Torque and Moment of Inertia Gizmos-VERIFIED BY EXPERTS 2021-GRADED A+
Document Content and Description Below
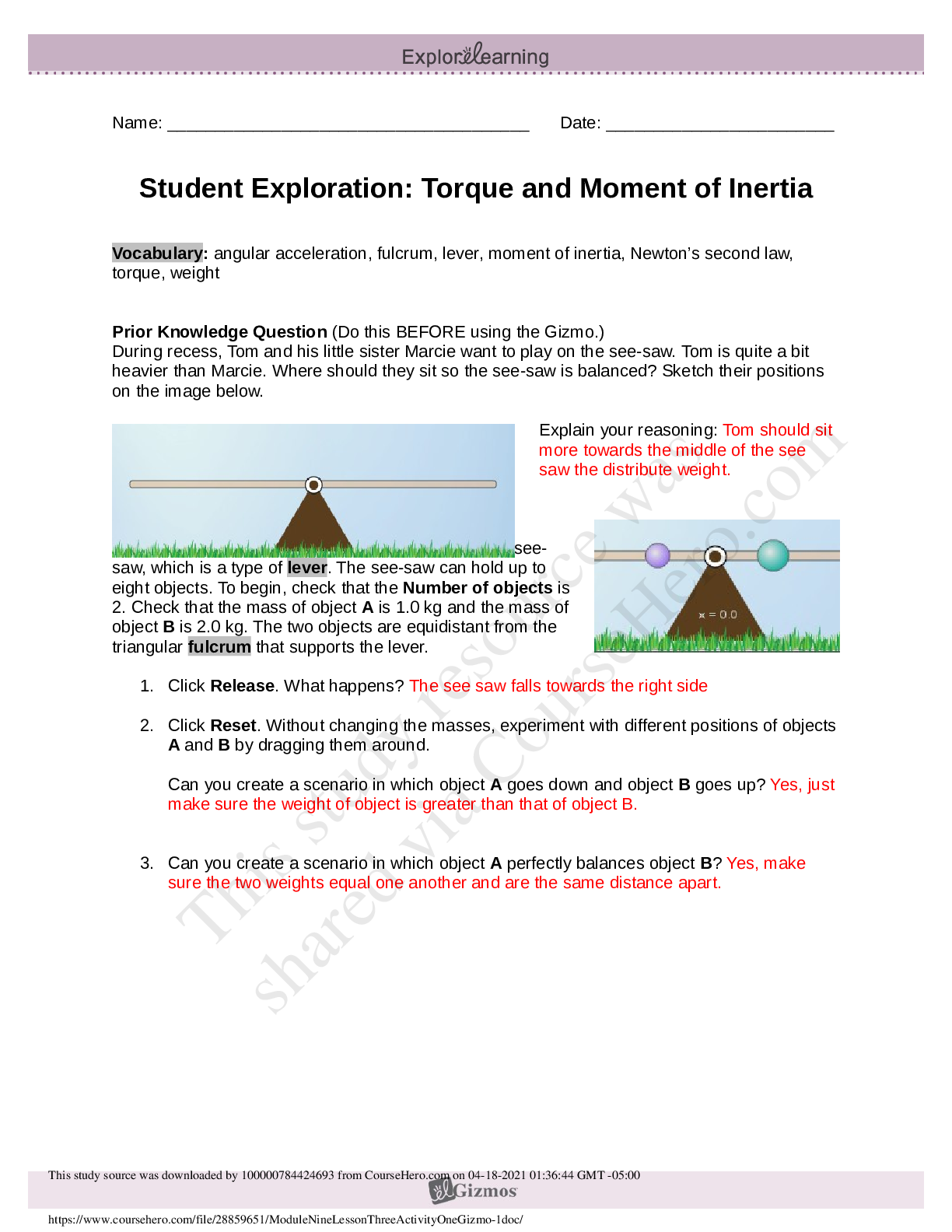
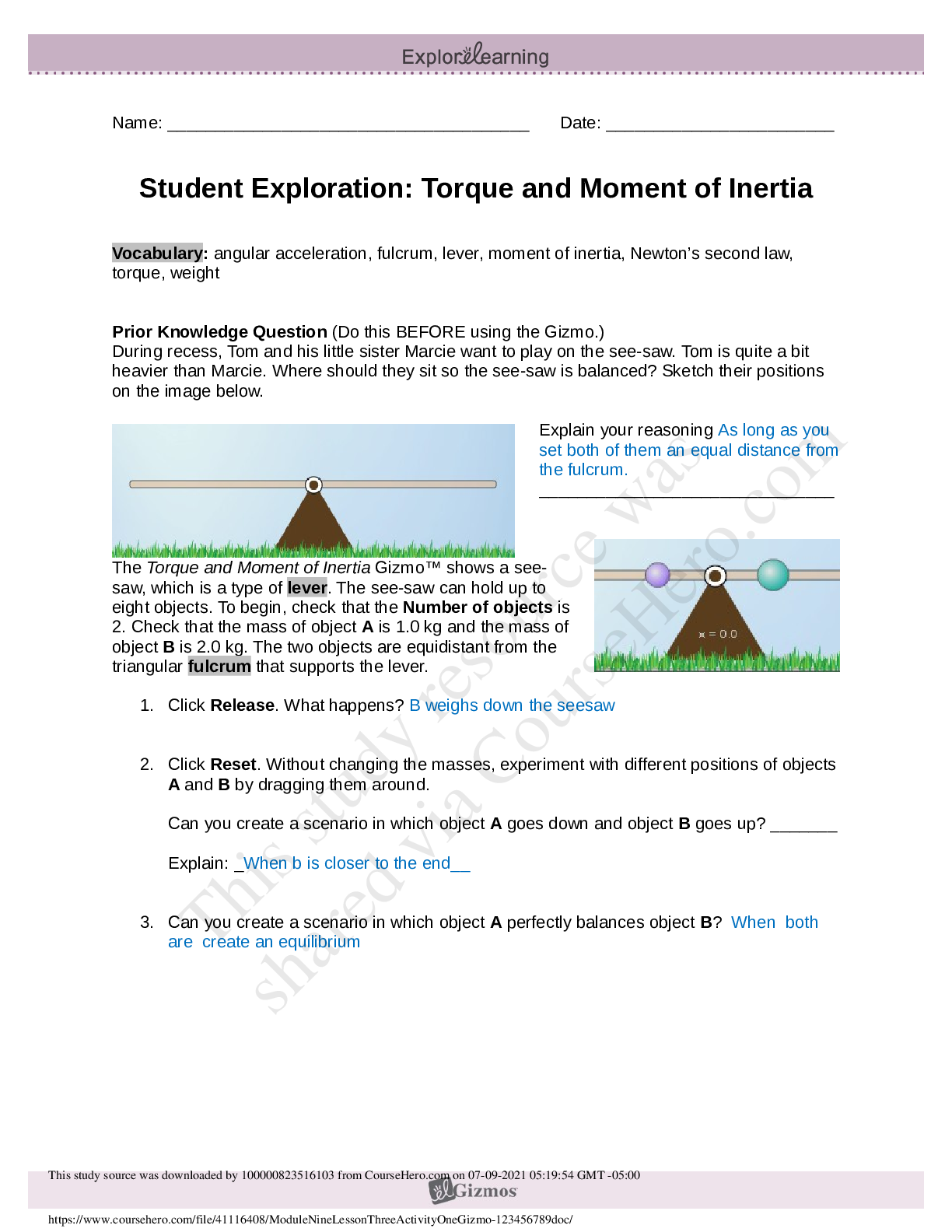
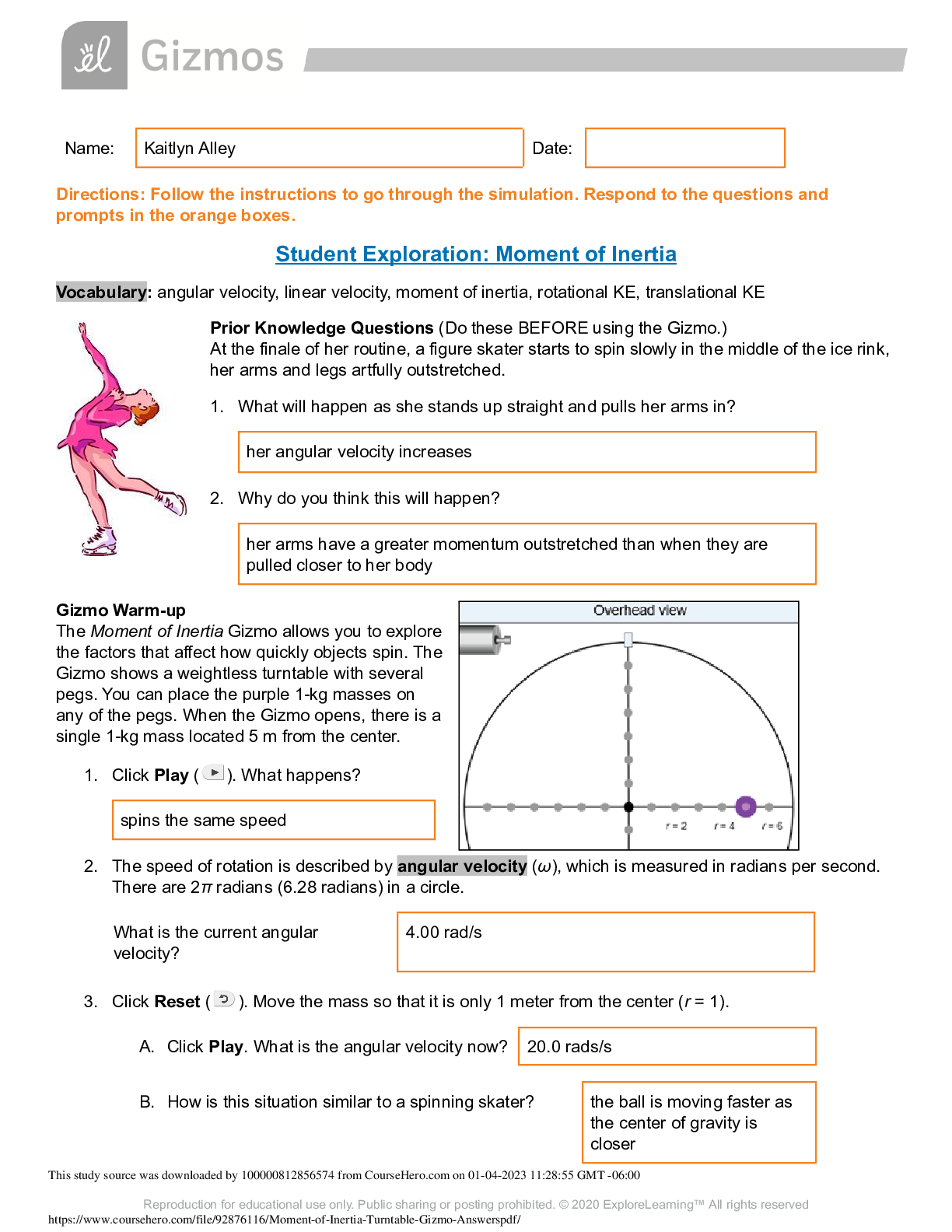
Student Exploration: Torque and Moment of Inertia Vocabulary: angular acceleration, fulcrum, lever, moment of inertia, Newton’s second law, torque, weight Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE... using the Gizmo.) During recess, Tom and his little sister Marcie want to play on the see-saw. Tom is quite a bit heavier than Marcie. Where should they sit so the see-saw is balanced? Sketch their positions on the image below. Explain your reasoning: Tom should sit closer to the fulcrum and Marcie should sit farther from the fulcrum. This way they are balanced on the seesaw. Gizmo Warm-up The Torque and Moment of Inertia Gizmo shows a see-saw, which is a type of lever. The see-saw can hold up to eight objects. To begin, check that the Number of objects is 2. Check that the mass of object A is 1.0 kg and the mass of object B is 2.0 kg. The two objects are equidistant from the triangular fulcrum that supports the lever. 1. Click Release. What happens? There is rotation in the clockwise direction where object B is. Since object B has more mass there is more force and torque in this direction. 2. Click Reset. Without changing the masses, experiment with different positions of objects A and B by dragging them around. Can you create a scenario in which object A goes down and object B goes up? __Yes__ Explain: If you increase the radius of object A to -2.0m and keep the radius of object 2 at 0.5m, then the torque on object A will be larger and it will go down. 3. Can you create a scenario in which object A perfectly balances object B? ___Yes____ Explain: If you increase the radius of object A to -1.0m and keep the radius of object 2 at 0.5m, there will be equal magnitude of torque in both directions. Activity A: Principle of the lever Get the Gizmo ready: Click Reset. Turn on Show ruler. Check that object A is 1.0 kg and B is 2.0 kg. Question: How can you use a light object to balance a heavy object? 1. Explore: Experiment with the Gizmo to see how you can balance a heavy object with a light object. What do you notice about the distances of each object from the fulcrum? The distance of object B increases as the mass of object A increases. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 28, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 28, 2021
Downloads
1
Views
455