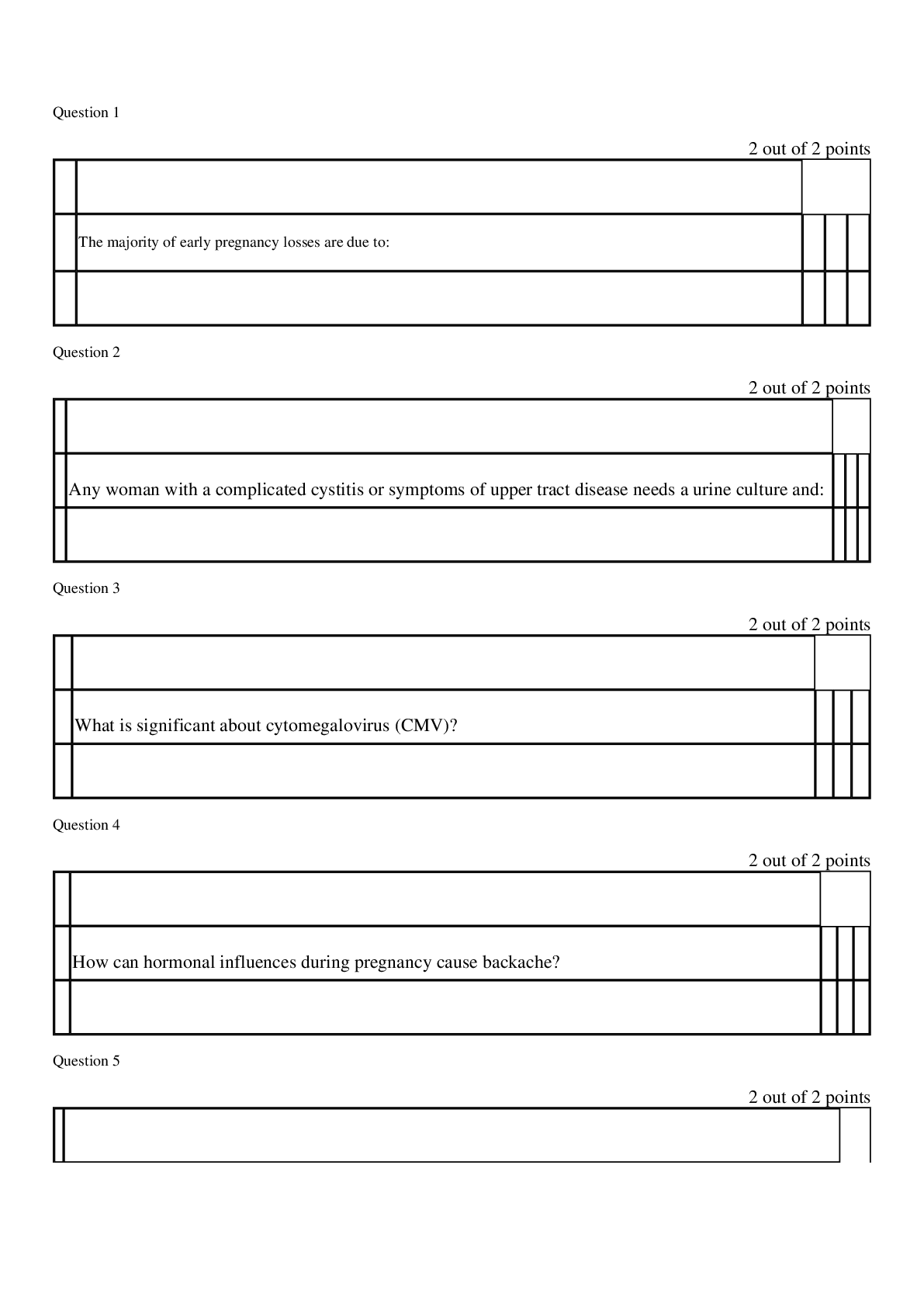
.png)
Walden University NURS 6501 Quiz 2
$ 14

CHEM 102 Winter 18 Exam 3 (B) Questions and Answers,100% CORRECT
$ 12

Pearson Edexcel AS Level 3 GCE (8PH0/01) Physics Advanced Subsidiary paper 1:Core Physics Question paper+mark scheme Wednesday 15 may 2024
$ 7

Solution Manual for Fundamentals of Python First Programs, 3rd Edition Kenneth A. Lambert
$ 13.5

ATI NURSING CARE OF CHILDREN PROCTORED EXAM TEST 2024 COMMONLY TESTED QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 12

VATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR FOCUSED REVIEW, Latest 2019/2020 (complete A+ guide)
$ 9

PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS PAPER 2 ECZ FINAL EXAM QUESTION PAPERS & SOLUTIONS 2024
$ 66
🧠 IOP3701 – Industrial Psychology: Testing and Assessment | Assessment 1 Guide | Verified Questions & Answers | (University of South Africa, EEA Focus, 2025 Edition)
$ 11
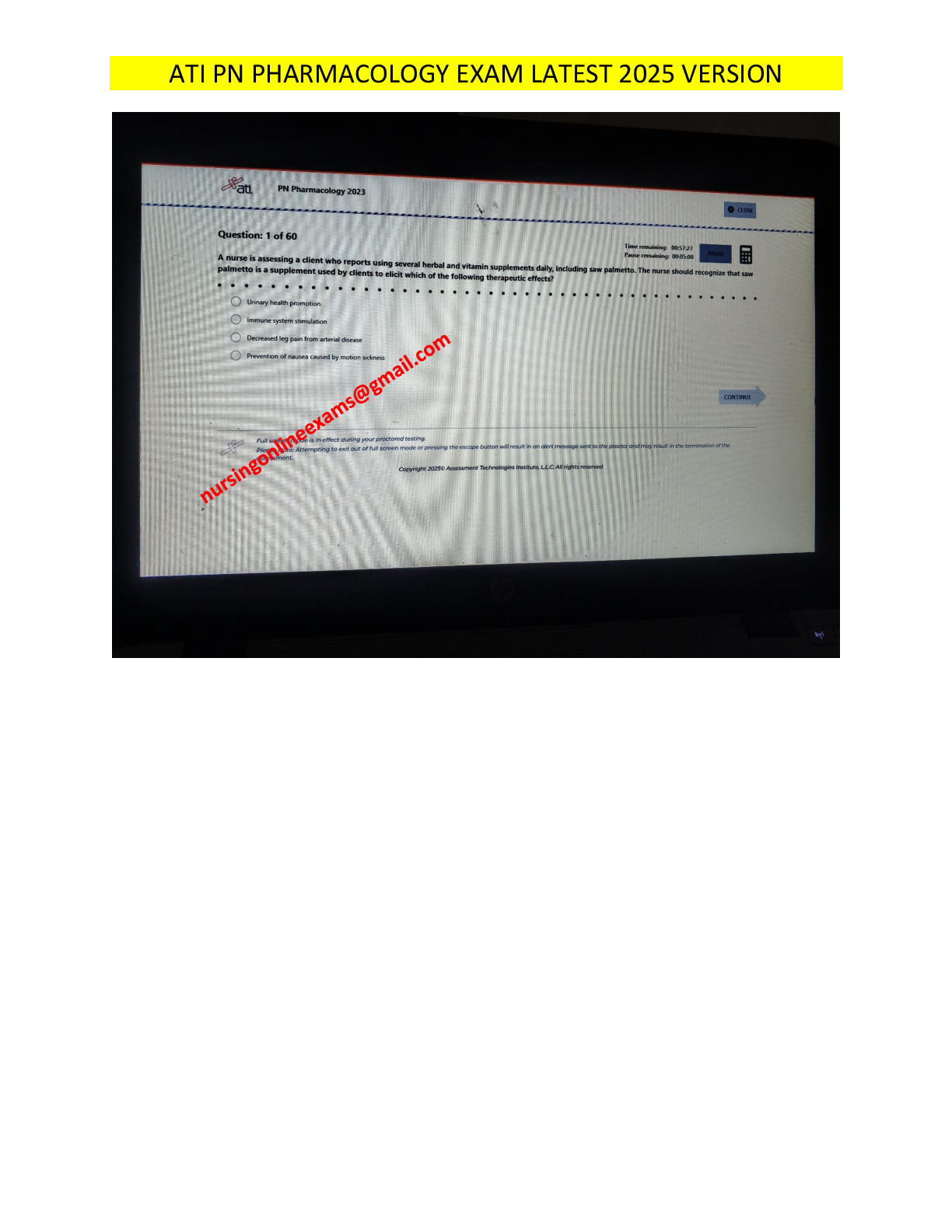
ATI PN Pharmacology
$ 69

(WGU D190) HIM 2002 INTRO TO HEALTHCARE IT SYSTEMS FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 10
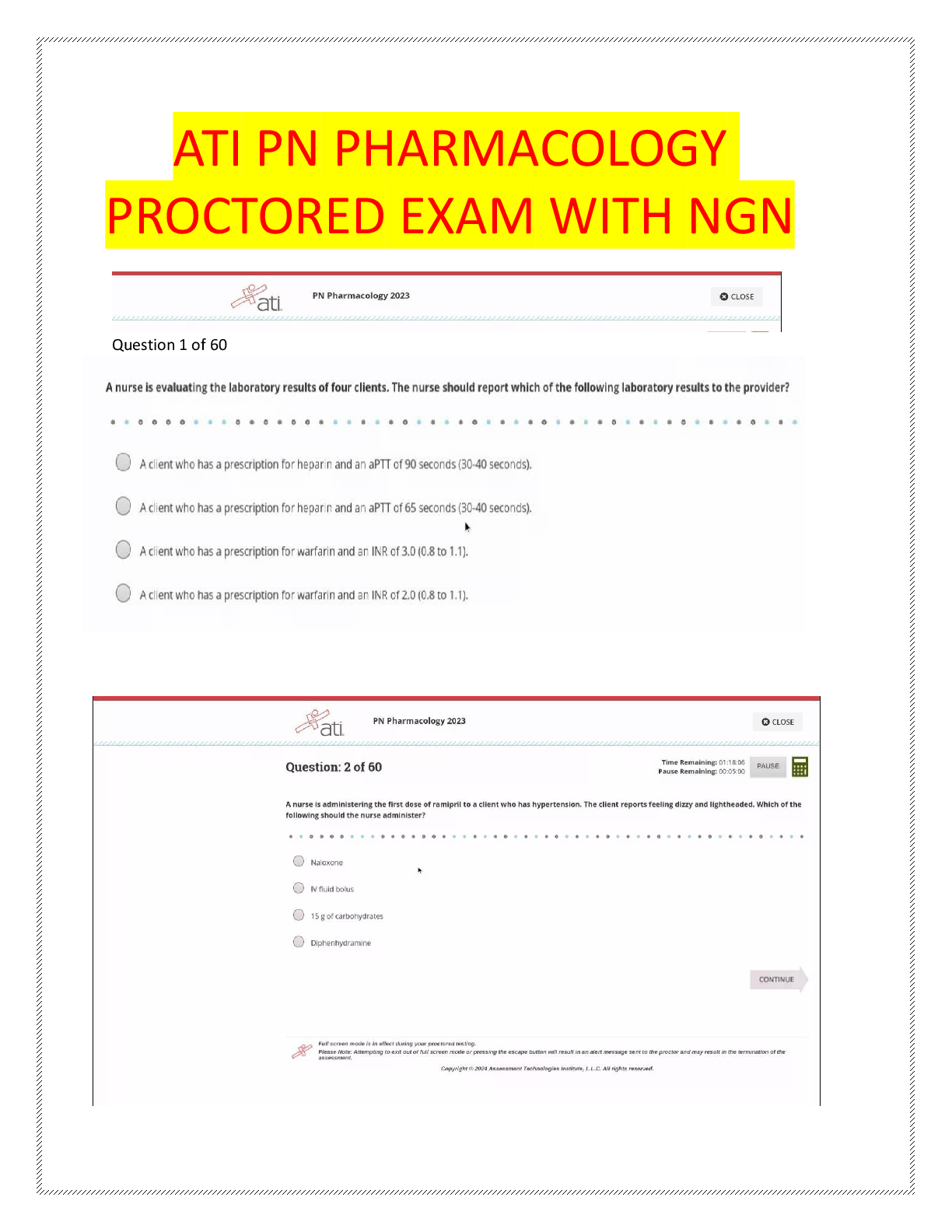
PN ATI Pharmacology
$ 70

NR 507 EDAPT Week 5 Alterations in Neurobiological Function! RATED A+
$ 9.5

Student Exploration: Effect of Environment on New Life Form 2021/2022
$ 10

eBook Policing and CBRN Hazards Advancing CBRN Competence in Police Education By Patrick Wengler
$ 29

MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATION CONCEPTS
$ 4.5

Chapter 23: Complications due to Adolescence
$ 3

Aerial Applicator General Test – Exam Prep & Study Guide
$ 14.5

NURSING EMPLOYMENT POLICY FINAL TEST LATEST MODULE QNS & ANS 20232024
$ 15
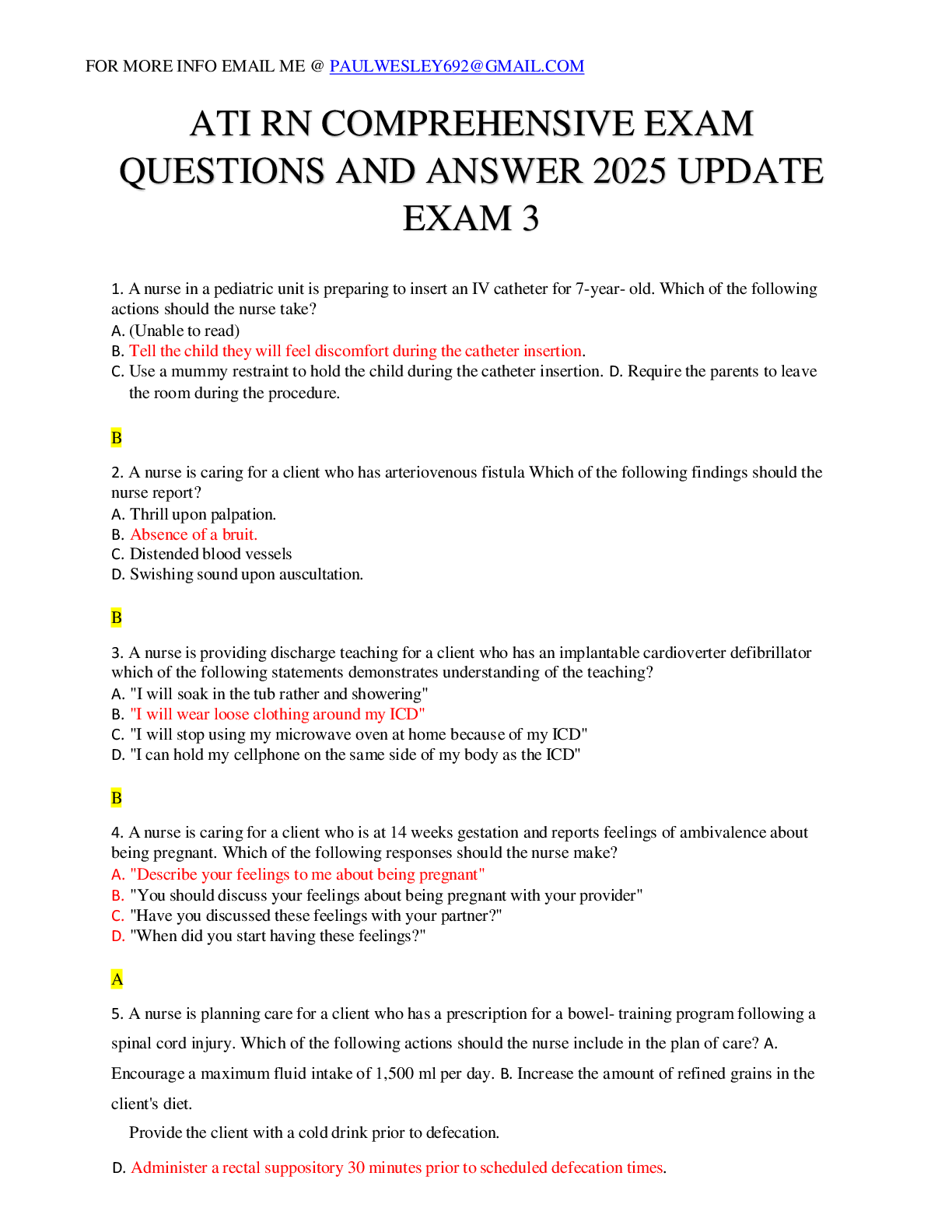
ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWER 2025 UPDATE EXAM 3