Chapter 7--Qualitative Research
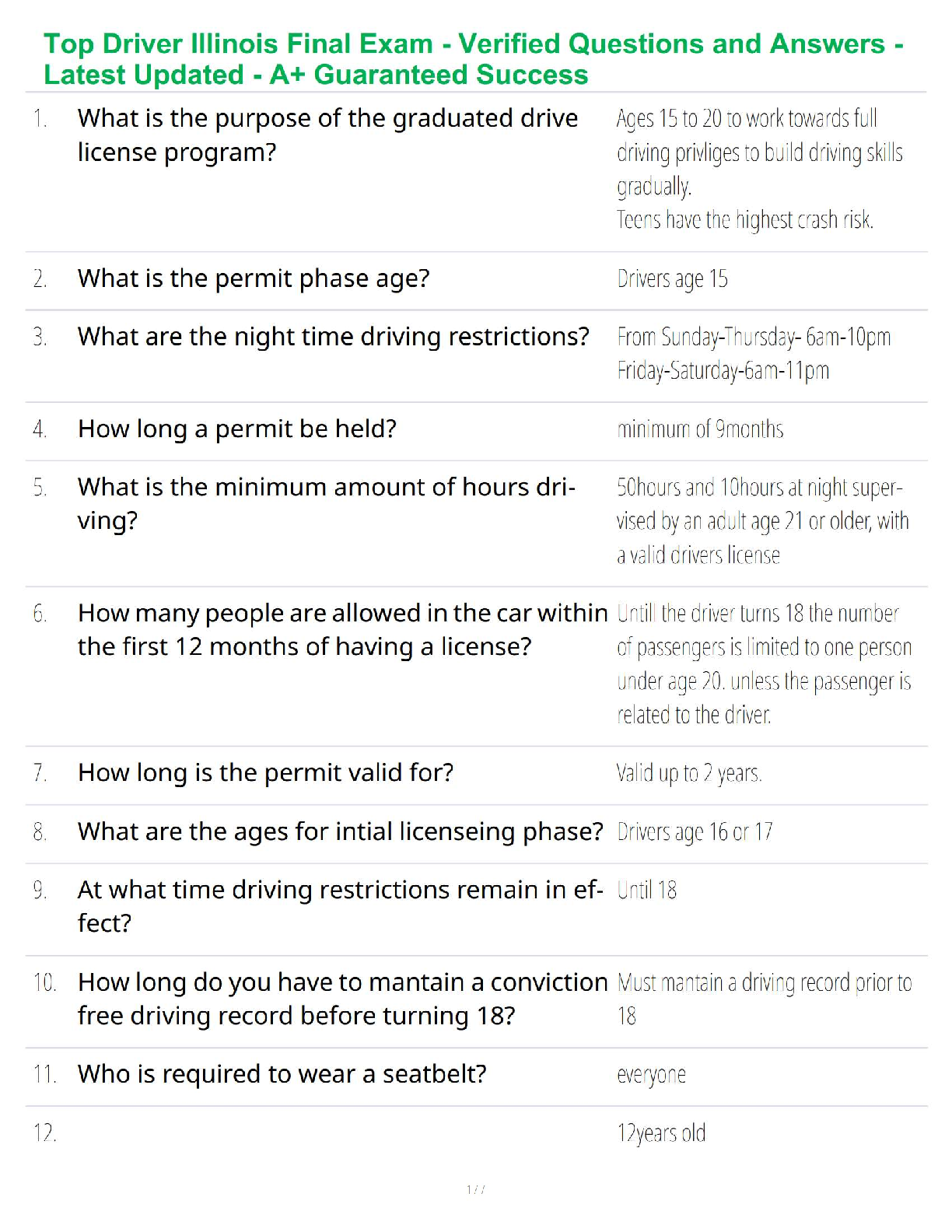
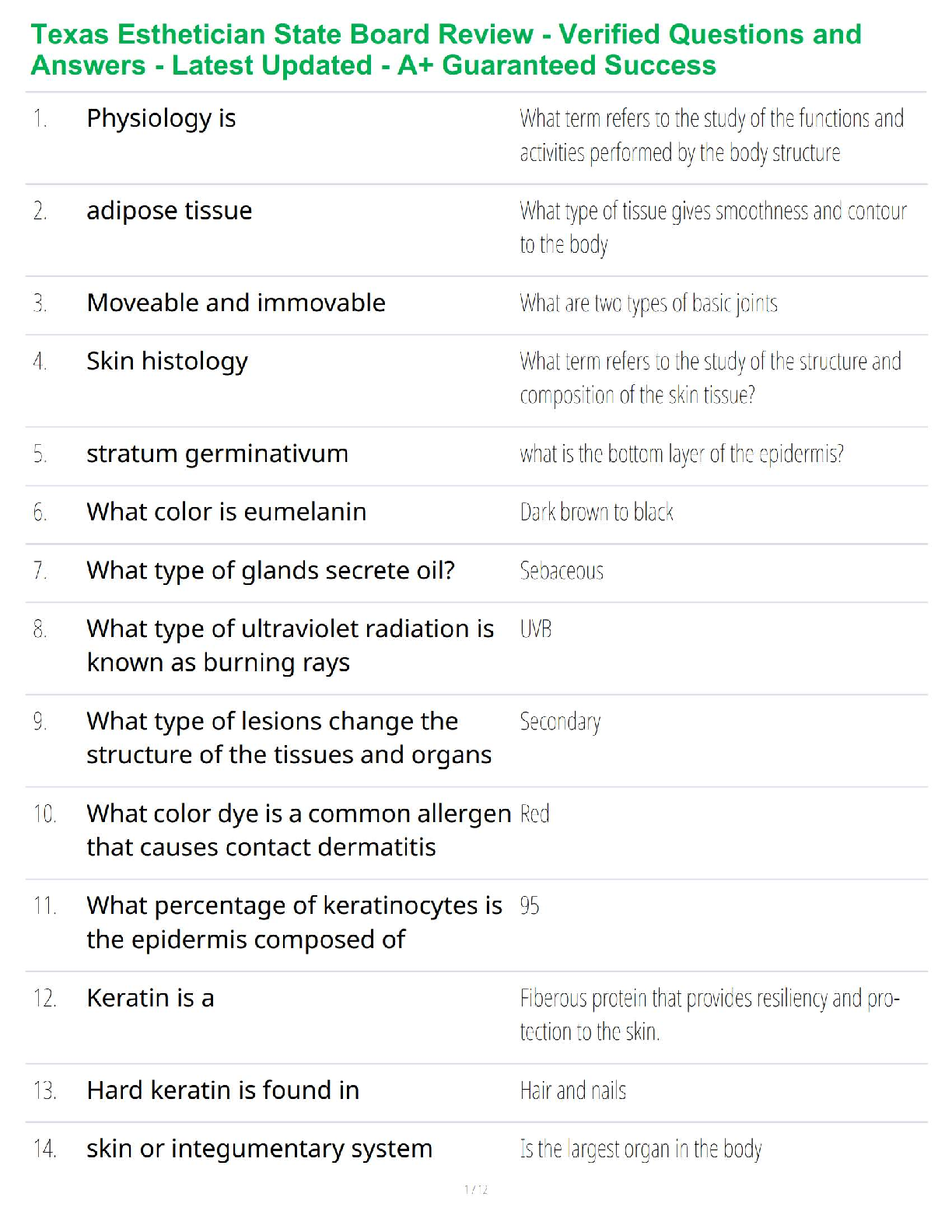
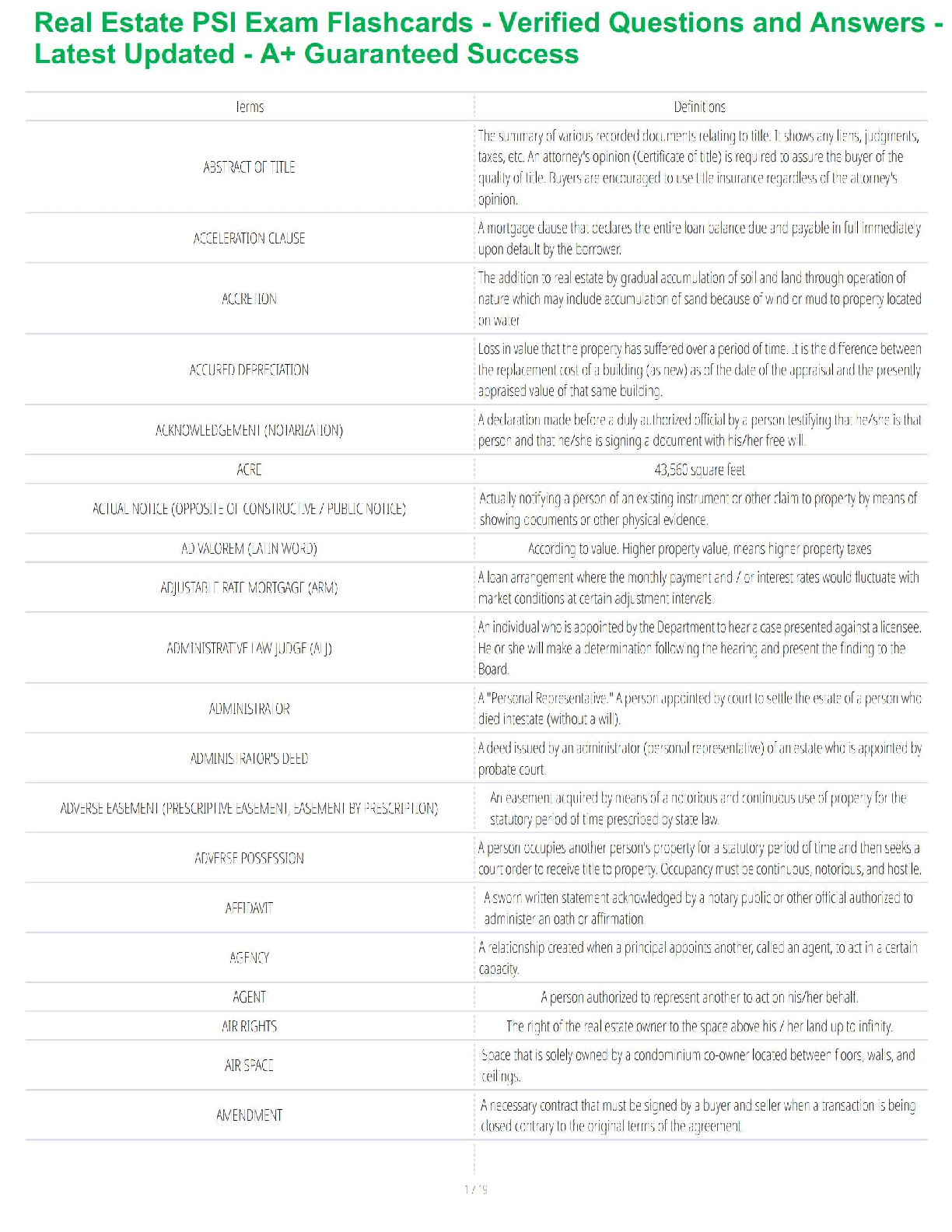
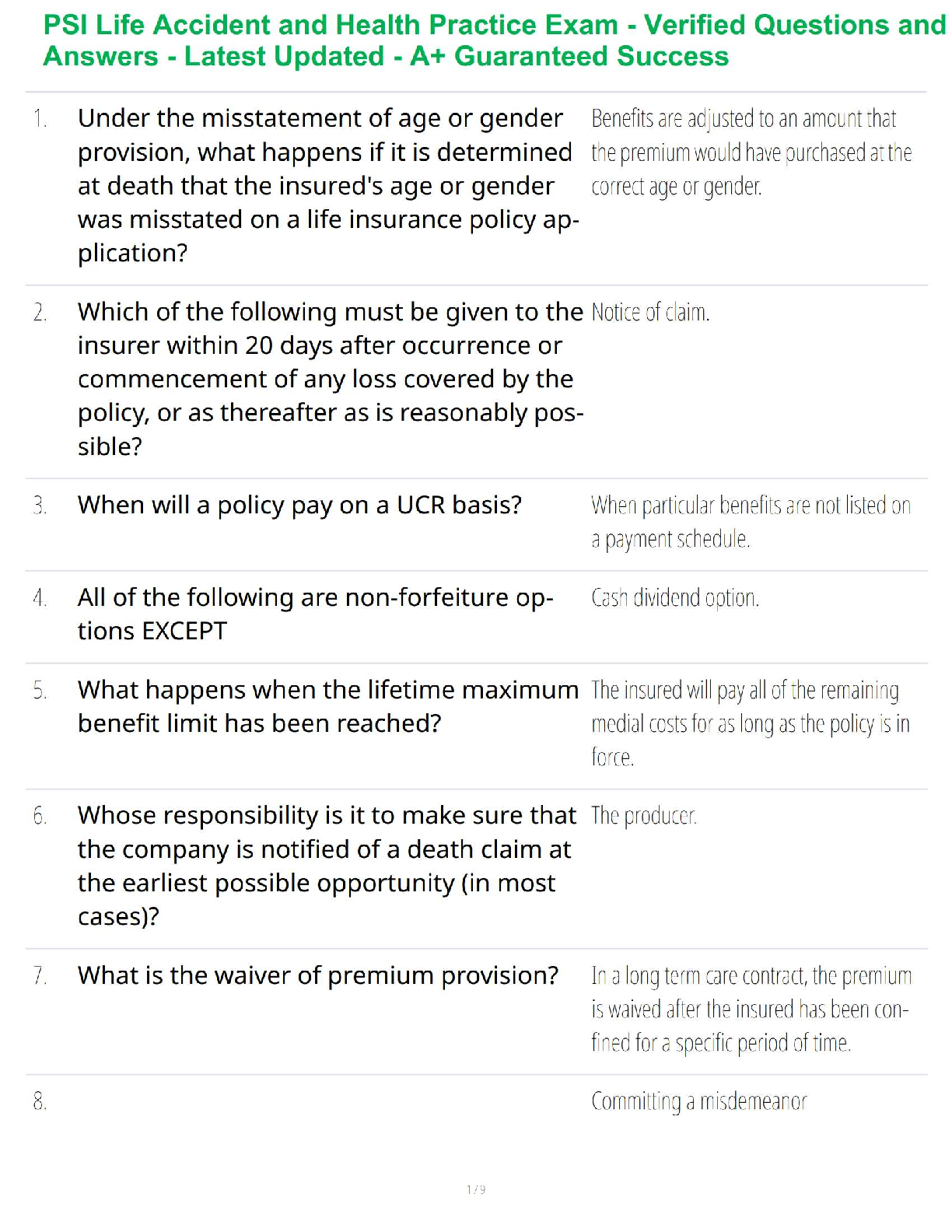
Student: ___________________________________________________________________________
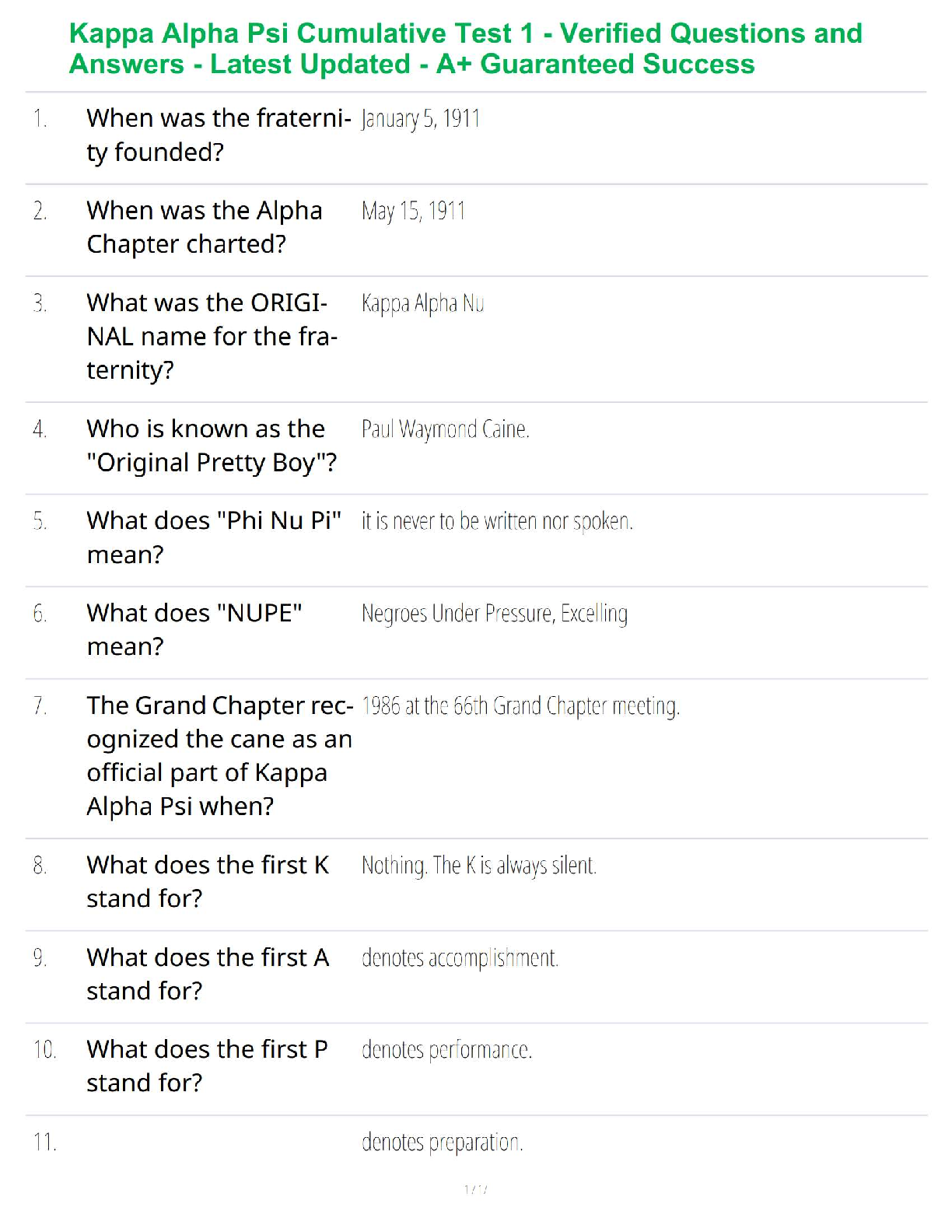
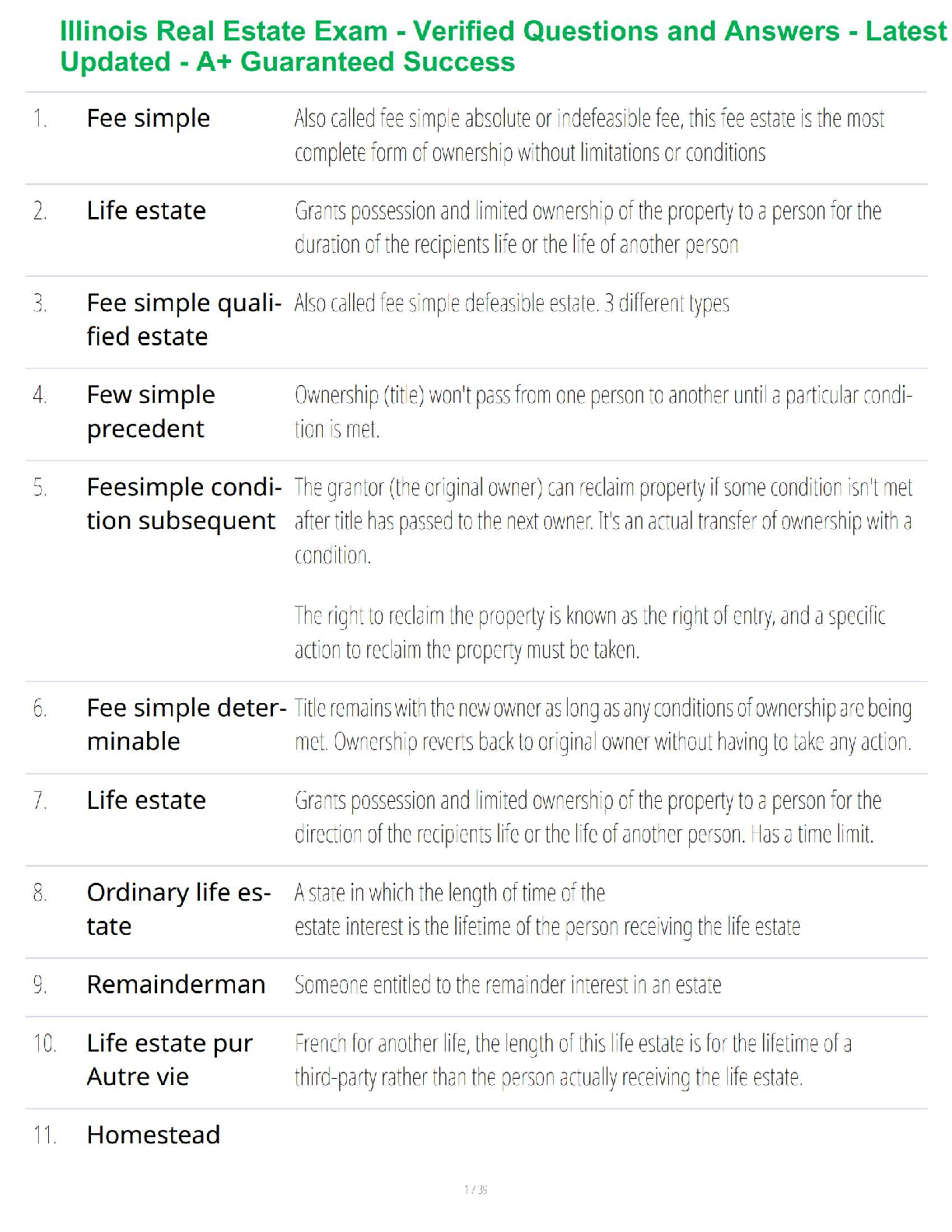
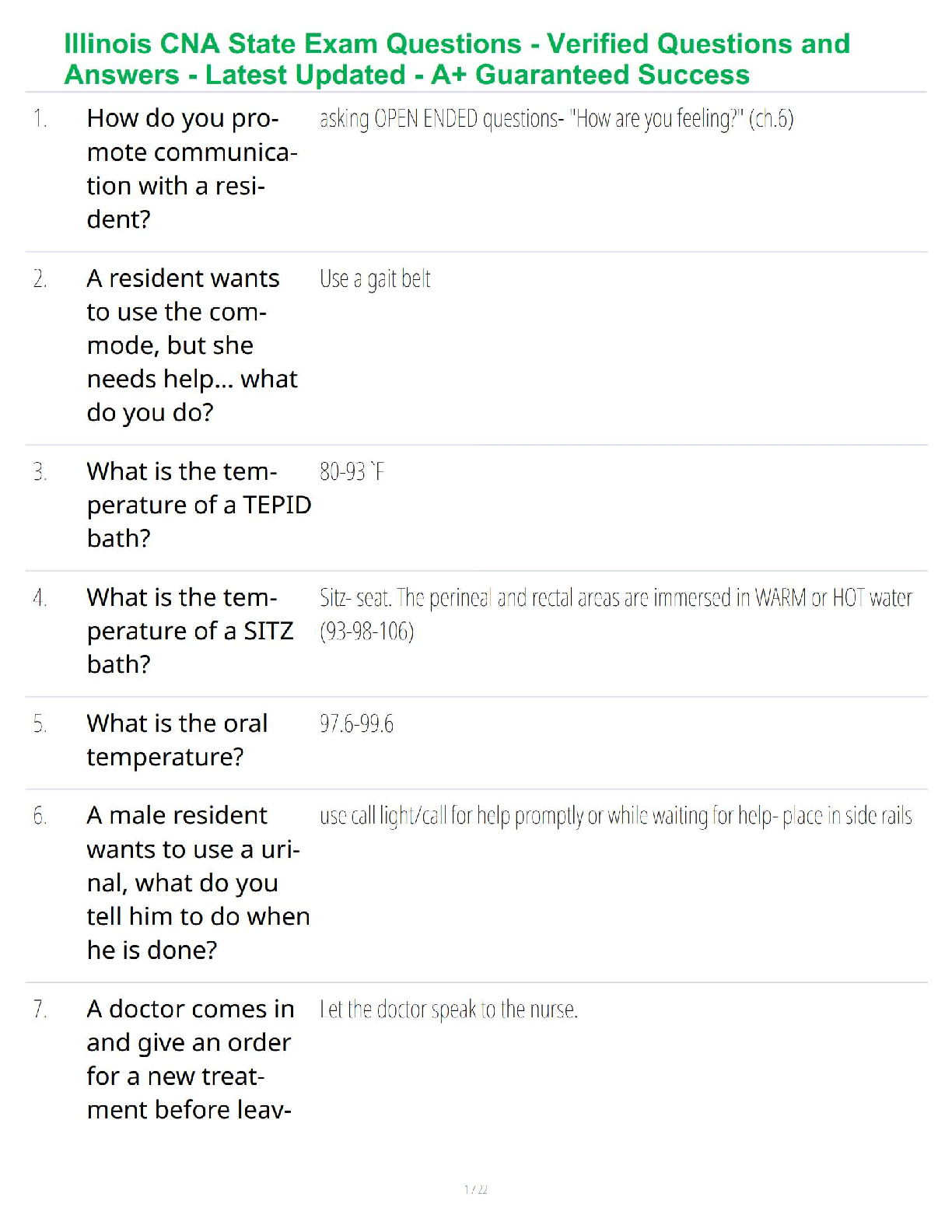
1. Qualitative research is subjective in the sense that the results are researcherdependent.
True Fa
...
Chapter 7--Qualitative Research
Student: ___________________________________________________________________________
1. Qualitative research is subjective in the sense that the results are researcherdependent.
True False
2. Quantitative research is especially useful when it is difficult to develop specific and
actionable decision statements or research objectives.
True False
3. Quantitative research address research objectives through empirical assessments that
involve numerical measurement and analytical approaches.
True False
4. Qualitative research is objective.
True False
5. When different researchers reach different conclusions based on the same interview,
the research lacks intersubjective certifiability.
True False
6. Qualitative research is cheaper than quantitative research.
True False
7. Most exploratory research designs produce qualitative data.
True False8. Phenomenology represents a philosophical approach to studying human experiences
based on the idea that human experience itself is inherently subjective and determined
by the context in which people live.
True False
9. A hermeneutic unit refers to a participant in a focus group interview.
True False
10. Studying cultures using methods that involve becoming highly active within that
culture is called phenomenology.
True False
11. Observation is a major way information is gathered in ethnography.
True False
12. Phenomenology represents an inductive investigation in which the researcher poses
questions about information provided by respondents or taken from historical records.
True False
13. Case studies involve documented history of a particular person, group, organization,
or event.
True False
14. A primary advantage of the case study is that an entire organization or entity can be
investigated in depth.
True False
15. Case studies are analyzed for important themes identified by the frequency with
which the same term arises.
True False16. A focus group typically involves a rigid question-and-answer session among
participants.
True False
17. Focus groups, while useful, take considerable time and effort to execute.
True False
18. Leapfrogging is a procedure in which one respondent stimulates thought among the
others in a focus group.
True False
19. The ideal size of a focus group is 20 to 25 people.
True False
20. A focus group moderator needs to be a good talker and dominate the group
discussion to keep it on track.
True False
21. A focus group discussion guide includes written introductory comments, informing
the group about the focus group purpose and rules and then outlines topics or questions
to be asked in the group session.
True False
22. A focus blog is established for the purpose of collecting qualitative data from an
informal, continuous focus group.
True False
23. In online focus group sessions, the moderator's ability to probe is greater than it is in
a face-to-face focus group session.
True False24. Laddering is an approach to probing, asking respondents to compare differences
between brands at different levels that produces distinctions at different levels.
True False
25. Depth interviews are less expensive than focus group interviews, especially if several
depth interviews are conducted.
True False
26. The sentence completion method is a type of free-association technique.
True False
27. The thematic apperception test (TAT) presents subjects with an ambiguous picture in
which consumers and products are the center of attention.
True False
28. The term interpretive research is often used to mean qualitative research.
True False
29. One advantage of qualitative research is that it is highly replicable.
True False
30. The primary barriers to scientific decisions are time, money, and consensus.
True False
31. Research that addresses business objectives through techniques allowing the
researcher to provide elaborate interpretations of business phenomena without
depending on numerical measurement is called _____.
A. preliminary research
B. primitive research
C. qualitative research
D. secondary research32. Kodetra is interpreting consumers’ blog postings on the Internet. Which of the
following best describes the type of research Kodetra is conducting?
A. independent business research
B. dependent business research
C. quantitative business research
D. qualitative business research
33. Qualitative research is considered to be _____ because the researcher must extract
meaning from unstructured responses.
A. researcher-dependent
B. less valid
C. less useful
D. object-dependent
34. All of the following are situations that often call for qualitative research EXCEPT
_____.
A. when it is difficult to develop specific and actionable decision statements or research
objectives
B. when conclusive evidence is desired
C. when the research objective is to develop an understanding of some phenomena in
great detail and in much depth
D. when a fresh approach to studying some problem is needed
35. Research that addresses research objectives through empirical assessments that
involve numerical measurement and analysis approaches is called _____.
A. quantitative business research
B. qualitative business research
C. extensive business research
D. grounded business research
36. Researcher-dependent results are _____.
A. subjective
B. objective
C. primary
D. secondary37. When different researchers reach the same conclusions based on the same interview
data, the research is said to have _____.
A. validity
B. intersubjective certifiability
C. subjective validity
D. qualitative validity
38. Which type of data are not characterized by numbers and instead are textual, visual,
or oral?
A. grounded data
B. quantitative data
C. subjective data
D. qualitative data
39. All of the following are qualitative research orientations EXCEPT _____.
A. phenomenology
B. grounded theory
C. case studies
D. ANOVA
40. Which qualitative research orientation originated in philosophy and psychology?
A. phenomenology
B. grounded theory
C. ethnography
D. anthropology
41. Ethnography is a qualitative research orientation originating in _____.
A. marketing
B. psychology
C. anthropology
D. sociology
42. Which qualitative research orientation originated in sociology?
A. phenomenology
B. grounded theory
C. ethnography
D. case studies43. Owen is a researcher who studies human experiences based on the idea that it is
inherently subjective and determined by the context in which people live. He focuses on
how a person’s behavior is shaped by the relationship he or she has with the physical
environment, objects, people, and situation. Which qualitative research orientation is
Owen using?
A. grounded theory
B. phenomenology
C. ethnography
D. case study
44. Which of the following is an important approach used in phenomenology?
A. netnography
B. ethnography
C. grounded theory
D. hermeneutics
45. Which of the following is an approach to understanding phenomenology that relies on
analysis of texts through which a person tells a story about him- or herself?
A. hermeneutics
B. ethnography
C. psychographics
D. psychodynamics
46. A text passage from a respondent’s story that is linked with a key theme from within
this story or provided by the researcher is called _____.
A. trace element
B. schemata
C. hermeneutic unit
D. case study
47. _____ is a way of studying culture through methods that involve becoming highly
active within that culture.
A. Grounded theory
B. Ethnography
C. Phenomenology
D. Case studies48. Cindy is an ethnographer who is trying to better understand how mothers take care
of toddlers. Being a mother herself, she was able to join a mother’s group and spent
considerable time immersed within that culture. From this immersion, she is able to
draw data from her observations. Cindy is referred to as a(n) _____.
A. interloper
B. participant-observer
C. moderator
D. mystery shopper
49. Which qualitative research orientation extracts a theory from whatever emerges from
an area of inquiry?
A. phenomenology
B. ethnography
C. grounded theory
D. case study
50. What is the distinguishing characteristic of grounded theory?
A. Culture is analyzed by participant-observation in which the researcher becomes
“grounded” in the culture over a long period of time.
B. It relies on analysis of texts in which a person tells a story about him- or herself.
C. The interplay among respondents allows them to piggyback off of each other’s ideas.
D. It does not begin with a theory but instead extracts one from whatever emerges from
an area of inquiry.
51. _____ represent(s) the documented history of a particular person, group, organization,
or event.
A. Case studies
B. Phenomenology
C. netnography
D. Attribution theory
52. When Schwinn studies its most successful retailer in depth in order to determine
some better ideas for displaying bicycles in its retail stores, this is an example of _____.
A. an experiment
B. a test market
C. a case study
D. causal research53. In case studies, _____ are identified by the frequency with which the same term (or a
synonym) arises in the narrative description.
A. themes
B. threats
C. links
D. ladders
54. An unstructured, free-flowing interview with a small group of people led by a trained
moderator is called a(n) _____.
A. interaction group interview
B. focus group interview
C. depth interview
D. ethnographic interview
55. Which of the following is the most common size of a focus group?
A. 1-2 participants
B. 3-5 participants
C. 6-10 participants
D. 12-20 participants
56. Betsy and six other women are participating in a research study that is an
unstructured, free-flowing interview. The researcher asked the group their feelings about
how they are treated at work. Betsy is participating in a _____.
A. case study
B. grounded research study
C. depth interview
D. focus group interview
57. Which of the following is an advantage of focus group interviews?
A. provide multiple perspectives
B. low degree of scrutiny
C. inexpensive
D. easy to use for sensitive topics58. In a focus group discussion, when the comments of one member triggers a stream of
comments from the other participants, this is called _____.
A. serendipity
B. piggyback
C. structure
D. themes
59. The person who leads a focus group interview and ensures that everyone gets a
chance to speak and facilitates discussion is called a(n) _____.
A. moderator
B. interviewer
C. facilitator
D. leader
60. Which of the following is a good characteristic for a focus group moderator to
possess?
A. good listener
B. ability to make people feel comfortable so that they will talk in the group
C. ability to control discussion without being overbearing
D. all of these choices
61. The written set of guidelines that describes an outline of topics to be covered by a
focus group moderator is called a _____.
A. discussion guide
B. TAT test
C. concept test
D. case study
62. A type of informal, “continuous” focus group established as an Internet blog for the
purpose of collecting qualitative data from participants is referred to as a _____.
A. net group
B. market blog
C. focus blog
D. focus unit63. Which of the following is a disadvantage of focus groups?
A. requires objective, sensitive, and effective moderators
B. may not be useful for discussing sensitive topics
C. high cost
D. all of these choices
64. When a professional interviewer holds a 90-minute discussion with one member of
the target market to find out why that respondent purchases a particular brand of
clothing, this is an example of a _____.
A. depth interview
B. concept test
C. focus interview
D. hermeneutic analysis
65. Which type of qualitative tool is an informal and almost completely unstructured
approach in which the researcher engages a respondent in a discussion of the relevant
subject matter?
A. depth interview
B. conversation
C. focus group
D. free-association
66. Hank is a researcher who is discussing football fan behavior with a respondent. His
approach is almost completely unstructured, and he enters into a discussion with few
expectations. What he wants is for a respondent to tell him about his or her experience
as a football fan. Hank will then try to derive meaning from the resulting dialog. Which
qualitative research technique is Hank using?
A. conversation
B. focus group
C. depth interview
D. case study
67. All of the following are advantages of semi-structured interviews EXCEPT _____.
A. ability to address more specific issues
B. responses are usually easier to interpret than other qualitative approaches
C. questions are administered without the presence of an interviewer
D. high degree of scrutiny68. Which qualitative tool simply records a respondent’s first cognitive reaction (top-ofmind) to some stimulus?
A. phenomenology
B. conversations
C. probing
D. free-association techniques
69. When the respondent is presented with: “People who watch football on television are
________,” and asked to fill in the blank, this is an example of a _____.
A. word association test
B. concept test
C. case study
D. sentence completion test
70. _____ are the researcher’s descriptions of what actually happens in the field and are
the text from which meaning is extracted.
A. Hermeneutics
B. Field notes
C. Discussion guides
D. Verbatims
71. Stephanie was asked to look at a picture of a woman sitting on a deserted beach and
to describe what was happening in the picture. She was then asked to tell what might
happen next. Stephanie was participating in a(n) _____.
A. aptitude test
B. focus interview
C. thematic apperception test
D. focus blog
72. Which of the following means the same conclusion would be reached based on
another researcher’s interpretation of the research?
A. validity
B. replicable
C. homogeneity
D. scrutiny73. Research that addresses marketing objectives through techniques that allow the
researcher to provide elaborate interpretations of business phenomena without
depending on numerical measurement is referred to as _____ business research.
________________________________________
74. Qualitative research results are _____ because they are researcher-dependent.
________________________________________
75. Most exploratory research designs do not usually product _____ data.
________________________________________
76. Ethnography originated from the discipline of _____.
________________________________________
77. _____ represents a philosophical approach to studying human experiences based on
the idea that human experience itself is inherently subjective and determined by the
context in which people live.
________________________________________
78. The typical ethnographic approach requires the use of _____.
________________________________________
79. An in-depth study of a major competitor in order to determine how to improve your
organization's product line offerings is an example of a(n) _____.
________________________________________
80. An unstructured, free-flowing discussion with a small group of consumers in a session
that is conducted by a moderator is called a(n) ______.
________________________________________
81. In a focus group, when the comments of one member stimulate another member to
say what she is thinking, this is called ________.
________________________________________82. The person who leads a focus group discussion is called a(n) ______.
________________________________________
83. A written set of guidelines prepared by a moderator that outlines the topics to be
discussed in a focus group session is called a(n) ______.
________________________________________
84. A focus group session that is conducted over the Internet is called a(n) ______ focus
group session.
________________________________________
85. A one-on-one interview between a professional researcher and a research respondent
about why she selected a specific insurance benefit option is an example of a(n) ______.
________________________________________
86. When an interviewer reads a list of words and asks the respondent to “say the first
thing that comes to mind after I say each word,” this is an example of a(n) _____
technique.
________________________________________
87. Research that leads to the same results and conclusions by different researchers is
_____.
________________________________________
88. Compare and contrast qualitative research and quantitative research and discuss
situations in which qualitative research is useful.89. Explain the role of qualitative data and quantitative data in exploratory research
designs.
90. Name and briefly describe the four qualitative research orientations.
91. Describe a focus group interview and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of
this technique.
92. Develop a discussion guide for a focus group on football fan behavior.93. Explain how the Internet is useful in conducting qualitative research.
94. Do exploratory research approaches using qualitative research tools have a role in
scientific inquiry? Explain why a decision may be based solely on these results
[Show More]
.png)