NUR 45 / (100 PRACTICE Questions and Answers with Rationales.) /most tested Questions / Download To Score A
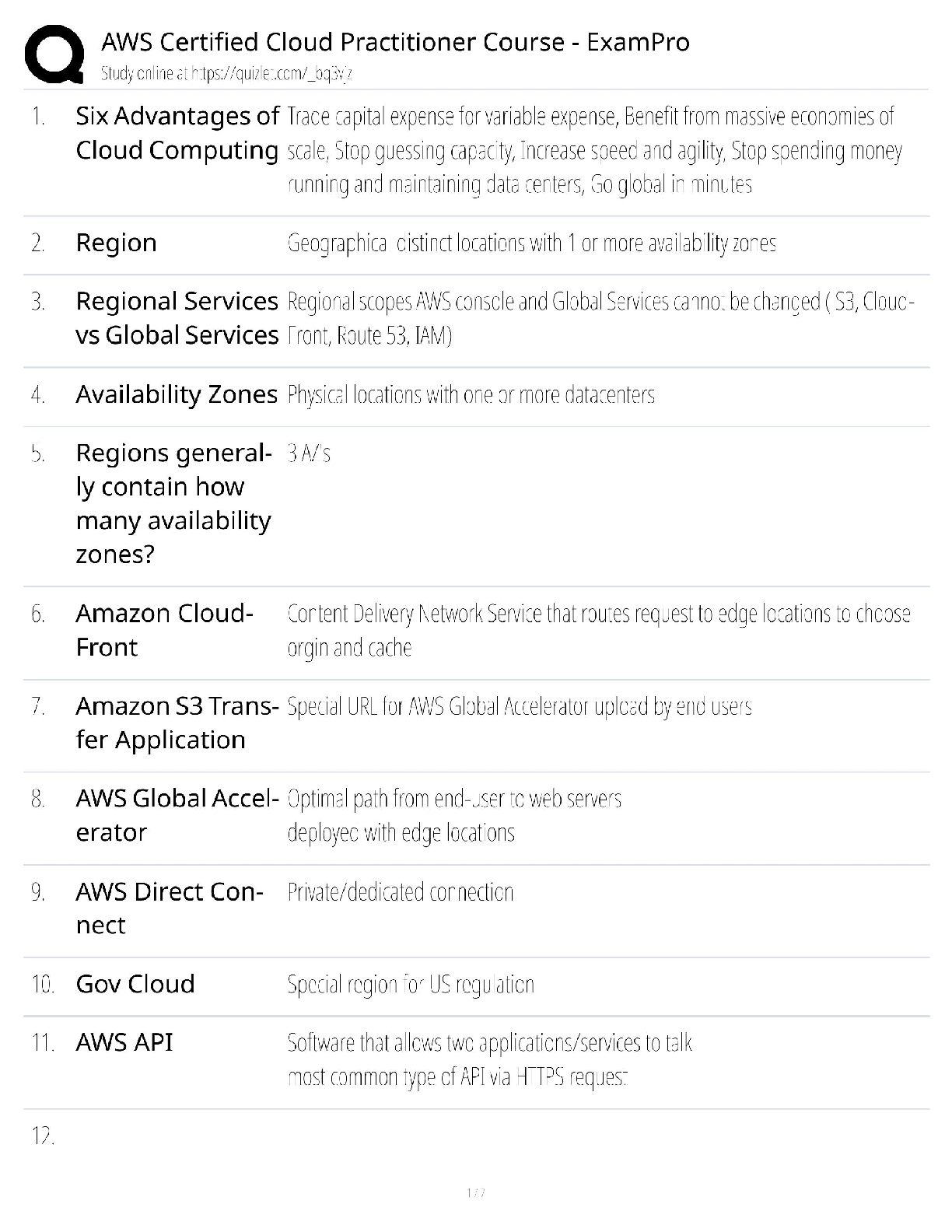
Document Content and Description Below
Practice Questions
1. Nurses in a unionized hospital are paid “compensatory pay” when working holidays equal to the number of hours worked with no extra compensation. Although they have suggested
...
changes during the annual survey of employee satisfaction, management refuses to consider another system for compensatory pay. A trained member listened to both nurses and management to make recommendations that were not legally binding. This type of settlement is termed:
a. picketing.
b. binding arbitration.
c. mediation.
d. grievance.
ANS: C
Mediation enlists the help of a trained person to listen to both sides; however, recommendations are not legally binding.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
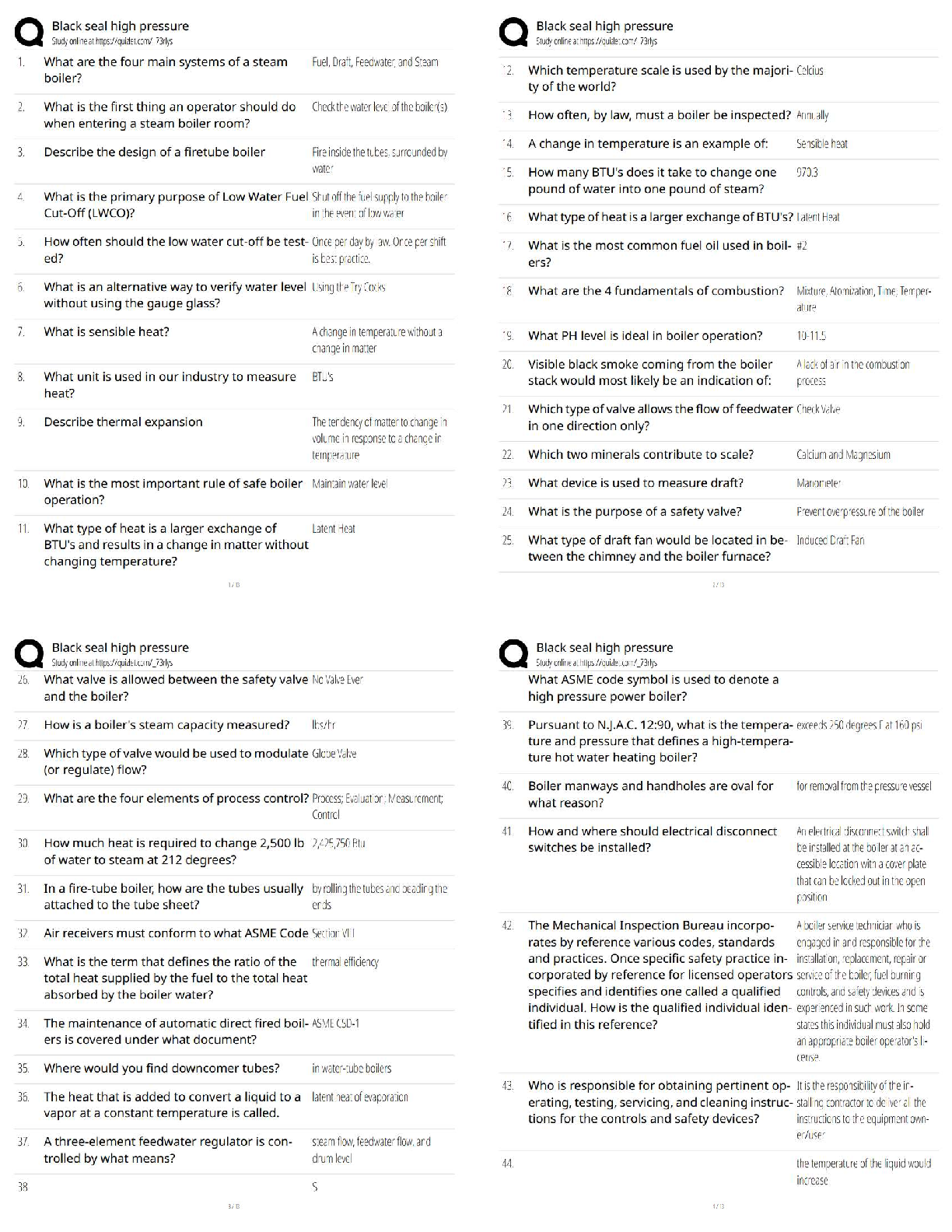
2. A nurse has been asked to serve as the charge nurse on the evening shift. The agency where the nurse is employed is considering unionization. If the charge nurse position is accepted, this nurse:
a. can be represented by the union because charge nurses are not considered part of the management team.
b. is part of the management team, so union participation would be a conflict of interest.
c. can file a grievance that will be arbitrated automatically by the union.
d. is ineligible for collective bargaining activities that deal with unfair labor practices.
ANS: A
Serving as charge nurse is part of a nurse’s professional role and not a management function.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 263-264
3. A nurse has heard rumors that other nurses are interested in unionizing but knows little about the purpose of unions. The nurse’s first action is to:
a. contact an arbitrator who has worked with other nurses in unions.
b. picket the agency where employed to gain inside information as to why unionization
is sought.
c. sign the dual-purpose union authorization card.
d. review the National Nurses United website for collective bargaining information.
ANS: D
The National Nurses United website gives information about collective bargaining for nurses.
DIF: Application REF: p. 259
4. Nurses in a nonprofit hospital have expressed an interest in forming a union to secure fair wages and ensure client safety. To form a core support group of nurses, the union organizer can conduct meetings to gather initial information:
a. away from the worksite with a group of managers to learn both sides of the situation.
b. at the worksite with staff nurses who are respected leaders.
c. in homes or local businesses with staff nurses.
d. after photographing management meeting to discuss their strategies to decrease interest in unionization.
ANS: C
The union representative meets with laborers (staff nurses) at a nonwork setting to gather information about grievances.
DIF: Application REF: p. 260
5. Mandatory overtime and reduction in RN staff have resulted in decreased client satisfaction and a sentinel event. Management is unwilling to discuss a change in staffing, and collective bargaining interest is sparked. A nurse is approached to sign a union authorization card. If signed, the card:
a. authorizes the union to serve as his or her legal representative.
b. indicates that the person is requesting additional information about collective bargaining.
c. indicates the nurse desires to share information about grievances.
d. gives permission for union dues to be deducted from pay.
ANS: A
A signature on a union authorization card indicates that the nurse gives the union the right to serve as legal representation.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 259-260
6. A group of RNs wish to seek union representation that would protect all workers in the agency including nonlicensed assistive personnel and non-nursing employees such as nutritionists and dietary workers. The type of union being sought is the strongest collective group and is known as a(n):
a. occupational union.
b. industrial union.
c. union shop.
d. right-to-work bargaining organization.
ANS: B
An industrial unionism is a single union for all workers in the agency.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
7. Physical therapists are represented by a union, nurses are represented by a separate union, and pharmacists have yet another union within a single agency. This type of union representation is known as:
a. occupational unionism.
b. industrial unionisms.
c. union shop.
d. power sharing.
ANS: A
Occupational unionism indicates separate unions for each occupation in an agency.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
8. Historically, what movement most influenced unionization in American health care agencies/hospitals?
a. Immigration laws protected foreign employees from discrimination in hiring or discharge on the basis of national origin and citizenship status.
b. Women entered the workforce, gaining voice to support unions.
c. The Industrial Revolution led to poor working conditions and the need to protect workers.
d. Nurses were exposed to communicable diseases, which led to death and disability.
ANS: C
The Industrial Revolution led to people working in factories where poor and unsafe working conditions were widespread.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 258-259
9. In recent Gallop Polls, nurses were voted as the most honest with the highest ethical standards of all professions. How does this degree of professionalism affect nurses’ desire to participate in organized strikes?
a. Nurses most often turn to collective bargaining strategies such as strikes to emphasize client safety initiatives.
b. Nurses use evidence-based studies that reflect both management and labor views to support participation in unionization.
c. Nurses often find union activities such as strikes in conflict with the need to serve and protect clients and their profession.
d. Nurses who strike can be legally punished for abandonment and negligence, considered to be professional misconduct.
ANS: C
Nurses are client advocates and promotion of professionalism is valued as evidenced by the public’s opinion related to honesty and professionalism.
DIF: Application REF: p. 262
10. A concern that nurses were being asked to perform tasks that went beyond the state’s nurse practice act was brought to the union’s attention. Nurses were informed that either mediation or binding arbitration will be used to resolve the issue. A novice nurse asks about the difference between these techniques and is informed that:
a. mediation is sanctioned by the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) to formally discuss concerns with management and labor.
b. binding arbitration is a formal discussion between labor and management in which
the arbitrator’s recommendations are compulsory.
c. mediation uses a trained person to negotiate a legally binding plan.
d. binding arbitration requires both labor and management to participate in discussions on the least destructive approach to allow self-governance by employees.
ANS: B
Binding arbitration requires that both parties meet in formal talks, and all parties must obey the arbitrator’s recommendations.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
11. A large corporation employs nurses all over the United States. Nurses in one agency learned that fellow nurses in another agency are striking because they are required to work 16-hour shifts to cover for nurses who have left due to unsafe staffing practices. The union of the nonstriking agency nurses decides to stop work to support the nurses who are striking; thus, this union:
a. is placing nurses at risk for a lawsuit because their direct employer did not cause the strike.
b. must be an industry union representing both parties.
c. is participating in a sympathy strike, which, if done correctly, is legal.
d. must pay for any losses incurred by the agency during the strike.
ANS: C
A sympathy strike occurs when a union stops work to support the strike of another union.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
12. A group of nurses interested in unionizing decides to contact the largest union in the United States representing registered nurses, which is the:
a. American Nurses Association.
b. United American Nurses.
c. National Nurses United.
d. National Labor Relations Board.
ANS: C
In 2009, the National Nurses United became the largest union representing nurses RNs as a result of a merger between the United American Nurses, California Nurses Association, National Nurses Organizing Committee, and Massachusetts Nurses Association.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 259
13. A nurse is interested in working in a large trauma center that is unionized but does not want to join the union or pay fees. She accepts the position but is not required to join or pay fees to the union based on which law?
a. National Labor Relations Act
b. Right-to-work law
c. National Labor Relations Act
d. Taft-Hartley Act
ANS: B
The right-to-work law prohibits membership or payment of union dues or “fees” a condition of employment, either before or after hiring.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257 | p. 260
14. A group of nurses are assembling outside a hospital protesting the use of foreign nurses after several nurses were terminated due to what the hospital called recurring “decreased census.” The nurses carry signs with messages asking potential patients to seek care elsewhere. The local newspaper picked up the story, and the hospital is receiving negative press. The nurses are participating in:
a. picketing.
b. collective bargaining.
c. a strike.
d. arbitration.
ANS: A
Picketing is a form of protest in which people (called picketers) congregate outside a place of work or location where an event is taking place. Often this is done in an attempt to dissuade others from going in (“crossing the picket line”), but it can also be done to draw public attention to a cause.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 257
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. A hospital is seeking a 2.5% wage reduction for all nurses as part of a new balanced budget plan; however, the plan provides for raises for upper-level management. This plan resulted in a call for a union to protect the nurses. When the union representative arrives, what questions should the nurses ask? (select all that apply)
a. Will the dues be used to support charity care when clients are unable to pay?
b. How effective has the union been in representing nurses’ best interest?
c. What percent of dues pays union personnel salaries?
d. Are dues used to promote research for terminally ill clients?
e. If arbitration is unsuccessful and a strike occurs, will nurses receive compensation during the strike?
ANS: B, C, E
Laborers (staff nurses) want a union with a successful track record of improving wages and benefits. Union dues are used to support union personnel, and the amount varies among different union groups; the higher the percentage of money that goes to pay union personnel salaries, the less money will be available to support members. Employers are not obligated to pay laborers during a strike, and unions may choose to pay employees while striking.
DIF: Application REF: p. 263, Box 14-1
2. A hospital refused to purchase a better grade of utility gloves, even after learning that the cheaper utility gloves are easily punctured during routine use. This unsafe situation led nurses to seek unionization. During the pre-election phase for unionization, which actions by union representatives are prohibited by the National Labor Relations Board? (select all that apply)
a. Scheduling a meeting in the agency’s cafeteria to determine employees’ interest in unionization
b. Distributing nondocumented information that female nurses receive lower annual performance evaluations than do male nurses
c. Distributing information about the benefits of unionization and grievances in a public parking garage located across from the hospital
d. Suggesting to workers the likelihood of job loss should the union not win the election
e. Signing authorization cards for employees who are on leave
ANS: A, B, D, E
Union representatives must meet in nonwork areas. Union representatives must not spread rumors of prejudices. Neither the union nor employers can spread falsehood about potential job loss or repercussion in the event of unionization. Union representatives cannot sign cards for employees.
DIF: Application REF: p. 259
3. It is important to realize that nurses may seek unionization if: (select all that apply)
a. physicians rotate on-call coverage among group members for complicated long-term clients.
b. scheduling is presented that provides adequate staffing on holidays by rotation of time off for holidays among nurses.
c. incident report trends indicate medication errors are caused by shift reports being taped and heard after nurses from the prior shift have left the unit.
d. physicians, nurses, nutritionists, and physical therapists visit concurrently with clients to plan care.
e. staff development activities are planned daily at 8 AM for 2 consecutive days to educate staff on new cardiac monitoring procedures while following normal staffing patterns.
ANS: C, E
Policies where shift reports are taped and heard after a prior shift has left have proved to lead to errors and unsafe care. Staff development activities should be scheduled to allow nurses to attend, and normal staffing patterns or time of training must coincide with nurses’ availability and ability to listen to and retain information (such as at the beginning or end of the shift while others provide coverage).
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 262
4. Mandatory overtime and reduction in RN staff have resulted in decreased client satisfaction and a sentinel event. Management is unwilling to discuss a change in staffing, and collective bargaining interest is sparked. During the pre-election period, what actions by management are prohibited? (select all that apply)
a. Seek individuals to spy on coworkers who are possible union supporters.
b. Photograph employees participating in information sessions about unionization.
c. Visit managers outside work to gain their perception of popularity of unionization.
d. Threaten that, should the union win, the company will relocate when there is no intention to relocate.
e. Require employees to declare their position on unionization prior to pick up paychecks.
ANS: A, B, D, E
During the pre-election period, management may not solicit spying. During the pre-election period, management may not photograph employees engaged in union activities. During the pre- election period, management may not lie about what will happen if the union is the victor in an election. During the pre-election period, management may not question employees about their preferences regarding union activity.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 261
CHP15
1. Consumers are concerned with security issues related to their confidential health information being placed in an electronic health record (EHR). However, when the security of the EHR is compared with that of paper-and-pencil records, the EHR is:
a. more secure.
b. less secure.
c. equivalent.
d. not comparable with the paper-and-pencil record.
ANS: A
Computer-based patient record systems, such as EHRs, provide better protection than paper- based systems. The EHR allows only authorized users to view data, and access to records can be audited for inappropriate use.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 271
2. During a search for the term informatics, when the nurse finds the domain “.edu,” the site is affiliated with a(n):
a. government agency.
b. commercial site.
c. educational institution
d. Internet service provider.
ANS: C
The domain of an educational institution is .edu.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 276
3. When paper-and-pencil medical records are compared with computer-based records:
a. paper-and-pencil records provide controls to determine who has viewed the health information.
b. information contained in a paper-and- pencil record has the capability of being more in-depth than that found in computer-based records.
c. patients have the right to know that the confidentiality of their records is strictly maintained, regardless of the type of medical record used.
d. patients must sign for each item of information released on the computer record.
ANS: C
Regardless of the type of record used, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) protects the confidentiality of the patient’s medical information and imposes legal consequences for those who breech confidentiality.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 271
4. A nurse is preparing a scholarly publication on the prevalence of hepatitis A worldwide. The most efficient and effective means of conducting an Internet search to gather information for this publication is to use:
a. a search engine such as Google or Yahoo.
b. a consumer health website.
c. a decision support system.
d. MEDLINE database.
ANS: D
MEDLINE is one of the scientific and research scholarly databases, and it would be the most appropriate for use in gathering information for a scholarly publication.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 276
5. A consumer is learning about electronic health records at a local health fair and states, “I am worried that someone can read my health information and I really don’t understand the difference between privacy and confidentiality.” The nurse explains that an example of confidentiality would be:
a. a pledge that states, “I will hold matters pertaining to my patients in strict intimacy.”
b. a patient who does not tell the physician that he has been treated for a sexually transmitted disease.
c. a teenager who sustains a broken arm and in the emergency department and withholds information about her use of recreational drugs.
d. locking medical records in cabinets to prevent unauthorized users from accessing patient information.
ANS: A
Confidentiality is keeping private the personal information that was given to a health care provider, unless others have a legitimate need to know.
DIF: Application REF: p. 271
6. A physician has installed a computer-based patient records system. An outside care provider who requests medical information must obtain the patient’s signed consent and then is assigned a password to gain access to the medical information. A monthly audit is conducted to determine for whom and for what purpose patient records have been accessed. This protection is referred to as:
a. privacy.
b. confidentiality.
c. security.
d. data capture.
ANS: C
Security is the limitation of access to health care information through passwords and other precautions.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 271
7. A nurse walks up to a computer in the hallway and presses the index finger to the sensor, thereby gaining access to patient data. A few moments later another nurse performs the same steps and is granted access. A visitor who is watching from a room walks over and places the index finger on the sensor, only to receive an “error and access denied” message. Security is being maintained by:
a. robot technology.
b. biometric technology.
c. telehealth.
d. ubiquitous computing.
ANS: B
Biometric fingerprint identification uses personal characteristics to allow access to health information.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 277
8. A nurse who is teaching a class to introduce telehealth to the staff would include which example?
a. A robot performs menial housekeeping chores for an invalid patient.
b. A computer software program alerts the nurse or physician who is reviewing orders that an order for a new drug can cause synergy of the theophylline inhaler.
c. A physician speaks into a computer, and the admission history is recorded and saved in the patient file.
d. While a patient in Wyoming performs peritoneal dialysis, a nurse watches remotely from California to ensure that all steps are being followed correctly.
ANS: D
Telehealth is the delivery of care to a patient who is at a distance from the health care provider.
DIF: Application REF: p. 273
9. An advanced practice nurse inputs into a computer software program the following clinical manifestations: open wound with tibia exposed, petechial hemorrhage, and temporary loss of consciousness. The computer diagnosis of fat emboli is generated by a system known as:
a. decision support.
b. telehealth.
c. robotic technology.
d. biometric technology.
ANS: A
Decision support systems are computer-based information systems that include knowledge-based systems designed to support clinical decision making.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 268-269
10. A nurse is preparing a presentation using different websites to collect information. The nurse is concerned that contact information and the author’s credentials are not listed for one of the websites reviewed. Which criterion required to establish a reputable website is missing?
a. Authority
b. Objectivity
c. Usability
d. Currency
ANS: A
Authority is the criterion that is related to the credentials and background that have prepared an author to publish on the subject.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 276
11. A nurse is interested in locating reliable information concerning noninvasive blood glucose monitoring. Information is located, and the author is a scientist who conducted studies within the last year on the effectiveness of a particular noninvasive blood glucose monitor. The scientist received funding from a pharmaceutical company to support the studies. The URL indicates the pharmaceutical company site.com. The nurse is concerned about this information’s:
a. authority.
b. objectivity.
c. accuracy.
d. currency.
ANS: B
Sites sponsored by organizations such as pharmaceutical companies may influence the content.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 276
12. A nurse providing care at the bedside receives an “alert” that a patient’s stat potassium level is
2.5 and digoxin (Lanoxin) is scheduled. The nurse holds the medication and prevents a possible complication. This feature of the Electronic Health Record is available through which core function of EHR?
a. Order entry/order management
b. Decision support
c. Patient support
d. Administrative support
ANS: B
Decision support provides reminders about preventive practices, such as immunizations, drug alerts for dosing and interactions, and clinical decision making.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 268-269
13. A nurse works on a unit where electronic health records (EHR) are being initiated and asks, “What is meant by ‘meaningful use’ standards that are in our education packet?” The best answer is that “meaningful use”:
a. identifies a set of EHR proficiencies and benchmarks that EHR systems must meet to be certain that they are functioning to their maximum capacity and meeting this standard allows companies/organizations to qualify for funds to defray cost of the EHR from Medicare.
b. refers to training competencies that all users must achieve to be able to access and transfer patient data/information.
c. refers to a requirement that at least 50% plus one of all patients have data entered into the EHR.
d. the requirement that rigorous confidentiality security is in place to protect all patient information from sources which have no right to the data.
ANS: A
Meaningful use is “A defined set of EHR capabilities and standards that EHR systems must meet to ensure their full capacity is realized and for the users (hospitals and physician practices) to qualify for financial incentives from Medicare.”
DIF: Application REF: p. 271
14. A nurse is caring for a patient who is to receive an antibiotic drug that causes severe skin damage when infiltrated. The order reads, “infuse over 1 hour by portacath.” The nurse accesses the Personal Digital Assistant for software that lists the steps to access a portacath. The nurse is using:
a. electronic health records.
b. point-of-care technology.
c. data management.
d. telehealth.
ANS: B
Using a Personal Digital Assist device to access information at the bedside is considered point- of-care technology. The nurse was able to retrieve the steps for accessing a portacath electronically while remaining at the bedside.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 273
15. The Institute of Medicine (IOM) (2003) recommends that EHR systems offer eight functionalities. A patient has a severe allergy to eggs and penicillin. Which of the eight functions of the EHR would address sharing this information?
a. Health information and data capture
b. Results/data management
c. Provider order entry management
d. Clinical decision support
ANS: A
The health information and data capture function includes information such as medical history, laboratory tests, allergies, current medications, and consent forms.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 269, Table 15-1
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. A new nurse asks, “Since Electronic Medical Records can improve quality care by having seamless data available for a patient, why doesn’t everyone just replace paper and pencil charts”? Barriers to a universal health information infrastructure include the fact that: (select all that apply)
a. competition from individual companies to build EMR prevent a universal infrastructure.
b. cost is prohibitive even with federal funding for larger health care systems.
c. preventive health reminders for immunizations and yearly screenings such as mammograms are used in clinical decision making.
d. insurance companies have halted sharing of some patient data due to fear of law suits.
e. the full capacity of EHRs has not been realized with only Stage 1 of 3 nearing completion.
ANS: A, E
It has been recommended that only a federal-based EMR would provide an infrastructure that allows access to comprehensive patient information. The first stage, years 2011 and 2012, forms the foundation for electronic data capture and information sharing.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 271
2. A nurse interested in quality improvement tools performed a search for cause and effect diagrams using www.ishikawa.com. A page opened that provided images and templates for performing fishbone diagrams. Which type of search did the nurse conduct?
a. Quick and dirty
b. Advanced
c. Brute force
d. Link searching
ANS: C
Brute force is a method of searching where you type in what you think might logically be a web address and see what happens.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 275
COMPLETION
1. Software programs that process data to produce or recommend valid choices are known as
.
ANS:
decision support systems
Decision support systems use software programs that process data to produce or recommend decisions by linking with an electronic knowledge base.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 269
16
1. Nurses and community officials are working together to ensure that churches and schools have needed supplies to provide shelter for large numbers of individuals in the event of a natural or manmade disaster. These activities represent which phase of a disaster continuum?
a. Preparedness
b. Relief response
c. Recovery
d. Crisis intervention
ANS: A
Every disaster response begins as a local event known as the preparedness phase, which consists of planning, preparedness, prevention, and warning.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 285
2. A nurse at a school notices that several students have “blisters” on their bodies. Further investigation reveals that a terrorist incident has occurred, causing smallpox. If the chemical, biologic, radiologic, nuclear, and explosive (CBRNE) agent categories are used, this incident would be classified as:
a. chemical.
b. biologic.
c. radiologic.
d. nuclear.
ANS: B
The biologic category refers to diseases such as plague or smallpox.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 284, Table 16-1
3. The Metropolitan Medical Response System (MMRS):
a. is totally financed by the federal government national disaster fund.
b. consists of responders who have obtained specialized training and equipment to deal with mass casualty events.
c. has a storehouse of medications and antidotes to be used during response in times of national emergencies.
d. arranges for patient admissions to federal hospitals.
ANS: B
The MMRS responds to disaster with trained individuals who have expertise in this type of situation and who have the equipment required to be effective.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 286
4. A community in the New Madrid fault zone experiences an earthquake resulting in injuries from propelled objects and abrasions for many victims. The local supply of antibiotics is quickly exhausted. Local authorities would contact the:
a. Commissioned Corps Readiness Force.
b. Strategic National Stockpile.
c. Department of Homeland Security.
d. local Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA).
ANS: B
The Strategic National Stockpile provides antibiotics, antidotes, and medical and surgical items when local and state supplies have been exhausted.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 287
5. During the relief response phase of a disaster resulting from a “dirty bomb”:
a. treatment for burns and poisoning is provided for victims.
b. emergency plans are coordinated between agencies.
c. reconstruction of destroyed facilities and homes begins.
d. food stores are collected for potential victims.
ANS: A
During the relief response phase of a disaster, emergency responders provide assistance to victims and stabilize the scene; with a dirty bomb, radioactive material causes burns and poisoning.
DIF: Analysis REF: p. 288
6. A nurse learns of a mass casualty disaster following a known terrorist attack. On arriving at the scene, the nurse knows that:
a. the response of local hospitals will be dictated by the federal government.
b. the same ground rules practiced in other settings and during smaller crises will be applicable.
c. the least experienced nurses will be assigned to triage low-risk victims and victims who have no chance of survival.
d. multiple incident commanders ensure a quick, effective response.
ANS: B
The fundamentals of nursing applied to other settings and situations can be used in a disaster.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 283
7. Nurses caring for the victims of a mass casualty incident:
a. determine the common terminology to be used by hospitals and participating agencies.
b. take charge of communicating with the news media.
c. determine whether there is a credible threat of a terrorist attack.
d. give priority for care to those with the greatest chance of survival rather than those most critically ill.
ANS: D
Care is shifted from categorizing patients at low, intermediate, and critical risk to using resources to serve those with the greatest likelihood of survival.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 283
8. During a community health fair the disaster medical assistance team (DMAT) informs participants that every community must be ready to provide disaster care. A participant asks, “In a disaster, the local community cannot possibly be effective, so why not have a plan to call federal agencies immediately to provide relief?” The correct response by the DMAT is:
a. “Unless known terrorist activities involving mass destruction occur, the federal government does not become involved.”
b. “The community is essentially the ‘first responder’ to any disaster.”
c. “The preparedness phase of a disaster is the responsibility of the community, the relief response phase is assigned to state agencies, and the recovery phase is the responsibility of federal agencies.”
d. “Unless local health care facilities are incapacitated, state and federal agencies will withhold assistance.”
ANS: B
Each disaster begins locally, and each community responds first and receives assistance from state and federal agencies when local resources are not adequate for the situation.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 285
9. A nurse who is conducting a staff in-service on the phases of a disaster continuum teaches participants that, during the impact/response stage, activities focus on:
a. community awareness in anticipation of a terrorist attack or natural disaster.
b. determining the effectiveness of the
disaster medical assistance team (DMAT).
c. the use of an all-hazards approach.
d. initiating response activities.
ANS: D
Response activities during the relief response phase consist of immediate actions to save lives and meet basic human needs.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 288
10. Following a terrorist attack, victims are exhibiting posttraumatic stress syndrome, and care providers are exhibiting compassion fatigue. Which federal response system should be initiated?
a. Strategic National Stockpile
b. Metropolitan Medical Response System (MMRS)
c. Commissioned Corps Readiness Force
d. National Disaster Medical System
ANS: B
The MMRS is concerned with deploying trained responders who are able to provide mental health care for victims and health care providers.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 286
11. The crisis communication officer may first inform the public or health care facility of a disaster or an act of terrorism. This representative has the responsibility to:
a. contain the facts to within the administration group.
b. incite the public to quickly take cover and obtain emergency supplies.
c. provide understandable and straightforward facts about the event within the facility and possibly to the news media.
d. inform the public that no information can be released until it has been confirmed by state and federal agencies.
ANS: C
The crisis communication officer is the first contact for patients, families, and employees within the facility or news media, so they may better understand the situation and know how to react and protect themselves.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 289
12. The disaster medical assistance team works quickly to contain contaminants from a chemical plant explosion. Afterward, personnel undergo a special process to remove harmful chemicals from equipment and supplies. This removal process is known as:
a. containment.
b. decontamination.
c. triage.
d. scene assessment.
ANS: B
Decontamination is the physical process of removing harmful substances from personnel, equipment, and supplies.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 280
13. A group of local volunteers respond to a tornado. Volunteers have completed an emergency response course and are able to assist with triage of injured citizens. They also participate in local health fairs to teach residents how to react during tornadoes. The responders are members of the:
a. Medical Reserve Corps (MRC).
b. Metropolitan Medical Response System (MMRS).
c. National Disaster Medical System (NDMS).
d. Commissioned Corps Readiness Force (CCRF).
ANS: A
The MRC are local volunteers trained to respond to local emergencies.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 285
14. Troops from the United States participating in a peace mission in a foreign country were the victims of suicide bombers and many soldiers were evacuated back home to receive specialized medical care. The nation’s medical responses will be augmented by:
a. the federally coordinated National Disaster Medical System.
b. local homeland communities where troops receive care.
c. the Medical Reserve Corps, which organizes and utilizes public health, nursing, medical, and other volunteers.
d. the National Incident Management System, which guides government,
nongovernmental organizations, and the private sector to work seamlessly during disaster situations.
ANS: A
The National Disaster Medical System supplements care for casualties evacuated back to the United States from overseas and federally declared disasters including national disasters, major transportation accidents, technologic disasters, and acts of terrorism.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 286-287
15. A nurse is informed that the Federal Bureau of Investigation has determined that a bomb has been detected and is in the possession of a known terrorist group. The government buildings in the local community are the target. This situation is termed a(n):
a. all-hazards approach.
b. biologic event.
c. credible threat.
d. natural disaster.
ANS: C
A credible threat is a situation in which the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) determines that a terrorist threat is probable and verifies the involvement of a weapon of mass destruction in the developing terrorist incident.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 280
16. The emergency response team responded to a terrorist attack where hundreds of people died following symptoms of chest tightness, palpations, seizures, and finally paralysis. A colorless odorless liquid known as Sarin (GB) was the agent, which is primarily inhaled with limited exposure through the skin. The concentration of Sarin has not been measured. What level is the minimum level of personal protection and safety equipment (PPE) that would be needed?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
ANS: B
Level B requires a high level of respiratory protection, but less skin protection, providing a chemical splash–resistant suit with hood and self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). It provides maximum respiratory protection but less skin protection than level A equipment.
DIF: Analysis REF: p. 289
17. A state is devastated by a tornado killing many people, destroying communication systems, utility services, homes, and medical facilities. The state requests immediate assistance from the
U.S. Congress and from surrounding states. The affected state should first contact the:
a. Emergency Management Assistance Compact (EMAC).
b. Institute of Medicine (IOM).
c. Red Cross.
d. Strategic National Stockpile.
ANS: A
The EMAC is an organization authorized by the U.S. Congress through which a state impacted by a disaster can request and receive assistance from other member states quickly and efficiently.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 280
18. A nurse is interested in learning the phases of the disaster continuum and realizes it has many similarities to the nursing process. To better understand the phases of a disaster, which is true when comparing the phases of the disaster continuum to the nursing process?
a. The preparedness phase of the disaster continuum is consistent with the assessment and planning steps of the nursing process.
b. The recovery phase of the disaster continuum is consistent with the planning step of the nursing process.
c. The recovery phase of the disaster continuum is consistent with the implementation step of the nursing process.
d. The response relief phase of the disaster continuum is consistent with the evaluation step of the nursing process.
ANS: A
The preparedness phase requires assessing possible needs of the community and planning appropriate interventions and is consistent with the assessment and planning steps of the nursing process.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 285
19. In the preparedness phase for disasters, the community plans for a possible terrorist attack using anthrax as the weapon of destruction. What treatments and/or preparations would be needed?
a. Vaccines and Level B Personal Protection Equipment (PPE)
b. Treatment for burns, decontamination, and Level A PPE
c. Social distance determination, decontamination for radioactive fallout
d. Identify and detect incendiary devices, treatment for burns and propellants
ANS: A
Anthrax is a biologic weapon and requires Level B protection since it is a known agent and can be carried in wind or surfaces. Timing of treatment is critical and vaccines are available.
DIF: Analysis REF: pp. 282-284, Table 16-1
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. Health care professionals have been activated to respond to a disaster, and the registered nurse who is coordinating the effort realizes that: (select all that apply)
a. in the event of a mass casualty incident, care is prioritized to those who have the greatest chance of surviving.
b. communities should use their own resources first to attempt to stabilize and organize the response.
c. state assistance occurs any time a disaster occurs, regardless of the community’s resources.
d. the emergency operating plan developed by one central agency rather than individual facilities should be put into operation.
e. strict protocols regarding the use of resources must be followed.
ANS: A, B
Care is shifted to doing the most good for the most people. Efforts begin at the local level.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 283-284
2. When teaching community preparedness for a community group, the nurse explains that components of the National Disaster Medical System (NDMS) provide for: (select all that apply)
a. a nationwide bomb disposal squad team for the rapid removal of explosive devices.
b. teams of health care providers who are
experts and have specialized supplies and equipment.
c. structures for patient evacuation from the disaster area to an unaffected area.
d. arrangements for hospitalization in federal and volunteer nonfederal acute care hospitals.
e. providing mental health care for the community, for victims, and for health care providers.
ANS: B, C, D
The NDMS provides specially trained teams of people along with equipment designed for disaster relief. The NDMS is responsible for removing patients from unsafe to safe areas. The NDMS coordinates efforts to evacuate victims to federal or nonfederal volunteer hospitals that can care for disaster victims.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 286
COMPLETION
1. The emergency preparedness term that is used to describe the process of limiting the emergency situation within a well-defined area is .
ANS:
containment
Containment is correct because the focus is to prevent the agent that caused the disaster from spreading.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 280
2. The term used during a pandemic disaster that refers to the attempt to contain germs by limiting socialization and personal interactions is .
ANS:
social distancing
The term social distancing refers to the attempt to keep people as far apart as possible so as to limit the possibility of spreading germs.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 291
CHP 21
1. Accrediting agencies such as The Joint Commission address staffing by:
a. imposing maximum staffing levels.
b. requiring a specific staff mix.
c. stipulating nurse-patient ratios.
d. looking for evidence that patients receive satisfactory care.
ANS: D
Accrediting agencies do not address minimum staffing levels; however, they do look for evidence that patients receive adequate care, and this can occur only with adequate staffing.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 369
2. Customer satisfaction is primarily based on:
a. access to modern, up-to-date facilities.
b. availability of an extensive menu selection.
c. personal interactions with employees.
d. having to undergo fewer invasive procedures.
ANS: C
Interactions between employees and patients/families actually affect clinical outcomes, functional status, and even physiologic measures of health.
DIF: Knowledge REF: p. 369
3. rNurses on a unit provide personal hygiene, administer medications, educate the patient and family about treatments, and provide emotional support. These nurses provide patient care based on which nursing delivery system?
a. Total patient care
b. Partnership nursing
c. Team nursing
d. Functional nursing
ANS: A
In total patient care nurses provide all aspects of patient care.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 370
4. A hospital converts to a system of care delivery in which RNs, LPNs, and unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are responsible for implementing a specific task, such as medication administration or personal hygiene, for the entire nursing unit. This type of delivery system is:
a. total patient care.
b. functional nursing.
c. team nursing.
d. primary nursing.
ANS: B
In functional nursing members of the team are assigned specific tasks such as assessment or medication administration.
DIF: Comprehension REF: pp. 370-371
5. The nurse who is responsible for following the patient from admission through discharge or resolution of illness while working with a broad range of health care providers is called a:
a. nurse manager.
b. case manager.
c. coordinator of patient-centered care delivery.
d. team leader in team nursing care delivery.
ANS: B
The case manager, in collaboration with an interdisciplinary team, oversees the use of health care services by clients throughout a course of illness.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 373
6. A patient is admitted with coronary artery disease and is scheduled for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). According to the clinical pathway the patient should be extubated and discharged from critical care the day after surgery. During surgery the patient’s oxygen saturation decreased drastically as a result of chronic tobacco abuse. Subsequently, the patient remained on the ventilator an additional 2 days postoperatively. According to the clinical practice guideline for CABG, this situation represents a:
a. patient outcome.
b. variance.
c. goal.
d. standard.
ANS: B
A variance is a deviation from the planned path.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 375
7. A patient is admitted with pneumonia. The case manager refers to a plan of care that specifically identifies dates when supplemental oxygen should be discontinued, positive-pressure ventilation with bronchodilators should be changed to self-administered inhalers, and antibiotics should be
changed from intravenous to oral treatment, on the basis of assessment findings. This plan of care is referred to as a:
a. patient classification system.
b. clinical pathway.
c. patient-centered plan of care.
d. diagnosis-related group (DRG).
ANS: B
A clinical pathway is a plan that specifies the timing and sequencing of major patient care activities and interventions by the interdisciplinary team for a particular diagnosis, procedure, or health condition.
DIF: Application REF: pp. 374-375
8. The nurse manager determines that four RNs, five LPN/LVNs, and two unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are required per shift to meet the needs of the patient population on the unit, according to acuity and census. The nurse manager is concerned with:
a. assignments.
b. staffing.
c. output.
d. productivity.
ANS: B
Staffing is the activity of determining that an adequate number and mix of health care team members are available to provide safe, high-quality patient care.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 367
9. A nurse manager is mentoring a novice nurse manager in determining staffing needs. The mentor explains, “We must determine the acuity level of the patient by:
a. assessing patient satisfaction with nursing care.”
b. quantifying the amount and intensity of care required.”
c. examining the skill mix and educational preparation of the staff.”
d. determining the number of hospital days required by the patients.”
ANS: B
Patient acuity is measured by determining the amount and intensity of care required.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 367
10. The nurse manager is planning staffing levels and realizes that the first step is to:
a. know the intensity of care needed by patients according to physical and psychosocial factors.
b. examine the educational level of the staff.
c. assess the skill level of caregivers.
d. review the budget to determine the financial consequences of past staffing patterns.
ANS: A
The nurse manager must determine the number and mix of health care providers according to the wide range of care requirements of individual patients.
DIF: Application REF: p. 367
11. A hospital is concerned with nurse retention and realizes that job satisfaction is a major influence. To enhance employee satisfaction related to staffing, the management team:
a. negotiates for additional agency nurses.
b. hires more part-time employees.
c. includes participatory management into staffing decisions.
d. uses “float” nurses to cover vacancies.
ANS: C
Staffing methods that include staff participation and enhance staff autonomy have been demonstrated to play a major part in ensuring employee satisfaction.
DIF: Application REF: p. 368
12. A patient is admitted for a hysterectomy, and the RN develops and implements the plan of care but also delegates to the LPN/LVN the responsibility of administering oral medications. While off duty, this RN receives a call requesting a change in the plan of care because the patient has developed deep vein thrombosis. The nurse who originally planned the care is practicing which type of nursing care delivery?
a. Modular
b. Primary
c. Team
d. Functional
ANS: B
The primary nurse assumes 24-hour responsibility for planning, directing, and evaluating the patient’s care from admission through discharge but may delegate or provide primary care during the shift when present.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 372
13. When deciding which staffing option to use on a nursing unit that will open soon, the manager realizes that:
a. continuity of care is enhanced and errors are reduced when nurses provide care over longer shifts and consecutive workdays, such as 12-hour shifts on 3 consecutive days per week.
b. the use of part-time nurses provides the variability needed to meet diverse patient needs.
c. satisfaction of the staff equates to satisfaction of patients.
d. nurses provide the same level of care, regardless of the work environment.
ANS: C
High nurse satisfaction is generally equated with high patient satisfaction and positive patient outcomes.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 368
14. A task force is considering factors that contribute to high-quality safe staffing. Which statement reflects an understanding of the American Nurses Association’s (ANA) recommendations?
a. Because patient needs remain constant on a daily shift, staffing needs at the beginning of the shift should be sufficient to provide safe, high-quality care.
b. Staffing should allow time for the RN to apply the nursing process so decisions result in high-quality, safe patient outcomes.
c. Patient acuity levels affect staffing by increasing the need for unlicensed personnel to provide routine basic care rather than increasing RNs in staff mix.
d. RN staffing is not cost-effective; thus is it important for staffing models to limit the number of RNs assigned per shift.
ANS: B
The ANA recommends that nurses have time to exercise professional judgment.
DIF: Analysis REF: p. 367
15. A nursing unit is comparing team nursing to the partnership model and finds that:
a. with the partnership model, an RN does not have to be part of the mix.
b. leadership abilities of the RN is a major determinant of effectiveness of care for both models.
c. the RN teaches the LPN/LVN or unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) how to apply the nursing process in team nursing.
d. with team nursing the RN cares for the patient while the team members work with the family or significant others.
ANS: B
The RN leads regardless of whether partnership model or team nursing is practiced.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 371 |p. 372
16. A nurse groups patients with criteria such as “high risk for falls,” “infection protocols,” and “special communication needs” to determine the mix and number of staff needed on a telemetry unit. The nurse is using:
a. a patient classification system to determine safe staffing levels.
b. diagnostic-related groups for Medicare billing.
c. case management to coordinate care.
d. clinical pathways to determine care.
ANS: A
Patient classification systems group patients according to care needs to determine safe staffing levels.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 367
17. A nurse makes patient care assignments as follows: RN1 has rooms 200-210; RN2 has rooms 211-221; RN3 has rooms 222-232. The two unlicensed assistive personnel have half the rooms, with one assigned to 200-215 and the second to 216-232. The care delivery model used in this situation is:
a. team.
b. primary.
c. partnership.
d. modular.
ANS: D
Modular (or geographic) assignments are based on a geographic location in the nursing unit.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 372
18. A patient has decided to stop hemodialysis because his renal failure progresses and he wishes to spend more time with family. Palliative care will continue, and the approach will be discussed with the patient and family as needed and at change of shift. The care delivery model in this situation is termed:
a. partnership.
b. patient-centered.
c. case management.
d. total patient care.
ANS: B
Patient-centered care models entail the health care team partnering with the patient and family to ensure that patients’ wants, needs, and preferences are the priority while allowing the patient and family to participate in decisions and educational needs.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 373
19. A nurse plans care knowing when specific recovery milestones are expected. The nurse is providing care via:
a. patient classification systems.
b. clinical pathways.
c. functional nursing.
d. case management.
ANS: B
Clinical pathways plans patient care activities and interprofessional interventions and desired patient outcomes within a specified time period for a particular diagnosis or health condition.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 366
20. 20.
An orthopedic unit is considering different types of care delivery models and staff have an opportunity to ask questions about how the models differ. The nurse manager provides an overview and uses the above visual to demonstrate which model of care delivery?
a. Team
b. Partnership
c. Primary
d. Functional
ANS: D
Functional care delivery models assign tasks to each provider. In the above visual, the LPN is responsible for oral medication administration, the unlicensed assistive personnel provide hygiene, and the RN is assigned to task that require the nursing process.
DIF: Application REF: pp. 370-371
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. While participating in a task force to proactively plan for nursing care delivery over the next 20 years, a nurse learns that dramatic changes will occur as a result of: (select all that apply.)
a. the increase in the number of minimally invasive procedures being performed for disease treatment.
b. care provided for patients over an extended period in acute care settings.
c. the reduction in the number of nurses and other health care professionals who are available to provide care.
d. the widespread illiteracy and decreased self-efficacy of the aging patient population.
e. the need to focus on social and environmental influences, educational level, and individual characteristics and values of the patient.
f. the devaluing of nursing as a means of improving patient outcomes.
ANS: A, C, E
Invasive surgical procedures are being replaced by laparoscopic procedures. The demand for nurses and other health care professionals cannot keep pace with the increased need for health care required by the growing older population. Care will focus on the unique lifestyles and values of a diverse population.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 376
2. Which factors would be considered in the first steps in developing an effective patient classification system? (select all that apply)
a. Planned procedures
b. Ethnic diversity of patients
c. Clinical competency of staff
d. Educational level of nurses
e. Age of patients
ANS: A, B, E
The first step in developing a patient classification system is to understand the intensity of care needs, which requires identifying specific patient characteristics and care requirements.
DIF: Comprehension REF: p. 368
3. A nurse responsible for staffing a medical-surgical unit must consider: (select all that apply)
a. the patient census.
b. physical layout of the unit.
c. complexity of care required.
d. educational level of all staff.
e. task preferences of the nurses.
ANS: A, B, C, D
The primary considerations for staffing a specific nursing unit are the number of patients; the level of intensity of care required by those patients (commonly referred to as patient acuity); contextual issues, such as architecture, geography of the environment, and available technology; level of preparation and experience of the staff members providing the care; and the quality of the nurses’ work life.
DIF: Application REF: pp. 367-368
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 34 pages

.png)
.png)




 And LETRS Unit 8 Final Assessment Test.png)