
MATH 225N Week 8 Assignment: Multivariate Relationships.100% CORRECT.
$ 10

Public-Finance-Mcqx
$ 30

Interventions Final Exam Study Guide
$ 17

NURS 231-Final Exam- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY.pdf
$ 12

MATH221 Week 7 Quiz
$ 15.5

NR 446 Lab prep NOTES LATEST UPDATE
$ 14

Nursing 402- ATI TEST B.pdf
$ 14
.png)
ENG 202Brit lit quizzes.
$ 9

NR443- ATI Type A-exam.pdf
$ 11

TEAS Test: Math Questions And Answers( Best Solution)
$ 13.5

MDC2_Final_Exam_Study_Guide__1.
$ 4

Comprehensive Developmental Milestones & Medical Knowledge
$ 35.5
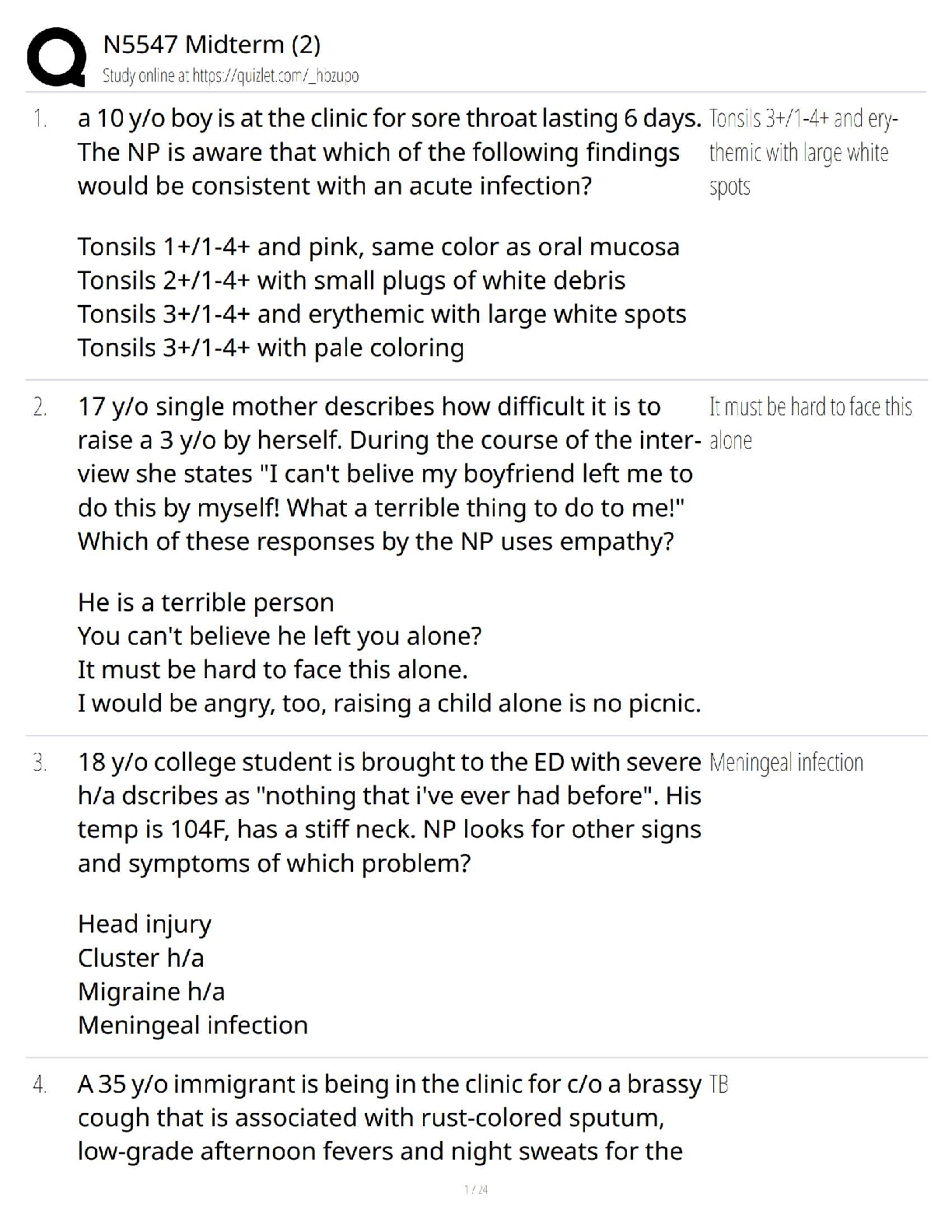
N5547 Midterm (2)
$ 13

HESI A2 CHEMISTRY
$ 7

Med Surg 2, 2019 →PRIORITY TWO.
$ 8

CCOU 301 Exam 4,100% CORRECT
$ 13

Assignment 3.docx ASSIGNMENT 3
$ 10
.png)
Prioritization & Delegation Set 2
$ 7

Quiz# 4.doc
$ 10

SATWORLD_TEST_07_MathKeys
$ 13

Multıple-Choıce-Questıons-And-Answer
$ 30

Pure Mathematics A Level: Practice Paper
$ 10
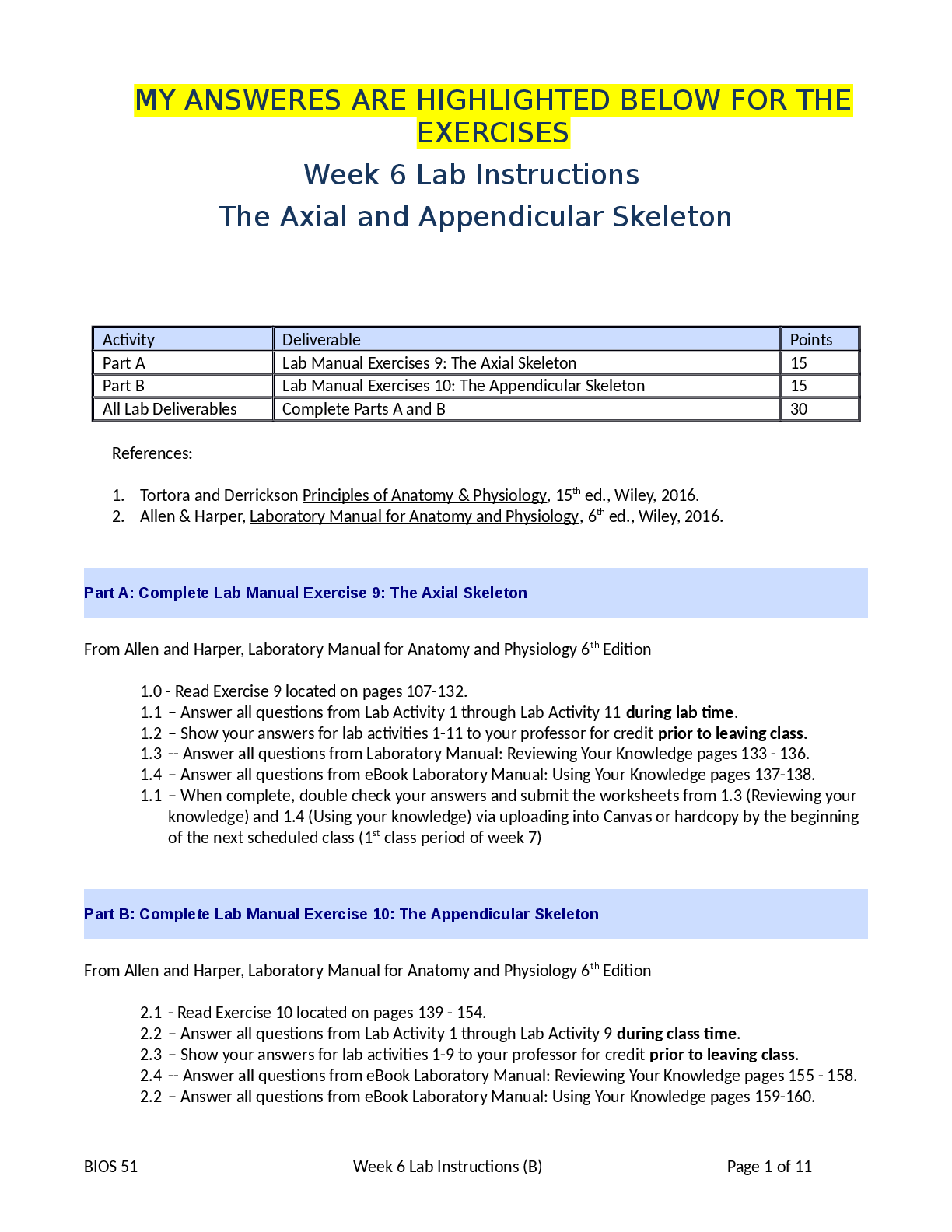
W6 lab instructions
$ 15

CAP Wright Brothers Achievement Exam Test
$ 12

TrueWay_ASL_1101_Final_Exam_Test_Answer_Sheet
$ 30

ASIS-CPP exam with complete solutions 2024
$ 16

MPP 3202 PHYSIOLOGY Exam 2 Study Guide
$ 13

Final Review Phram Questions
$ 15

OCR GCE Further Mathematics A Y543/01: Mechanics Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for Autumn 2021
$ 10

NRNP 6635 FINAL EXAM
$ 14

CGP Practice Exam Paper A-level Mathematics| Practice set 1 Paper 1, 2 & 3| Practice set 2 Paper 1, 2 & 3| Marking Scheme for All Sets| mathematical Formula Booklet| Statistical Tables
$ 35

Quiz# 2.doc
$ 10.5

ECONS 200 UOFA FINAL EXAM VERSION 2 2025
$ 20

NR602 WEEK 8 FINAL EXAM
$ 15

NRNP 6560 Midterm Exam
$ 18

mcqs-in-physiology
$ 30
 (1).png)
NSG 6020 Midterm Study Guide
$ 10

Test Bank Chapter 9
$ 30

Quiz 5 MAT 540
$ 11

RN COMPREHENSIVE ONLINE PRACTICE 2019 A.docx
$ 15

Testbank Chapter 24- Development and Birth
$ 19

(WGU D278) ITEC 2113 Scripting & Programming Foundations Objective Assessment Guide 2024
$ 12

NR 599 MIDTERM REVIEW
$ 13

HESI A2 VERSION 1 READING COMPEHENSION
$ 15

Assignment 1 Unit 3 M1
$ 11

bsc2347 mod4quiz docx
$ 11

Module 2 Respiratory Lab Test A&PI Portage Learning.
$ 13

Funds Proctored Exam Rationales
$ 15

HESI A2 FILE,GRADED A.
$ 15

MATH 225N / MATH225N MATH Statistic Week 7 Hypothesis Testing Questions and Answers - Latest 2022 - 100% verified version
$ 14

Medtech Laws Exam
$ 30

NR 446 EXAM 1 STUDY GUIDE FALL 2020
$ 14

12-Rules-to-Learn-to-Code



























