A Level Further Mathematics A Y544/01 Discrete Mathematics Mark Scheme - Autumn 2021
$ 5.5
University of California, Los Angeles LIFESCIENC 30A. Midterm1 Solutions.
$ 13
.png)
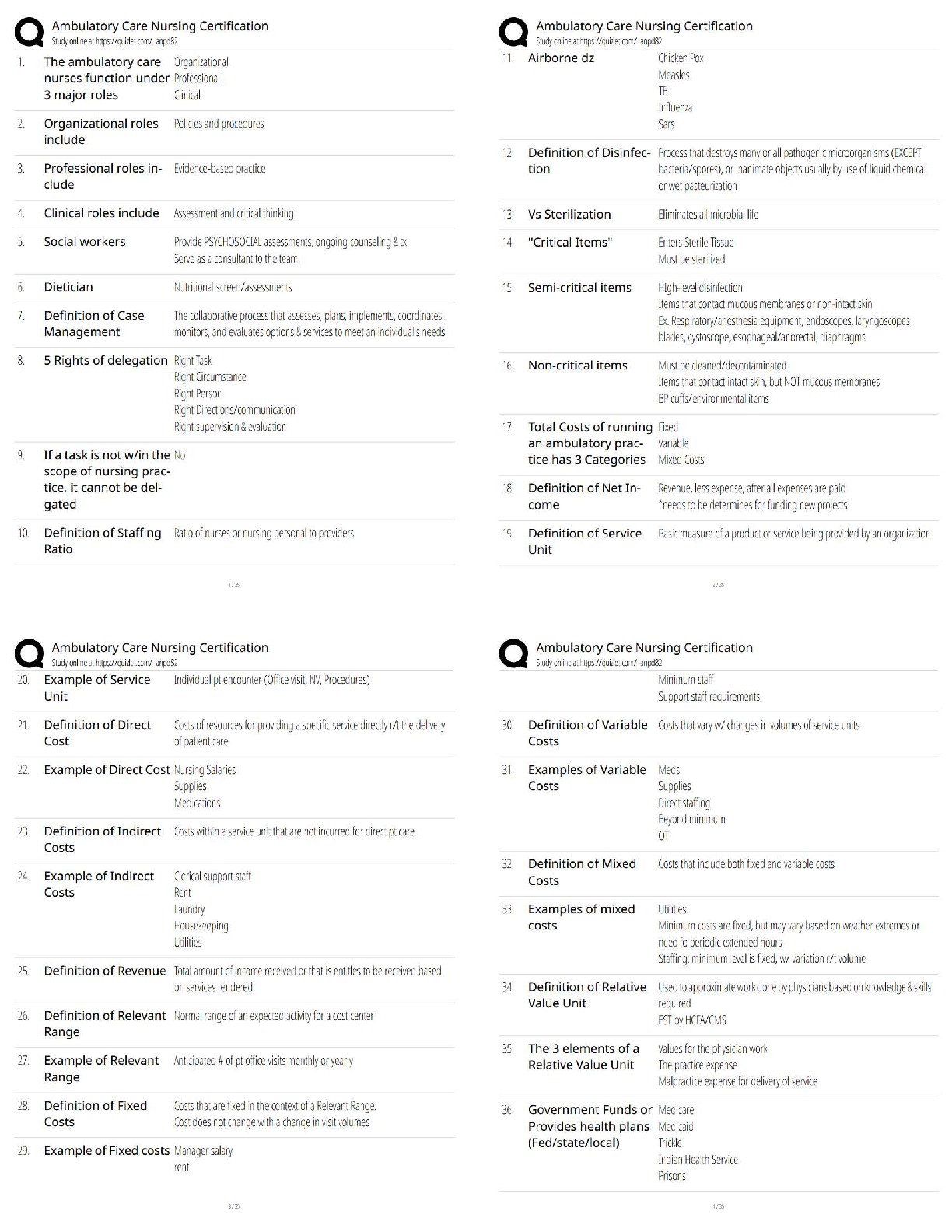
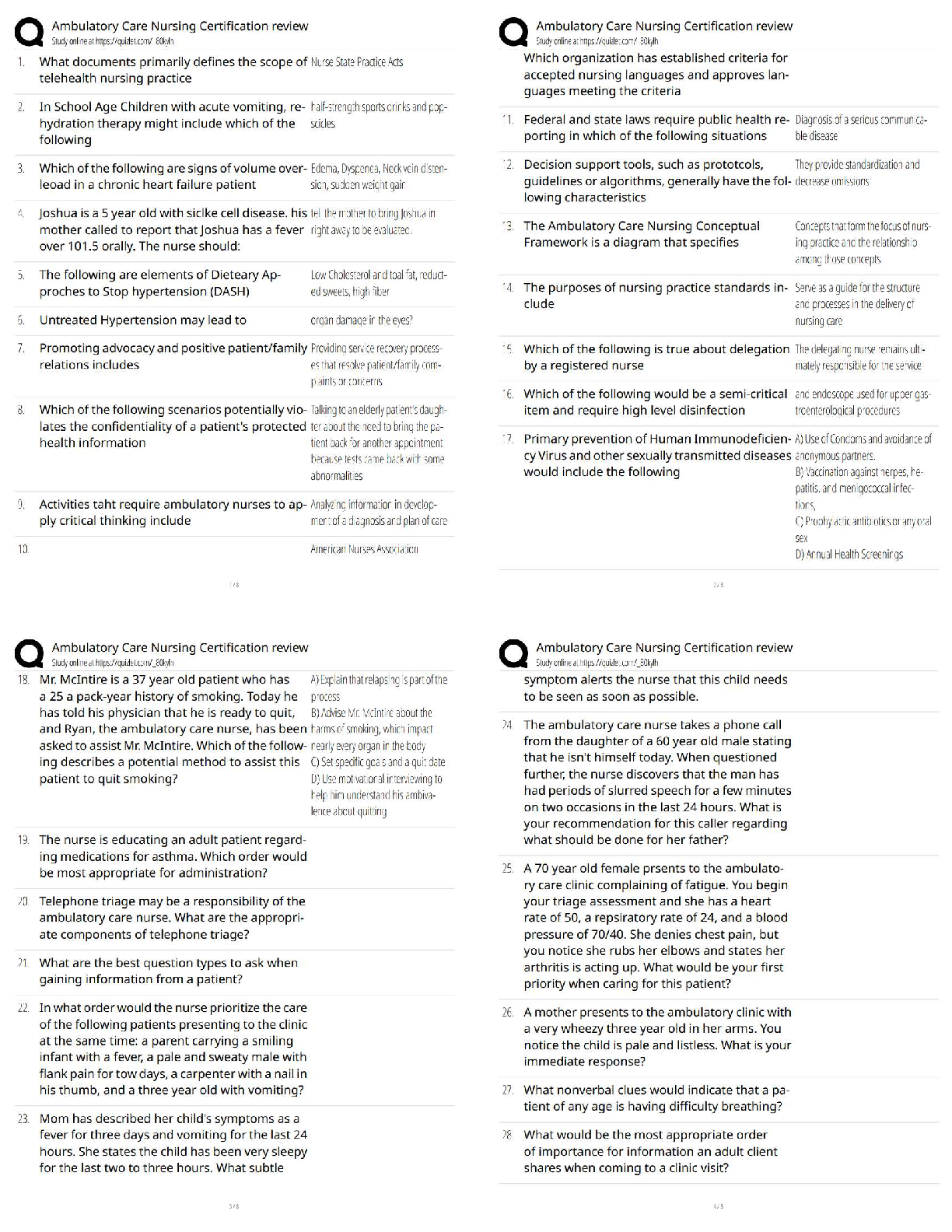
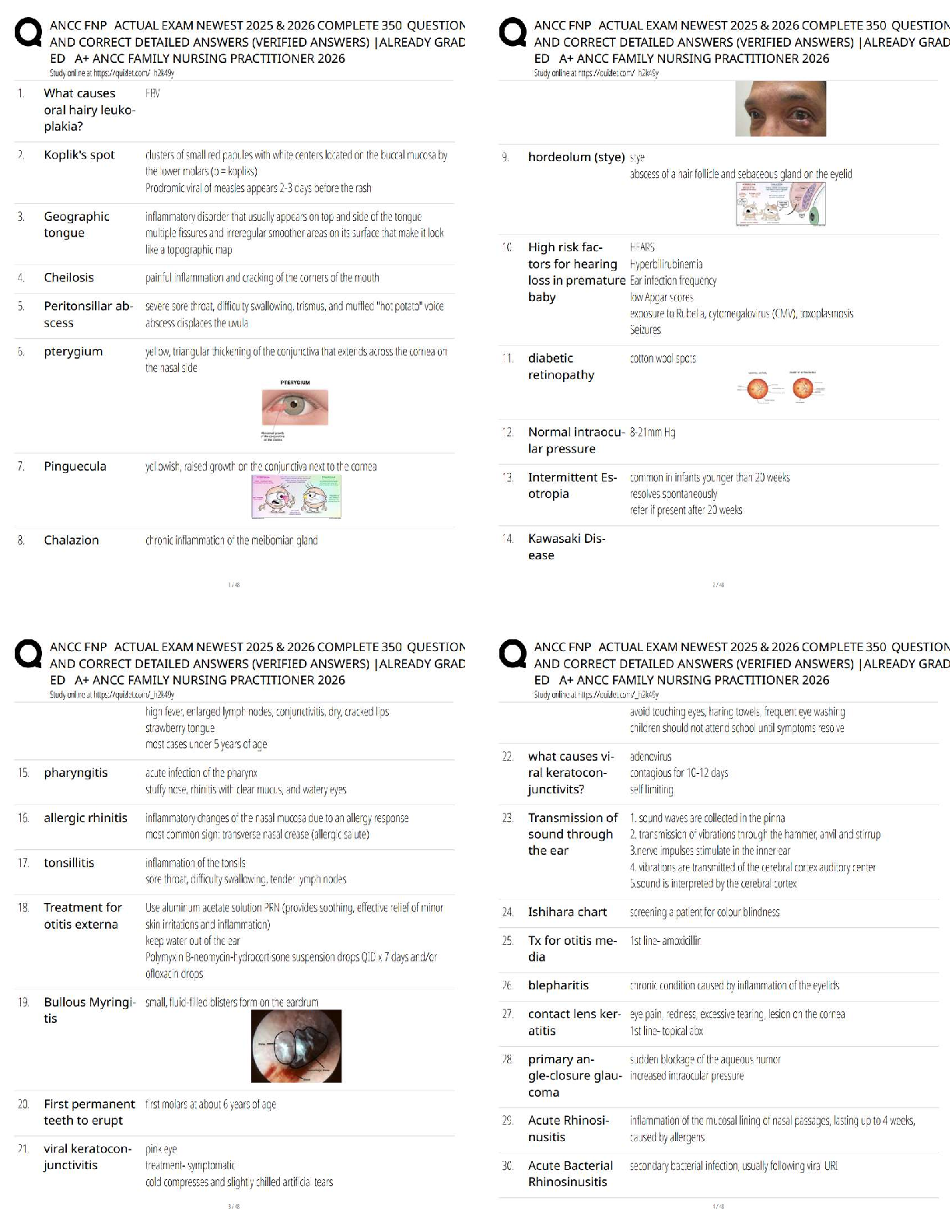
WGU C207 OA Questions and Answers with Complete Solutions
$ 15

Cyber Awareness 2022 Knowledge Check Already Passed
$ 6

Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS Paper 6 Alternative to Practical QUESTION PAPER - March 2022
$ 5.5

eBook [PDF] Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos 1st Edition By Steven H. Strogatz
$ 20

eBook Biomechanics of Human Communication Neurophysiology, Regulation, and Systems Thinking 1st Edition By S. Faye Molicki
$ 30

Pearson Edexcel GCE In Economics B (9EB0) Paper 2: Competing in the Global Economy Mark Scheme (Results) November 2021
$ 7.5

AAPC CPC FINAL EXAM UPDATED 2025 WITH QUESTIONS AND 100% CORRECT ANSWERS GUARANTEED A+
$ 19

CNA Chapter 7 Quiz (Answered) Verified Answers 100% 2023
$ 5

Homework 1 - Solution
$ 7

Solution Manual for Database Systems, The Complete Book, 2e Hector Garcia-Molina, Jeffrey Ullman, Jennifer Widom
$ 23
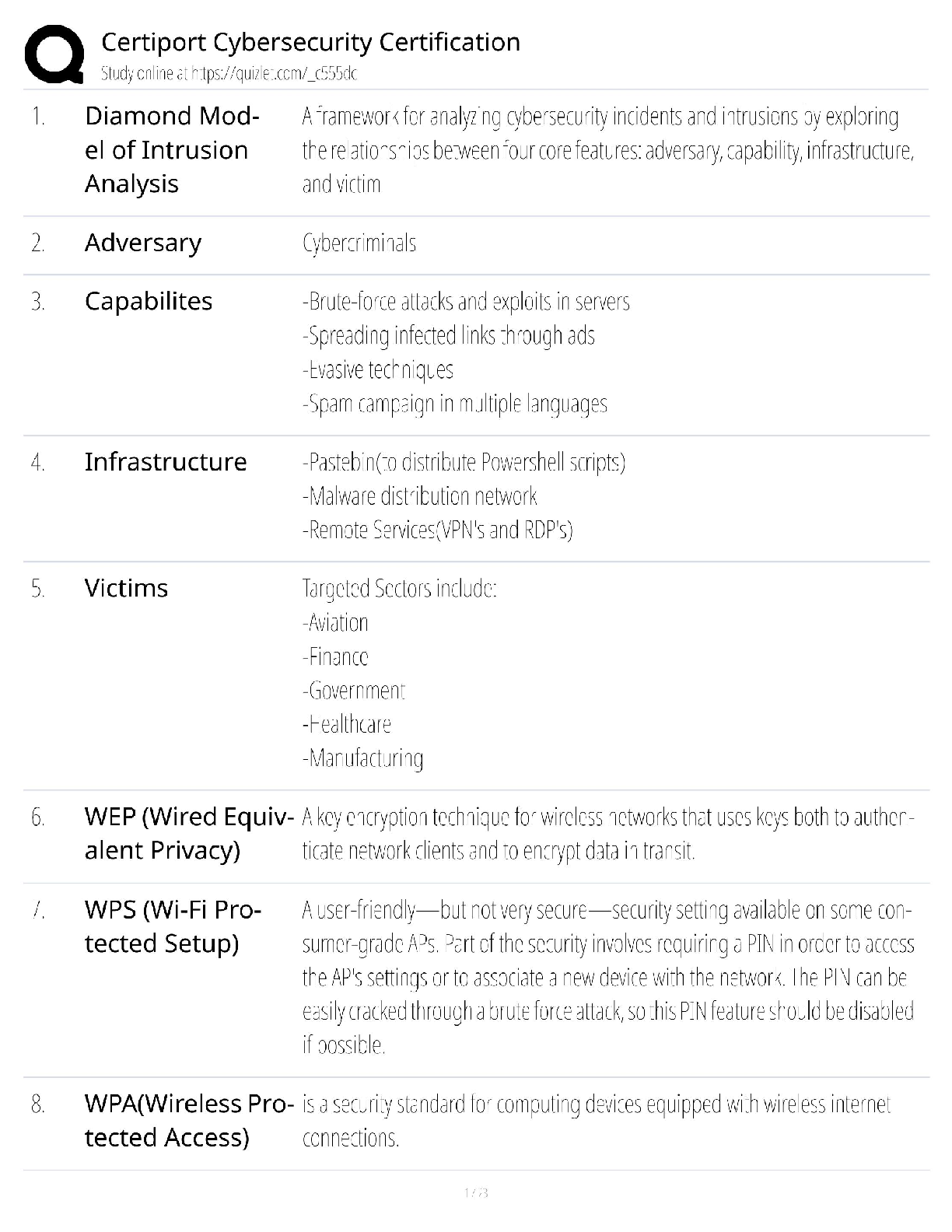
Certiport Cybersecurity Certification / 2024 Exam Prep / ITS-303 Practice Tests / Pass Guaranteed
$ 15.5
.png)
WGU D220 Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

University of the People MATH 1201 College Algebra - Term 3 Final Exam -Proctored.
$ 8
.png)
WGU C464 - Introduction to Communication Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

Yoost & Crawford: Fundamentals of Nursing: Active Learning for Collaborative Practice, 2nd Edition Review Questions
$ 8

Sophia - College Algebra - Milestone Study Guide Revisions, 16 Updated Study Guide, Correctly Answered Questions, Test bank Questions and Answers with Explanations (latest Update), 100% Correct, Download to Score A
$ 30

eBook [PDF] Public Health An Introduction to the Science and Practice of Population Health 1st Edition By James Shultz, Lisa Sullivan, Sandro Galea





.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)