doesnt have much impact. D. You can chat with your doctor on social media sites. 25. One goal of the Healthy People 2020 initiative is to increase the number of people who have some form of health insurance. What percentage of the population is the target? A. 25% B. 35% C. 55% D. 100% 26. A nurse is working with a woman who is 4 months pregnant. The woman has had a series of temporary housing, has no job, and is wearing clothing that is obviously way too big for her. What action can the nurse take to most improve the health of this woman and child? A. Arrange transportation for her to get to a community food bank. B. Consult a social worker to help her apply for the WIC program. C. Encourage the woman to make her return appointment before leaving. D. Ask the woman to fill out an application for the federal Medicare program. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse working in a women’s health clinic has several patients who are from a minority culture, live in the inner city, lack employment that offers benefits, have large families, and often lack transportation to health care. Which of these factors are considered broad determinants of health? (Select all that apply.) A. Access to health care B. Employment C. Environment D. Family size E. Race 2. The community health nurse knows that the public health intervention model is focused on which of the following intervention levels? (Select all that apply.) A. Community B. Family C. Government D. Hospitals E. Patient 3. A nurse working in the community uses the public health intervention model to combat diabetes mellitus type 2. Using this model, which interventions are appropriate? (Select all that apply.) A. Community: Encourage high-risk patients to have glucose screening. B. Community: Lobby for funds to build walking and biking trails. C. Community: Subsidize community gardens in areas where produce is expensive. D. Individual/family: Educate about the benefits of daily exercise. E. Societal: Pressure Congress for laws requiring insurance incentives for health promotion. 4. The community health nurse is aware that the goals of Healthy People 2020 include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Creating physical environments that promote health B. Developing healthy behaviors in children and teens C. Eliminating health disparities and increasing equity D. Improving the health of all groups in the country E. Increasing the average life span for all adults 5. What does the nursing student understand about health disparities in the United States? (Select all that apply.) A. African American babies die by age 1 at a rate times that of European Americans. B. Asian American babies have the highest rate of preterm birth of any other group. C. Despite large expenditures, health resources are unevenly distributed. D. European Americans have double the number of low-birth-weight babies than other groups. E. Sudden infant death syndrome is most prevalent in American Indian and Alaska native babies. 6. The public health nurse explains to students that diversity is an increasing phenomenon in this country. What facts about this phenomenon does the nurse share with the students? (Select all that apply.) A. As immigrants acculturate, their unique cultural care needs will diminish. B. By 2050, the minority population in America is estimated to be 50%. C. Hispanics, blacks, and Asians are the historically designated minority groups. D. One in five people in this country will be over the age of 65 by the year 2030. E. Racial differences are rooted in biological factors that explain illness trends. 7. Which of the following activities should the perinatal nurse encourage women who come for preconceptional counseling to consider? (Select all that apply.) A. Choosing breastfeeding or bottle feeding B. Decreasing risk for exposure to toxoplasmosis C. Decreasing fetal risks related to the work environment D. Ensuring folic acid supplementation E. Ensuring iron supplementation 8. A mother brings her 6-month-old infant and 18-month-old child to the health clinic for a routine visit. The nurse counsels the mother about lead exposure testing. Which information should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. About one-fourth of all homes where kids under 6 live are contaminated by lead. B. Both of your children should have testing for lead at this time. C. Lead exposure may cause anemia, seizures, and mental retardation if not treated. D. Lead testing for children is recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics. E. We can test your older child for lead exposure, but it is too early for the 6-month-old. . 9. The clinic nurse is interviewing a woman and her daughter who describe their address astemporary. The mother appears thin, pale, and tired. Her blood work confirms anemia and pregnancy. What actions by the nurse would be most helpful? (Select all that apply.) A. Call the Department of Children and Family Services. B. Discuss nutrition needs for pregnancy. C. Facilitate the womans opportunity to return for prenatal care. D. Determine if the family is in a safe location. E. Provide shelter information for this family. 10. The clinic nurse explains to a student that an appropriate nursing action is screening all children for child abuse. What other information does the nurse give the student about child abuse? (Select all that apply.) A. It is frequently carried out by a stranger. B. The most common form is neglect. C. It is most often perpetrated by a parent. D. Only 1 out of 1,000 girls is sexually abused. E. It is part of an ongoing cycle of violence. 11. The jail nurse is interviewing a woman who has been brought to the clinic for prenatal care. Which of the following are appropriate actions for the nurse to perform? (Select all that apply.) A. Assess the woman for drug and alcohol abuse and possible withdrawal. B. Assess the womans health knowledge and health literacy. C. Ask if the woman has other children and who is caring for them. D. Determine if the woman has risk factors for pregnancy complications. E. Inquire about the womans criminal history and background. 12. Which childhood illnesses are the subject of a Healthy People initiative regarding vaccinations? (Select all that apply.) A. Asthma B. Measles C. Meningitis D. Mumps E. Pertussis 13. A nurse is working with a patient determined to have low health literacy and has taught the patient vital self-care measures for a chronic illness. How will the nurse best determine if the patient has understood the information? (Select all that apply.) A. Ask for a return demonstration of the skills taught. B. Assess if the patient will take brochures written for this illness. C. Encourage the patient to explain how the information fits into his or her daily life. D. Give the patient a written quiz at the end of the teaching session. E. Have the patient repeat the information in her or his own words. 14. A nurse has helped organize and staff a free vaccination clinic for underserved populations in a central location of the city. The nurse is unhappy that so few people came to the clinic. In evaluating this outcome, what factors does the nurse recognize as potentially leading to the problem? (Select all that apply.) A. Clinic hours B. Inability to miss work C. Lack of insurance D. Lack of transportation E. Language barriers Chapter 3: The Evolving Family(FREE) Nursing School Test Banks Chapter 3: The Evolving Family MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The clinic nurse is taking a history from a woman who came to the clinic to get test results. The patient brought a coworker with her because she is worried. The patient asks to have her coworker remain in the exam room when the doctor describes the test findings. The patient states that the friend is like a sister. The nurse would most correctly identify the two women as which of the following? A. Extended family B. Family C. Family of choice D. Family of origin2. The clinic nurse understands that children who come for well-child visits at age 10 are in the process of developing which of the following attributes? A. Attachment B. Coordination C. Personal values D. Self-identity 3. A new mother with a 2-month-old daughter tells the family clinic nurse that she is experiencing a lack of sleep because of infant night feedings and her husbands shift work and excessive overtime. Which of the following is the best description of this family concern? A. Caregiver strain B. Coping stress C. Lack of support D. Parental maladaptation 4. A patient describes her spouses dependence on oxycodone terephthalate (Percocet), which began following knee surgery last year. Although the prescription was finished some time ago, the spouse continues to obtain and take Percocet. Because of the spouses need for the medication, the patient has to do all the yard work, child care, and meal preparation. How would the nurse describe the patients behavior? A. Enabler B. Impaired caregiver C. Inadequate dyad partner D. Overstressed parent 5. A mother brings her 8-year-old daughter to the clinic for the third time in 2 months. The mother states that her daughter is very active and often falls down. The mother states that her daughter eats well, but the childs weight falls below the 10th percentile. The clinic record shows the child had multiple bruises on her arms at the time of the last two visits. Today the nurse notes that the child has areas of ecchymosis on her left leg and ankle. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the child and her mother again about the childs bruises. B. Question the child about her accident-prone behaviors. C. Speak with the child alone, asking if she feels safe at home. D. Teach the mother to keep a diary of what her child is eating. 6. The clinic nurse notices that each time a child with leukemia is brought in to see the doctor, her mother and aunt accompany her. The mother states that she finds her daughters illness to be very traumatic and is having difficulty coping. The childs aunt encourages the childs mother and distracts the child while her blood work is being drawn. The childs aunt could be described as taking on which of the following roles? A. Child-caregiver role B. Kinship role C. Socializer role D. Therapist role 7. The nurse observes a woman and her sister who live together. They are trying to support one another and provide extended care to their mother who has recently been diagnosed with Alzheimers disease. The two sisters describe their experience with a homemaker who visits their home to help bathe their mother. They say she is humorous and cheerful and absorbs their mothers attention for the whole time she is present. This is a positive description of which component of Bowens family systems theory? A. Communication B. Family relationship building C. Family rituals D. Triangulation 8. A nurse is assessing a single person at a clinic visit. How would the nurse classify this patients family? A. Family of choice B. Family of origin C. Not in a family D. Nuclear family 9. A patient tells the nurse about living in a commune. What does the nurse understand about this family structure? A. Family with distant relatives included B. Group of men, women, and children C. Kinship care provided to children D. Unmarried man and woman living together 10. A nurse is assessing a child with very poor social skills. What conclusion can the nurse make about the childs family? A. Emotional or mental illness B. Not filling socialization needs C. Poorly educated, poor job skills D. Probably lower-income status 11. A nurse is working with family members who have been striving to improve their functioning as a family unit. What behavior would suggest to the nurse that the family is meeting its goals? A. The children are in multiple activities to develop talents. B. The desire to be understood guides most communication. C. Family members gave up some activities in order to eat dinner together on most nights. D. The parents have a strong desire for the children to succeed. 12. A nurse works a great deal with refugees and is frustrated because, as a group, they dont seem to want to implement desired health behaviors. What action by the nurse would be most helpful? A. Conduct a health screening and educational event each month. B. Provide written information in the groups native language. C. Teach selected group representatives to be lay health educators. D. Try to establish relationships within the refugee community. 13. A patient is dismissed from the hospital and is receiving nursing care at home to help in the recovery from a serious illness and operation. The visiting nurse notes that the family is in a state of disarray and members are disorganized and not communicating. The patient is trying to direct everyones actions. The nurse calls a family meeting. What action by the nurse is best? A. Encourage family members to make to do lists and assign chores. B. Explain that changes in one person require changes in the others. C. Make a referral to a counselor or mental health nurse practitioner. D. Tell the family members that for the patient to recover, they have to assume his or her role. 14. A nurse who works with families uses Duvalls family developmental theory as the core of nursing practice. What action by this nurse takes priority? A. Assessing the developmental stage of the family B. Determining how the family interacts with society C. Observing what roles each family member assumes D. Tailoring teaching to the specific needs of the family 15. A nurse is working with a blended family of 1 year with five children aged 3, 7, 13 (twins), and 19. The parents seem overly stressed and anxious and do not seem to work well as a unit. What can the nurse conclude about this family? A. Communication problems are the core of the parents stress. B. Economic stressors are impacting the parental dyad. C. The family is in too many developmental stages to master any of them. D. There are too many children to give each one adequate attention. 16. A family practice nurse is working with a patient who is asking for anti-anxiety medications to deal with the stress and frustration of an adult child who wont leave the home. Based on knowledge of the tasks of launching children, which resource should the nurse suggest first? A. Anger management counseling B. Contact numbers for vocational training C. Information on a parenting workshop D. Marriage and couples counseling 17. A patient has been dismissed from the hospital after a serious illness and needs several weeks of home care and rehabilitation. When the visiting nurse comes to the house, it is apparent that the family is not functioning. The house is dirty, there is little food available, and one parent and an older child are arguing about picking up a younger sibling from school. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Ask the parents if they need financial resources for the basic necessities. B. Assess each family member for the roles he or she plays in the family. C. Contact child protective services or social work to assess the home environment. D. Provide referrals for family and couples counseling in the community. 18. A nurse who uses the structural-functional theory would assess which of the following when working with families? A. Communication patterns B. How things get done C. If goals are being met D. Looseness of boundaries 19. A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to a mother of a toddler. Using communication theory, which information is the most appropriate? A. Dont nod your head yes when you say no. B. Explain things in several different ways. C. There is no need to see if a toddler understands. D. You shouldnt yell at such a young child. 20. A nurse is working with a woman who is newly married and pregnant and says she is distressed because she and her husband seem to be so different and they argue over petty issues. What action by the nurse using group theory would be best? A. Ask the woman if she can remember why she and her husband fell in love. B. Caution her that this level of disagreement will cause stress to the unborn baby. C. Offer the woman a referral to a community counseling center for couples therapy. D. Reassure her that this is normal and help her brainstorm ways to work cooperatively. 21. A clinic nurse is using group theory to assess a family whose youngest child recently moved back home after graduating from college and is unable to find a job. Which statement by a parent would indicate to the nurse that goals for norming have been met? A. Im glad my son stays in his room in the basement all day so he doesnt bother us. B. Its hard to decide how much food to buy because we dont know where hes eating. C. My son is gone a lot of the time, so we really dont notice that he moved back in. D. We have agreed not to have a curfew as long as we know when he will be home. 22. A student observes as an adult brother and sister lash out at the nurse caring for their hospitalized parent. The parent lives at home but is dependent on the children for care and is obviously neglected. The nurse has informed the children that social work will be involved in their fathers case. How does the nurse explain this interaction? A. Dont worry; they will calm down eventually. B. Families often get emotional in these situations. C. They are focusing attention on me, not the problem. D. This family is obviously highly dysfunctional. 23. A nurse working with a married couple notes that both parties seem to try to be dominant in their sessions. According to Bowens family systems theory, which question asked by the nurse would yield the most useful information? A. Are you each a first-born, middle child, or youngest sibling? B. How demonstrative were each of your parents when you were growing up? C. How many children were in each of your families? D. What socioeconomic classes did you both grow up in? 24. A nurse working in a pediatric clinic is attempting to assess a school-age child who is disrespectful of the nurse and parent and tears up a magazine when asked to sit down. What conclusion can the nurse make about this family? A. The child is not getting enough attention from the parents. B. The family is from an underserved community group. C. Financial stress has caused family strife and fighting. D. The parental disciplinary approach is inconsistent. 25. A family with a loud, disobedient child has been working with a nurse. Which action observed by the nurse indicates that goals for the diagnosis of impaired parenting have been met? A. The father delivers consequence to the child calmly. B. The father only asks the child twice not to do something. C. The mother doesnt cry when disciplining her child. D. The mother states that the child is still testing the limits. 26. A female patient from a refugee community is in the emergency department and needs urgent surgery. The patient defers making a choice on the operation, preferring to wait for a cultural elder to arrive. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Encourage the patients family to talk her into having the operation. B. Explain kindly to the patient that her situation cannot wait. C. Respect the patients choice and wait for the elder to arrive. D. Take the patient to surgery under the principle of implied consent. 27. A nurse wishes to assess how often members of a family consume alcohol or use drugs during a typical week. What type of family assessment tool would this nurse choose? A. Ecomap B. Genogram C. Qualitative D. Quantitative 28. A mother is worried about her three children developing an inherited medical condition because many members of her family have died from this disease. To start an assessment of this family, which tool should the nurse choose? A. Ecomap B. Genogram C. Problem list D. Quantitative tool 29. A nurse explains the benefits of a strengths-and-problems list to a student. Which is the best explanation? A. Can use their strengths to work on identified priority problems B. Demonstrates that each family has both strengths and problems C. Forces people to be accountable and take responsibility for problems D. Lets families see which members have problems affecting them 30. A nurse working with a pregnant woman who is a recent immigrant to the United States notes that her husband rarely accompanies her to prenatal visits, and when he does, he sits in the waiting room. What action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the patient what role men in her culture play in pregnancy. B. Ask the woman why her husband doesnt seem involved. C. Encourage the man to participate in order to support his wife. D. Research the couples cultural background and health beliefs. 31. A family has weekly game nights and monthly family together days. The nurse documents these events as examples of which of the following? A. Family beliefs B. Family bonding C. Family building D. Family rituals 32. A nurse is working with a family that has the nursing diagnosis of altered family processes. When formulating goals, whom does the nurse include? A. Entire family B. No one else C. Parents D. Physician 33. A 17-year-old high school senior is resentful about caring for younger siblings so the parents can have a date night once every 2 weeks. The teen often forgets and schedules work or social activities that override the parents plans. The parents are angry that the teen is so indifferent to their needs. What action by the family indicates that goals for the diagnosis of impaired family processes have been met? A. Parents and teen mutually plan date nights in advance. B. Parents consistently discipline teen for forgetting. C. Teen acknowledges forgetting date night on purpose. D. Teen expresses feelings about being made to babysit. 34. A nurse is working with a family with the diagnosis of impaired family processes. Although both parties worked, one person worked part time and had the main responsibility for the household. The other spouse retired recently and has not taken on more of this role. Both people are angry and resentful. What goal would be best for this couple? A. Adapt to role changes positively within 2 months. B. Divide up household duties between spouses more evenly. C. Express feelings using I statements within 1 month. D. Learn to discuss anger and other negative emotions. 35. A patient is being discharged from a psychiatric facility after a suicide attempt. The family consists of the patient, two parents, and two other teenage children. What action should the nurse teach the entire family as a priority? A. Assess for drugs or alcohol in the patients room. B. Encourage the patient to take medications. C. Monitor the patient for signs of suicidal thoughts. D. Plan menus that contain nutritious food items. 36. A nurse is working with a family in which one member has schizophrenia. Using systems theory, for which concern should the nurse specifically assess this family? A. Balance B. Boundaries C. Childrens ages D. Subsystems 37. A grade school nurse is conducting vision screening before school and notes the student is accompanied by an older sister who has also brought a middle school child. The older child states that time is a problem because middle school starts in a few minutes and tells the younger child to go right to the classroom after the screening, then leaves. What question by the nurse would be most appropriate to ask the youngest child during the screening? A. Do you feel safe at home or is someone hurting you there? B. Does your sister always bring you and your sibling to school? C. Have you ever seen your parents drinking a lot or using drugs? D. Why arent your parents available to bring you to school? 38. A patient has just been admitted to the hospital in critical condition. In caring for the entire family, what action by the nurse is most important? A. Assessing who in the family will make decisions B. Determining if the family needs financial resources C. Ensuring each member understands the situation D. Orienting the family to visiting hours on the unit 39. A hospice nurse is making the initial home visit to a patient who just returned home after a lengthy hospitalization. What action by the nurse is most appropriate to help the family continue to function? A. Assess the degree of comfort in family caregiving. B. Ensure the family understands the hospice concept. C. Provide information about available hospice services. D. Refer the family to a community counseling center. 40. An immigrant family is working with a nurse on improving family dynamics. The nurse notes that the teenage children do not subscribe to their parents social and cultural mores and identify more with their native-born American friends. What description of the children is most accurate to record in the familys chart? A. Acculturated B. Assimilated C. Disconnected D. Lost children MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse is explaining to a student why it is so important to consider the entire family as the patient. What explanation for this is best? (Select all that apply.) A. Families are a rich source of information and support. B. Families will have to take over the caregiving role at home. C. If they are not included, families tend to interfere in care. D. The patient has to reintegrate into the family upon discharge. E. The patients background context includes the family. 2. The nurse explains to the student that television and movies have often portrayed families in certain ways, depending on the decade. Which of the following statements about this trend are correct? (Select all that apply.) A. 1950s1960s: nuclear family, simple issues, father dominated B. 1960s1970s: extended families, lower income, divorced parents C. 1980s1990s: exploring social issues, stressed family closeness D. 1990s: single parents, social issues including poverty and abuse E. New millennium: alternative family structures, extended family 3. A nurse working in the community understands that health is often affected by social stressors. Which of the following are examples of societal pressures having a negative impact on the health of todays families? (Select all that apply.) A. Economic trends affecting access to health care B. Increased HIV/AIDS in women and children C. Loss of resources in public schools D. Restricted health-care access for adult males E. Violence and increased teen suicides 4. A nurse using family systems theory to work with patients and their families would do which of the following? A. Assess how school, work, and church impact the family. B. Describe the developmental stage the family is in. C. Determine if there are any family secrets or taboos. D. Listen to how information is shared with providers. E. Observe how family members interact with each other. 5. The nurse using developmental theory offers anticipatory guidance on preventing injuries to the family of a preschooler. What concepts guide this information? A. Coordination lagging behind activity B. Development of personal values and ethics C. Impact of friends and peer group D. Poor judgment about safety risks E. Toddlers increasing physical abilities 6. The family nurse completes a genogram map when conducting a family assessment. Appropriate information the nurse should include in the genogram map includes which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Congenital diseases in the family B. Country of origin for family members C. Dates of birth for all family members D. Dates of divorce and deaths for family members E. Three or more generations 7. The nurse assesses the communication in a family that includes a single mother, a teenage son and daughter, and a grandmother. During the family interview, the daughter answers many questions while the son and mother are quiet and the grandmother is absent. What conclusions can the nurse make about this family? (Select all that apply.) A. The communication patterns are healthy. B. The daughter may have a lot of power. C. The grandmother does not want to be involved. D. The grandmother may have little power. E. The mother and son may have a coalition. 8. The clinic nurse keeps resource numbers and contacts for assistance with situations in which family members may potentially require assistance to restore balance and function to the family. These developmental crises may include which of the following situations? (Select all that apply.) A. Home fire requiring a lengthy hotel stay B. Hospitalization of a family member C. Identification of domestic violence D. Postpartum depression in a young family E. The anticipated birth of a new baby 9. A nurse assessing a family includes which components in the assessment? (Select all that apply.) A. Dietary habits B. Family size and structure C. Parenting style D. Religious affiliation E. Socioeconomic status 10. A nurse is assessing a family whose patriarch died recently. Using Kbler-Rosss stages of grieving, what stages should the nurse assess for? (Select all that apply.) A. Bargaining B. Dealing C. Denial D. Remorse E. Shock Chapter 4: Caring for Women, Families, and Children Across the Life Span MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The clinic nurse knows that providing an influenza vaccination clinic for patients aged 65 years and older is best described as an example of what kind of health care? A. Disease prevention B. Health promotion C. Health screening D. Secondary prevention 2. The family clinic nurse encourages a patient to continue breastfeeding her 8-month-old infant to facilitate maturation of the infants immune system. When does this occur? A. 12 months B. 16 months C. 18 months D. 24 months 3. The clinic nurse is working with a mother who wants to know the best age for teaching children about the names and functions of sexual organs. What should the nurse tell her? A. 5 to 6 years of age B. 6 to 7 years of age C. 8 to 9 years of age D. 9 to 11 years of age 4. The pediatric clinic nurse tells the parents that infants can roll over, presenting a safety hazard, at what age? A. 1 month B. 2 months C. 3 months D. 4 months 5. The family clinic nurse reviews nutritional information with a 15-year-old patient. The patient is concerned about being short and wonders if growth will continue. The nurse explains that the typical increase in height during adolescence is how much? A. 15% B. 25% C. 30% D. 35% 6. A school nurse is interviewing a high school student sent to the office for frequent crying episodes. The student admits to thinking of suicide and has made a previous attempt. The nurse determines that the teen has a suicide plan but does not yet have access to the materials needed to carry out the plan. How does the nurse interpret and act on this information? A. High risk: Call the school district counselor. B. High risk: Contact 911 immediately. C. Low risk: Send a referral home with the student. D. Moderate risk: Call the parents to come get the teen. 7. The family clinic nurse initiates conversation with a 16-year-old adolescent male who is 5 feet 10 inches and weighs 250 pounds (113.6 kg). Which of the following is the most appropriate question for the nurse to ask the adolescent regarding his weight? A. Are you willing to talk about your weight gain this year? B. Do you realize your weight puts you into an obese category? C. Do you participate in any activities or exercise? D. What do you think about your weight right now? 8. A nurse is observing a mother and her 10-month-old infant. The mother is interacting happily with the child while letting the baby eat pieces of hot dog. What action by the nurse is best? A. Compliment the mother on her parenting skills. B. Document that the baby is eating finger foods now. C. Stop the mother from feeding the hot dog to the baby. D. Teach the mother that hot dogs are poor nutrition. 9. A nurse is teaching new parents about dental care for their baby. Which information should the nurse provide? A. Brush the babys teeth with special baby toothpaste. B. The child should see a dentist before the age of 2. C. All teeth should be in by age 2. D. Wipe the babys gums with moist gauze. 10. A public health nurse is visiting a family home where there is a newborn. Which assessment finding by the nurse warrants immediate intervention? A. A cat is sitting on the kitchen counter by the stove. B. Roaches are evident in the kitchen and in the pantry. C. The baby is on a carpet that is stained and worn out. D. The crib has dirty bumper pads and a dirty comforter. 11. A mother who has three older children now has a newborn. She complains to the physician that sleeping on his back has caused her baby to have a funny-shaped head that the other kids didnt have. She doesnt want to continue having the baby sleep on his back. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Document the comments and alert the physician to the concern. B. Encourage her to put the baby on his stomach during the day. C. Explain that babies need to sleep on their sides at all times. D. Tell her that back-sleeping isnt important after 5 months of age. 12. A clinic nurse is working with an extremely obese teen. Besides nutrition and related health effects, what else should the nurse assess the patient for? A. Alcoholism B. Hepatitis C C. Lanugo D. Seat-belt use 13. A school nurse is evaluating a teenager who is returning to school after breaking her fibula. The nurse notes the student has a blood pressure of 90/56 mm Hg, has a pulse of 58 beats/minute, and is wearing three layers of clothing. What action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the student if she had pain medication this morning. B. Document the findings and send the student to classes. C. Have the student lie down and call 911 immediately. D. Question the student about eating and exercising patterns. 14. A nurse is assessing a teen who has the nursing diagnosis of sleep pattern disturbance. What statement by the teen indicates that goals for this diagnosis have been met? A. I dont want to cut out any more evening activities. B. I sleep until about noon on Saturdays to catch up. C. I take a long nap when I get home from school each day. D. I try to keep the same sleep and wake times all week. 15. The school nurse wants to create a safe driving program for the high school students. In order to have the greatest impact on safety, on which issue should the nurse focus? A. Female driving B. Late-night driving C. Seat-belt use D. Sleep deprivation 16. The parents of a 16-year-old boy are frustrated because the teen is always participating in risky activities and getting hurt, and has a group of friends of whom the parents do not approve. What action by the nurse would be most helpful? A. Encourage an after-school program that includes rock climbing, rafting, and hiking. B. Reassure the parents that risk taking is just a normal part of adolescence. C. Show the teen statistics on preventable injuries and deaths among teenagers. D. Tell the teen his risky behavior can lead to injuries and worries his parents. 17. A school nurse is preparing educational activities for all high school students on reproductive health. The principal cautions that the program can only contain information about sexual abstinence. Which action by the nurse would be most appropriate? A. Argue that abstinence-only programs do not work and are not valuable. B. Discuss the need to have information appropriate to the teens experience. C. Plan the program but encourage questions not related to the prepared material. D. Prepare an abstinence-only program because teens should not have sex. 18. A nurse is teaching conflict-resolution strategies to a group of teen mothers at risk for violence. Which statement by a participant indicates understanding? A. Friends of mine have said they would be willing to help in a crisis. B. If good communication doesnt solve the problem, I will leave. C. If we cant settle our differences, we will have to start talking all over again. D. My mother can help my boyfriend and me resolve a conflict. 19. A young couple is in the clinic for a prenatal exam. The woman expresses concern that her husband continues to binge drink and use drugs on weekends. What action by the nurse is best? A. Assess the father for reasons why he continues to abuse alcohol and illicit drugs at his age. B. Explain that if there are drugs in a house with a baby, the baby can be taken away. C. Help the husband see how his drug and alcohol use is inconsistent with the father role. D. Warn the husband that he will be putting the baby at risk unless he stops this activity. 20. The nurse is assessing a young woman who is overweight. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Ask if she knows how overweight she is. B. Assess the woman for stress-related problems. C. Caution her about related chronic illnesses. D. Encourage the woman to exercise more. 21. A nurse is teaching a 24-year-old male about reproductive health. Which information should the nurse provide this patient about testicular cancer? A. Annual screening is recommended for testicular cancer. B. If the epididymis is tender to the touch, that is concerning. C. Perform a testicular self examination after a warm shower. D. Because testicular cancer is rare at this age, no action is needed. 22. A woman presents to the family practice clinic complaining of abdominal pain, pain during ovulation, and heavy periods. What action by the nurse is best? A. Facilitate a vaginal ultrasound. B. Obtain consent for a laparoscopy. C. Prepare the woman for a pelvic exam. D. Provide education on ibuprofen (Motrin). 23. A patient is in the clinic for an annual exam. Her past medical history includes endometriosis for which she takes medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera). What assessment finding would the nurse relate to the medical condition or medication? A. 20-lb weight gain B. Cold intolerance C. Facial acne D. Facial hair growth 24. A nurse reads in a patients chart that the Bethesda system terminology used to describe her cervical cytology and histology is AIS. What can the nurse conclude about this womans treatment? A. Follow-up in 1 month B. Possible chemotherapy C. Repeat test in 3 months D. Use of luprolide (Lupron) 25. A 21-year-old woman who has not been sexually active is in the clinic and requests a Gardasil vaccination. After giving the shot, what instruction does the nurse provide to her? A. Return in 1 month for the next shot. B. Return in 2 months for the next shot. C. Return in 6 months for the next shot. D. Return in 1 year for the next shot. 26. A young woman has had three urinary tract infections (UTIs) in the last year. What teaching should the nurse plan for this patient? A. Avoid sexual intercourse during your period. B. Take prophylactic antibiotics daily. C. Void every 4 hours while awake. D. Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom. 27. The nurse prepares to offer health screening and promotion activities for women aged 4060. Which activity does the nurse plan to include as a priority for this group? A. Alzheimers disease screening B. Breast cancer screening C. Gardasil vaccinations D. Influenza vaccinations 28. A nurse is volunteering for the local chapter of the cancer society and is planning breast cancer screening and educational activities in the community. In order to have the most impact on this disease, which women should the nurse target? A. African Americans B. Asian Americans C. Caucasian Americans D. Native Americans 29. A postmenopausal woman asks the nurse about reducing her breast cancer risk. The woman is overweight, consumes one alcoholic drink daily, does not smoke, and works at a desk. What response by the nurse is best? A. Exercise regularly. B. Lose weight. C. Stop drinking. D. Take aspirin daily. 30. A preoperative nurse is caring for a patient who will undergo an open breast biopsy. What action by the nurse takes priority? A. Ensure that an informed consent is signed and witnessed. B. Inventory and label all of the patients belongings. C. Orient the patients significant others to the waiting room. D. Premedicate the patient on arrival to the pre-op holding area. 31. A nurse in a family practice clinic sees several generations of the same family. For which family members should the nurse arrange routine screening colonoscopies? A. Daughter, age 52 B. Grandfather, age 80, no history of polyps or cancer C. Grandmother, age 72, history of polyps D. Grandson, age 30, no gastrointestinal symptoms 32. A nurse is reviewing the results of several patients cholesterol and lipid screenings. For which patient is the action appropriate? A. HDL cholesterol 66 mg/dL: Evaluate patient for cardiovascular risk. B. LDL cholesterol 98 mg/dL: Instruct patient to take fish oil 3 gm daily. C. Total cholesterol 240 mg/dL: Teach heart-healthy lifestyle changes. D. Triglycerides 132 mg/dL: Refer to dietician for comprehensive diet education. 33. A 53-year-old woman is having her annual physical and tells the nurse she has not had a period for 7 months. She wants to know if she has undergone menopause. What response by the nurse is best? A. No, at your age, fluctuations in your menstrual cycle are normal findings. B. No, menopause only begins in women after the age of 55. C. Yes, not having a period for more than 6 months is diagnostic of menopause. D. You have to go 1 year without a menstrual period to be sure that menopause has occurred. 34. A nurse is evaluating several patients for possible hormone therapy to reduce severe symptoms of menopause. For which patient would hormone therapy be recommended? A. 53 years old, smoker, estrogen-progestin therapy B. 54 years old, history of endometrial cancer 10 years ago, estrogen only C. 55 years old, history of hysterectomy 4 years ago, estrogen only D. 76 years old, went through menopause 16 years ago, estrogen-progestin 35. A woman suffering from severe vasomotor menopausal symptoms wants to use complementary or alternative therapies instead of hormone therapy. What advice by the nurse is best? A. Acupuncture has been shown to work better than other body therapies. B. Herbs are a great option as they do not typically have side effects. C. Mindbody, manipulative, or traditional Chinese medicine are safer than herbs. D. Research shows that black cohosh significantly reduces hot flashes. 36. A nulliparous 53-year-old woman is in the clinic complaining of lower abdominal fullness, heavy menses, and severe menstrual cramping. What treatment does the nurse anticipate for this woman? A. Administration of leuprolide (Lupron) B. Hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy C. None; issue will resolve spontaneously D. Surgical removal of the ovaries 37. A nurse notes that a womans chart lists dyspareunia as a diagnosis. In planning education for the patient, which topics would the nurse include? A. Black cohosh and soy nuts B. Kegel exercises and use of a pessary C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications D. Water-based vaginal lubricants 38. A nurse is working with an older adult who has never exercised despite understanding the health benefits. What can the nurse do to improve the chances that this adult will begin an exercise regimen? A. Ask the patient if dancing sounds like fun. B. Encourage the patient to join a fitness club. C. Explain how exercise increases independence. D. Have the family talk with the patient about it. 39. An older patient has never exercised, but wants to begin now. What response by the nurse is best? A. At your age, exercise will not benefit you. B. Good for you! I am so proud of you! C. Remember to stretch before exercising. D. Start with exercising for only 5 minutes a day. 40. The nurse notes that a patients chart contains the results of an MMSE. What can the nurse surmise about this patient? A. Behind on recommended immunizations B. Concerns about cognitive functioning C. Tracking changes in bone density D. Worried about cardiovascular health 41. A 65-year-old patient is in the clinic for an annual influenza vaccination. What other health promotion activity should the nurse encourage specifically for this patient? A. Heart-healthy eating B. Participating in social activities C. Pneumococcal vaccination D. Regular exercise 42. A nurse is educating a woman on the use of denosumab (Prolia). What information should the nurse provide? A. Return in 6 months for another injection. B. Take this medication on an empty stomach. C. Take this medication with milk or food. D. You may have increased night sweats. 43. A nurse is planning breast education for women. What information does the nurse plan to provide about breast cancer screening recommendations? A. Annual screening after age 40 B. MRI to replace mammography C. No routine screening after age 65 D. Periodic screening if high risk 44. A college nurse offers screening programs for students. At what age should the nurse encourage women to have their first Pap test? A. At age 19 B. At age 21 C. Before sexual activity D. No specific age 45. A clinic nurse sees adolescent girls frequently. Many of the girls should be screened for gonorrhea and Chlamydia infection, but they balk at having a pelvic exam. What option can the nurse offer these girls? A. Blood draw B. Limited pelvic exam C. No alternative D. Urine collection 46. At what age should the nurse prepare patients to begin thyroid function screening? A. 30 years B. 40 years C. 50 years D. 60 years 47. The mother of a 5-month-old baby complains that her child seems hungry even after breastfeeding 10 times a day. What assessment question would help the nurse plan anticipatory teaching? A. Are you sure your breasts are emptying? B. Does the baby put everything in his mouth? C. Does your baby sit in a high chair yet? D. Is your baby using the pincer grasp yet? MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse teaches expectant mothers about the differences between breast milk and commercially prepared infant formulas. What does the nurse tell the mothers about breast milk? (Select all that apply.) A. Fewer nutrients B. Less casein C. Less protein D. More calories E. More carbohydrates 2. A community health nurse is packing a kit of play items for the families who will be visited today. One family has an infant and a preschooler. Which toys should the nurse include in the kit? (Select all that apply.) A. Blocks B. Coloring books C. Ride-on train D. Simple board game E. Stuffed animals 3. A nurse is preparing to educate a group of parents about injury prevention in adolescents. Which topics should the nurse plan to include as priorities? (Select all that apply.) A. Bicycle safety B. Gun safety C. Home safety D. Driving safety E. Water safety 4. A 17-year-old girl comes to the health department clinic to renew her oral contraceptive pills. During the physical examination, the nurse observes that the girl has broken blood vessels on her face and her lips are cracked and chapped and her fingers are callused. What further actions will the nurse perform? (Select all that apply.) A. A weight assessment B. Assessment for depression C. Draw blood for electrolytes D. Discussion about anorexia nervosa E. Discussion about bulimia 5. The clinic nurse talks with parents about the signs and symptoms of substance use because their 12-year-old twins will be attending a new school in the fall and they wish to be prepared. The nurse correctly describes the potential symptoms of substance abuse, including which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Chronic cough B. Euphoria C. Irritability D. Nausea and vomiting E. Red and glazed eyes 6. The clinic nurse educates young adults that the most common infectious health risks associated with tattoos include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Chlamydia infection B. Gonorrhea C. Hepatitis D. Human papilloma virus (HPV) E. Staphylococcus infection 7. The nurse providing health promotion to a group of young adult women would plan to offer which services as a priority? (Select all that apply.) A. Aspirin prophylaxis B. Breast cancer screen C. Colorectal cancer screen D. Influenza vaccine E. Tobacco and alcohol screen 8. A nurse works with many older patients and provides information about safer sexual practices and risks. What physical factors increase an older womans risk for acquiring human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection? (Select all that apply.) A. Increased promiscuity B. Isotonic dehydration C. Decreased vaginal pH D. Loss of vaginal elasticity E. Vaginal dryness 9. The nurse working with older women knows that risk factors for osteoporosis include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Asian ethnicity B. Excessive consumption of caffeine C. Large frame D. Regular physical activity E. Cigarette smoking 10. A visiting nurse is seeing an older woman with the nursing diagnosis of risk for trauma related to decreased bone density secondary to osteoporosis. Which assessment findings would indicate to the nurse that a priority goal for this diagnosis has been met? (Select all that apply.) A. All scatter rugs have been removed. B. Burned-out light bulbs have been replaced. C. Hot water heater temperature is set to 110F. D. Patient wears non-skid shoes or slippers. E. Pets have been given away to friends. 11. The reproductive care clinic nurse teaches young women about their risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Which factors does the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Alkaline pH of the vagina B. Increased genital mucosal surface area C. Increased number of pubic hair follicles D. Prolonged exposure to semen E. Temperature of the vaginal area OTHER 1. Match the types of play with their characteristics. _____ Assume roles in games; games have goals a. Solitary play _____Playing with the same items, but not really playing together b. Onlooker play _____ Plays alone, no regard for those in the area c. Parallel play _____ Play together, but little organization d. Associative play _____ Observes other children while playing alone e. Cooperative play There are five types of play: solitary play (child plays alone without regard for those around him or her), onlooker play (child observes others playing and may talk to them, may alter his or her own play, or may continue playing as he or she was doing), parallel play (playing with the same materials and items, but not playing together), associative play (play together in a peer group, but in a loosely organized manner), and cooperative play (assume roles in games, games have goals, and rely on each other to continue and progress). 2. Match each description with the correct disorder. Disorders may be used more than once. Descriptions may have more than one answer. 1. _____Rectum presses into vagina a. Cystocele 2. _____Symptoms include constipation b. Rectocele 3. _____ Bladder herniates into vagina c. Enterocele 4. _____Difficulty completing a bowel movement 5. _____ Damaged muscles appear higher in the colon 6. _____ Symptoms include difficulty in voiding, incontinence, and dyspareunia Chapter 5: Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The perinatal nurse reads in a chart that a woman has a lesion on her perineum. Where would the nurse assess this lesion? A. Greater vestibular or vulvovaginal glands B. Skin-covered region between the vagina and the anus C. Small portion of tissue around the anus D. Small portion of tissue surrounding the vaginal opening 2. The perinatal nurse knows that the lowest portion of the true pelvis is which of the following anatomical landmarks ? A. Pelvic outlet B. Linea terminalis C. Sacral promontory D. Sacrum 3. The clinic nurse knows that the part of the uterine cycle that occurs during the period of time between ovulation and the onset of menses is known as which of the following? A. Ischemic phase B. Menstrual phase C. Proliferative phase D. Secretory phase 4. The perinatal nurse explains to the new nurse that the maternal pelvic shape can determine the fetal presentation. A fetus in a transverse presentation may be due to which maternal pelvic type? A. Android B. Anthropoid C. Gynecoid D. Platypelloid 5. The clinic nurse explains to a student that the hormone responsible for limiting the maternal immune response to pregnancy is which of the following? A. Human chorionic gonadotropin B. Progesterone C. Prostaglandin D. Relaxin 6. A woman who might be pregnant is excited to learn when she will know the gender of the baby. What is the best response by the nurse? A. 5 weeks B. 6 weeks C. 8 weeks D. 12 weeks 7. The pediatric nurse explains to the student that production of testosterone by the male embryo causes what to occur? A. Creation of a gonad B. Formation of the male genital tract C. Production of spermatozoa D. Stimulation of external genitalia growth 8. The nursing instructor explains to the students that external female genitalia develop under what influence? A. Absence of androgens B. Ductal pair dominance C. Ovary production D. Process of oogonia 9. A woman sustained a moderate blow to the lower pelvic region in an occupational accident. She is surprised to find out that no bones were broken. What explanation by the nurse is best? A. Blunt force trauma doesnt cause fractures. B. Pelvic bones are very hard to fracture. C. Some fractures dont show up right away. D. You have a fat pad in front of your pelvis. 10. A new nurse is attempting to catheterize a female patient. The nurse has a difficult time and after three attempts, finally inserts the catheter into the bladder and has urine output. What suggestion by the more experienced nurse is best? A. Leave the incorrectly placed catheters where they are while inserting a fresh one. B. Place the patient in a high Fowlers position and have another nurse adduct the legs. C. Position the patient prone with another nurse abducting the patients legs. D. To save the patient some charges, use the same catheter for two attempts. 11. A nurse is examining a patients Skenes glands. What action is best to visualize these structures? A. Place a gloved finger in the rectum. B. Place a gloved finger in the vagina. C. Pull the urethral margins apart. D. Use a speculum and a bright light. 12. A nursing instructor is planning to teach students about the process of oogenesis. Which information does the nurse plan to include? A. All polar bodies in the ovary become ova. B. It is regulated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). C. The graafian follicle eventually secretes prolactin. D. It usually occurs in a twice-monthly cycle. 13. A woman is having an infertility workup and has been told she has scarring of her fallopian tubes. What action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the woman how many sexually transmitted infections she has had. B. Assess the woman for previous vaginal infections and their treatment. C. Gently tell the woman that nothing can be done about scarring of the tubes. D. Question the woman about genetic defects or family history of infertility. 14. The nurse manager on the high-risk OB unit has been told by an OB office nurse to prepare for a woman with a spinal cord injury (SCI) to deliver there. The woman wants to try a vaginal birth. What response by the nurse manager is best? A. Assess the level of the womans spinal cord injury. B. Assure the office nurse that vaginal birth is possible. C. Explain that women with SCI do well with a water birth. D. Tell the office nurse that vaginal birth is impossible. 15. A pregnant woman calls the OB clinic nurse to complain of sharp abdominal pain with coughing or sneezing. What action by the nurse is best? A. Explain that the pain is from stretching of the ligaments. B. Have the woman count her contractions each hour while awake. C. Place the woman on bedrest until her next clinic visit. D. Tell the woman to come to the clinic today. 16. A pregnant woman has a midpelvis pelvimetry measurement of 3.8 inches (9.65 cm). What action by the labor and delivery nurse is most important? A. Encourage attendance at childbirth classes. B. Explain that vaginal birth will be possible. C. Instruct her to drink 10 glasses of water daily. D. Obtain consent for possible cesarean delivery. 17. The nurse explains to the student that the development of the lining of the uterus is mediated by which hormone? A. Follicle-stimulating hormone B. Luteinizing hormone C. Progesterone D. Prostaglandin 18. A 17-year-old female is brought to the family practice clinic by her mother, who is worried that her daughter has not yet developed secondary sex characteristics. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Assess a family pedigree for genetic influences. B. Explain that some girls dont develop until their 20s. C. Inform them that the daughter will be tested for estrogen deficiency. D. Obtain a urine sample for a pregnancy test. 19. A patient in the emergency department has a positive serum hCG. What can the nurse surmise about this patient? A. Lactating B. Menopausal C. Menstruating D. Pregnant 20. A patient inquires why ibuprofen (Motrin) and not acetaminophen (Tylenol) is usually prescribed for menstrual discomfort. Which response by the nurse is best? A. Cheaper than Tylenol B. Fewer side effects C. Inhibits prostaglandins D. Works more quickly 21. In providing anticipatory guidance to a 12-year-old female who has developed breast buds, what information should the nurse provide? A. Breast self-exam is now important. B. First period will occur in 6 months. C. Growth of pubic hair will occur next. D. Maximum height has been obtained. 22. A family practice nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to an 11-year-old boy. What information about puberty should the nurse plan to include? A. Boys start puberty about 2 years earlier than girls. B. Circulating estrogen may cause breast enlargement. C. Testosterone production is the last stage of puberty. D. The first sign of puberty is testicular enlargement. 23. A 14-year-old girl asks the school nurse why her periods are so irregular. What is the best response by the nurse? A. All young girls have irregular periods. B. Dont worry; this is totally normal. C. Estrogen levels are still pretty low. D. You should be seen by your physician. 24. A nurse reads in a female patients chart that she is Tanner stage V. What can the nurse conclude about this patient? A. Beginning puberty B. Midpoint of puberty C. Sexually immature D. Sexually mature 25. The nursing instructor explains to a class that important effects of estrogen in the proliferative phase of the uterine cycle include which of the following? A. Causes uterine spiral arteries to constrict, limiting blood flow B. Causes changes in cervical mucus to facilitate sperm penetration C. Leads to changes causing the uterus to be receptive to a fertilized ovum D. Results in rupture of endometrial blood vessels and the onset of menses 26. A nurse is teaching a patient how to track her menstrual cycle. What day does the nurse tell the patient to label as day 1? A. First day after the menstrual cycle B. First day of the menstrual cycle C. Last day before the menstrual cycle D. Last day of the menstrual cycle 27. A woman is in the family planning clinic to learn about her cycle and the best times to get pregnant. What information should the nurse plan to teach her? A. An ovum can be fertilized for 12 to 24 hours after ovulation. B. Pregnancy can only occur during the follicular phase. C. There are no physiological signs that demonstrate ovulation. D. You cant easily get pregnant if your cycles are irregular. 28. A nurse has taught a woman about the physical signs that accompany ovulation. Which statement by the patient indicates that teaching has been effective? A. I can still conceive for up to 48 hours after ovulation. B. My temperature will go down after ovulation. C. Thin, watery cervical mucus means I am no longer fertile. D. Sticky cervical mucus helps hold the sperm in place on the egg. 29. A woman complains of irregular menstrual periods and wonders if she is in perimenopause or menopause. Her laboratory work shows high levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and low levels of estradiol. What response by the nurse is best? A. No, in menopause the FSH is low and the estradiol is high. B. No, those two laboratory findings are not related to the climacteric phase. C. These laboratory findings usually indicate menopause or perimenopause. D. Yes you are definitely in menopause right now. 30. A woman who is postmenopausal is in the clinic complaining of urinary incontinence and wants to know why this is occurring. Otherwise she has no other complaints. What response by the nurse is best? A. Im not sure; lets ask the physician why this could occur. B. Low estrogen levels after menopause causes the urinary tissues to atrophy. C. Most older women experience some incontinence. D. You may have a urinary tract infection or other medical problem. 31. A healthy-appearing 68-year-old woman is in the clinic for a physical exam. Her laboratory work shows decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and increased levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. What conclusion can the nurse make about this patient? A. Eats an unhealthy diet B. At risk for long-bone fractures C. Increased cardiovascular risk D. Probably does not exercise 32. A woman in the clinic complains of severe hot flashes associated with perimenopause. Her past medical history includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 10 years ago. The nurse can anticipate teaching the woman about what treatment? A. A trial of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor B. A trial of the anticonvulsant phenytoin (Dilantin) C. Hormone replacement with estrogen only D. Hormone replacement with estrogen-progestin 33. A nurse is teaching a group of middle school students about the functions of the male reproductive tract. Which information should the nurse include? A. Maturing sperm are stored in the epididymis. B. Seminal fluid is secreted by the ductus deferens. C. Spermatogenesis occurs in the bulbourethral glands. D. The prostate, found only in men, has no known function. 34. The nurse knows that in any volume of ejaculate, what percentage of sperm is motile? A. 25% B. 35% C. 40% D. 50% 35. A nurse working in the infertility clinic counsels a couple about male fertility. What assessment question to a male by the nurse would yield the most important information? A. Do you get plenty of exercise? B. Do you wear boxer shorts or briefs? C. How much alcohol do you drink? D. Have you been circumcised yet? 36. A nurse working with a couple in the infertility clinic notes the diagnosis of cryptorchidism on the mans chart. What assessment question by the nurse is most important? A. Did you have surgery for your undescended testes? B. Do you have a family history of testicular cancer? C. Do you use lead shielding when you get x-rays? D. For how long did you undergo chemotherapy? 37. A nurse is teaching a class about gender maturation. What information is most accurate? A. Gender is determined by 8 weeks of gestation, when sex organs are visible. B. Gender maturity is not fully complete until old age. C. It is a lengthy process that spans from the embryonic stage through puberty. D. The process begins and ends during fetal development. 38. A mother brings her 9-year-old daughter to the family practice clinic. She is worried because the daughter already has definite breast buds and is asking to wear a bra. What response by the nurse is best? A. At what age did you develop breast buds or start menstruating? B. Does anyone in your family have a history of precocious development? C. The average age for breast budding is 9.8 years, so she is normal. D. This is too early for breast buds; she may need endocrine studies. 39. The nurse teaching a course in human reproduction informs the class that which reproductive structure is the first to form in the embryo? A. Gonad B. Mesoderm C. Mesonephric duct D. Oocyte 40. The nurse teaches a class that which of the following is the first gender change to occur in the embryo? A. Destruction of the Y chromosome in the female embryo B. Development of dominance in the primitive duct structure C. Formation of primitive external genitalia that are visible on ultrasound D. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis in male and female embryos, respectively 41. A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to a group of elementary school girls and their parents. What information is most accurate? A. Around age 10, girls will get interested in shaving their underarms. B. By age 12, both boys and girls are at their maximal height. C. Moms, you should buy feminine supplies for your daughter before she is 14. D. You wont need to worry about bras until at least age 14. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. What information does the nurse understand about the labia minora? (Select all that apply.) A. Contain the Skenes glands and Bartholins glands B. Constitute the primary organ of sexual pleasure in women C. Provide lubrication and protective bacteriocidal secretions D. Resemble mucous membrane and do not have hair follicles E. Share an extensive lymphatic network with other vulvar structures 2. A teenager is asking questions about her hymen. Which of the following are correct responses by the nurse? (Select all that apply.) A. An intact hymen is a positive indication of virginity. B. Bright red bleeding is always present following hymenal tearing. C. The hymen can widen or perforate with tampon use, vulvar injury, or intercourse. D. It is a small portion of tissue around the vaginal opening in young girls. E. It will widen and perforate only with intercourse. 3. The perinatal nurse mentor teaches the new nurse about the functions of cervical mucus. What information should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Provides an acidic environment for sperm B. Acts as a bacteriostatic agent C. Provides a barrier to sperm during nonfertile phases D. Provides an easy-flowing pathway during fertile phases E. Forms an operculum to protect the pregnancy 4. The perinatal nurse understands that the functions of the vagina include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Manufactures a cervical plug during pregnancy B. Produces lubrication for intercourse C. Provides a receptacle for sperm D. Serves as a lower portion of the birth canal E. Stimulates the penis during intercourse 5. The OB nurse knows the menstrual cycle is controlled by the complex interplay of hormones that are secreted by which physiological structures? (Select all that apply.) A. Anterior pituitary B. Cerebral cortex C. Hypothalamus D. Ovaries E. Posterior pituitary 6. A nurse is planning an educational seminar focused on changes associated with perimenopause and postmenopause. Which topics should the nurse plan to include? (Select all that apply.) A. Eating foods high in calcium B. Getting plenty of rest and sleep C. Keeping the room cool at night D. Need for increased antiperspirant E. Using vaginal lubricants 7. A nurse is planning an educational program for middle school boys focused on physical changes they can expect with puberty. Which topics should the nurse plan to include? (Select all that apply.) A. Changes in patterns of hair B. Deepening of the voice C. Growth spurt D. Narrowing waist E. Thinning skin OTHER 1. Match the pelvic types with their descriptions. Pelvic types may be used more than once. a. Gynecoid _____ Best suited for childbirth b. Android _____ Fetal descent more likely to be in a posterior presentation c. Anthropoid _____Fetal descent is often in a transverse presentation d. Platypelloid _____ Triangular or heart-shaped _____ Only found in 3% of women _____ Traditional form found in about 50% of women _____Oval shaped at the inlet but in the anterior-posterior plane _____ Characteristics cause difficulty during fetal descent 2. Match the hormones and their functions. a. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone 1. ____ Controls the development and function of the adrenal cortex b. Somatostatin 2. _____ Stimulates the maturation of the mammary glands during pregnancy c. Adrenocorticotropic hormone 3. _____ Regulates thyroid hormones d. Oxytocin 4. _____ Also known as growth hormoneinhibiting hormone; inhibits the release of growth hormone e. Prolactin 5. Among other things, it is responsible for developing muscle mass and protein synthesis f. Corticotropin-releasing hormone 6. _____ Appears to provide a protective action by minimizing a maternal immunological rejection that could cause miscarriage g. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone 7. _____ Stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone from the anterior pituitary h. Growth hormone 8. _____ Stimulates uterine contractions and the release of milk from milk ducts during lactation 3. The nurse understands that the genetic possibility of a woman having a male or a female child is based on the single sex chromosome provided by each parent (mother is XX, father is XY, and each contributes one chromosome). Fill in the boxes below with the possibilities based on the single chromosome that is contributed by each parent in these four possible combinations. For the purpose of this exercise, the mothers chromosomes are designated X(m1) and X(m2), and the fathers are designated X(f) and Y(f). The result of any XX chromosome pair yields a girl, and XY a boy. 1. Mothers sex chromosome _____ Fathers sex chromosome _____ Child is a _____________ 2. Mothers sex chromosome _____ Fathers sex chromosome _____ Child is a _____________ 3. Mothers sex chromosome _____ Fathers sex chromosome _____ Child is a _____________ 4. Mothers sex chromosome _____ Fathers sex chromosome _____ Child is a _____________ Chapter 6: Human Sexuality and Fertility MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The reproductive health nurse counsels a 17-year-old woman who is interested in initiating contraception. Which of the following would be a short-term positive outcome of the visit? A. Able to describe how to obtain and use the contraceptive chosen B. Continued use and pregnancy prevention for 6 months C. Lack of side effects and complaints about the method after 3 months D. Voiced satisfaction with this method over 6 months 2. The clinic nurse is counseling a woman who had a Nexplanon rod implanted. The nurse reminds her that she will need an appointment to replace this birth control method in what time frame? A. 12 months B. 24 months C. 36 months D. 48 months 3. A 24-year-old lactating woman asks about contraceptive options. The family planning clinic nurse recommends an oral contraceptive formulated with which ingredients? A. Biphasic formulation B. Estrogen-progestin C. Progestin only D. Triphasic formulation 4. A woman is interested in the transdermal contraceptive patch. She is 55 tall and weighs 200 lb (90.9 kg). What information should the nurse provide this patient as a priority? A. It may cause skin irritation. B. She cant use the patch at her weight. C. The patch is about 95% effective. D. Withdrawal bleeding occurs monthly. 5. A nurse works with many women who self-identify as lesbian or bisexual. What action by the nurse would best address this populations needs? A. Aggressive screening for sexually transmitted infections B. Assisting with procedures related to conception C. Providing information on increased cancer risks D. Using questions that do not assume sexual orientation 6. The nurse working in a family practice clinic assesses women for sexual dysfunction. Which woman would the nurse assess as having a sexual dysfunction? A. Complains about lack of arousal but still has intercourse B. Enjoys a platonic relationship with her gentleman friend C. Needs increased foreplay in order to reach an orgasm D. No desire for intimacy and is comfortable with the situation 7. A nurse is working with a patient who has the nursing diagnosis of altered sexuality patterns. What action by the nurse takes priority? A. Assists with the physical exam B. Establishes a trusting relationship C. Reviews the past medical history D. Takes a comprehensive sexual history 8. A nurse is assessing a patient who complains of an inability to achieve orgasm. The patient was recently started on several new medications. Which one would the nurse evaluate as possibly contributing to this problem? A. Atenolol (Tenormen) B. Clonidine (Catapres) C. Levothyroxine (Synthroid) D. Sertraline (Zoloft) 9. The nurse is assessing a sexually active heterosexual woman who does not use birth control. The nurse explains that the chance of becoming pregnant with each act of unprotected intercourse is what percentage? A. 510% B. 1015% C. 1520% D. 2025% 10. A nurse is working with a young woman planning to become sexually active. She has the nursing diagnosis of knowledge deficit related to contraceptive choices. Which action by the patient would indicate that a priority goal has been met? A. Can describe how to use method chosen and its side effects B. Is able to choose the best fit from contraceptive choices C. Obtains the contraceptive method previously desired D. Willing and able to explain contraceptive method to partner 11. A teenage girl wishes to obtain birth control and is interested in a diaphragm. What advice does the nurse provide? A. Good choice because it is cheap B. Good choice because it is easy to use C. Poor choice because it is not effective D. Poor choice because it requires planning 12. A woman who was recently fitted for a diaphragm is in the clinic for a follow-up visit. Which statement by the patient indicates that teaching was effective? A. An added benefit is that it contains my menstrual flow. B. Baby oil is a cheap and effective lubricant for the diaphragm. C. I leave the diaphragm in place for 6 hours after intercourse. D. This diaphragm will have to be replaced within 3 years. 13. A nurse is working with a young couple whose contraceptive choice is latex condoms. What statement by either partner indicates the need for more teaching? A. Man: I dont carry these in my wallet in my pants pockets. B. Man: I make sure I am using the correct size of condom. C. Woman: I ask him to check the expiration dates each time. D. Woman: I buy nonoxynol-9 spermicide to use with condoms. 14. Which of the following women would the nurse advise to use a back-up contraceptive in addition to their birth control pills? A. Being treated for tuberculosis B. Is a diabetic taking insulin C. On antibiotics for bronchitis D. Takes inhalers for asthma 15. A woman is being started on oral contraceptive pills. Which screening assessments should the nurse perform or assist with? A. Blood pressure B. Breast exam C. Pelvic exam D. Weight 16. A patient has been taught about the vaginal contraceptive ring. Which statement by the patient indicates that further teaching is needed? A. If it comes out at all, I need back-up contraception for a week. B. The exact position of the ring is not vital for its function. C. Using tampons is allowed with the vaginal contraceptive ring. D. Vaginal contraceptive rings are about 96% effective. 17. The nurse is teaching a group of women about hormonal emergency contraception. Which of the following is not a benefit of this type of contraception? A. Available in some forms over the counter B. Can be taken up to 120 hours after intercourse C. Over-the-counter version has only two pills D. Typically has no side effects 18. A nurse in an emergency pregnancy clinic is evaluating women for the IUD method of emergency contraception. Which woman would not be considered a good candidate for this method of emergency contraception? A. Does not wish to have an abortion B. Had sexual intercourse 4 days ago C. Took over-the-counter morning-after pill today D. Was raped by a stranger 19. A student nurse is giving a patient an intramuscular Depo-Provera injection. Which action by the student would cause the instructor to intervene? A. Assesses that the patients last period started 57 days ago B. Injects the medication deeply into the gluteus maximus C. Instructs the woman to return in 3 months for another shot D. Massages the site when the patient complains of pain 20. A patient has been taught about her Depo-Provera contraceptive injection. Which statement by the patient indicates that education has not been effective? A. Daily weight-bearing exercise will be important. B. I can become pregnant right after stopping the shots. C. I should add a calcium supplement to my diet. D. Hopefully I wont have any periods while on this medication. 21. An adolescent is in the family practice clinic to obtain birth control. She began menstruating 4 days ago and wants the Depo-Provera injection because of the convenience associated with the method. What action by the nurse is best? A. Administer the injection as prescribed. B. Assist the teen in choosing another method. C. Document that education was completed. D. Obtain a urine sample for a pregnancy test. 22. Prior to a sterilization procedure, which action by the nurse takes priority? A. Obtaining informed consent from the partner B. Obtaining pre-approval for Medicaid patients C. Obtaining pre-approval from the insurer D. Obtaining the womans informed consent 23. A woman who is 10 weeks pregnant is being counseled by the nurse regarding her upcoming elective abortion. What information should the nurse provide? A. A local anesthetic will be injected into your vagina. B. The exact name of the procedure is dilation and extraction. C. They may use a seaweed product to dilate your cervix. D. You wont need to have any cervical dilation at all. 24. A woman had an elective surgical abortion 7 weeks ago and calls the clinic to ask when her menstrual periods should return. What response by the nurse is most appropriate? A. I will ask the physician to prescribe misoprostol (Cytotec). B. It usually takes 1 to 3 months for your menstrual periods to return. C. Please come in to the clinic today for a checkup. D. You should be seen in the emergency department. 25. A woman is in the clinic for a checkup 4 weeks after elective surgical abortion and has the nursing diagnosis of spiritual distress related to discrepancy between religious beliefs and reproductive choices. Which statement by the patient indicates that goals for this diagnosis have been met? A. I dont ever want to go through anything like that again. B. I found out that my religion doesnt forbid birth control. C. I talked to my minister and feel better about my choice. D. I will be much more careful about contraception now. 26. A woman who desires a second-trimester medical abortion has been educated about the procedure, side effects, and follow-up. What statement by the patient indicates that additional teaching is needed? A. I understand that I might need several doses of the prostaglandins. B. I will get over-the-counter medication to treat any headache that I get. C. I will watch for dizziness when standing if I have vomiting or diarrhea. D. If I get a fever with chills, I should go to the emergency department. 27. A nurse reads on a womans chart that she has a past history of Asherman syndrome. What does the nurse conclude about this patient? A. Has had an abortion B. Has had multiple miscarriages C. Has never been pregnant D. Has a uterine abnormality 28. After an abortion, when should the nurse advise the patient to return for a follow-up visit? A. 2 weeks B. 4 weeks C. 6 weeks D. 8 weeks 29. A nurse is reviewing a 36-year-old womans chart. The woman has the diagnosis of infertility. What does the nurse conclude about this woman? A. Has a medical condition that prevents pregnancy B. Has been attempting to get pregnant for 12 months C. Has delayed pregnancy and childbirth for too long D. Has not conceived in 6 months of actively trying 30. During the initial visit with a couple in the infertility clinic, what action by the nurse is best to promote a trusting relationship? A. Explain the process of a workup and its sensitive nature. B. Give written information with a timeline of testing. C. Go over the cost of a workup and insurance coverage. D. Ask the couple if they have considered adoption as an alternative option. 31. A nurse is explaining that a woman will undergo follicular monitoring to evaluate her response to ovulation induction. For what test does the nurse prepare her? A. 3-D ultrasound and color flow Doppler B. Endometrial biopsy C. Hysterosalpingography D. Laparoscopy 32. A woman is having hysterosalpingography and begins complaining of severe left shoulder pain. What action by the nurse is best? A. Administer morphine sulfate, 12 mg intravenously. B. Ask the patient if she took a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) prior to the procedure. C. Determine exactly where the woman is in her monthly cycle. D. Inform the physician so the procedure can be stopped. 33. A woman is being treated for infrequent ovulation. The nurse should educate her about what medication? A. Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) B. Chlorambucil (Leukeran) C. Estradiol (Estrace) D. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) 34. A woman is receiving clomiphene citrate (Clomid). What assessment finding warrants immediate intervention by the nurse? A. Chest pain worse with inspiration B. Complaints of anxiety and depression C. Headache and bilateral eye pain D. Increase in blood pressure of 10% 35. A woman in the infertility clinic is concerned that her religion may object to assisted reproductive technologies. Which process should the nurse explore with the woman as possibly acceptable? A. FET (frozen embryo transfer) B. GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer) C. IVF-ET (in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer) D. ZIFT (zygote intrafallopian transfer) 36. A nurse is counseling a couple about fertility prior to the husband beginning chemotherapy for cancer. The couple wish to delay childbirth until the husband is in remission. What information from the nurse is most accurate? A. Donor sperm are usually used in cases such as yours. B. Have you considered cryopreservation of your sperm? C. Most chemotherapeutic drugs dont affect fertility. D. You shouldnt wait, because remission may not occur. 37. A woman asks the nurse about taking chasteberry tree supplements. What response by the nurse is best? A. Herbal supplements have no side effects. B. There are no scientific data supporting the use of this supplement. C. This herb is known to promote ovulation. D. Try it first, as herbs are inexpensive. 38. A woman is tracking her basal body temperature and is having inconsistent results. When assessing the patient, the nurse discovers that the patient has seasonal allergies. The nurse needs to assess for what further information? A. Any over-the-counter allergy medications taken B. How long the patient has suffered from allergies C. Signs and symptoms the patient has with her allergies D. What grasses, trees, molds, and pollens affect her 39. A woman with hypertension is experiencing infertility. After reviewing her medication list, which medication does the nurse advise the woman to discuss with her primary care provider? A. Atenolol (Tenormin) B. Enalapril (Vasotec) C. Isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil) D. Methyldopa (Aldomet) 40. The nurse has educated a woman about bromocriptine mesylate (Parlodel). Which statement by the patient indicates that she needs more teaching about this drug? A. I may get a metallic taste in my mouth when using this drug. B. My endometriosis will regress with this medication. C. Some side effects include vomiting, headache, and dizziness. D. This medication normalizes follicle-stimulating hormone. 41. A woman has been taking progesterone via intramuscular injection. She calls the clinic to complain of swollen ankles. What response by the nurse is best? A. Advise her to come to the clinic for an EKG. B. Assess how much sodium is in her daily diet. C. Have her go to the nearest emergency department. D. Reassure her that this is a common side effect. 42. A woman is in the clinic complaining of frequent constipation. During the assessment, the patient states that she has been trying to conceive for many months. Which of the following should the nurse ask this patient about using? A. Bisocodyl (Dulcolax) suppositories B. Fleet enemas C. Psyllium (Metamucil) D. Senna (Senekot) MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. Masters and Johnson described the four phases of human sexual response. Which phases did they include? (Select all that apply.) A. Excitement B. Orgasm C. Plateau D. Resolution E. Response 2. A nurse is working with women and issues of reproductive health practices to help meet the National Health Goals related to reproductive life planning. Which goals are included in this document? (Select all that apply.) A. Increase the number of private pharmacies that supply emergency contraception. B. Increase the proportion of subsequent births to 18 months from 12 months. C. Increase the proportion of young males who receive reproductive health care. D. Reduce the number of publicly funded family planning clinics that offer abortion. E. Reduce the proportion of women with unplanned pregnancy despite contraception. 3. A couple is interested in fertility-awareness-based (FAB) family planning. The nurse should advise them about what drawbacks that accompany this method? (Select all that apply.) A. Depends on tracking cycles on a calendar B. Less than 50% effective in family planning C. May interfere with sexual spontaneity D. Requires months of charting cycles before use E. Requires a lot of motivation and education 4. The clinic nurse obtains a history from women who wish to use a cervical cap as their method of contraception. The nurse assesses for relative or absolute contraindications to this contraceptive device, including which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Patient is a commercial sex worker. B. Patient has history of an abnormal Pap test. C. Patient has human papillomavirus infection. D. Patient has silicone allergy. E. Patient is nulliparous. 5. The family planning clinic nurse reviews the signs and symptoms of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) with a patient who is being fitted for a diaphragm. The nurse explains that the patient should promptly seek medical attention if she develops which of the following manifestations? (Select all that apply.) A. Develops a generalized red rash B. Develops a fever over 101.1F (38.4C) C. Experiences difficulty breathing D. Feels lightheaded, is dizzy, or has chills E. Has swelling of the face or neck 6. The nurse teaches a patient the acronym ACHES for the serious symptoms that must be reported immediately when taking oral contraceptive pills. Which manifestations does this include? (Select all that apply.) A. Abdominal pain B. Chest pain C. Headaches D. Eye pain E. Sore muscles 7. The clinic nurse uses the acronym PAINS when teaching a woman about warning signs associated with her intrauterine device (IUD). Warning signs include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Breast tenderness B. Fever and/or chills C. Inability to feel the strings D. Spotting E. Vaginal discharge 8. A nurse is explaining contraceptive options to a young woman. What benefits of an IUD does the nurse describe? (Select all that apply.) A. Appropriate with dysmenorrhea B. No interference with spontaneity C. No daily attention required D. No hormonal side effects associated with the Copper T 380A E. One-time expense 9. A nurse is counseling women about the lactational amenorrhea method of contraception. Which of the following women would the nurse advise to use another method of contraception if pregnancy is not desired? (Select all that apply.) A. Baby is 5 months old and started on cereals. B. Baby is 8 months old; menses have not resumed. C. Baby is 4 months old; breastfed exclusively. D. Dad feeds 5-month-old baby the mothers stored breast milk. E. Mother uses breast pump while at work. 10. A woman has decided to have an elective abortion. What information can the nurse provide to make the experience less stressful and to better prepare her? (Select all that apply.) A. Average waiting time to be seen B. Cost and range of services provided C. How many patients the clinic sees D. How to access social services E. Potential for protesters to be present 11. A nurse is counseling a woman who wishes to undergo an elective medication abortion. The nurse should assess the woman for what psychosocial considerations? (Select all that apply.) A. Availability of a close friend who can stay with the woman B. Feeling that medication pregnancy termination is a natural, less stressful process C. Potential for trauma at seeing or handling the products of conception D. Previous use of alcohol or other substances for coping E. Type of birth control the woman plans to use after the abortion 12. A nurse is assessing a couple who are in the clinic complaining of an inability to get pregnant. Which questions are most important at this time? (Select all that apply.) A. Do you get up right after intercourse? B. Do you know how to track your cycle? C. How do you know when you ovulate? D. How often do you have intercourse? E. What sexual positions do you use? 13. A nurse is instructing a man on the correct procedure for semen analysis. Which instructions should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Abstain for 23 days before collecting the sample. B. Collect the sperm sample through masturbation. C. Have the sample in the laboratory within 3 hours of collection. D. Store the sample on ice while bringing it to the lab. E. Store the sample on your body during transport. 14. An infertility clinic nurse explains to the student that the process of sperm washing has several benefits. Which benefits should the nurse explain to the student? (Select all that apply.) A. Improves chances of fertilization B. Increases sperm motility C. Makes the sperm denser D. May correct sperm clumping E. Removes sperm impurities 15. The nurse is concerned about a woman who is undergoing her second in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle. The patient is anxious, sad, and worried that her partner does not feel as motivated as she does to try to achieve a pregnancy. Which actions by the nurse are most appropriate? (Select all that apply.) A. Ask the woman to consider herbal supplements like blue cohosh. B. Encourage the woman to talk honestly with her partner. C. Explain that it takes an average of five attempts to become pregnant with IVF. D. Instruct the woman to engage in relaxation techniques. E. Encourage the woman and her partner to contact a support group such as RESOLVE. 16. A nurse is teaching a couple about the postcoital test. What information should the nurse provide about the test? (Select all that apply.) A. It assesses the quality and quantity of cervical mucus at ovulation. B. It assesses the quality of sperm function at the time of ovulation. C. It may cause cramping and discomfort when samples are obtained. D. The woman should have nothing by mouth for 6 hours before the test. E. The woman should return to the clinic 6 to 12 hours after intercourse. 1. Place the following methods of birth control in order of their effectiveness, starting with the most effective. Condoms Depo-Provera Diaphragm Natural family planning Oral contraceptive pills Withdrawal Chapter 7: Conception and Development of the Embryo and Fetus MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A faculty member explains the Human Genome Project to a class of nursing students. Which information about this project is correct? A. It began in the 1980s to find the basic building blocks of human proteins. B. The findings will be used to create better matches for animal-to-human transplants. C. The goal is to identify exact DNA sequences and genes occurring in humans. D. Information from the project is being used to find preventative measures for diseases. 2. A nurse is interested in studying the functions and interactions of the genes in the human genome. What branch of science should this nurse pursue? A. Biology B. Genetics C. Genomics D. Inheritance 3. A nursing instructor is explaining genetic concepts to a class of students. Where in the cell does the instructor tell the students that each persons genes can be found? A. Golgi body B. Lysosome C. Mitochondria D. Nucleus 4. A couple wishes to determine the chances of having a blue-eyed baby. Both parents have brown eyes, but have heterozygous gene pairs for eye color. Calculate the odds of their having a child with blue eyes. A. 10% B. 20% C. 25% D. 50% 5. A nurse reads in a patients chart that the patient has a condition caused by monosomy X. What can the nurse conclude about this patient? A. Female with one missing X chromosome B. Female with very feminine features C. Male with one extra X chromosome D. Male with very feminine features 6. A nurse has completed a family pedigree on a patient with a known autosomal dominant inheritance disorder. No one else in the family has been affected by this disorder. How does the nurse explain this finding to the patient? A. Genetic variation occurred via a mutation. B. Information about the family is incorrect. C. The patient is not biologically related to the family. D. The patients diagnosis must be incorrect. 7. A nurse is counseling a couple whose child has been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. They understand that this is an inherited disease, but dont know how the child got it, as neither of them is affected. What response by the nurse is best? A. Are you certain that you (points to man) are the biological father? B. Maybe each of you has a mild case that hasnt been diagnosed yet. C. Something in your environment must have altered one of the genes. D. This is a recessive disorder, meaning that each of you is just a carrier. 8. A couple wishes to know the chances of passing on an X-linked dominant heritable disorder to their four sons. The fathers family has the disorder. The sons appear healthy, but the couple wants to be prepared for possible future events related to the disease. What information does the nurse give them? A. All of them will be affected. B. Half of them will be affected. C. None of your sons will be affected. D. One of the four will be affected. 9. A nursing faculty member is explaining the process of fertilization to a class of students. One student asks the instructor to clarify the term secondary oocyte. What description is best? A. An oocyte in the secondary position during transportation B. An oocyte in which the first meiotic division has occurred C. The second egg released by the ovary during ovulation D. The second egg to reach its place in the fallopian tube 10. The perinatal nurse understands that 4 days after fertilization, the morula now contains how many cells? A. 2 B. 4 C. 8 D. 16 11. The nursing faculty member explains to a class that embryonic stem cells have a special feature. Which feature is the instructor describing? A. Ability to develop into any type of human cell B. Able to nourish the blastocyst as it develops C. Gives rise to the embryo and placenta D. Secretes a mixture of lipids and other liquids 12. A student asks the faculty member to explain the term nidation. Which explanation is best? A. Blood vessel development B. Degradation of the zona pellucida C. Implantation of the fertilized ovum D. Sperm washing 13. The experienced perinatal nurse explains hormone function to a new graduate. Which hormone does the nurse describe as being responsible for regulating glucose availability for the fetus? A. Estrogen B. Human chorionic gonadotropin C. Human placental lactogen D. Progesterone 14. The perinatal nurse understands that maternal antibodies pass through the placenta by which mechanism? A. Active transport B. Facilitated diffusion C. Osmosis D. Pinocytosis 15. A student has read that hematopoiesis occurring in the wall of the yolk sac declines after the eighth week of gestation and asks the instructor for clarification. What statement by the faculty member is most accurate? A. All of the blood needed is transported across the placenta. B. Bone marrow production of blood begins in week 8. C. The fetal liver takes over that function then. D. You must have misread that information. 16. The nurse assessing a newborns umbilical cord stump would document which finding as normal anatomy? A. One artery, one vein B. One artery, two veins C. Two veins, two arteries D. One vein, two arteries 17. The perinatal nurse explains the function of Whartons jelly to a class of expectant parents. What description is most accurate? A. Collection of blood from the maternal circulation B. Gooey uterine substance that cushions the fetus C. Precursor cells from which blood cells originate D. Protects the umbilical cord from compression 18. The perinatal nurse is explaining blood transport though fetal circulation to the new nurse. How does the perinatal nurse describe the foramen ovale? A. Opening in the hearts septum between the right and left atria B. Vascular channel between the pulmonary artery and the descending aorta C. Vascular channel connecting the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava D. Vascular route connecting the heart to the extremities 19. A couple has been told that there is a problem with their pregnancy. They only remember the term ductus venosus. The nurse explains that there is a problem in the circulation between which two structures? A. Pulmonary artery and descending aorta B. Pulmonary vein and pulmonary artery C. Right and left atria in the heart D. Umbilical cord and inferior vena cava 20. A student reviewing the anatomy and physiology of fetal circulation learns that fetal blood enters the aorta through which structure? A. Ductus arteriosus B. Ductus venosus C. Foramen ovale D. Portal circulation 21. A student reviewing the anatomy and physiology of the fetal circulatory system learns that the highest concentration of oxygen in fetal blood is measured at what level? A. 1020 mm Hg B. 2025 mm Hg C. 3035 mm Hg D. 4050 mm Hg 22. A student asks the faculty member to explain why the fetus has such a low PO2. What explanation by the faculty member is most accurate? A. Blood from the mother is deoxygenated. B. It keeps the ductus arteriosus open. C. It maintains the maternal circulation. D. It supports the foramen ovale. 23. The nurse discussing fetal development describes the hormone responsible for suppressing the maternal immunological response to the fetus, thereby facilitating physiological acceptance of the pregnancy. Which hormone is the nurse describing? A. Estrogen B. Human chorionic gonadotropin C. Human placental lactogen D. Progesterone 24. A clinic nurse explains to a pregnant woman that the amount of amniotic fluid present at 7 or 8 months gestation is approximately what volume? A. 500 mL B. 750 mL C. 800 mL D. 1,000 mL 25. A pregnant woman is confused about the terms embryo and fetus. How does the nurse explain the difference? A. The baby cant be called a fetus until the limbs and organs have formed. B. The baby is an embryo until 8 weeks gestation; then it is called a fetus. C. There really isnt any difference between the terms; they are interchangeable. D. Your baby is a fetus until the kidneys are matured and he makes urine. 26. A nurse teaching a prenatal class instructs the participants that early organ system development occurs during which period of time? A. Embryonic period B. Fetal period C. Pre-embryonic period D. Post-embryonic period 27. A woman is starting on birth control, but tells the nurse she wants to become pregnant next year. What action by the nurse is most important? A. Ask the woman to describe how her life will be different in the next year. B. Educate the woman about the need for folic acid supplementation before conceiving. C. Have the woman make a pre-pregnancy appointment for next year before she leaves. D. Tell the woman that it is difficult to get pregnant right after stopping birth control. 28. A newborn has rachischisis. What action by the nurse takes priority? A. Contact the palliative care team for interventions. B. Discourage the family from seeing the infant. C. Obtain informed consent for immediate surgery. D. Prepare to provide the baby total parenteral nutrition. 29. A woman in her 26th week of pregnancy is in preterm labor. What can the nurse conclude about this babys ability to survive? A. Cannot survive, as all organ systems are too immature B. Might survive, as lungs can breathe air with rhythmic breathing C. Probably will not survive, as all organ systems have not formed D. Will survive, because all body systems are completely mature 30. A baby is born with several congenital anomalies. The parents are distraught and begin questioning each other about what they did wrong during the pregnancy. What response by the nurse is best? A. Chances are you did everything right; we may never know why this happened. B. Usually these types of issues result from toxic environmental exposures. C. You are lucky you did not have a miscarriage and instead have a wonderful baby. D. You cant worry about that now; you have a baby who needs you. 31. A nurse is assessing a pregnant woman who says she drinks 5 to 7 alcoholic drinks per week. What action by the nurse is best? A. Advise the woman to decrease her drinking to 3 to 4 drinks per week. B. Explain that during pregnancy, alcohol in any amount can harm the fetus. C. Teach her that for women, the safe alcohol limit is 1 drink in an hour. D. Tell the woman to substitute caffeinated beverages for the alcohol. 32. A preterm infant is jittery and has an oxygen saturation of 88%. After stabilizing the newborn, what action by the nurse is most important? A. Assess the mother for caffeine use during pregnancy. B. Assess the mother for opioid use during pregnancy. C. Call Child Protective Services (CPS) to take the child away. D. Question the father about maternal drug abuse. 33. A neonate whose mother is a drug addict is listless and sweating. What action by the nurse takes priority? A. Check the babys blood sugar. B. Have the mother hold the baby to her skin. C. Obtain an oxygen saturation. D. Place the baby on a cardiac monitor. 34. A pregnant woman tells the perinatal nurse that she stopped abusing other drugs when she learned that she was pregnant but kept using marijuana because it is so harmless. What response by the nurse is best? A. Agree with the patient that marijuana is less dangerous than other drugs. B. Ask the patient what other drugs she used before discovering she was pregnant. C. Inform the mother that the child may have withdrawal syndrome after birth. D. Tell the mother that marijuana use can affect language and cognitive development. 35. A male baby is born with undescended testes. After caring for the newborn, what question by the nurse is most important? A. Did your other children have this problem? B. Do you have cats and litter boxes at home? C. Have you been exposed to measles? D. How old is the house in which you live? 36. The prenatal clinic nurse is providing information to a pregnant woman who is at 15 weeks gestation. The patient asks when she should expect to feel fetal movement. Which of the following is the most appropriate answer by the nurse? A. 15 to 18 weeks B. 17 to 20 weeks C. 18 to 21 weeks D. 20 to 24 weeks 37. During preconception counseling, the nurse explains that the fetus is most vulnerable to the effects of teratogens during which time period? A. 2 to 8 weeks B. 4 to 12 weeks C. 5 to 10 weeks D. 6 to 15 weeks 38. During prenatal classes for expectant parents, the perinatal nurse explains that fetal brain development is most critical during which gestational weeks? A. 2 to 8 B. 3 to 16 C. 5 to 24 D. 6 to 14 39. The birthing center nurse caring for a 21-year-old laboring woman is given a report about the patients cocaine use throughout pregnancy. This history prompts the labor nurse to assess for which condition? A. Abruptio placentae B. Cephalopelvic disproportion C. Hypotension D. Placenta previa 40. The birthing center nurse is assisting with pain management for a laboring woman at 18 weeks gestation. The fetus is born and the weight is 450 gm. The nurse would document this birth as which of the following? A. Abortion B. Fetal loss C. Neonatal death D. Stillbirth ANS: A The loss of a fetus before 20 to 22 weeks of gestation is referred to as an abortion because the fetus is considered too immature to survive outside the uterus. Fetal loss and neonatal death are not medical terms. Stillbirth is the intrauterine death of a fetus old enough to survive outside the womb. 41. A 26-year-old woman has come for preconception counseling and asks about caring for her cat, because she has heard that she should not touch the cat during pregnancy. Which of the following is the nurses best response? A. If someone else changes the litter box you should be okay. B. It is more important to avoid eating raw vegetables now. C. That is correct; in fact, you should give the cat away. D. You probably already have had toxoplasmosis from the cat. ANS: A Toxoplasmosis is usually acquired by consuming raw or poorly cooked meat that has been contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasmosis may also be acquired through close contact with feces from an infected animal (usually cats) or soil that has been contaminated with T. gondii. The nurse should advise the woman to avoid poorly or undercooked meat and changing the cats litter box. The other statements are inaccurate. 42. A couple has undergone prenatal testing and their fetus has an identified congenital anomaly. What action by the nurse is best? A. I know how you feel; my daughter has a cleft lip. B. Im sure you will come to love your baby anyway. C. It is normal for both of you to be afraid, sad, or angry. D. You are lucky you found out now and can prepare. ANS: C The nurse plays an important role in situations such as this by providing support and education. The nurse should use empathetic and therapeutic communication and be sure to include the father. The other statements are not examples of therapeutic communication and sound dismissive. 43. A baby is born with trisomy 18. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Allow the family members to express their grief and anger. B. Call the hospital chaplain to counsel the parents. C. Make a referral to a home health agency for home visits. D. Prepare the parents for the babys imminent death. ANS: A Trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome) is a rare genetic disorder with a poor prognosis; approximately 70% of infants die within the first 3 months of life. The nurse should allow the family to grieve. The parents may or may not welcome a visit from a religious person and the nurse should ask them before calling a chaplain. A home health-care agency may or may not be needed; further assessment is needed. The baby may not die immediately, so preparing the parents for an imminent death is unwarranted. 44. An obstetrical nurse is taking a medication history from a pregnant woman. One of the womans medications is classified as category D. What action by the nurse is best? A. Advise her to stop the medication right away. B. Encourage her to find herbal substitutions. C. Have her call her primary care provider immediately. D. Tell her to cut the medication dose in half until she gives birth. ANS: C A category D medication is one with well-documented risks to the fetus. In some situations, this may be acceptable if the medication is prescribed for a life-threatening situation or for a disease for which safer drugs cannot be used or do not exist. The nurse should help the woman contact her primary care provider during the OB visit to discuss the continued used of the medication. The nurse should not advise the woman to just stop the medication; she needs to discuss this with the primary care provider, but that needs to be accomplished quickly. The nurse should not encourage substituting herbal preparations or cutting the medication dose in half. 45. A parent wonders why his baby needs all the blood samples to test for different diseases. What response by the nurse is best? A. Many serious disorders can be found before they cause damage or death. B. This is a hospital policy; if you want to opt out you need to sign a waiver. C. We see a lot of these diseases in our community so we screen for them. D. Your baby doesnt need the blood tests if you dont want them. ANS: A Newborn screening was the first population-based screening program to test for genetic conditions. Many diseases that cause an increased risk for infection, liver damage, mental retardation, or even death can often be identified through these tests. The hospital may require an opt-out waiver, but this is not the best initial answer. Some of the diseases are uncommon but potentially devastating, so the screening is not done for diseases only seen in one community. Parents can opt out of some or all tests, depending on the state in which they live, but the nurse should first educate the parent about why the tests are so important. 46. A woman is admitted with rubella. What action by the nurse manager is best? A. Place the woman on droplet precautions. B. Put the woman in contact isolation. C. Tell the nurses to use good hand-washing techniques. D. Use standard precautions only. ANS: A Rubella (German measles) is spread through respiratory droplets. The patient should be put on droplet precautions. Nurses should use good hand-washing techniques for all patient contacts. 47. A newborn nursery nurse is arranging genetic screening for several newborns. The nurse should educate the parents of which baby about screening for Tay-Sachs disease? A. African American baby B. Asian baby C. Caucasian baby D. Jewish baby ANS: D Tay-Sachs disease is the most common genetic disease among people of Jewish ancestry. The nurse should educate the parents with Jewish ancestry about screening for this disease. 48. A pediatric nurse is reviewing the chart of a new school-age patient. The chart notes the child is on a phenylalanine-free diet. What does the nurse conclude about this patient? A. Has Canavan disease B. Has familial dysautonomia C. Has phenylketonuria (PKU) D. Has Tay-Sachs disease ANS: C Children with PKU are born without an enzyme to metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine. If not treated with a life-long phenylalanine-free diet, the child can have severe mental and physical retardation. The other diseases do not require this diet. 49. A student has read that fetal development progresses in a cephalocaudal fashion and asks the faculty member for clarification. What explanation by the faculty member is best? A. From feet to head B. From head to feet C. Inward to outward D. Outward to inward ANS: B Cephalocaudal development proceeds from head to feet. 50. A nursing student asks the faculty member to define lanugo. Which description is best? A. Fine, downy hair on the fetus B. Immune complexes in the amniotic fluid C. Initial scalp hair on the fetus D. Outer layer of pale, wrinkled skin ANS: A Lanugo is the fine, downy hair seen on fetuses. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The perinatal nurse explains to a childbirth class that which of the following are the primary functions of the placenta? (Select all that apply.) A. Creates blood vessels in the fetus B. Protects the fetus from pathogens C. Provides hormones that maintain the pregnancy D. Removes waste products from the fetus E. Transfers nutrients to the fetus ANS: B, C, D, E The placenta serves several functions, including providing nutrition and oxygen to the fetus, carrying waste products away from the fetus, providing hormones that help to maintain the pregnancy, and protecting the fetus from pathogens. The placenta does not create blood vessels in the fetus. 2. The perinatal nurse explains to a student the different mechanisms by which substances are transported across the placenta. Which mechanisms are included? (Select all that apply.) A. Active diffusion B. Bulk flow C. Endocytosis D. Osmosis E. Pinocytosis ANS: A, B, C, E Several mechanisms exist to transport substances across the placenta. These include passive or simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active diffusion, pinocytosis, endocytosis, bulk flow, accidental capillary breaks, and independent movement. 3. The nursing instructor is explaining mechanisms of substance transport across the placenta. Which substances require facilitated diffusion? (Select all that apply.) A. Carbon dioxide B. Fatty acids C. Globulins D. Glucose E. Oxygen ANS: D, E Glucose and oxygen require facilitated diffusion to cross the placenta. Carbon dioxide and fatty acids move by simple diffusion. Globulins move via pinocytosis and endocytosis. 4. The nursing instructor is explaining the function of the placenta in hormone production. Which hormones does the instructor include in this discussion? (Select all that apply.) A. Estrogens B. Human chorionic gonadotropin C. Human placental lactogen D. Luteinizing hormone E. Progesterone ANS: A, B, C, E The placenta produces four main hormones: estrogens, human chorionic gonadotropin, human placental lactogen, and progesterone. Luteinizing hormone is produced in the anterior pituitary gland. 5. During prenatal class, the nurse teaches expectant couples about the importance of the amniotic fluid and its functions. What functions does the nurse describe? (Select all that apply.) A. Cushions the fetus from mechanical injury B. Facilitates symmetrical growth of fetal limbs C. Helps regulate fetal body temperature D. Provides nourishment to the fetus E. Prevents the amnion from adhering to the fetus ANS: A, B, C, E Amniotic fluid allows for symmetrical fetal growth, cushions the fetus from mechanical injury, and aids in fetal musculoskeletal development. Amniotic fluid prevents adherence of the amnion to the fetus and is essential for normal fetal lung development and temperature regulation. Amniotic fluid does not provide nourishment to the fetus. 6. The nurse explaining fetal growth and development to a class of expectant parents describes events that occur during weeks 9 to 12 as which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. External genitalia are distinguishable. B. Hair appears on the eyebrows and head. C. Intestines become visible in the abdomen. D. Ossification centers appear in the skeleton. E. Rapid eye movements occur and fingernails form. ANS: A, C, D During gestational weeks 9 to12 several events occur: distinguishable external genitalia appear, ossification centers in the skeleton appear, and the intestines leave the umbilical cord to become an abdominal organ. Hair growth occurs during weeks 17 to 20. The baby develops rapid eye movements and fingernails during weeks 21 to 25. 7. A perinatal nurse is assessing a woman who is approximately 10 weeks pregnant. The woman smells like cigarette smoke. What actions by the nurse are best? (Select all that apply.) A. Advise her to stop smoking now so that the baby can be of normal weight. B. Ask the woman if either she or her partner smokes. C. Determine how many cigarettes she smokes a day. D. Describe the behavior problems her child may develop. E. Explain that nicotine deprives the fetus of oxygen. ANS: A, B, E If the nurse smells cigarette smoke, assessing the woman for smoking or exposure to second-hand smoke is appropriate. Exposure to nicotine causes vasoconstriction and deprives the fetus of essential oxygen and nutrients needed for growth and development. Consequences include low birth weight and small-for-gestational-age babies. If the woman stops smoking during the first trimester, the baby will have a similar birth weight to babies whose mothers did not smoke. The absolute number of cigarettes per day is not as important as determining if she does smoke and advising her to quit now. Childhood behavior problems are often attributed to cocaine use during pregnancy. 8. A nurse is assessing a woman for TORCH infections. What diseases are included in this acronym? (Select all that apply.) A. Cytomegalovirus B. Hepatitis B C. Roseola D. Toxoplasmosis E. Varicella zoster ANS: A, B, D, E TORCH stands for toxoplasmosis, other infections, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus. Other infections include varicella zoster virus, human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, human parvovirus B19, and syphilis. Roseola is not included. 1. Match each term with its definition or description. a. Autosome 1. _____ Large female chromosome b. X chromosome 2. _____ Gene pair in which the gene pairs are different c. Y chromosome 3. _____ Genetic makeup of an individual d. Homozygous 4. _____ Observable expression of a persons genotype e. Heterozygous 5. _____ Non-sex chromosome common to both males and females f. Genotype 6. _____ Smaller male chromosome g. Genome 7. _____ Gene pair in which both genes are identical h. Phenotype 8. _____ Complete set of genes present in a person ANS: 1b, 2e, 3f, 4h, 5a, 6c, 7d, 8g An autosome is a non-sex chromosome common to both males and females. The X chromosome is the larger female chromosome, whereas the Y chromosome is the smaller male chromosome. Homozygous gene pairs have identical genes, whereas heterozygous gene pairs have differing genes. A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual. The genome is the complete set of genes present in each person. The phenotype is the observable genetic differences expressing a persons genotype, such as hair and eye color. 2. Match each TORCH disease with its possible effects on the newborn or characteristics. Diseases may be used more than once or not at all. a. Toxoplasmosis 1. _____ Without intervention, maternal transmission to the fetus is about 25% b. Rubella 2. _____ The most common viral infection in the fetus c. Cytomegalovirus 3. _____ Bullae, microcephaly, hydrencephaly, and encephalitis can occur d. Herpes simplex virus 4. _____ No known risks if infection occurs after 20 weeks gestation e. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) 5. _____ Late manifestations include keratitis, snuffles, deafness, and bowing of the shins f. Varicella zoster virus 6. _____ Symptoms in the mother seem to be flu-like g. Syphilis 7. _____ Maternal infection in the first trimester can lead to spontaneous abortion 8._____Maternal infection during the first trimester leads to a 20% chance of fetal infection ANS: 1e, 2c, 3d, 4f, 5g, 6a, 7c, 8b Toxoplasmosis has symptoms often referred to as flu-like. Maternal infection with rubella in the first trimester leads to a 20% chance of the fetus being infected. Cytomegalovirus is the most common viral infection in the fetus, and spontaneous abortion may result from maternal CMV infection in the first trimester. Herpes simplex infection leads to manifestations such as bullae, microcephaly, hydrencepahly, and encephalitis. Without medical intervention, vertical (maternal-to-child) transmission of HIV is about 25%. Varicella zoster virus carries no known risk to the fetus after 20 weeks gestation. Late syphilis symptoms include keratitis, snuffles, deafness, and bowing of the shins. Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 3. Trace a drop of blood through the fetal circulation using the structures provided. _____ Aorta _____ Ductus arteriosus _____ Ductus venosus _____ Foramen ovale _____ Head and extremities _____ Left ventricle _____ Right atrium _____ Superior vena cava ANS: 5, 8, 1, 3, 6, 4, 2, 7 Blood travels through the fetus in a unique pattern. Most blood enters the inferior vena cava through the ductus venosus, empties into the right atrium, and passes through the foramen ovale into the left atrium. It then travels to the left ventricle, into the aorta, and out into the rest of the systemic circulation. Blood returns to the heart from the head through the superior vena cava, goes through the right side of the heart before entering the pulmonary artery, or bypasses the lungs and enters the aorta through the ductus arteriosus. Chapter 8: Physiological and Psychosocial Changes During Pregnancy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse has learned that which hormone is primarily responsible for maintaining a pregnancy? A. Estrogen B. Human chorionic gonadotropin C. Oxytocin D. Progesterone ANS: D Progesterone is the hormone primarily responsible for maintaining a pregnancy. Estrogen promotes hyperplasia and hypertrophy during pregnancy. After implantation, the trophoblast secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, which prompts the corpus luteum to continue progesterone production until the placenta takes over the job. Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions during labor. 2. A patient who is 28 weeks pregnant calls the obstetrical clinic and complains of irregular, painless contractions that last for 10 to 15 seconds. What response by the nurse is best? A. If they last more than 60 seconds or become regular, come in. B. Oh, you are just having what are called Braxton Hicks contractions. C. Pregnant women often experience this type of contraction. D. You should come in to the clinic as soon as possible today. ANS: A Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular and painless and last less than 60 seconds. Their function is to prepare the uterine muscles for effective labor. If they become regular or last longer than 60 seconds, the woman needs medical attention. The other statements all contain some truthful information, but none provides the woman with the knowledge she needs to remain healthy. 3. The nurse caring for perinatal patients understands the term decidua to mean which of the following? A. Collateral uterine circulation B. Endometrial lining of the uterus C. Endometrial tissue covering the embryo D. Placental remnants left in the uterus ANS: B The decidua is the endometrium lining the uterus and consists of three layers. The decidua capsularis is the endometrial tissue that covers the embryo. Decidua does not refer to collateral circulation or placental remains. 4. A nurse is assessing a patient in the womens clinic for Chadwicks sign. How does the nurse perform this assessment? A. Auscultates the womans abdomen for fetal heart tones B. Inspects the vulva and vagina for a bluish tint C. Palpates the womans abdomen for a fluid wave D. Percusses the womans abdomen for uterine margins ANS: B Chadwicks sign is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy and consists of a bluish discoloration of the cervix, vulva, and vagina. The nurse would inspect the woman for this discoloration. 5. An instructor is explaining to students in the OB rotation that Goodells sign is which of the following? A. Bluish cervical discoloration B. Cervical softening C. False labor contractions D. Slowed fetal heart tones ANS: B Goodells sign is softening of the cervix that occurs due to hormonal influences. It is not related to fetal heart tones or contractions. Chadwicks sign is a bluish discoloration of the cervix, vulva, and vagina. 6. A nurse is teaching a woman who is in her first trimester of pregnancy about physical changes she can expect. Which information should the nurse provide? A. Diminishing sexual interest occurs. B. Harmful agents are able to invade the uterus. C. Leukorrhea is an abnormal condition. D. Pregnant women are more susceptible to yeast infections. ANS: D Glycogen levels are increased in vaginal cells during pregnancy, and this change creates an environment more hospitable to Candida albicans. Thus pregnant women are more susceptible to yeast infections. For some women, the increased pelvic congestion leads to increased sexual interest and orgasmic ability. Harmful agents are kept out of the uterus by the mucus plug. Leukorrhea is a normal finding in pregnancy due to hyperplasia of the vaginal mucosa and increased mucus production from the endocervical glands. 7. A woman who gave birth 2 months ago calls the perinatal clinic crying because her hair is falling out in large amounts. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Advise the woman to make an appointment with a dermatologist. B. Explain that this symptom will end once she stops breastfeeding. C. Reassure the woman that her hair will grow back within a year. D. Tell the woman its really extra hair that grew in pregnancy. ANS: C New hair growth may be stimulated during pregnancy, but after birth, this process reverses and hair shedding occurs for 14 months. Virtually all hair will be replaced within 612 months. The nurse should educate the woman about this natural process. Although telling the woman that she had extra hair in pregnancy is accurate, simply stating this fact does nothing to ease her distress. The woman does not need to see a dermatologist. The process is not related to breastfeeding. 8. A pregnant woman in the perinatal clinic complains of a diffuse, reddish discoloration of her palms. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Ask if she has been exposed to measles. B. Assess her for Reynauds phenomenon. C. Explain that this is a normal finding. D. Take the womans vital signs. ANS: C Palmar erythema is a reddish discoloration of the palms and occurs in about 60% of Caucasian women and in about 35% of African American women during pregnancy. Although the nurse should assess the patients vital signs during the visit, there is no need to do so specifically tied to this condition. Palmar erythema is not related to measles or Reynauds phenomenon, which is a vascular condition. 9. A woman in her third trimester of pregnancy complains of a painful burning sensation in her hands and lower arms. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Advise the woman to elevate her hands at night. B. Document the finding and alert the provider. C. Encourage the woman to see a neurologist. D. Request a prescription for pregabalin (Lyrica). ANS: A Edema that occurs during pregnancy can lead to fluid collection in the wrist and puts pressure on the median nerve. This leads to carpal tunnel syndrome, characterized by burning pain and paresthesia in the (usually dominant) hand or hands up to the elbow. The nurse should advise the woman to elevate her hands at night. Carpal tunnel syndrome usually resolves after pregnancy, but if it persists, the woman may require surgical treatment. The nurse should always document abnormal findings and alert the provider, but further action is needed. Lyrica is used for nerve pain and would not be suggested here. 10. A pregnant woman in the perinatal clinic complains of occasional fainting. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Educate her that this is a frequent occurrence in pregnancy. B. Encourage her to carry small snacks with her at all times. C. Instruct her to lie down when the warning signs occur. D. Tell her to lie down on her left side if she has warning signs. ANS: D Syncope, or fainting, is occasionally seen in pregnancy and is often preceded by warning signs such as lightheadedness, sweating, nausea, yawning, or sensations of warmth. The nurse should instruct the woman to sit or lie down when these warning signs occur. Lying on the left side is preferred to avoid compressing the vena cava. Simply saying that this occurs frequently does not help the woman take care of herself. This symptom is not related to food intake. 11. A woman in the emergency department is in her third trimester and is bleeding heavily from a laceration on her thigh from a car crash. She is pale and diaphoretic. Her blood pressure is 138/82 mm Hg. What can the nurse conclude from this information? A. Blood loss from the laceration has not been that great. B. She is in shock from the trauma of the injury and blood loss. C. Her increased blood volume is maintaining the blood pressure. D. Her vital signs and physical assessment do not match. ANS: C Maternal blood volume increases by 40 to 50% near term. The nurse would expect the blood pressure to be low due to the blood loss, but the pregnancy-related extra volume is maintaining the blood pressure at normal levels. The vital signs and physical assessment do not match, but that is vague and does not explain the inconsistency. The patient is not in shock. 12. A woman in the third trimester of her first pregnancy complains of excessive fatigue. Her hemoglobin is 11.2 g/dL. What action by the nurse is best? A. Arrange hospital admission for blood transfusions. B. Assess the womans diet for adequate iron and protein. C. Inform the woman that this is a normal finding in pregnancy. D. Tell the woman to get more sleep at night and to take naps. ANS: B Anemia of pregnancy occurs mainly due to hemodilution. The mean acceptable hemoglobin level in pregnancy is 1112 g/dL. Some women experience fatigue due to this change. Sleep disturbances can contribute to the fatigue, but the nurse should ensure that the woman is adequately hydrated and is eating a diet high in protein and iron. She does not need transfusions. Informing the woman that this is normal does not give her the information she needs to care for herself. If sleep disturbances are a contributing factor, extra sleep can help. 13. A woman in her second trimester of pregnancy is in the clinic for a checkup. She complains of feeling short of breath at times. Her lungs are clear and her oxygen saturation is 98%. Her vital signs are all normal. What action by the nurse is best? A. Alert the provider to the symptoms. B. Encourage slow, deep breathing. C. Document the findings. D. Facilitate a chest x-ray. ANS: B Many pregnant women verbalize an increased awareness of the need to breathe and can perceive this as dyspnea. Because there are no other abnormalities, the nurse should reassure the woman that this is normal and encourage slow, deep breathing while resting with the head elevated. 14. The perinatal nurse reads the diagnosis of ptyalism in a patients chart. What teaching does the nurse plan for this patient? A. Chew food thoroughly before swallowing. B. Drink plenty of decaffeinated beverages. C. Eat something before getting up in the morning. D. Lozenges and chewing gum can help. ANS: D Ptyalism is excessive production of saliva. The etiology is uncertain, but chewing gum and using lozenges can offer limited relief. The other measures are not helpful for this condition. 15. A pregnant woman is complaining of frequent heartburn. What statement by the patient indicates to the nurse that teaching has been effective? A. Drinking less alcohol should prevent this. B. Eating larger, less frequent meals will help. C. I should take antacids before each meal. D. I will not lie down for 1 hour after eating. ANS: D Heartburn, or pyrosis, occurs due to changes in the function of the cardiac sphincter, which allows reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. Self-care measures for this condition include eating small meals and remaining upright for at least an hour after meals. Antacid use should be limited. Pregnant women should not drink alcohol at all. 16. A student asks the nurse why so many pregnant women get cholecystitis. Which response by the nurse is best? A. Inefficient emptying leads to stasis of bile and inflammation, or cholecystitis. B. Pregnant women crave high-fat foods that cause gallbladder irritation. C. Some pregnant women have a genetic predisposition to gallbladder problems. D. Vascular changes to the liver capsule cause bile to back up into the gallbladder. ANS: A The gallbladder muscle becomes more relaxed during pregnancy, resulting in inefficient emptying. Stasis of the bile occurs, which then leads to infection or inflammation (cholecystitis). High-fat meals can worsen the symptoms, which include epigastric pain. However, this is not the primary etiology. This condition is not related to genetic predisposition and liver vascular changes. 17. What information should the nurse plan to teach a pregnant woman regarding safety in the third trimester? A. Dont drive after dark. B. Exercise to maintain good posture. C. Use handrails when using the stairs. D. Wear supportive shoes. ANS: C Pregnant women experience laxity of the ligaments, separation of the pubis symphysis, and changes in their center of gravity, which places them at risk for falling. The most immediate action the woman can take is to use caution when negotiating stairs. Exercise can help with toning abdominal muscles and can reduce some of the symptoms of these changes, but results take time. Wearing supportive shoes and avoiding driving after dark are not related. 18. A pregnant woman calls the clinic to complain of sharp, right-sided lower abdominal pain. Which question by the nurse would elicit the most relevant information? A. Do you have a fever, constipation, or any diarrhea? B. Have you fallen down or experienced any kind of injury in the last few days? C. Have you tried placing either a heating pad or an ice pack on your abdomen? D. Is the pain worse between your navel and hip bone or closer to the hip? ANS: A Sharp pain in the lower abdomen is frequently due to round ligament pain. However, more serious conditions need to be ruled out first. Appendicitis must be considered. Because the appendix is pushed up and posterior by the uterus, the typical location of pain on the right side between the umbilicus and anterior iliac crest (McBurneys point) is not accurate. The nurse should ask about fever or changes in bowel habits. Trauma is not as likely a cause of this pain. After ruling out a serious medical condition, the nurse can advise the patient to use heat to help relieve the pain. 19. According to Rubin (1975), completion of what task is paramount for a pregnant woman to master in order to have successful integration of the maternal role? A. Incorporating the pregnancy into her total identity B. Learning to adapt to all the physiological changes C. Recognizing a before pregnant and after pregnant self D. Reorienting all relationships to put the pregnancy first ANS: A According to Rubin (1975), there are specific tasks a pregnant woman must accomplish to integrate the maternal role into her identity. In order to accomplish these tasks, the pregnant woman has to incorporate the pregnancy into her total identity. The other tasks are not part of Rubins theory. 20. A father accompanies his partner to her OB clinic visit. The woman is near term. The father confides to the nurse that the patient is cranky, irritable, and yells at him for no reason. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Explain why the woman needs emotional support. B. Instruct the mother to get more rest during the day. C. Reassure the father that this behavior is normal in pregnancy. D. Teach the father assertive communication skills. ANS: A As they near term, women are tired and looking forward to the end of the discomforts of pregnancy. Women at this stage need considerable emotional support from family and friends as they await childbirth. The nurse should explain these psychological changes in the woman and encourage the father to be as supportive as possible. Simply reassuring the father of the normalcy of this situation does not help him or help the woman. More rest might be helpful to some women. Assertive communication skills are not as important as knowing how best to support the woman at this time. 21. The nurse is explaining to a student that a pregnant woman needs to complete a process called binding in. Which is the best explanation of this phenomenon? A. Becoming excited about the impending childbirth B. Incorporating the pregnancy into the womans reality C. Learning to not focus on ones own discomforts D. Renegotiating roles within the womans family ANS: B Binding in is the process in which the woman accepts the pregnancy and incorporates it into her total reality and self-concept. The other options are all small parts of this process. 22. A woman is in her second trimester of pregnancy. Which behaviors by the womans family or friends would best indicate to the nurse that they are accepting the unborn child? A. An older sibling is talking about my baby brother or sister. B. Close friends throw a baby shower for the expectant mother. C. Immediate family members express delight over the pregnancy. D. The parents state that no matter what the gender, they will love the baby. ANS: A Accepting the unborn child is critical to adjusting successfully to the pregnancy. For this woman in her second trimester, having immediate family members begin relating to the unborn child is consistent with their place in the family. A sibling talking about being a big sister or big brother to the new baby is an example. In the first trimester friends and family need to accept the pregnancy and unborn child. In the third trimester, the woman must develop unconditional acceptance of the child. 23. A woman is in the first trimester of her first pregnancy and confides to the nurse that she is not really sure if she is happy because so many things in her life will change. She is not sure she is willing to alter her current lifestyle. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Ask the woman if she would like to see a counselor. B. Reassure the woman that ambivalence is normal now. C. Refer the woman to an expectant-mother support group. D. Tell the woman she needs to think of her unborn child. ANS: B An expectant mother must learn to give to her unborn child in the process of successfully negotiating the tasks of pregnancy. It is normal for a first-time mother to grieve for the impending loss of her lifestyle. The nurse should reassure the woman. A referral to a support group may be helpful for some women. The woman probably does not need a counselor. Telling the woman to think of the unborn child is disrespectful and dismissive. 24. To provide anticipatory psychosocial guidance to a woman entering her third trimester, what topic should the nurse plan to include? A. Extreme fatigue may make the woman very vulnerable at the end. B. She may feel overwhelmed with the physical discomforts of pregnancy. C. Initial feelings of uncertainty will go away at childbirth. D. She may worry about impending childbirth but see it as a relief. ANS: D Around the seventh month of pregnancy, the woman begins to feel extremely vulnerable and worries about the impending labor and birth. At the same time, she is exhausted and sees this event as delivering her from the pregnancy. This contradiction can be disconcerting for some women who have not been educated about the normalcy of its occurrence. Fatigue is not the driving force for the vulnerability, although it can contribute to it. Uncertainty about ones ability to be a parent can continue past childbirth. Concern with physical discomforts is more acute in the first trimester for most women. 25. A nurse works with pregnant adolescents during pregnancy and for the first 2 years afterward. Which teen demonstrates the most successful resolution of the conflict between normal growth and development tasks and tasks associated with being a new mother? A. Attends alternative school with an on-site day care B. Lives at home with parents who care for the infant C. Needs strong encouragement to keep appointments D. Plans activities around the baby one day at a time ANS: A The teen mother has conflicting developmental tasks to negotiate. Adolescents must develop a personal value system; choose a vocation/career; develop body image, sexuality, and a stable identity; and attain independence from their parents. The teen who continues to go to school with an on-site day care is providing child care for her baby and finishing her education, both of which are role-appropriate. The teen whose parents care for the infant is not fully involved as a mother. The teen who needs strong encouragement to keep appointments and the teen who only plans activities one day at a time are not future oriented. 26. A woman is in her fourth month of pregnancy and is in the clinic for a scheduled visit. She confides to the nurse that her husband seems detached and is no longer interested in hearing about the pregnancy. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Explain that paternal reactions vary widely. B. Offer a referral to a marriage counselor. C. Reassure the woman that this behavior changes after the birth. D. Tell her that men are usually jealous of the baby. ANS: A Mens reactions to pregnancy and impending childbirth vary widely, from alienation to nurturing to dominance. The nurse should provide guidance by explaining the different paternal responses. A referral to a marriage counselor may or may not be needed. Simply reassuring the woman that this behavior will go away is not accurate or helpful. Stating that men are usually jealous is stereotypical and inaccurate. 27. A nurse is working with a woman in her second trimester and her partner. The partner comes to clinic appointments but spends his time texting on his cell phone in the waiting room. The woman states that this behavior makes her sad. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the father to turn off his cell phone in the clinic. B. Assess the woman for ongoing relationship problems. C. Invite the father into the exam room to listen to the babys heartbeat. D. Refer the couple to counseling for depression. ANS: C Fathers have developmental tasks to accomplish during a womans pregnancy. During the second trimester, a father may seem disconnected and binding in may take longer than it did for the mother. This may be due to the remoteness of the fetus and father. Actions that can make the baby seem more real to the father will be helpful. A warm invitation to come into the exam room and listen to fetal heart tones is the best option. Asking the father to turn off his cell phone is likely to be perceived as disrespectful and will not be helpful. Assessing for relationship problems and referring the couple for counseling may be indicated in some situations, but is not the best choice here. 28. A nurse manager on the high-risk OB unit wants to improve the experience of women admitted for lengthy stays. What action by the manager is best? A. Designate a specific chaplain to visit women every day. B. Develop a program to help women attain developmental tasks. C. Initiate primary nursing to provide consistency in caregiving. D. Provide open visitation and special events for siblings. ANS: B Although all options can be very beneficial, the biggest challenge women in the high-tech environment of this unit face is stress that hinders development of their maternal role. One solution may be a program specifically designed to help women negotiate their roles and prepare for parenting. Of course, spiritual care should be respectful of individual beliefs. 29. A woman has given birth to a child with a cleft lip. What action by the patient would best indicate that goals for the diagnosis of dysfunctional grieving have been at least partially met? A. Birth announcements include photo and wording to explain cleft lip. B. Father accepts information about a cleft lip/cleft palate support group. C. Mother watches demonstration of holding baby appropriately for feeding. D. Parents express concern about their abilities to care for the baby. ANS: A Dysfunctional grieving (or other types of grieving) can occur with perinatal loss, including birth of a less-than-perfect child. When the parents demonstrate acceptance of the child as he or she is, they are meeting a goal for this diagnosis. Sending birth announcements with photos and wording to explain the anomaly demonstrate that they accept the child and expect others to do so as well. Passively accepting information about a support group or watching a feeding demonstration do not show real parental involvement. Most parents have concerns about their abilities to care for a baby, perfect or not. 30. A pregnant woman has the nursing diagnosis of risk for ineffective role performance. What statement by the patient indicates that she is meeting a maternal task associated with the second trimester? A. All of this morning sickness and fatigue are distressing. B. I dont understand why I feel drawn to pregnant women. C. I really will miss my girls nights out at the local bars. D. This baby seems so real to me since I feel him move. ANS: D In the second trimester, a woman begins to feel the babys movement, and this makes her truly aware of the fetus as a separate being. Being concerned with ones own well-being rather than that of the fetus is common in the first trimester. Being drawn to other pregnant women is a general principle and is not tied to a specific trimester. Giving up favorite activities, or accepting other trade-offs for the baby, generally occurs in the first trimester. 31. A woman in the first trimester of her first pregnancy is upset and worried about physical changes, the labor and birth process, and being able to care for a newborn. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the woman about her exposure to newborns. B. Assess the woman for access to a knowledgeable support person. C. Provide information about childbirth preparation classes. D. Reassure the woman that these fears are natural. ANS: C The importance of childbirth education classes cannot be overemphasized by the nurse. The other options may be helpful, but they are not nearly as beneficial as getting the woman involved in childbirth education classes. Simple reassurance that fears are normal does not help the woman care for herself. Asking about exposure to newborns is likely to be of little help. The woman should be assessed for a support system, but this is not as important as attending classes. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nursing instructor explains to a class of students that the pituitary gland has many functions related to pregnancy. Which of the following functions are performed by hormones secreted by this gland? (Select all that apply.) A. Cause the corpus luteum to produce progesterone B. Influence ovarian follicular development C. Maintain the pregnancy D. Prompt ovulation E. Stimulate the uterine lining ANS: B, C, D, E The pituitary gland secretes hormones that influence ovarian follicular development, prompt ovulation, and stimulate the uterine lining to prepare for pregnancy. After implantation, the trophoblast secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, which prompts the corpus luteum to continue progesterone production until the placenta takes over this action. 2. The nurse is explaining to a student that several physiological factors cause a pregnant woman to be prone to venous thrombosis and embolic phenomena. What factors are included? (Select all that apply.) A. Dehydration B. Increased blood factors C. Sedentary lifestyle D. Venous stasis E. Volume overload ANS: B, D Blood factors VII, VIII, IX, and X increase during pregnancy, which leads to a hypercoagulable state in pregnancy. Poor blood return from the lower extremities (venous stasis) combine with this hypercoagulable state to make the pregnant woman more prone to thrombosis and embolic events. Sedentary lifestyle is not a physiological factor, and most pregnant women are not sedentary. Volume status is not directly related. 3. A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to a pregnant woman regarding normal changes in the nose and nasal passages. What information should the nurse provide? (Select all that apply.) A. Blow your nose gently. B. Dry mucous membranes cause bleeding. C. Increase your fluid intake. D. Stuffiness is common. E. Use decongestant spray. ANS: A, C, D Nasal stuffiness and congestion are common complaints in pregnancy. Increased fluid intake can help thin the mucus and mobilize it. Decongestant sprays should be avoided due to the rebound effect. Blowing the nose gently can help prevent nosebleeds that are common due to nasal edema. 4. A patient is complaining of constipation. What teaching should the nurse plan to provide? (Select all that apply.) A. Avoid vigorous exercise. B. Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day. C. Dont strain to move your bowels. D. Eat small, frequent meals. E. Increase your fiber intake. ANS: B, C, E Constipation is a common problem in pregnant women. Nurses should advise women to drink 8 to 10 glasses of water a day, avoid straining to have a bowel movement, and increase their fiber intake. Exercise is important to prevent constipation. Small, frequent meals are not related. 5. A pregnant woman had several urinary tract infections (UTIs) in her last pregnancy and wants to avoid them during this pregnancy. What advice by the nurse is best? (Select all that apply.) A. Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water daily. B. Drink a glass of apple juice daily. C. Empty the bladder before intercourse. D. Void every 1 to 2 hours while awake. E. Void every 2 to 3 hours while awake. ANS: A, E To avoid UTIs, women should be encouraged to drink 8 to 10 glasses of water a day, to void every 2 to 3 hours while awake, and to void immediately after intercourse. Drinking apple juice and voiding every 1 to 2 hours are not recommended. 6. In providing anticipatory guidance to a couple expecting their first child, which tasks and activities does the nurse discuss with the parents? (Select all that apply.) A. Honing communication and listening skills B. Learning to cope with a lack of sexual activity C. Negotiating household roles and daily tasks D. Reorganizing the house for a new member E. Reviewing patterns of money management ANS: A, C, D, E According to Duvall, members of the expectant family have many tasks to do as they set about preparing for the birth of their child. Some of these include negotiating household roles, reorganizing the home, reviewing (and possibly changing) patterns of money management, adapting the sexual relationship to the physical changes of pregnancy, and reorienting roles with family and friends. As emotional responses can be unpredictable, good communication skills are vital. 7. A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to a pregnant woman who has another child. Which information should the nurse plan to include? (Select all that apply.) A. School-age: can fully grasp the reality of the pregnancy B. School-age: too young to attend sibling classes C. Teen: may feel resentment and embarrassment D. Toddler: may be excited to play with the new baby E. Toddler: may regress in behavior ANS: C, E Toddlers typically inhabit their own little world in which they are the center. They may react with indifference and also may regress in their behavior. School-age children may be interested, but they are unable to fully grasp the situation. Sibling preparation classes are a good way to involve and educate them. The teenager may feel resentment or be embarrassed that his or her parents are sexual beings. 8. A nurse is providing anticipatory guidance regarding psychosocial adaptations to pregnancy to a group of women. Which topics are consistent with their associated trimesters? (Select all that apply.) A. First trimester: ambivalence about the pregnancy B. First trimester: separation from the fetus C. Second trimester: active dreams and fantasy life D. Second trimester: becoming more introspective E. Third trimester: realignment of roles and tasks ANS: A, C During the first trimester, the woman may feel ambivalent about the pregnancy. In the second trimester, active dreams and fantasy life are common. Separation from the fetus is a task of the third trimester, as is becoming more introspective. Realignment of roles and tasks typically occurs in the second trimester. Chapter 9: The Prenatal Assessment MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse places his or her hands on the maternal abdomen to gently palpate the fundal region of the uterus. This action is described as which Leopold maneuver? A. First maneuver B. Second maneuver C. Third maneuver D. Fourth maneuver ANS: A Leopold maneuvers are a four-part clinical assessment method to determine the lie, presentation, and position of the fetus. The first maneuver determines which fetal body part (e.g., head or buttocks) occupies the uterine fundus. The examiner faces the patients head and places the hands on the abdomen, using the palmar surface of the hands to gently palpate the fundal region of the uterus. 2. The nurse includes screening for intimate partner violence in the first prenatal visit for all patients. Which of the following is an appropriate question for the nurse to ask? A. I need to ask you, do you feel safe from abuse right now? B. Is your partner threatening or harming you in any way right now? C. This is something we ask everyone: Do you have any abuse in your life right now? D. We ask everyone this: Do you feel safe in your living environment and relationships? ANS: D Intimate partner violence is a difficult subject to discuss and the nurse may fear insulting or psychologically hurting the patient more. A nonthreatening approach is to ask patients directly whether they feel safe going home and whether they have been hurt physically, emotionally, or sexually by a past or present partner. 3. The clinic nurse talks with a patient about her possible pregnancy. The patient has experienced amenorrhea for 2 months, nausea during the day with vomiting every other morning, and breast tenderness. She is convinced she is pregnant and is reluctant to pay for a pregnancy test. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Agree that these signs usually signal pregnancy so no test is needed. B. Delete the order for the pregnancy test and inform the provider. C. Explain that these symptoms can be caused by other conditions. D. Inform the woman that this is standard procedure and must be done. ANS: C Presumptive signs of pregnancy are those subjectively reported symptoms that could be caused by another condition and include amenorrhea, nausea and vomiting, frequent urination, breast tenderness, perception of fetal movement, skin changes, and fatigue. The nurse should explain this and encourage the woman to have the pregnancy test. Simply telling the woman this is standard procedure does not educate her to make an informed decision. 4. A woman in the prenatal clinical is concerned because her partner, who was supportive and excited about becoming pregnant, has suddenly become more withdrawn and seems ambivalent toward the pregnancy. What response by the nurse is best? A. Are you in a relationship that causes you to be afraid? B. Oh dont worry; they all feel this way sometimes. C. This is a normal reaction to the reality of the pregnancy. D. Your partner will come around to being excited soon. ANS: C Despite planning a pregnancy, many women (and their partners) become ambivalent when faced with a positive pregnancy result. The reality of the many changes soon to come often causes them to reconsider their desire to become pregnant. There is also an aspect of self-preservation involved; many women still die from complications associated with pregnancy. The best response by the nurse is to help the woman recognize that this is a normal response. There is no need to ask the woman about intimate partner violence at this point. The other two options are dismissive and do not serve to educate the woman. 5. A nurse is working with a pregnant woman who has the nursing diagnosis of altered family processes. What statement by the patient indicates that a major goal for this diagnosis has been met? A. At least Im getting better sleep now that I dont urinate every 2 hours. B. My husband has been doing more around the house so I can rest more. C. The kids are really excited about getting a new baby brother or sister. D. We finally have the nursery painted and furnished so its ready for baby. ANS: B A major goal for this diagnosis is that the family recognizes the demands the pregnancy places on the woman and alters routines and activities to accommodate her. When the patient states that her husband is doing more around the house so she can rest more (a need in pregnancy), this shows resolution of the goal. The other statements are positive ones, but do not show family members adapting to new roles and responsibilities. 6. A nurse is reviewing the prenatal care schedule for a woman who is 10 weeks pregnant. When does the nurse advise the woman to return for her next appointment? A. 2 weeks B. 4 weeks C. 6 weeks D. 8 weeks ANS: B Prenatal visits are usually every 4 weeks until the woman reaches 28 to 32 weeks gestation. Then visits are scheduled every 2 weeks until the 36th week. After that point, visits are weekly until birth. 7. A woman who is 32 weeks pregnant has concluded a prenatal visit. The nurse should schedule the next prenatal visit for which gestational week? A. 33 weeks B. 34 weeks C. 38 weeks D. 40 weeks ANS: B Women are seen once every 4 weeks until 28 to 32 weeks gestation, when the schedule changes to every 2 weeks. The nurse should schedule this womans next visit at 34 weeks. 8. The prenatal nurse believes in advocating for the patient. What action by the nurse best reflects this role? A. Documenting the patients preferences for childbirth care B. Helping the woman formulate and vocalize questions C. Informing women of options related to labor and birth D. Teaching women about physical changes during pregnancy ANS: B The role of the advocate includes speaking for the patient when she is unable to do so herself and ensuring that the patients questions are answered in a thorough way that she can understand. The nurse helping a patient formulate and voice questions is the best demonstration of the advocate role. Documenting preferences is a good start, but is not comprehensive enough to encompass the role. Teaching is also part of the advocate process, but does not constitute speaking for the patient or helping her to do so. 9. The nursing student in the perinatal clinic asks the registered nurse why so many pregnant women seem to be stressed despite their happy condition. What response by the nurse is best? A. Its the effect of all those hormones. B. Many are afraid of labor and birth. C. Most pregnant women dont feel well. D. Pregnancy is a developmental crisis. ANS: D Pregnancy, no matter how planned and wanted, is a developmental crisis for the woman and her family. It requires role changes and restructuring of tasks of daily living. This leads to stress. One benefit of prenatal care is having a nurse who can help the woman (and family) adjust and find positive ways to cope. Hormones and fear may play a part, but these answers do not provide a comprehensive explanation. There are physical discomforts associated with pregnancy, but, again, this answer is not comprehensive. 10. A prenatal nurse manager wants to help pregnant women in the clinic decrease their stress. Which action by the manager would be best? A. Conduct childbirth preparation classes on site B. Display pictures of fetal development C. Institute primary nursing care for all patients D. Partner with a counseling service for referrals ANS: C Women release oxytocin as a response to stress and when they engage in tend and befriend activities. Oxytocin appears to buffer the stress response and produces a calming effect. One strategy nurses can use to employ this physiological phenomenon is to provide continuity of care. Primary nursing, in which each patient is assigned a primary nurse who sees them at each visit, is an excellent choice to capture the benefits of this effect. The other options could all help reduce stress in some women and in some situations, but providing continuity of care could benefit all patients in the clinic. 11. A nurse uses the CARE model when working with patients. How can this nurse use the model to help reduce racially related disparities in care for pregnant women? A. Ensure a clear exchange of valuable information. B. Pay due attention to another person. C. Provide resources, authority, or opportunities. D. Support or defend another individual. ANS: C Unfortunately, racial disparities still exist in health care today. The nurse can use the CARE model to help address this issue. CARE stands for communication, advocate, respect, and enable. All options are components of the model, but the one that could best help to address this disparity is providing the resources, the authority, and the opportunity to do something. Enabling women to obtain the care they need and reducing barriers would go a long way in meeting the Healthy People 2020 objective of improving access to prenatal care for all women. 12. The nurse assesses a pregnant patient during the first prenatal visit. Which question by the nurse is the best example of therapeutic communication? A. Do you understand the prenatal visit schedule? B. Do you use drugs or drink alcohol? C. Have you experienced quickening? D. To begin, what questions may I answer? ANS: D The first prenatal visit is extremely important and is a vital time for the nurse to use therapeutic communication to help establish a professional, caring relationship. The nurse should avoid yes-no questions and medical jargon that could be intimidating. Open-ended questions elicit the most information; when the nurse begins by asking what questions she or he can answer, that leaves an opening for the patient to express any concerns or questions at that time. 13. The nurse explains that the childbearing year is an ideal time to make healthy changes for the entire family. Which action does the nurse suggest? A. Avoiding alcohol and smoking B. Creating healthy menus for family meals C. Getting plenty of sleep each night D. Planning a parents date night each week ANS: B Pregnancy and the childbearing year is an ideal time for the entire family to make healthy changes. Planning and preparing healthy foods are important parts of prenatal care that can have a positive impact on the entire family. The other options are good for the pregnant woman and her partner, but dont have as big of an impact on the whole family. 14. A nurse has taught a pregnant woman about good nutrition during pregnancy at her first prenatal visit. What statement by the patient indicates that more teaching is needed? A. I buy a lot of yellow and orange vegetables. B. I have switched to buying only 1% milk. C. We eat a lot more poultry these days. D. We eat salmon once a week at least. ANS: D Healthy nutrition is important during pregnancy, and pregnant women should eat plenty of yellow and orange vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and lower-fat meats. Fish is a great source of protein; however, pregnant women should eat fish lower in mercury, such as whitefish, haddock, pollock, sole, and trout. 15. A pregnant woman in her first trimester is having her first prenatal visit. She tells the nurse that she takes red raspberry leaf regularly. What response by the nurse is best? A. Discuss the cardiovascular problems associated with this substance. B. Explain that it is safe to use during pregnancy. C. Inform the woman that safety has not been established. D. Tell the woman she should not use it during pregnancy. ANS: B Red raspberry is safe to use during pregnancy, and it may be beneficial in relieving the symptoms of morning sickness and in assisting in the birth of the baby and placenta. The other statements apply to blue cohosh. 16. A woman who is a Jehovahs Witness returns for a second prenatal visit and is discussing her plan of care with the nurse. The patient has returned a signed form in which she refuses all blood products. What action by the nurse is best? A. Advise the woman of potential complications. B. Inform the health-care provider of her choice. C. Place the signed form on the patients chart. D. Refer the woman to a tertiary birthing center. ANS: C Patients who are Jehovahs Witnesses do not usually consent to the use of blood products. When working with a patient with these beliefs, the nurse should discuss all alternatives with the patient (including all types of blood products available) and send her home with a packet containing a consent form in which she details which (if any) blood products she will accept. This signed form should be available in three places: the patient should have a copy, a copy should be placed on her chart, and the hospital where she will give birth should also have a copy. Teaching potential complications related to the womans choices should have already been done. Informing the health-care provider is important, but without a written document, this is not a complete action. Depending on patient, provider, and facility preferences, a patient who refuses blood products may need to be referred to another facility. 17. A patient being seen for the first time in the perinatal clinic has multiple complaints, such as fatigue, anger outbursts, chronic pelvic pain, and feelings of anxiety. What action by the nurse is best? A. Assess the woman for a history of sexual assault. B. Document the patients complaints on the chart. C. Refer the woman to a psychiatric nurse practitioner. D. Review the womans past medical history with her. ANS: A Women who have been victims of sexual assault often complain of various emotional difficulties, such as depression, anger, anxiety, and gynecologic problems. They are often reluctant to disclose their past history of abuse. When women have these complaints, the nurse should investigate the possibility of sexual assault. Documentation should be thorough; however, this answer is not complete. The patient may or may not need a referral; the nurse needs to assess the patient further. Reviewing past medical history is an important part of assessing a patient, but does not take into account the unique nature of this problem. 18. A woman undergoing her first prenatal visit for a current pregnancy is reluctant to discuss her past obstetrical history with the nurse. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Document the womans refusal to answer these particular questions in the chart. B. Explain that past obstetrical experiences frequently recur in later pregnancies. C. Inform the woman that the clinic cannot provide comprehensive care without a complete history. D. Tell the woman that you need the information in order to continue with the prenatal visit. ANS: B A complete obstetrical history should cover the current pregnancy as well as all other pregnancies because complications experienced in previous pregnancies often recur. The nurse should gently explain this in a nonthreatening, nonjudgmental manner, focusing on helping the woman obtain the best outcomes possible. Documentation is always an important nursing responsibility, but the nurse needs to act and not just document. Informing the woman that the clinic cannot provide comprehensive care without the history or telling her that she needs to provide more information to continue the visit is judgmental and sounds vaguely threatening. 19. A student asks what the phrase probable signs of pregnancy means. The instructor provides which answer? A. Objective signs seen by an examiner; can be from other conditions B. Objective signs seen by an examiner; only caused by pregnancy C. Subjective signs reported by the patient; can be from other conditions D. Subjective signs reported by the patient; only caused by pregnancy ANS: A Probable signs of pregnancy are objective signs observed by an examiner that usually result from physical changes in the reproductive system during pregnancy, but that can be caused by other conditions. They include abdominal enlargement, Piskaceks sign, Hegars sign, Goodells sign, Chadwicks sign, Braxton Hicks sign, a positive pregnancy test, and ballottement. 20. A nurse is assessing a patient for Chadwicks sign. In order to do this correctly, what action does the nurse take? A. Assesses the color of the patients vaginal mucosa and cervix. B. Feels the patients abdomen for passive fetal movement. C. Obtains a urine specimen for a pregnancy test. D. Palpates the patients abdomen for uterine asymmetry. ANS: A Chadwicks sign is a bluish discoloration of the vaginal mucosa and cervix. The nurse needs to visually inspect this anatomy to determine if the patient has a positive Chadwicks sign. Ballottement is the passive movement of the unengaged fetus. Obtaining urine for a urine test is a diagnostic test, not a physical assessment. An asymmetrical uterus with a soft prominence on the implantation side is a positive Piskaceks sign. 21. The nurse reads positive Hegars sign in a patients chart. What can the nurse conclude about the patient? A. Patient had a miscarriage B. Patient is post-partum C. Patient is pregnant D. Patient may be pregnant ANS: D Hegars sign is softening of the lower uterine segment and is a probable sign of pregnancy, so the nurse concludes that the patient may be pregnant. A positive Hegars sign can also be caused by pelvic congestion. 22. A patient in the emergency department is complaining of fever, burning with urination, bloody urine, and amenorrhea for 1 month. To evaluate her symptoms, what action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the woman if her menstrual periods are usually regular. B. Collect a urine sample for a pregnancy test. C. Instruct her in obtaining a midstream urine sample. D. Obtain an order for an intravenous pyelogram (x-ray of the urinary tract). ANS: C This woman has symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) and may be pregnant. A urine sample will help with evaluation of all of her symptoms, but blood in the urine can produce a false-positive pregnancy test. To assist the woman in providing a suitable urine specimen for laboratory testing, the nurse teaches her how to obtain a midstream urine sample. Obtaining an order for an intravenous pyelogram is not indicated at this time. 23. A nurse reads in a pregnant womans chart that she is para 3. What does the nurse understand about this womans obstetrical history? A. Is now in her third trimester B. Currently pregnant with triplets C. Three babies born alive D. Three pregnancies delivered past 24 weeks of gestation ANS: D The term parity means the number of pregnancies carried to a point of viability, which is generally accepted as at least 24 weeks of gestation. This woman has had three pregnancies that went past that point. Parity does not refer to trimester, the number of babies in the current pregnancy, or the outcome of previous pregnancies. 24. A woman calls the prenatal clinic to inquire if she should have the seasonal influenza vaccination. What advice should the nurse provide? A. Flu does not cause many problems in pregnancy. B. No, vaccinations are not safe in pregnancy. C. Yes, you should get the flu vaccination. D. You should wait until your third trimester. ANS: C Pregnant women who contract influenza have an increased risk of both needing medical care and requiring hospitalization. Vaccination against influenza is considered safe throughout pregnancy and preventing this disease is an essential element of prenatal care. The most effective way to prevent contracting influenza is through immunization. 25. A nurse is assessing a woman who is at 29 weeks of gestation. The nurse measures the womans fundal height, which is 58.42 cm (23 inches). What does the nurse conclude about this information? A. The nurse cannot make a conclusion. B. Fundal height is just right. C. Fundal height is too big. D. Fundal height is too small. ANS: D Measuring fundal height is usually initiated around 22 weeks of gestation. The measurement is recorded in centimeters and should closely approximate the weeks of gestation. A woman who is 29 weeks pregnant should have a fundal height of 29 cm (11.4 inches). This woman’s fundal height is too small for her gestation. 26. A nurse is performing the third Leopold maneuver on a woman who is gravida 3, para 3 and is currently 37 weeks gestation. The nurse’s fingers can be pressed together below the presenting part, which is firm to the touch. What action should the nurse take regarding this assessment data? A. Facilitate a referral to a primatologist. B. Inform the health-care provider immediately. C. Prepare the woman for a breech delivery. D. Reassure the woman and document the findings. ANS: D The third Leopold maneuver is performed to confirm the presentation noted in the first maneuver and to determine if the presenting part is engaged. If the presenting part moves upward so that the examiners fingers can be pressed together, the presenting part is not engaged. In a first pregnancy, engagement usually occurs around 37 weeks gestation; with subsequent pregnancies engagement may not occur until labor has begun. If the presenting part is firm, it is the head. If the presenting part is soft, the fetus is in the breech position. This woman is in her third pregnancy, so the lack of engagement is not abnormal. The presenting part was firm, so the baby is not breech. There is no need to inform the health-care provider immediately or facilitate a referral to a higher level of care. The nurse should reassure the woman and document the findings. 27. The nurse auscultates fetal heart tones on a woman in her third trimester of pregnancy and counts a heart rate of 92 beats/minute. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Apply oxygen at 6 L/minute. B. Assess the maternal heart rate. C. Document the findings in the chart. D. Turn the woman on her left side. ANS: B The normal fetal heart rate is 110160 beats/minute. If the nurse assesses a lower rate, the maternal heart rate should be assessed. If the two heart rates are similar, the nurse has inadvertently counted only the maternal rate. The nurse should attempt to locate the fetal pulse and try again. If the two rates differ (i.e., the fetal heart rate is truly 92 beats/minute), the nurse should place the woman on her left side, apply oxygen by mask, and seek assistance. Documentation should always occur. 28. The nursing faculty member explains to a class of nursing students that the ethnic/cultural group with the highest rate of teen pregnancy is which group? A. African Americans B. Asian Americans C. European Americans D. Hispanic Americans ANS: A The birth rate in African American teens is higher than in any other ethnic/cultural group. 29. A pregnant teen is in the clinic for a prenatal visit. The nurse needs to obtain informed consent. What action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the teen to call a parent and get consent over the phone. B. Have the teen sign the consent and then place it on the chart. C. Let the teen keep her appointment, but limit it to teaching only. D. Tell the teen that she must return with her parent/guardian. ANS: B A pregnant teen is considered emancipated, so she can sign for her own care. The nurse should obtain and document informed consent from the teen. The other actions are not necessary. 30. A 40-year old primigravida has undergone nuchal translucency screening. The results show a finding of 3.3 mm. What information should the nurse provide the parents? A. The fetus has an open neural tube defect. B. The fetus has an increased risk for genetic disorders. C. These results are inconclusive. D. These results are normal in an older mother. ANS: B Nuchal translucency screening is performed between 11 and 14 weeks of gestation via ultrasound. A measurement greater than 3 mm indicates an increased risk for trisomies 13, 18, and 21. 31. A nurse is assessing a 40-year old primigravida who is an insulin-dependent diabetic and who smokes. What does the nurse understand about these conditions related to prenatal screening tests? A. Second-trimester markers will be affected but not third-trimester markers. B. The presence of nicotine invalidates the results of most screening tests. C. The woman will have an overall effect of a higher inhibin level. D. There is no significant effect on prenatal screening test results. ANS: C Inhibin levels are increased by about 60% in women who smoke and decreased by about 12% in insulin-dependent diabetics. The overall effect will be an increased inhibin level. 32. A nurse is counseling a 40-year-old woman about her risks of giving birth to a child with Down syndrome. What information does the nurse provide? A. The risk doesn’t go up until you are over 45. B. The risk is less than 1 in 1,000. C. The risk is about 1 in 85. D. The risk is about 1 in 20. ANS: C A woman’s risk of having a baby with Down syndrome is approximately 1:85 at age 40. 33. A woman has returned to the clinic for her second prenatal visit. Her blood pressure is significantly higher than on her previous visit. What action should the nurse do first? A. Administer oxygen and inform the provider. B. Ask the woman to lie down on the table. C. Ensure that the blood pressure cuff is the appropriate size. D. Take the blood pressure again. ANS: C Taking and recording maternal vital signs is an important component of every prenatal visit. Because this blood pressure reading is significantly different, the nurse should first ensure that the correct-sized cuff is being used and that the situation (i.e., maternal position) is consistent with the last reading. There is no need for oxygen or to have the woman lie down, unless the nurse determines that the woman was lying down for her last blood pressure measurement. The nurse should not take the blood pressure again until those factors are verified. 34. A woman asks the perinatal nurse about gestational diabetes because she has been reading about it. The nurse should inform the patient that screening for this condition is usually done at what time during the pregnancy? A. Around 24 to 28 weeks gestation B. End of the first trimester C. Mid-pregnancy D. Normally offered around week 37 ANS: A Routine screening for gestational diabetes is usually offered around 24 to 28 weeks gestation. 35. A patient has had a screening test for gestational diabetes and the 1-hour result is 250 mg/dL. What does the nurse conclude about this patient? A. Results are high; the patient has gestational diabetes. B. Results are inconclusive; will repeat test in one month. C. Results are lower than expected; seek endocrine consult. D. Results are normal; no gestational diabetes. ANS: A The normal 1-hour result for a gestational diabetes screen is less than 140 mg/dL. This patient has tested positive for gestational diabetes. 36. A nurse reads a patients chart and sees the diagnosis pediculosis pubis. What does the nurse understand about this condition? A. The patient has abnormal pubic hair growth. B. The patient has an old episiotomy. C. The patient has human papillomavirus. D. The patient has pubic lice. ANS: D Pediculosis pubis is pubic lice. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nursing instructor informs the class of the many benefits of prenatal care. What benefits does the instructor include? (Select all that apply.) A. Allows women informed decision making B. Decreased pregnancy-related maternal death C. Improved pregnancy outcomes D. Increased cost associated with more frequent visits E. Increased early identification of abnormal findings ANS: A, B, C, E There are many benefits to prenatal care. Nurses play a vital role in ensuring that women receive information and are able to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy. Women who receive prenatal care have a five-fold decrease in pregnancy-related maternal death and improved pregnancy outcomes. One of the main concepts of prenatal care is early identification of deviations from the normal pregnancy. Increased immediate costs may be an outcome (not a benefit) of prenatal care as compared to women who do not receive prenatal care, but long-term costs are often higher. 2. A pregnant woman asks a neighbor who is a nurse about using a midwife instead of a physician for her prenatal, labor, and childbirth care. What information does the neighbor share with the pregnant woman about certified nurse midwives (CNMs)? (Select all that apply.) A. CNMs are able to see women experiencing complications. B. CNM practice is physician dependent. C. There is an increased need for medical interventions with CNMs. D. There is increased patient satisfaction with CNMs. E. There is a lower rate of cesarean births with CNMs. ANS: D, E Certified nurse midwives are educated in both nursing and midwifery and are certified by the American College of Nurse-Midwives. Midwifery practice is the independent management of womens health care, focusing on pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period, care of the newborn, and family planning/gynecological needs. CNMs see healthy women experiencing an uncomplicated pregnancy. These women experience a lower rate of cesarean births and medical interventions. Continuity of prenatal care has a major effect on patient satisfaction. 3. During the first prenatal visit, a nurse teaches a pregnant woman about emergencies for which she needs to be seen immediately. Which situations does the nurse include in this education? (Select all that apply.) A. Headache not associated with visual disturbances B. Low, dull backache or pelvic pressure C. Maternal fever over 100.5F (38.1C) D. Nausea and vomiting especially upon arising in the morning E. Reduction in fetal movements ANS: B, C, E Emergency warning signs the nurse teaches the patient include reduction in fetal movement; signs of preterm labor (low, dull backache; pelvic pressure; uterine contractions; menstrual cramps); vaginal fluid loss or vaginal bleeding; maternal fever over 100.5F; persistent headache associated with blurred vision or flashing lights in front of the eyes; continuous vomiting with weight loss, dehydration, weakness, dizziness, or fainting; or feeling that something is just not right. A headache not associated with visual disturbances and some limited nausea and vomiting without signs of dehydration are not emergencies. 4. A nurse is using the RADAR model when working with women in the perinatal clinic. What actions does the nurse include when assessing patients with this model? (Select all that apply.) A. Ask only when injuries are suspicious. B. Assess the patients safety. C. Document findings in the chart. D. Review options and referrals with the patient. E. Routinely screen every patient. ANS: B, C, D, E The acronym RADAR stands for routinely screen every patient (not just when injuries seem suspicious); ask directly, kindly, and in a nonjudgmental way; document your findings, assess the patients safety; and review options and provide referrals. 5. The student nurse in the perinatal clinic asks why it is so important to screen women for intimate partner violence during the first prenatal visit. What information does the registered nurse provide the student? (Select all that apply.) A. Approximately one in three women has been a victim of abuse. B. Intimate partner violence is more common than preeclampsia. C. Many women may abuse substances to cope with the violence. D. Partners abuse over 300,000 pregnant women each year. E. Violence rarely occurs for the first time during pregnancy. ANS: B, C, D Intimate partner violence (IPV) is the most common form of violence women are exposed to worldwide. In the United States, approximately 25% of women (or one in four) have been the victim of intimate partner violence, including over 324,000 pregnant women. IPV is more common than preeclampsia or gestational diabetes, both of which are significant problems in pregnant women. Many women cope with this violence by turning to substance abuse, both prescription and nonprescription. Shockingly, IPV may occur for the first time during pregnancy. 6. A woman comes for her first prenatal appointment at 31 weeks gestation with her first pregnancy. Which of the following are appropriate statements by the nurse? (Select all that apply.) A. Do you have questions before I begin your prenatal history and information sharing? B. Have you had care in another clinic? I cant believe this is your first appointment! C. I am interested in hearing about your life and what prompted you to begin your prenatal care today. D. It is nice to meet you and I will try to help you get caught up in your prenatal care. E. Now that you are finally here, we need you to come monthly for the next two visits and then weekly. ANS: A, C, D Assessment of the patient and gathering data are important components of the first prenatal visit. However, the nurse needs to use professional communication skills in order to elicit information from the patient about personal details of her life and potentially embarrassing information. Questions that show openness and acceptance are best. Stating that you cant believe this is the patients first prenatal visit and the comment now that you are finally here are judgmental and will not help to establish a trusting relationship. 7. A nurse is caring for a woman who is positive for hepatitis B. What other screening tests does the nurse facilitate for this patient? (Select all that apply.) A. Cytomegalovirus B. Hepatitis B for household members C. Hepatitis B for intimate contacts D. Hepatitis C E. Parvovirus ANS: B, C, D Women who are positive for hepatitis B should have screening for hepatitis C. Their household contacts and intimate contacts should also be screened for hepatitis B. There is no correlation between hepatitis B and either cytomegalovirus or parvovirus. 8. The nurse advocates for smoking cessation during pregnancy and teaches pregnant women about the effects of tobacco exposure. Which of the following are potential harmful effects of prenatal tobacco use that the nurse should plan to include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.) A. Continued childhood respiratory problems B. Congenital diabetes C. Gestational hypertension D. Preterm labor and birth E. Small-for-gestational-age infant ANS: A, D, E Effects of tobacco use during pregnancy are well documented and predispose to premature rupture of the membranes, preterm labor, placental abruption, placenta previa, and infants who are small for gestational age. These effects continue well into childhood and are associated with upper respiratory problems, such as infections, asthma, and wheezing. Exposure to tobacco products is not associated with congenital diabetes or gestational hypertension. 9. The nurse recognizes that a pregnant adolescent must successfully complete developmental tasks to be an effective mother. Which tasks does the nurse understand this to include? (Select all that apply.) A. Accepting this pregnancy and telling parents/friends B. Growing up and accepting responsibility C. Maintaining her freedom D. Seeing herself as a mother E. Setting reasonable goals for herself ANS: A, B, D, E For a teenager to successfully adapt and fulfill the role of being a mother, she must achieve four major developmental tasks: gain acceptance of pregnancy, set goals, view self as a mother, and grow up. Maintaining freedom is antithetical to growing up and accepting the responsibility of motherhood. 10. A nurse assesses the pregnant woman for recreational drug use as part of the first prenatal visit. What harmful effects of recreational drugs does the nurse teach the woman about? (Select all that apply.) A. Cocaine: placenta previa B. Ecstasy: cleft palate C. Marijuana: intrauterine growth restriction D. Methamphetamine: spontaneous abortion E. Heroin: macrosomia ANS: B, C, D Approximately 3% of pregnant women use nonprescription drugs such as cocaine, Ecstasy, marijuana, methamphetamines, and heroin. Ecstasy can cause congenital abnormalities such as cleft palate. Marijuana can cause intrauterine growth restriction. Methamphetamines can cause spontaneous abortion. Cocaine can cause placental abruption (not previa). Heroin can lead to spontaneous abortion, intrauterine growth restriction, preterm labor/birth, or stillbirth. 11. The nurse is explaining to students in the perinatal clinic that some adolescents are at higher risk of teen pregnancy than others. Which teens does the nurse include in these high-risk groups? (Select all that apply.) A. Homeless teens B. Incarcerated teens C. Teens from two-parent homes D. Teens with reliable information E. Teens with religious affiliations ANS: A, B Teens who lack the support, security, and love of a family home are more likely to engage in high-risk behaviors, including sex at an early age. Incarcerated teens are the most vulnerable group. Teens from middle-class, two-parent homes; teens who are able to obtain reliable information and who do not receive the message that sex is a taboo subject; and teens with religious affiliations have lower rates of teen pregnancy. 12. The nurse schedules a patient for her first prenatal appointment with the certified nurse-midwife (CNM) in the clinic. About what topics does the nurse help the patient formulate questions to ask the CNM? (Select all that apply.) A. An opportunity to meet other patients who have delivered with this practice B. The CNMs beliefs and practices concerning epidural anesthesia and episiotomies C. Use of complementary and alternative methods during labor and birth D. What happens if the patient gives birth when the CNM is not available E. Whether the CNM will be available by phone or Internet to answer questions ANS: B, C, D, E A womans journey through the pregnancy experience can have long-term effects on her self-perception and self-concept. Therefore, it is especially important that the patient choose a care provider with whom she can openly relate and who shares the same philosophical views on the management of pregnancy. Although in unusual circumstances a patient may give permission for the CNM to provide her information to a patient with a similar situation, routinely sharing personal information with other patients would be a violation of confidentiality principles and laws. 13. The nurse provides increased support to a woman during her first prenatal visit for her current pregnancy. The patients first pregnancy ended in a miscarriage. The nurse understands that the reasons the patient may be ambivalent about this baby include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Awareness of a new 24-hour responsibility B. Needs related to a second pregnancy C. Potential role/relationship changes D. Previous perinatal loss E. Unresolved grief and mourning ANS: A, C, D, E Ambivalence is a normal response to pregnancy that is in part related to the anticipated role changes that will occur. The loss of a previous pregnancy brings many emotions to a subsequent pregnancy. This patient should be counseled for her previous loss, unresolved grief and mourning, potential role changes, and new responsibilities as a parent if she carries this pregnancy to term. 14. The nurse explains to a newly diagnosed pregnant woman at 10 weeks gestation that her rubella titer indicates that she is not immune. Which of the following should the nurse teach the patient? (Select all that apply.) A. Avoid contact with all children until after you have given birth. B. Be retested in 3 months and obtain the vaccination if not immune. C. Do not become pregnant for 4 weeks after you receive the vaccination. D. Receive the rubella vaccine during the postpartum period. E. Seek medical care immediately for fever, runny nose, or rash. ANS: C, D Rubella (German measles) is one of the most commonly recognized viral infections known to cause congenital problems. If a woman contracts rubella during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus has a 90% chance of being adversely affected. A maternity patient who is not immune to rubella should be offered the rubella immunization following childbirth, ideally prior to hospital discharge. She should also be taught to avoid becoming pregnant for at least 4 weeks after the immunization. The patient should report signs or symptoms of rubella during pregnancy to her health-care provider, but she does not need to seek medical care immediately. Avoiding contact with all children is unreasonable. There is no reason to be retested in 3 months, because she cannot receive the vaccination until after she has given birth. 15. A student nurse asks the OB clinic nurse why a pregnancy test is needed if a woman has missed several menstrual periods in a row. The nurse explains that amenorrhea can be caused by several conditions other than pregnancy, including which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Chronic illness B. Endocrine disorders C. Fatigue D. Infections E. Psychological factors ANS: A, B, D, E Amenorrhea is a presumptive sign of pregnancy, meaning that the same signs can be caused by conditions other than pregnancy. Amenorrhea can be caused by chronic illness; endocrine, metabolic, or psychological factors; or infection. 16. The perinatal nurse explains to a group of nursing students that there are positive signs of pregnancy. Which of the following does the nurse include in this explanation? (Select all that apply.) A. Fetal heartbeat B. Fetal movement palpated by the examiner C. Intermittent uterine contractions D. Positive pregnancy test E. Visualization of the fetus ANS: A, B, E Positive signs of pregnancy are those attributable only to the presence of a fetus and include fetal heartbeat, fetal movement palpated by an examiner, and the visualization of a fetus. A positive pregnancy test and intermittent uterine contractions are presumptive signs of pregnancy and may be caused by other conditions. A positive pregnancy test can be caused by certain medications, premature menopause, choriocarcinoma, or blood in the urine. Intermittent uterine contractions (Braxton Hicks contractions) can be caused by uterine leiomyomas or other tumors. 17. A pregnant woman in the perinatal clinic is a commercial sex worker and states that she frequently has unprotected sexual intercourse. The nurse should educate this woman about which complications of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? (Select all that apply.) A. Ectopic pregnancy B. Frequent multi-fetal pregnancy C. Gestational hypertension D. Preterm labor E. Spontaneous abortion ANS: A, D, E STDs (sometimes referred to as sexually transmitted infectionsSTIs) predispose to a number of complications, including ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, preterm labor, and increased neonatal morbidity. All pregnant women should be screened for STDs. STDs are not associated with frequent multi-fetal pregnancy or gestational hypertension. 18. A woman in the OB clinic complains of multiple, fluid-filled blisters in her genital area that make walking extremely painful. What information should the nurse provide this patient? (Select all that apply.) A. There are serious adverse fetal effects of this disease. B. There is no cure for herpes simplex virus infection. C. Transmission to your baby causes eye infections. D. You can start antiretroviral medications immediately. E. We will take blood cultures for a bacterial infection. ANS: A, B The patients symptoms are suggestive of herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. HSV can cause serious consequences, including increased risk of pregnancy loss (60%) and severe neurological consequences in the infants who do survive. There is no cure, but several medications are available for treatment. Unfortunately, the safety of these medications during pregnancy and lactation has not been firmly established. Gonorrhea can cause neonatal eye problems (ophthalmia neonatorum). Antiretroviral medications are used for HIV infections. Blood cultures for bacterial infection are not warranted, as HSV is a viral infection. 19. A nurse is teaching a group of middle school girls about the complications associated with teen pregnancy. What topics should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Anemia B. Hypertensive problems C. Gestational diabetes D. Preeclampsia E. Preterm birth ANS: A, B, D, E Pregnant teens face an increased risk for many problems, including anemia, hypertensive problems, preeclampsia, and preterm birth. They are not at higher risk for developing gestational diabetes. 20. A nurse is running for public office and plans to fund a comprehensive program to prevent teen pregnancy. When asked how to justify the cost of such a venture, what information could the nurse provide? (Select all that apply.) A. A quarter of teen mothers give birth to a second child within 2 years of the first child. B. Fifty percent of teen mothers go on welfare within 5 years of the birth of their first child. C. Only a small percentage of teen mothers will complete any education beyond high school. D. The rate of teen pregnancy in America is double that of other developed countries. E. There are so many teenage mothers they are overwhelming the health-care system. ANS: A, B, C, D Teen pregnancy has enormous social and personal repercussions, including high rates of teen mothers on welfare, high rates of teen mothers having a second child within 2 years, low rates of teen mothers gaining education beyond high school, and high rates of teen pregnancy in the United States. Teen mothers are not overwhelming the health-care system. 21. A nurse is educating a woman who is 38 years old and experiencing her first pregnancy. When planning care for this woman, what information does the nurse take into consideration? (Select all that apply.) A. Chronic health conditions are more likely in this age group. B. Genetic screening is not recommended for women over age 30. C. Gestational diabetes is seen more frequently in this age group. D. Multiple gestations are rarely seen in women over age 35. E. Older prim gravidas are at higher risk for cesarean birth. ANS: A, C, E Older women who are pregnant have unique potential problems. These include a higher likelihood of chronic illness that impacts the pregnancy; obstetrical complications such as vaginal bleeding, preeclampsia, multiple gestation, gestational diabetes, preterm labor, dysfunctional labor, and cesarean birth; and increased incidence of Down syndrome, for which genetic screening should be offered. 22. A woman is having a triple-screen test during her second trimester of pregnancy. The nurse teaches the patient that this test includes which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin B. Inhibin A C. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein D. Nuchal translucency testing E. Unconjugated estriol ANS: A, C, E The triple screen includes maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, unconjugated estriol, and free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin. The inhibin A is included in the quadruple screen. Nuchal translucency testing is offered in the first trimester as part of the combined screen. 1. A pregnant womans last normal menstrual period started on June 8, 2013. Calculate her expected date of birth (EDB) using Naegles rule. Her EDB is what date? ANS: March 15, 2013 The calculation is based on the first date of the womans last normal menstrual period. Add 7 days to that date (= June 15, 2013). Subtract 3 months (= March 15, 2013). Add 1 year (= March 15, 2014). 2. A pregnant womans last normal menstrual period started on July 27, 2013. Calculate her expected date of birth (EDB) using Naegles rule. Her EDB is what date? ANS: May 3, 2013 The calculation is based on the first date of the womans last normal menstrual period. Add 7 days to that date (= August 3 [remember that July has 31 days]). Subtract 3 months (= May 3). Add 1 year (= May 3, 2013). 3. A woman is 10 weeks pregnant with her third baby. She has two living children with normal delivery histories. Using the GTPAL system, the nurse would document this womans obstetrical history as ____________________. ANS: G3T2P0A0L2 The woman is pregnant for the third time: G3. She has carried two pregnancies to term: T2. She has had no preterm deliveries: P0. She has not had any abortions: A0. She has two living children: L2. Chapter 10: Promoting a Healthy Pregnancy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The prenatal clinic nurse visits with a 32-year-old man. His partner is pregnant with her first child and is now at 12 weeks of gestation. The man states that he has been experiencing nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and weight gain. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Ask the womans health-care provider to prescribe the man anti-nausea medication. B. Assess for cancer risk factors, as weight gain and vomiting are unusual together. C. Encourage the man to make an appointment with his primary health-care provider. D. Explain that these symptoms are normal and often seen in men with pregnant partners. ANS: D Couvade syndrome is when a male partner experiences the same maternal signs and symptoms as the woman. The nurse should reassure the man that this is an often-occurring finding. The nurse would not need to encourage the man to make an appointment with his health-care provider unless the symptoms became severe. The womans primary health-care provider does not need to prescribe anti-emetics, nor does the nurse need to assess the man further for cancer risk factors. 2. After questioning a pregnant woman about her fluid intake, the nurse discovers that the patient is drinking four glasses of diet cola per day. Which response by the nurse is best? A. As long as you get enough fluid, soda is all right to drink. B. Less than two cups of caffeine a day is probably OK. C. The major worry with soda is the sugar content. D. You really should switch to decaffeinated colas. ANS: B The primary sources of caffeine for pregnant women are coffee, tea, and soda. Research shows that small amounts of caffeine (less than 2 cups a day) are probably safe; however, higher amounts cause central nervous system stimulation and can increase the chance of spontaneous abortions, stress the fetuss metabolic system, and decrease blood flow to the placenta. Women should be encouraged to restrict their intake of caffeinated beverages and taught that even decaffeinated beverages still 3. A perinatal nurse is assessing a pregnant womans medications and finds that one of them is categorized as Category D. What information should the nurse provide this patient? A. Studies have not found human fetal risk, although animal fetuses are harmed by it. B. There are no associated fetal risks with this drug and it is safe to take in pregnancy. C. There havent been any studies of this drug in human fetuses; I wouldnt take it. D. We have to decide if the benefits of this drug outweigh the risk, as it can harm the fetus. ANS: D There are five categories of drugs based on fetal risk: Category A: no associated fetal risk, safe to take during pregnancy; Category B: no associated fetal risk in animals, fetal risk in humans not identified; Category C: evidence of adverse effects in animal fetuses, fetal risk in humans not identified; Category D: evidence of adverse effects and fetal risk in humans, benefits and risks must be considered before prescribing; and Category X: evidence of fetal risk and congenital anomalies in humans, risks outweigh the benefits, should not be prescribed during pregnancy. 4. The nurse explains to the prenatal class attendees that at full term about 10 to 11% of the maternal weight gain is attributed to which of the following? A. Blood, uterine, and breast tissue B. Fetal tissue C. Maternal reserves D. Placental fluid ANS: D During early pregnancy, maternal weight gain is related to an increased blood volume, which is necessary to supply the enlarging uterus and to support fetal growth and development. As the pregnancy progresses, enlargement of the placenta and fetal body add to the womans increase in weight. By term, maternal extracellular fluid, blood, uterine tissue, and breast tissue comprise 35% of the gestational weight gain; the maternal reserves comprise 27%; fetal tissue comprises 27%; and placental fluid comprises 11% of the total maternal weight gain (Cunningham et al., 2010). 5. The prenatal clinic nurse meets with a 30-year-old woman who is experiencing her first pregnancy. The patients quadruple-marker screen result is positive at 17 weeks of gestation. Which action by the nurse is most important? A. Call the social worker for a consultation. B. Document the findings in the womans chart. C. Facilitate a referral to a genetics counselor. D. Prepare the woman for intrauterine death. ANS: C Feedback: All women should be offered screening with maternal serum markers. The triple-marker screen and the quadruple-marker screen test for the presence of alpha-fetoprotein, estradiol, human chorionic gonadotropin, and other markers. These tests screen for potential neural tube defects, Down syndrome, and trisomy 18. If the screen is positive, the woman should be referred to a genetics specialist for counseling and further testing, such as chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, should be performed (ACOG, 2007). There is no indication that the woman needs a social work consult or that she will experience intrauterine death. Documentation should be complete, but is not the most important action for the nurse to take. 6. A nurse is teaching a nonsmoking pregnant woman about the iron tablets she was just prescribed. What information is most important for the nurse to teach the patient? A. Calling the doctor right away for dark, tarry stools B. Drinking at least one glass of orange juice a day C. Stopping the prenatal vitamins while taking iron D. Taking the medication between meals and with milk ANS: B Vitamin C enhances the absorption of iron, and a nonsmoking woman should be able to get sufficient iron from a glass of citrus juice daily. Iron tablets should be taken between meals, using a beverage other than tea, coffee, or milk. Dark, tarry stools are a known side effect of iron. Women on iron should also be on prenatal vitamins. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 7. A 21-year-old pregnant woman smokes 8 to 10 cigarettes per day. The clinic nurse reviews the patients diet with her and notes that she does not eat fruits or vegetables. Which action should the nurse recommend to this patient? A. Cut down on smoking and eventually quit. B. Eat non-produce sources of vitamin C. C. Take an over-the-counter vitamin C supplement. D. Try to drink one glass of orange juice daily. ANS: C Food sources rich in vitamin C include produce such as red and green sweet peppers, oranges, kiwi fruit, grapefruit, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, cantaloupe, broccoli, sweet potatoes, tomato juice, cauliflower, pineapple, and kale. Most pregnant women are able to meet the recommended daily allowance (80 to 85 mg) by including at least one daily serving of citrus fruit or juice or vitamin Crich food source, but women who smoke need more (NIH, 2011). Although it is important for the woman to quit smoking, this alone will not help her meet her dietary need for Vitamin C. Because she does not eat the primary sources of this vitamin, an over-the-counter supplement would be her best option. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 8. An 18-year-old woman at 18 weeks gestation is being seen in the prenatal clinic. Her weight gain is 25 pounds over her prepregnant weight. Which is the perinatal nurses best approach to care at this visit? A. Ask the patient to complete a 3-day dietary recall while she is in the clinic. B. Explain the possible concerns related to excessive weight gain in pregnancy C. Explain to the patient that weight gain is not a concern in pregnancy. D. Teach the patient about the expected normal weight gain during pregnancy. ANS: A This woman has gained much more than the average weight gain in the first trimester (12.5 kg). Nutrition and weight management play an essential role in the development of a healthy pregnancy. Not only does the patient need to have an understanding of the essential nutritional elements, she must also be able to assess and modify her diet for the developing fetus and her own nutritional maintenance. To facilitate this process, it is the nurses responsibility to provide education and counseling concerning dietary intake, weight management, and potentially harmful nutritional practices. The nurse should facilitate this process while the woman is at her appointment. After assessment and mutually planning nutritional goals, the nurse can educate the woman about the possible concerns related to excessive weight gain and teach about the normal trajectory of weight gain during pregnancy. This series of actions follows the nursing process best. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 9. A woman comes to the clinic for her 24-week prenatal visit. This is her second pregnancy. The patient does not wish to know her weight and when her clinic record is reviewed, her total weight gain for this pregnancy is 5 pounds. She is very concerned about her changing body shape. What disorder does the nurse suspect? A. Anemia B. Anorexia nervosa C. Gestational diabetes D. Gestational hypertension ANS: B Anorexia nervosa is characterized by a distorted body image and an intense fear of becoming obese. Patients with anorexia nervosa lose weight either by excessive dieting or by purging themselves of calories they have ingested. Because this woman has gained very little weight and has concerns about her body shape, the nurse should suspect anorexia and assess the patient further. Anemia, gestational diabetes, and gestational hypertension do not manifest with these symptoms. Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 10. A 24-year-old pregnant woman at 26 weeks gestation is experiencing her third pregnancy. The patients obstetric history includes one full-term birth and one preterm birth; both children are alive and well. Today, the patient arrives at the clinic with complaints of fatigue, insomnia, and continuous backache. She reports that she is a nurse on an oncology unit and is worried about continuing to work her 12-hour shifts. What advice by the nurse would be most appropriate? A. Can you ask your manager about light-duty work at your job? B. See if you can take more breaks at work to rest and drink water. C. With your previous premature birth, you might need to reduce your working hours. D. You can continue to work as long as you want to and feel able to. ANS: C Although many women do continue to work throughout their pregnancies, certain medical problems and pregnancy complications are a red flag for the woman to reduce her work hours. Examples of these conditions include back problems, preterm labor (both of which this woman has), diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease, hypertension, and a history of spontaneous abortion. Light duty may be an option in addition to decreasing the work hours. Taking more breaks might be advised as well, but with this womans history and current health complaints she should consider decreasing her working hours. Other factors the nurse should discuss with the patient are the amount of heavy physical labor she does and her exposure to chemotherapeutic agents, both of which are possible environmental hazards to the pregnancy. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 11. A woman in the perinatal clinic is upset that her impending childbirth will cause her to lose her job. What assessment question by the nurse would yield the most important information regarding this situation? A. After you give birth, you will probably want to quit your job anyway. B. Can you make an appointment with human resources to discuss this? C. Where do you work and how long have you been there? D. Why do you think you will be fired after your baby is born? ANS: C The Family Medical Leave Act of 1993 guarantees most women (and men) 12 weeks of unpaid family leave following the birth or adoption of a child. The employee has the right to return to the job without loss of seniority, pay, or benefits. This act applies to federal, state, or local government organizations and any other organization that has 50 or more employees working within 75 miles of the workplace. The employee must have worked at this job at least 12 months or for at least 1,250 hours in the previous year to be eligible. By asking the woman where she works and how long she has been there, the nurse is assessing if the workplace must adhere to this act. Telling the woman she will probably want to quit her job is dismissive of her concerns. Making an appointment with human resources might be a good suggestion, but only after the nurse has assessed the patients eligibility for the Family Medical Leave Act. Asking why questions is considered a communication barrier, as many people become defensive when questions are worded this way. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 12. The clinic nurse is assessing a woman in her 30th week of pregnancy. Her fundal height is 23 centimeters. What other assessment finding would the nurse correlate with this condition? A. Blood glucose 112 mg/dL B. Hemoglobin 9.2 g/dL C. Leukorrhea D. Platelet count elevated ANS: B True anemia, or iron-deficiency anemia, occurs when the hemoglobin level drops below 10 g/dL. The bloods decreased oxygen-carrying capacity causes a reduction in oxygen transport to the developing fetus. Decreased fetal oxygen transport has been associated with intrauterine growth restriction and preterm birth. The patients lower-than-expected fundal height measurement could also be indicative of intrauterine growth restriction. The blood glucose, although slightly high, is not related, nor is leukorrhea (a common finding in pregnancy) or an elevated platelet count. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 13. The perinatal nurse would assess which newborn system as a priority after birth if a woman admitted to cocaine use during her pregnancy? A. Cardiovascular system B. Endocrine system C. Integumentary system D. Respiratory system ANS: A Although it is difficult to assess for complications from cocaine because of the likelihood of multi-drug abuse, common complications seen from its use include congenital abnormalities in the skull, brain, face, eyes, intestines, heart, limbs, genitals, and urinary tract. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment/Management of Care Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 14. A new patient is being assessed by the perinatal nurse. For exercise, the woman practices yoga five times a week, walks her dog, and swims. What action should the nurse do first? A. Ask if any yoga positions involve arching the back. B. Explain that swimming is a great exercise for all women. C. Instruct the woman to stop exercising if she gets fatigued. D. Tell her that no extra water is needed if she is swimming. ANS: A Women should adhere to some basic safety guidelines when formulating an exercise program. These guidelines include monitoring the breathing rate; ensuring that the ability to walk and talk comfortably is maintained during the physical activity; stopping the exercise when tired; avoiding exercises that can cause any degree of trauma to the abdomen or those that include rigorous bouncing, arching of the back, or bending beyond a 45-degree angle; and maintaining an adequate fluid intake. Because yoga involves different positions, the nurse should assess whether the patient engages in positions that involve arching the back. Swimming is good exercise and she should stop exercising if she gets fatigued, but asking about positions involves an immediate possible threat to the safety of the fetus. Extra water is needed no matter what type of exercise is being done. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Heath Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 15. Which patient would the perinatal nurse assess as being most at risk for maternal attachment problems? A. 18 year-old married woman with a supportive family who lives nearby B. 20-year-old woman with remote history of chlamydia and gonorrhea C. 22-year-old alcoholic who has been sober for 10 years D. 52-year-old unemployed divorced woman who thought she was in menopause ANS: D Maternal attachment to the fetus is an important area to assess and can be useful in identifying families at risk for maladaptive behaviors (Youngkin et al., 2012). The nurse should assess for indicators such as unintended pregnancy, intimate partner violence, difficulties in the partner relationship, sexually transmitted infections, limited financial resources, substance use, adolescence, poor social support systems, low educational level, and the presence of mental conditions that might interfere with the patients ability to bond with and care for the infant. The divorced, unemployed woman experiencing an unexpected pregnancy has the most risk factors. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 16. The nurse in a family practice clinic is working with a woman of childbearing age who recently was married and has no plans to have children yet. Which action by the nurse is most important? A. Asking the woman when the couple plans to get pregnant B. Encouraging the woman to review her birth control plan C. Instructing the woman to get 0.4 mg of folic acid daily D. Reviewing the womans family history for genetic defects ANS: C Because of the strong connection between folic acid deficiency and the subsequent development of neural tube defects, all women of childbearing age should take a folic acid supplement of at least 400 mcg/day (0.4 mg/day). Because the woman may not realize that she is pregnant early in her pregnancy when neural tube defects occur, prophylactic supplementation is recommended. The other options may be applicable too, but they are not as important as educating the woman about the importance of folic acid. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 17. The perinatal nurse recommends muscle-strengthening exercises to a woman who is pregnant for the first time. The woman states that she does not want to be muscle-bound and masculine. What response by the nurse is best? A. As long as you use lighter weights, you wont get muscle-bound. B. OK, what do you think about swimming for exercise then? C. Strengthening muscles will decrease risks of ligament and joint injury. D. Stronger muscles will make the labor process much easier on you. ANS: C Muscle strengthening benefits the woman as she copes with the physical changes of pregnancy, which include weight gain and postural changes. Muscle-strengthening exercises also help to decrease the risk of ligament and joint injury. The other options do not explain this information, making it much less likely she will participate in these exercises. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 18. The perinatal nurse notes that a patient has the diagnosis of ptyalism. What topic should the nurse include in the patients teaching plan? A. The benefits of acupuncture B. The need to eat more red meat C. The importance of strict vulvar hygiene D. The suggestion to suck on hard candy ANS: D Ptyalism is an excessive production of saliva. Possible helpful strategies include sucking on hard candy, brushing the teeth often, drinking plenty of water in small sips, and consuming small frequent meals with fewer starchy foods. Acupuncture can help with nausea and vomiting, vulvar hygiene would be recommended for leukorrhea, and eating more red meat may help with dietary insufficiencies. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 19. The prenatal nurse has reviewed a patients 3-day diet recall and notes that the patient typically eats a deli meat sandwich or hot dog, chips, and an apple for lunch. Breakfast consists of cereal, milk, and juice; and dinner contains meat, a starch, vegetables, and a salad. What action by the nurse is most important? . A. Advise the woman to obtain more calories from protein. B. Assess the womans knowledge of proper food handling. C. Discuss adding fish such as tuna or swordfish to the diet. D. Weigh the woman and document her weight in the chart. ANS: B Pregnant women should be taught proper food handling to prevent foodborne illnesses. Deli meats, hot dogs, and luncheon meats should be stored at 40 or less, heated before eating, and consumed within 4 days. Tuna should be eaten in moderation and fish such as shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish should be avoided in pregnancy because of mercury poisoning. Promoting safety is a priority. The woman may or may not need more calories from protein. Obtaining the patients weight and documentation are important prenatal activities, but are not the best answer because the nurse needs to assess the womans knowledge and practice of safe food handling first. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 20. A student nurse asks the faculty about the importance of preconception counseling. Which response by the faculty is best? A. It is the best time to find any conditions that could have a negative effect on a pregnancy. B. Its a good time to educate women about birth control options before they need them. C. Reproductive care is an important part of any womans health care. D. The Centers for Disease Control mandates that all women get preconception care. ANS: A Preconception counseling is an ideal time to identify conditions (physical, psychosocial, environmental, or social) that could lead to a future negative pregnancy outcome. The patient can be educated about the risks and assist in developing a plan to mitigate or avoid them. Providing birth control options can be an important part of preconception care, but this answer is too limited to be the best choice. Stating that reproductive care is important is vague. A goal of Healthy People 2020 is to increase the number of women getting preconception and prenatal care. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 21. A patient in the prenatal clinic had a negative rubella titer. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Have the laboratory draw rubella titers as a double-check. B. Instruct the woman to avoid anyone who may have the disease. C. Prepare to administer a rubella vaccination to the woman. D. Reassure the woman that rubella has few fetal consequences. ANS: B Rubella (German measles) can cause fetal abnormalities if the pregnant woman contracts it during the first trimester, so all pregnant women are screened for immunity. A positive test means the woman is immune to the disease, whereas a negative test indicates susceptibility to it. The woman needs to avoid people who may be ill with rubella and be immunized after her delivery. There is no need for a double check of the results. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 22. A woman in her second trimester continues to smoke a pack of cigarettes a day despite stating that she understands why smoking is bad for her and for her fetus. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Assess the patient for past trauma and abuse. B. Document the information in the patients chart. C. Review prior teaching done regarding smoking. D. Show photos of babies born with abnormalities. ANS: A Research shows that women who continue to smoke during pregnancy often report high levels of trauma and abuse and higher levels of PTSD symptoms. Women who smoke as a coping mechanism are even more likely to smoke during pregnancy (Lopez, Konrath, & Seng, 2011). The nurse should assess for these factors. Documentation is important, but is not the best answer because the nurse does not do anything to assist the patient; documentation alone is the answer only when the data are normal. Reviewing prior teaching may be helpful, but if the nurse does not help the patient address the core issue of smoking, this review will be unhelpful and a waste of time. Showing babies born with abnormalities is demeaning and could be interpreted as threatening. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 23. A nurse is reviewing the care plan for a woman in the third trimester of her first pregnancy. Which action by the patient best indicates positive adaptation to the pregnancy and impending motherhood? A. Attended three prenatal classes with her partner to learn about labor B. Continues to exercise, maintains a healthy diet, quit smoking recently C. Educated about pregnancy, fetal growth and development, and motherhood D. Has prepared a well-stocked nursery complete with stimulating toys ANS: C Attending prenatal classes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and having a prepared space for the baby are all tasks that indicate some degree of positive adaptation to a pregnancy. However, the best indicator of positive adaptation is when the woman can be described as well educated on pregnancy, growth and development of the fetus, and motherhood. This is much more inclusive than the other individual tasks. Cognitive Level: Evaluation/Evaluating Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Evaluation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 24. A patient on the postpartum floor of the hospital has a body mass index (BMI) of 38 and just gave birth to a healthy baby girl by Cesarean section. Which action by the nurse takes highest priority? A. Administering pain medication promptly when requested B. Assisting the woman to begin breastfeeding the infant C. Educating the woman about healthy weight loss D. Monitoring the incision site and using strict hand-washing technique ANS: D All of these interventions are appropriate for this patient. However, patient safety is the priority. Women with Level 2 obesity (BMI 3539.9) are at higher risk of wound infection and breakdown. The nurse should place a priority on hand hygiene and close monitoring of the incision. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 25. A pregnant woman is being discharged from the hospital after an episode of preterm labor that has resolved. She asks the nurse if she can now return to her low-impact aerobics class. Which response by the nurse is best? A. As long as its low impact, it should be OK to return. B. Make sure you can talk while you are exercising. C. Preterm labor is a contraindication for aerobic exercise. D. Wait 72 hours; if you dont have more contractions, its OK. ANS: C Premature labor, along with several other conditions, is an absolute contraindication to aerobic exercise during pregnancy. Although being able to talk while exercising is an important safety tip, this woman should not be engaging in any aerobics for the duration of this pregnancy. Cognitive Level: Applying/Application Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 26. A pregnant woman has been brought to the emergency department by the rescue squad with symptoms of heat exhaustion after competing in an outdoor race on a hot day. Before discharge, the nurse teaches about appropriate exercise during pregnancy. The husband asks if the womans having heat exhaustion will harm the baby. Which response by the nurse is most accurate? A. Definitely; thats why pregnant women should not do aerobic exercise. B. Fetal temperature depends on moms temperature, so the fetus may be affected. C. The baby is in a fluid environment and wont get overheated. D. Yes, but if we rapidly cool mom down, there wont be any problems. ANS: B The fetus is unable to reduce body temperature through perspiration or other means and instead must rely on the mothers body for temperature regulation. Possible complications of maternal hyperthermia include spontaneous abortion, preterm labor, and fetal distress. The nurse should educate the couple about exercise that wont increase the maternal temperature too much. Complications are possible, not definite; the baby being in a fluid environment does not regulate its temperature, and women who are pregnant can engage in aerobic activity following safety guidelines. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 27. A perinatal clinic nurse educated a pregnant woman about basic prenatal exercises. On a return visit, which statement by the patient indicates that teaching goals have been met? A. I have learned to isolate the right muscle for Kegel exercises. B. Its hard to find 30 minutes a day for exercise, but I have done it. C. Jumping rope is great exercise and keeps my weight in control. D. When I get fatigued with these exercises, I just push through it. ANS: A Kegel exercises are among the basic prenatal exercises taught to all pregnant women. In order to do them correctly, the woman needs to learn to isolate the pubococcygeal (PC) muscle. Women can obtain benefits from exercising as little as 10 minutes a day; jumping rope should be avoided because it involves too much bouncing; and when the pregnant woman is fatigued, she should rest. Cognitive Level: Evaluation/Evaluating Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Evaluation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 28. A woman in her second trimester wants to continue her weight-lifting and exercise plan. Which exercise would the nurse advise against participating in? A. Calf stretches B. Weight lifting C. Pelvic tilts D. Walking lunges ANS: D Lunges may injure connective tissue in the pelvic area and should be avoided. The other exercises are acceptable, but the woman should be cautioned to use resistance bands instead of free weights. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 29. A pregnant woman lifts weights regularly with a partner. What modification to this activity should the nurse suggest? A. Adjust the weight bench so that it is tilted, not flat. B. Do fewer repetitions by using heavier weights. C. Do not hold your breath for more than 30 seconds. D. Use free weights instead of resistance bands. ANS: A Lifting from a supine position can cause vena cava syndrome and decreased placental perfusion, so the woman should be instructed to adjust the weight bench to a tilted position. Heavy weights can overload the loosened joints, so using lighter weights with more repetitions is recommended. Holding the breath can cause a Valsalva maneuver, which decreases placental perfusion. Resistance bands are preferred to reduce the likelihood of abdominal injury. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 30. A pregnant woman is complaining of urinary frequency and is worried about incontinence. Which teaching strategy should the nurse use when counseling this woman? A. Minimize fluid intake during the day. B. Perform sit-ups to strengthen the abdomen. C. Teach the woman how to perform Kegel exercises. D. Void infrequently to train the bladder. ANS: C There are several physiological factors that cause urinary frequency and possible incontinence during pregnancy. Kegel exercises can improve both symptoms. The patient should remain well hydrated and void frequently. Sit-ups will not help with urinary frequency. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 31. An expectant couple complains of dyspareunia. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Assess the womans family history and genetic background. B. Explain that this condition is a normal finding during pregnancy. C. Instruct the couple that sex during pregnancy is not advised. D. Suggest sexual positions that might be more comfortable. ANS: D Dyspareunia is painful intercourse that may result from pelvic congestion and impaired circulation caused by the enlarging uterus during pregnancy. The nurse should reassure the couple that having sex during pregnancy is acceptable (unless there are medical reasons to contraindicate it) and suggest positions for sex that might be more comfortable for the woman. There is no reason to assess the womans family history and genetic background. Simply explaining that dyspareunia is normal is dismissive of the couples concern, although they should be reassured that this does sometimes happen and then they should be offered education on ways to alleviate it. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 32. A patient who has a previous diagnosis of round ligament pain is in the clinic for a follow-up visit. Which statement by the patient would indicate that teaching objectives for this problem have been met? A. I have been supporting my uterus with a pillow when resting. B. I have been trying all sorts of over-the-counter medications. C. I havent had any black, tarry stools at all since I was here. D. That black cohosh has really helped with my abdominal pain. ANS: A Round ligament pain is a common discomfort of pregnancy and the nurse can teach self-care measures such as supporting the uterus with a pillow when resting, warm baths, applying heat, and wearing a pregnancy girdle. Pregnant women should be taught to avoid all medications (both prescription and over the counter) without consulting with their health-care provider. Black, tarry stools are not related to round ligament pain. Black cohosh is a uterine stimulant and should be avoided during pregnancy. Cognitive Level: Evaluation/Evaluating Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Evaluation Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 33. A pregnant woman in her third trimester presents to the emergency department after fainting upon rising from a supine position. Which activity should the nurse perform first? A. Call the cardiology department for an EKG. B. Determine the fetal heart rate. C. Obtain a blood glucose reading. D. Teach her to rise slowly from a reclining position. ANS: C Supine hypotension is caused by the pressure of the enlarging uterus on the inferior vena cava while the woman is in a supine position. Vena caval compression impedes venous blood flow, reduces the amount of blood in the heart, and decreases cardiac output, causing dizziness and syncope. Pathological causes of supine hypotension include cardiac or respiratory disorders, anemia, hypoglycemia, dehydration, anxiety, and stress. Hypoglycemia can be treated rapidly if that is the cause. The other actions are appropriate as well, but the priority action would be to identify a condition that is readily treatable. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 34. A woman who is 26 weeks pregnant has a blood pressure of 158/100 mm Hg. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Assess the womans risk for other cardiovascular problems. B. Have her rest for 20 minutes, then reassess her blood pressure. C. Obtain a urine dipstick for proteinuria and assess for headache. D. Prepare to teach the woman about anti-hypertensive medication. ANS: C Preeclampsia is defined as a blood pressure greater than 140/90 mm Hg after 20 weeks gestation accompanied by proteinuria. Other signs and symptoms include headache, visual changes, and edema. The nurse should suspect this condition and confirm it with a urine test for protein and by asking about the other symptoms. Assessing for other cardiovascular risk problems and teaching about anti-hypertensive medications are not warranted in this situation. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 35. A nurse is planning to teach a prenatal class on the Dick-Read method of childbirth. Which information should the nurse plan to include? A. After birth, the newborn is placed in a tub of warm water. B. Consciously controlled breathing is the main coping strategy. C. Relaxation is vital because pain is caused by fear and tension. D. The Dick-Read method means a totally medication-free birth. ANS: C The founder of the Dick-Read method of childbirth was convinced that the pain associated with labor and birth was caused by tension and fear. These conditions stimulate the womans sympathetic nervous system, decrease blood flow to the uterus, and lead to uterine hypoxia. Relaxation restores the blood flow. Placing the baby in a warm tub of water is a component of the LeBoyer method; consciously controlled breathing as the main coping strategy is part of the Lamaze method; and although Dick-Read did not advocate for the use of pain medication, he did approve it when the woman was unable to relax or was experiencing complications. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 36. A nurse is helping a pregnant woman prepare for a planned home birth. What action by the nurse takes priority? A. Advising the woman to get a prescription for pain medication filled beforehand B. Attempting to convince the woman that giving birth at the hospital is a better choice C. Ensuring the woman has safe, rapid, and available transportation to a nearby hospital D. Giving the woman a list of local obstetricians who will assist at a home birth ANS: C Home births are an option for women who have low-risk pregnancies and no labor complications. However, according to a position statement by the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG), women who choose to deliver at home should be well- informed and should ensure access to rapid and timely transportation to the closest hospital in case of emergency (ACOG, 2011). Obstetricians will not deliver babies at home. Although pain management may be an important consideration, this is not as important as ensuring the safety of both mother and baby. Trying to convince the woman to go against her beliefs is disrespectful. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Planning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 37. A nurse is describing various childbirth options to an expectant couple. The woman states I want to do Lamaze because I hear you will have no pain with this method. Which response by the nurse is best? A. If done right, you will have no childbirth pain. B. Lamaze empowers you to cope with the pain. C. No, Lamaze emphasizes epidural pain control. D. Pain is a natural and normal part of childbirth. ANS: B Although Lamaze does teach that pain is a natural and normal part of childbirth, it also empowers the woman with strategies to cope with the pain in positive ways that facilitate the labor and birth process. It does not promise a pain-free childbirth and decisions about medications are left to the woman who has been educated about their effect on childbirth. Stating simply that pain is a normal part of childbirth without elaborating on how it is managed will not alleviate the patients concern. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 38. A womans birth plan specifies the Odent method of childbirth. Early in her admission, the woman asks about having an epidural for pain control. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Advise the woman that this will change her birth plan B. Ask why she wants pain control with natural childbirth C. Facilitate having the epidural catheter placed D. Review the breathing techniques for managing pain ANS: A The Odent method involves the womans giving birth in a warm water bath. Not every woman is a candidate for this method, including women who have rupture of the membranes or other complications that require continuous fetal monitoring. Epidural anesthesia requires continuous fetal monitoring, so if she chooses an epidural, she will not be able to use the Odent method. The nurse should advise her of this so that the woman is well informed before making a final decision. Asking why she wants pain control sounds judgmental. Breathing techniques are the primary method of coping with pain in the Lamaze method. If the woman decides to go ahead with the epidural, then by all means the nurse should facilitate its placement. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 39. A woman admitted in labor asks if she can have a doula present with her. The nurse understands that a doula is which of the following? A. A massage therapist with a specialty in labor massage B. A trained labor coach standing in for the womans partner C. A woman who is experienced in labor and provides support to the woman D. Someone who is trained and licensed to deliver babies in the hospital ANS: C A doula is a woman who is experienced in childbirth and who provides physical and emotional support to the mother during labor, birth, and the postpartum period. A doula is not a massage therapist, nor a trained labor coach, and a doula is not licensed to deliver babies. Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Caring Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 40. A woman in her third trimester is complaining of numbness and tingling in her fingers. Which action should the nurse take first? A. Assess the woman for hyperventilation. B. Educate her about a thermoskin carpal tunnel glove. C. Facilitate an appointment for a nerve conduction study. D. Reassure her that the condition is temporary. ANS: A Carpal tunnel syndrome is commonly seen in pregnancy and can be caused by either hyperventilation or from nerve compression of the median and ulnar nerves in the arm. If the woman is hyperventilating, the nurse can educate her about conscious control of breathing, which would provide relief quickly and easily. If hyperventilation does not seem to be the causative factor, the nurse can educate her about strategies for symptom control. These methods include maintaining good posture, elevating the hands on pillows when sleeping, wearing a wrist brace, and/or using a thermoskin carpal tunnel glove. Simply reassuring the woman that the condition is temporary does nothing to increase her comfort. A nerve conduction study is not needed at this time, but if the condition persists after childbirth, it could be an option. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 41. A nurse is assessing a woman pregnant with her third child. She has a history of pregnancy-related varicosities. Which action by the nurse takes priority? A. Advising the woman not to cross her legs while pregnant B. Assessing the womans pedal pulses and circulation C. Having the woman rate her leg pain on a 1-to-10 scale D. Teaching the woman to wear knee-high stockings ANS: B Assessment is the first step of the nursing process, and issues related to airway, breathing, and circulation are priorities for all patients. The nurse should first assess the patients circulation, including pedal pulses, warmth, skin color, and capillary refill. After a circulatory assessment is complete, the nurse should assess pain. After a thorough assessment, the nurse can plan teaching. Self-care measures include not crossing the legs, not wearing constrictive clothing such as knee-high stockings, and elevating the legs at least twice a day. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 42. A student nurse is working in the OB clinic as part of a preceptorship. The student is counseling a woman in her first trimester who complains of insomnia due to nasal congestion. Which action by the student warrants intervention by the students preceptor? A. Advises the woman to use over-the-counter nasal saline spray B. Assesses the patient for other allergy and cold symptoms C. Instructs the woman to use decongestants and antihistamines D. Suggests the woman take a hot, steamy bath at bedtime ANS: C Congestion is a common complaint in pregnancy. Self-care measures include occasional saline drops; hot, steamy showers; increasing fluids;, and using a vaporizer or humidifier. It is important to rule out upper respiratory infections such as colds or allergies when a woman complains of nasal congestion. Women should avoid decongestants in the first trimester. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse teaches the prenatal class attendees about herbal medications that may cause uterine contractions and preterm labor. Which of the following herbal preparations should be avoided because they act as uterine stimulants? (Select all that apply.) A. Black cohosh B. Dong quai C. Ephedra D. Mugwort E. Senna ANS: A, D During preconception counseling and pregnancy, nurses should educate couples to avoid the following common uterine stimulants that may cause preterm labor: barberry, black cohosh, feverfew, goldenseal, mugwort, pennyroyal leaf, and yarrow root. Dong quai is an anticoagulant, ephedra is a cardiac stimulant, and senna can overstimulate digestion and metabolism, causing fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 2. A 22-year-old woman is experiencing her third pregnancy. Her obstetrical history includes one first-trimester elective abortion and one first-trimester spontaneous abortion. The patient is a semi-vegetarian who drinks milk and eats yogurt and fish as part of her daily intake. Which of the following should the nurse include in the patients dietary teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A. Consuming red meat B. Eating foods high in zinc C. Increasing calcium intake D. Restricting sodium E. Taking an iron supplement ANS: B, E Semi-vegetarian diets include fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products but no beef or pork. Pregnant women who adhere to this diet may consume inadequate amounts of iron and zinc. Most women cannot consume enough iron through their diets while pregnant, so an iron supplement should be suggested. The nurse can also educate the patient about foods high in zinc so that she can increase her intake. Although red meat does contain iron, consuming meat goes against the womans chosen lifestyle and it would be disrespectful of the nurse to suggest this. Increasing calcium and restricting sodium intake are not helpful advice in this situation. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Basic Care and Comfort Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 3. For which diseases does the prenatal nurse recommend a newly pregnant woman be screened? (Select all that apply.) A. Chlamydia B. Hepatitis A C. Mumps D. Rubella E. Varicella ANS: A, D, E Pregnant women should be screened for sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis B, HIV, rubella, and varicella. When contracted during the first trimester, rubella causes a number of fetal deformities. Varicella (chickenpox) is another common childhood disease that may cause problems in the developing embryo and fetus. Therefore, all pregnant women are screened for rubella and varicella. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 4. An expectant father seems to be ambivalent about the impending birth of his child. Which actions by the nurse are most important? (Select all that apply.) A. Ask the father if he has fears for his partner. B. Assess the woman for intimate partner violence (IPV). C. Call the social worker to assess the fathers financial situation. D. Give the father written information about childbirth. E. Reassure the father that conflicting emotions are normal. ANS: A, E Expectant fathers can experience fears and ambivalence about the womans pregnancy. Some common concerns include fear for the womans safety and health, financial concerns, and worry that he is not ready for this responsibility. The nurse should reassure the father that these feelings are normal and can further the discussion by assessing for these common emotions. There is no indication that either partner suffers from IPV, it is premature to call the social worker before a problem has been identified, and giving the father written information on childbirth may not address his concerns. In addition, the nurse should assess literacy prior to giving written information and should be prepared to discuss it. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 5. A nurse is educating a pregnant woman who has a history of pica about healthier eating. Which nutrients should the nurse include in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A. Calcium B. Folic acid C. Iron D. Vitamin C E. Vitamin D ANS: A, C, D, E Specific nutritional deficiencies associated with pica include deficiencies in iron, calcium zinc, thiamine, niacin, vitamin C, and vitamin D. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 6. A nurse is conducting a class on the Lamaze method of childbirth. Which core values does this nurse plan to teach? (Select all that apply.) A. A womans ability to give birth can be diminished by the care provider. B. Conscious breathing is the main coping strategy in Lamaze. C. Lamaze birthing is medication free and epidurals are not given. D. The birth coach is only present to provide comfort to the laboring woman. E. Women are capable of and have the wisdom to give birth. ANS: A, B, E The womans innate ability to give birth, the use of conscious breathing as the main coping strategy, and the fact that the womans confidence and ability to give birth can be either enhanced or diminished by the care provider and place of birth are some of the core concepts of the Lamaze method. Lamaze educators provide information on pain control and stress that each woman needs to make the decision about pain management that is best for her. Birth partners are taught to assess the woman for hyperventilation during the transition period of labor. Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 7. A woman is admitted to the hospital with a birth plan that specifies the Bradley method of childbirth. Which actions by the nurse are most appropriate for this patient? (Select all that apply.) A. Assist the woman in conserving energy for childbirth. B. Call the anesthesiologist to place an epidural. C. Ensure the patient has a quiet environment. D. Establish a relationship with the husband-coach. E. Turn the lights down in the patients room. ANS: A, C, D, E The Bradley method emphasizes inward relaxation, allowing the woman to conserve energy for the impending birth. There is an emphasis on darkness, solitude, and quiet in order to reduce stimulation and enhance the calm and comfort needed by the woman. The Bradley method is also known as husband-coached childbirth. The nurse will need to establish a professional, caring relationship with both the woman and her partner. Medication is discouraged in this method. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 8. A nurse is explaining childbirth education choices to an expectant couple. The nurse explains that although each method is different, all methods emphasize some similar concepts. Which concepts does the nurse describe as similar across different methodologies? (Select all that apply.) A. Biological B. Financial C. Psychosocial D. Relational E. Social ANS: A, C, E Although they are different, all childbirth preparation classes incorporate a holistic approach to childbearing, which encompasses the biological, psychological, and social factors related to the experience. Chapter 11: Caring for the Woman Experiencing Complications During Pregnancy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A woman presents to the perinatal clinic with abdominal pain. She has missed one period and, following a transvaginal ultrasound, pregnancy is confirmed. However, implantation has occurred in the right fallopian tube. The ectopic mass is 3 cm and has not ruptured. The nurse prepares the patient for which therapy? A. Laparoscopic salpingostomy B. Methotrexate C. Partial salpingectomy D. Salpingectomy by laparotomy ANS: B Methotrexate, a chemotherapeutic drug and folic acid inhibitor that stops cell production and destroys remaining trophoblastic tissue, is used in the management of uncomplicated, non-life-threatening ectopic pregnancies. Patients are considered to be eligible for methotrexate therapy if the ectopic mass is unruptured and measures 4 cm or less on ultrasound examination. The other options would not be needed. Cognitive Level: Application/Applying Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Moderate PTS: 1 2. The prenatal clinic nurse assesses a woman at 15 weeks gestation. The patients blood pressure, measured twice at intervals 1 hour apart with a cuff that fits appropriately, is 146/96 mm Hg. The nurse understands the patient has which condition? A. Chronic hypertension B. Gestational hypertension C. Preeclampsia D. Transient hypertension ANS: A Chronic hypertension is defined as hypertension that is present and observable prior to pregnancy, or hypertension that is diagnosed before the 20th week of gestation. Hypertension is defined as a blood pressure greater than 140/90 mm Hg. Hypertension for which a diagnosis is confirmed for the first time during pregnancy and that persists beyond the 84th day postpartum is also classified as chronic hypertension. Gestational hypertension occurs after 28 weeks without proteinuria and is a temporary diagnosis used until more diagnostic testing can be accomplished. Preeclampsia is an increased blood pressure seen after 20 weeks gestation accompanied by proteinuria. Transient hypertension describes women who develop gestational hypertension but have no preeclampsia and whose blood pressure returns to normal within 12 weeks postpartum. This diagnosis is used only after pregnancy. Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 3. The perinatal nurse is assessing a woman who is at 35 weeks gestation in her first pregnancy. She is worried about having her baby too soon, and she is experiencing uterine contractions every 10 to 15 minutes. The fetal heart rate is 136 beats/minute. A vaginal examination performed by the health-care provider reveals no cervical changes since her last examination. Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of V-shaped cervical funneling. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Educate the woman on benefits of corticosteroids. B. Facilitate admission to the high-risk OB unit. C. Prepare to administer a dose of magnesium sulfate. D. Reassure the woman that she is not in preterm labor. ANS: D Preterm labor is defined as regular uterine contractions and cervical changes before the end of the 37th week of gestation. Many patients present with preterm contractions but only those who demonstrate changes in the cervix are diagnosed with preterm labor. Because this woman has no demonstrated cervical changes, she does not have the diagnosis. Also reassuring is the infrequency of her contractions; a defining characteristic of preterm labor is persistent uterine contractions (4 every 20 minutes or 8 per hour). Another reassuring finding is the presence of V-shaped cervical funneling ; a change to U-shaped cervical funneling in a woman with a shortened cervix is associated with preterm labor in high-risk women with a prior spontaneous preterm birth. The woman does not require corticosteroids or magnesium sulfate or admission to the high-risk OB unit. Cognitive Level: Analysis/Analyzing Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Difficulty: Difficult PTS: 1 4. The perinatal nurse is caring for a woman at 26 weeks gestation who has a history of hypertension that has been well controlled. Today she presents with a blood pressure of 156/102 mm Hg and she has 2+ protein on urine dipstick. Which initial action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Arrange admission to the high-risk OB unit. B. Instruct the woman on strict bedrest. C. Obtain a clean-catch urine sample. D. Prepare to administer IV anti-hypertensives. 5. A 22-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Her blood pressure is 90/58 mm Hg, her pulse is 120 beats/minute, and she complains of dizziness. Which action by the nurse takes priority? A. Assess the woman for sexually transmitted infections. B. Collect a urine sample for pregnancy testing. C. Obtain informed consent for a salpingectomy. D. Start two large-bore IVs for fluid replacement. 6. A woman in her second trimester of pregnancy presents to the perinatal clinic with complaints of scant vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and shoulder pain. What action should the nurse perform first? A. Assess her for a history of preterm labor. B. Obtain a blood sample for a b-hCG test. C. Prepare the woman for a pelvic exam. D. Request an order for methotrexate (Rheumatrex). 7. A nurse is caring for a patient who has been diagnosed with an incomplete molar pregnancy. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Advise the woman that she can try to get pregnant in 3 months. B. Arrange a consultation with a radiation oncology nurse. C. Facilitate screening for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). D. Give the patient information on perinatal loss support groups. 8. A nurse is assessing a 52-year-old primigravida woman who presents complaining of moderate dark-brown vaginal bleeding. On physical exam, her uterus is large for dates. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Assess the womans diet for folic acid intake. B. Facilitate an ultrasound examination. C. Instruct the woman on a fetal kick count. D. Prepare the woman for pelvic cultures. 9. A woman who recently had a miscarriage is in the clinic for follow-up. She sees the diagnosis spontaneous abortion on her chart and becomes visibly upset, stating, I did not have an abortion! Which response by the nurse is best? A. Dont be upset; that is just a medical term used commonly. B. I can come back and talk to you when you are not so upset. C. I see you are upset. Does it help to know this means miscarriage? D. No one is accusing you of having an abortion. 10. A student in a perinatal clinic asks the clinic nurse what an incomplete abortion is. Which response by the nurse is best? A. Complete loss of all products of conception before 20 weeks gestation B. Fetal death before 20 weeks with retention of all products of conception C. Loss of some, but not all, products of conception before 20 weeks D. When the patient initiates an abortion, but then stops the procedure 11. The nurse finds a woman who has recently suffered her third complete abortion crying and saying Why me? What did I do to deserve being punished like this? Which response by the nurse is best? A. Ask the woman if she uses illicit drugs or drinks alcohol during pregnancy. B. Explain that most miscarriages are related to genetic abnormalities. C. Offer to call a clergy member or social worker to visit with the woman. D. Reassure the woman that she is not being punished. 12. A nurse is assessing a woman in the perinatal clinical with diagnosed cervical insufficiency. The woman is in her 18th week of a viable pregnancy. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Assist with obtaining informed consent for a cerclage. B. Draw blood to assess the maternal Rh status. C. Facilitate a transvaginal and abdominal ultrasound. D. Refer the woman to a perinatal grief specialist. 13. A woman is being dismissed after undergoing placement of a cerclage. The woman is married with a husband who travels frequently and the couple has two other children. Which action by the nurse is most helpful? A. Arrange for the visiting nurse to administer IV antibiotics. B. Educate the woman on the need for strict bedrest. C. Enlist the services of a social worker to help her plan care for her other children. D. Teach the woman about the side effects of metachlopramide (Reglan). 14. The nurse manager in a perinatal clinic is reviewing research related to care of patients with cervical insufficiency and preterm birth. What practice change might result from this review of the literature? A. Administering fewer doses of Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) B. Decreased utilization of cerclage placement in women with preterm labor C. Measuring serial cervical lengths in all women pregnant with singletons D. Providing betamethasone (Celestone) as long-term therapy 15. A woman is hospitalized with hyperemesis gravidarum. Which other member of the health-care team should the nurse ensure is involved in this patients care as a priority? A. Chaplain B. Diabetic educator C. Mental health nurse practitioner D. Registered dietician 16. A nurse has admitted a patient with hyperemesis gravidarum and is reviewing the physicians orders. Which order should the nurse question? A. Betamethasone (Celestone) 100 mg IV every 8 hours B. Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) 75 mg rectally every 46 hours C. Metoclopramide (Reglan) 10 mg IV every 8 hours D. Promethazine (Phenergan) 25 mg IV every 4 hours 17. A pregnant patient in the second trimester is in the emergency department after a motor vehicle crash. She has a severe laceration of her arm resulting in a large blood loss. Which assessment should the nurse perform first? A. Blood pressure B. Fetal heart tones C. Pulse D. Respiratory rate 18. A nurse is teaching a woman pregnant in the second trimester who has been diagnosed with a partial placenta previa. Which information is most important to document? A. Patient and partner show no anxiety or helplessness and were given educational support material. B. Patient instructed that bleeding may occur as placenta totally covers the cervical os. C. Patient instructed to tell all health-care providers that vaginal exams are prohibited. D. Patient received information about placenta previa and understood it well. 19. A nurse has admitted a woman pregnant in her third trimester with moderate vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain. After assessing maternal vital signs, obtaining the fetal heart rate, and starting an IV line, which action should the nurse do next? A. Administer betamethasone (Celestone) just prior to delivery. B. Discuss pros and cons of continuous fetal monitoring. C. Facilitate laboratory work, including blood type and screen. D. Obtain informed consent for emergent delivery. 20. A woman with a history of previous abruptio placentae with fetal demise is being seen in the perinatal clinic. She is now pregnant again in her early second trimester. She tells the nurse she is a Jehovahs Witness and she wants her chart to reflect her refusal to accept blood products if she hemorrhages again. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Ask the woman to consider an exception in order to save her babys life if needed. B. Document the information on the chart and inform the health-care provider. C. Encourage the woman and provider to discuss appropriate delivery sites. D. Tell the woman a court can order the transfusion to save the baby. 21. A nurse wants to conduct a community education session for women at high risk of preterm birth. Which teaching site would best meet this objective? A. After services at a predominantly African American church B. At the local Asian and African markets during a weekday C. In the lobby of several OB-GYN clinics in the suburbs D. Near the food court at the local shopping mall 22. A woman who is in her third trimester and is at risk for preterm birth calls the clinic to get the results of her fetal fibronectin test (fFN). The nurse sees the result is negative. Which advice to the patient is most appropriate? A. Come to the perinatal clinic for a screening ultrasound. B. Continue the current management plan as directed. C. Go to the hospital immediately for imminent delivery. D. Plan to continue taking betamethasone (Celestone) for 1 week. 23. A woman who is 36 weeks pregnant presents to the perinatal clinic with complaints of backache, pelvic fullness, and uterine contractions. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Arrange admission to the hospital. B. Obtain a clean-catch, midstream urine sample. C. Obtain blood for a type and screen. D. Prepare to administer a tocolytic agent. 24. A woman at 32 weeks gestation is admitted to the high-risk OB unit with a diagnosis of preterm labor. On assessment the nurse finds the following: blood pressure, 182/96 mm Hg; pulse, 106 beats/minute; respirations, 16 breaths/minute; regular uterine contractions of 5 in 10 minutes; and fetal heart rate of 145 beats/minute. She is dilated to 8 cm. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Administer the ordered dose of betamethasone (Celestone). B. Call for an immediate electrocardiogram (EKG). C. Document the findings and prepare for emergent delivery. D. Prepare to administer magnesium sulfate (Sulfamag). 25. A woman is admitted to the high-risk OB unit with the diagnosis of preterm labor. Orders include bedrest with continuous fetal monitoring, administration of magnesium sulfate (Sulfamag) and betamethasone (Celestone), and laboratory work. In reviewing the patients record, the nurse notes a history of hypertension that is well controlled with nifedipine (Procardia) and diet-controlled diabetes mellitus type 2. Which action by the nurse is best? A. Assist the woman to choose appropriate food items from the menu. B. Call the physician to question the orders and document the conversation. C. Order a pressure-relieving mattress overlay and perform a skin assessment. D. Prepare to give the magnesium sulfate and betamethasone as ordered. 26. A woman who is 28 weeks pregnant is admitted to the high-risk OB unit with preterm premature rupture of the membranes. Four hours after admission, the nurse notes the following: temperature: 38.5C (101.5F), maternal pulse: 122 beats/minute, and white blood cell count: 23,000 mm3. Which action by the nurse takes priority? A. Document the findings and notify the health-care provider. B. Facilitate fern testing or Nitrazine testing on vaginal fluid. C. Prepare to administer a prn dose of acetaminophen (Tylenol). D. Reassure the woman that these are expected findings. 27. A new nurse is caring for a woman previously diagnosed with preeclampsia who was admitted to the high-risk OB unit after suffering a seizure in the perinatal clinic. The new nurse is preparing to administer a dose of magnesium sulfate (Sulfamag). Which action by the nurse warrants intervention by the unit manager? A. Explains to the patient that her vital signs and EKG will be monitored frequently B. Piggybacks the Sulfamag into a main line using an infusion pump C. Places 10% calcium gluconate in a secure location in the patients room D. Runs the Sulfamag as the main IV line through an infusion pump 28. A pregnant patient is brought to the emergency department after a roll-over motor vehicle crash. After assessing and stabilizing the patients airway, breathing, and circulation, which of the following actions should the nurse perform next? A. Assess the woman for further injuries. B. Attach continuous fetal monitoring leads. C. Determine the date of the patients last tetanus booster. D. Prepare to transfer the woman to the delivery suite. 29. A nurse is caring for a woman receiving continuous electronic fetal monitoring. Which action by the nurse is most important? A. Educate the woman and her partner about the importance of electronic fetal monitoring. B. Ensure clearly readable monitoring strips are placed in the patients chart per protocol. C. Offer diversionary activities for the woman and partner while they are in the hospital. D. Restrict visitors in order to decrease the chance of being exposed to infectious illness. 30. A perinatal nurse has developed a birth plan with a woman who is in her third trimester and has a physical disability. Which action by the nurse would be best for this patient? A. Arrange for a social work home visit after the woman gives birth and goes home. B. Consult with the OB clinical nurse specialist to plan for the womans birth. C. Notify the unit manager about the upcoming delivery of a woman with a disability. D. Prepare a written birth plan document and ensure the woman has a copy to take with her. 31. A student nurse asks the perinatal nurse why teenagers might be vulnerable to intimate partner violence. Which answer by the nurse is best? A. Because teens are dependent on others for their everyday living needs. B. Being younger and smaller makes them more apt to be physically abused. C. Pregnant teens are often addicted to drugs and alcohol, or are prostitutes. D. So many teens make bad choices, and choosing abusive men is one of them. 32. The nurse has admitted a patient to the high-risk OB unit with preterm premature rupture of the membranes. After obtaining maternal vital signs and the fetal heart rate, which action should the nurse do next? A. Assess for coping skills in the woman and her partner. B. Attach the woman to continuous electronic fetal monitoring. C. Consult social work for diversionary activities to enhance bedrest. D. Prepare to administer antibiotics for presumed chorioamnionitis. 33. A patient in the high-risk OB unit has suffered a seizure and is now postictal. She is on oxygen at 2L/minute. Which assessment by the nurse warrants immediate intervention? A. Fetal heart rate is 98 beats/minute on electronic fetal monitor strip. B. Maternal oxygen saturation is 94% by pulse oximetry. C. Mother is sleeping soundly and is difficult to arouse. D. Mothers respiratory rate is 12 breaths/minute. 34. A pregnant patient with a long-standing history of cardiovascular disease is admitted to the high-risk OB unit. The patient will have internal continuous electronic fetal monitoring until delivery. Which action by the nurse takes priority? A. Assess the womans vital signs every hour until delivery. B. Consult with the physician about prophylactic antibiotics. C. Educate the woman and partner about this modality. D. Prepare an infusion of magnesium sulfate (Sulfamag). 35. A woman pregnant with triplets is a patient in the high-risk OB unit. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Document serial, individual fetal monitor strips. B. Label the monitor lines in descending fetal order. C. Monitor the fetuses simultaneously with a triplet monitor. D. Obtain fetal monitor strips in presenting order. 36. A nurse is caring for a pregnant woman admitted to the high-risk OB unit. Which finding indicates to the nurse that outcomes for a priority nursing diagnosis have been met? A. Patient can list community resources available for her after childbirth. B. Patient describes skills she and partner use for dealing with stress. C. Patient states that with next pregnancy, she will obtain consistent prenatal care. D. Patients blood pressure is 128/62 mm Hg without orthostatic changes. 37. A postpartum woman being dismissed complains to the nurse that she has extreme fatigue, shoulder pain, and has noticed what looks like blood in her urine. Which laboratory finding would the nurse correlate with these symptoms? A. Arterial blood pH: 7.35 B. Blood glucose: 100 mg/dL C. Platelet count: 98,000/mm3 D. White blood cell count: 9,000/mm3 38. A nurse is preparing to dismiss a woman and her infant from the hospital. The woman is Rh(D)-negative and the infant is Rh(D)-positive. This was her first pregnancy. Which nursing action is most appropriate? A. Administer Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) and document accurately. B. Assess the father to see if he has ever received an injection of RhoGAM. C. Educate the woman on the need for RhoGAM if she delivers an Rh(D)-negative baby. D. Instruct the woman to get RhoGAM with her next pregnancy, not for this one. 39. A woman with a history of heart failure is in labor and has the following vital signs: blood pressure: 100/58 mm Hg, pulse: 120 beats/minute, respiratory rate: 36 breaths/minute, oxygen saturation: 88%. Which action should the nurse perform first? A. Administer oxygen at 10 L/min per rebreather mask. B. Call the health-care provider to report the results. C. Document the findings in the patients chart. D. Increase the womans IV infusion to 150 mL/hour. 40. A patient on the high-risk OB unit is receiving magnesium sulfate. The nurse notes that her magnesium level is 14 mEq/L. Which of the following actions by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Bring the crash cart to the patients room. B. Document the findings in the womans chart. C. Order another blood level in 6 hours. D. Prepare to administer calcium gluconate. 41. A pregnant woman who has diabetes mellitus is in the high-risk OB clinic for a checkup. The nurse notes that her hemoglobin A1C (HbAIC) is 5%. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Arrange a referral to the diabetic nurse educator. B. Assess for factors leading to noncompliance. C. Document the findings in the patients chart. D. Schedule another HbAIC in 4 weeks. 42. A pregnant patient is admitted with possible deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Orders are left to start warfarin (Coumadin) 5 mg p.o., once daily. Which of the following actions by the nurse is most appropriate? A. Call the physician to clarify the order and document the conversation. B. Instruct the patient not to get out of bed without assistance. C. Start the warfarin as soon as it is available from the pharmacy. D. Teach the patient about the risks and benefits of anticoagulation. 43. A pregnant woman is HIV-positive. She is asking about ways to decrease the risk of vertical transmission to her baby. Which option given by the nurse would confer the least risk to the baby? A. Antiretroviral medications (zidovudine [ZDV]) B. Cesarean delivery C. Cesarean delivery plus antiretroviral medications for the newborn D. Vaginal delivery plus antiretroviral medications for the newborn 44. A nurse is caring for a pregnant woman on the high-risk OB unit who is anticipating a long stay on bedrest. Which action by the nurse would be most helpful to help diminish the physical complications associated with imposed bedrest? A. Arrange a social work consult for coping assessment. B. Assess and document the womans skin each shift. C. Consult physical therapy for in-bed exercises. D. Help the woman select high-protein foods from the menu. 45. A nurse manager on the OB unit is auditing patient charts. One record documents the care of a patient having a seizure. The record describes the time and length of the seizure, medications given, maternal and fetal vital signs, and outcome of treatment. Which action by the manager is best? A. Compare the chart with charts of similar patients. B. Educate the staff on better documentation practices. C. Have the nurse rewrite the documentation. D. No action is needed; continue with chart audits. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The perinatal nurse is educating a group of women on common causes of miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion. Which of the following does the nurse describe? (Select all that apply.) A. Cervical anatomic defects B. Chromosomal abnormalities C. Maternal infections D. Recreational drug use E. Working during pregnancy 2. A nurse is conducting an educational class for expectant couples. What information about preterm birth does the nurse include in the discussion? (Select all that apply.) A. A diagnosis of preterm labor requires cervical changes. B. African Americans have the lowest rate of preterm birth of all ethnic groups. C. The vast majority of infants born at 29 weeks gestation survive. D. Today, 1 in 25 babies are born prematurely in America. E. Worldwide, preterm birth is the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. 3. Which of the following does the nurse recognize as complications of premature birth? (Select all that apply.) A. Osteoporosis B. Cerebral palsy and mental retardation C. Diabetes mellitus type 1 D. Intraventricular hemorrhage E. Retinopathy of prematurity 4. A nurse is teaching a woman the actions to take in the event the woman believes she is in preterm labor. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.) A. Come to the hospital immediately if you dont feel contractions. B. Drink 2 to 3 glasses of a non-caffeinated beverage after emptying your bladder. C. Feel for uterine contractions for the next 2 to 3 hours. D. Lie down on your back with pillows under your knees. E. Seek additional health care if you have 4 or more contractions in 1 hour. 5. A nurse is caring for a woman on a continuous IV of magnesium sulfate. Which actions are appropriate for patient safety? (Select all that apply.) A. Administer the bolus from the main bag, then change to the maintenance rate. B. Double-check each new bag and dose/rate change with another nurse. C. Ensure that a supply of romazicon (Flumazenil) is available in the patients room. D. Perform handoff report at the bedside, verifying the dose and orders by both nurses. E. Place color-coded tags on each IV line, bag, and pump to label them clearly. 6. A nurse is conducting a nonstress test on a pregnant woman. The nurse understands that which of the following conditions can lead to loss of fetal heart rate reactivity? A. Central nervous system irritability B. Certain congenital abnormalities C. Fetal acidbase disturbance D. Fetal hypoxia E. Fetal sleep cycle 7. A perinatal nurse is working with a woman who has had four perinatal losses in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. The nurse should anticipate orders for which of the following diagnostic tests? (Select all that apply.) A. Cervical cultures B. Hysterosalpingogram C. Maternal/paternal karyotype D. Sickle cell screening E. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels 8. A nurse is caring for a laboring woman from an unfamiliar culture who has limited English skills. Which nursing actions are important to provide nursing care to this patient? (Select all that apply.) A. Allow artifacts that have religious or cultural significance to remain with the woman. B. Assess the womans beliefs about childbirth, breastfeeding, and postpartum nutrition. C. Communicate with the woman and family using a professional interpreter. D. Identify community resources that are culturally appropriate and acceptable. E. Restrict visitors to one person who can then communicate with the other family members. 9. A nurse is assessing all patients in the perinatal clinic for culturally related increased risk for gestational diabetes mellitus. Which patients would the nurse assess as being in the highest risk groups? (Select all that apply.) A. African American B. Caucasian C. Chinese D. Hispanic E. Native American 10. A nurse in the perinatal clinic explains to a student nurse that which of the following patients are at highest risk of developing gestational diabetes? (Select all that apply.) A. A17-year-old in her second pregnancy B. A 24-year-old pregnant woman with placenta previa C. A 32-year-old woman with a BMI of 40 D. A woman whose first baby weighed 10.5 lb (4.7 kg) E. A woman whose mother and sister had gestational diabetes 11. The perinatal nurse describes risk factors for placenta previa to the student nurse. Which of the following risk factors does the nurse include? (Select all that apply.) A. Cocaine use B. Previous cesarean birth C. Previous use of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) D. Tobacco use E. Young maternal age 12. A pregnant woman in her second trimester arrives at the labor unit triage station with complaints of lower abdominal cramping and urinary frequency. Appropriate nursing actions include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Assess the fetal heart rate. B. Assess the patients pulse rate. C. Insert an indwelling Foley catheter. D. Obtain a urine sample for culture and sensitivity. E. Palpate the patients abdomen for contractions. 13. The perinatal nurse knows that tocolytic agents are most often used to do which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A. Allow for transport of the woman to a tertiary care facility B. Facilitate administration of antenatal corticosteroids C. Prevent development of fetal respiratory distress syndrome D. Prevent maternal infection E. Prolong pregnancy as long as possible PTS: 1 14. A nurse is caring for a pregnant 16-year-old who is homeless and occasionally spends time in a homeless shelter. She has been seen in the clinic before for sexually transmitted infections (STIs). She weighs 92 lb (41.8 kg) and occasionally uses crack cocaine. Which risk factors does this patient have for a negative pregnancy outcome? (Select all that apply.) A. Age of 16 years B. Being homeless C. Crack cocaine use D. History of STIs E. Low weight Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering Content Area: Pediatrics/Maternity Patient Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Difficulty: Easy PTS: 1 OTHER 1. Match the terms on the left with the statements on the right. Answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. Placenta previa _____ Can be described as complete, partial, or marginal b. Abruptio placentae _____ Condition in which the umbilical cord is implanted in the membranes rather than in the placenta c. Vasa previa _____ May be associated with previous cesarean birth _____ One risk factor is closely spaced pregnancies _____ Premature separation of the normally implanted placenta from the lining of the uterus _____ Can resolve as the uterus enlarges in the third trimester _____ Maternal abdominal trauma is one risk factor _____ Classic sign is vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal pain in the third trimester [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 278 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$27.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 30, 2020
Number of pages
278
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 30, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
172










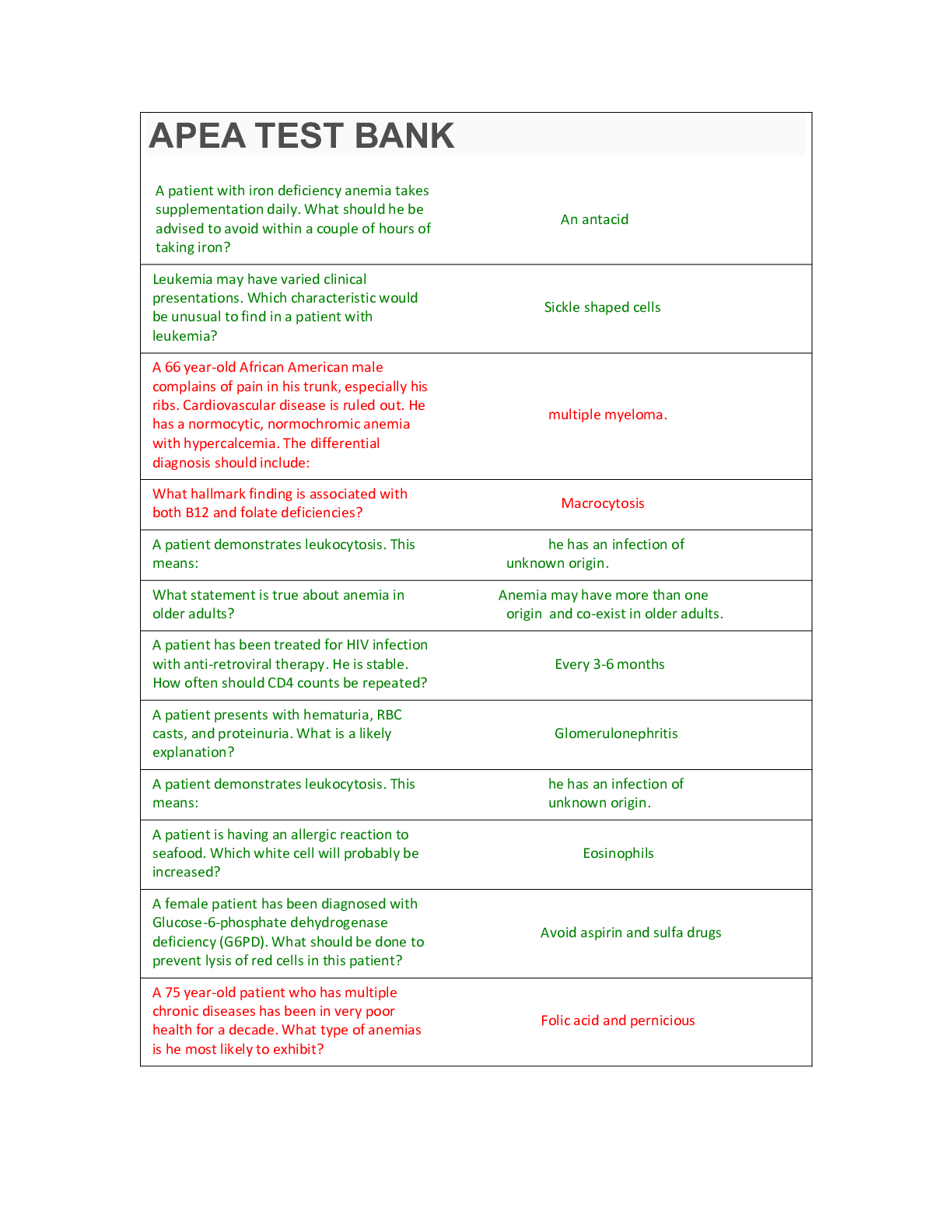








.png)

