NURSING 2362 - Module 1 Exam (Questions and Answers)
Document Content and Description Below
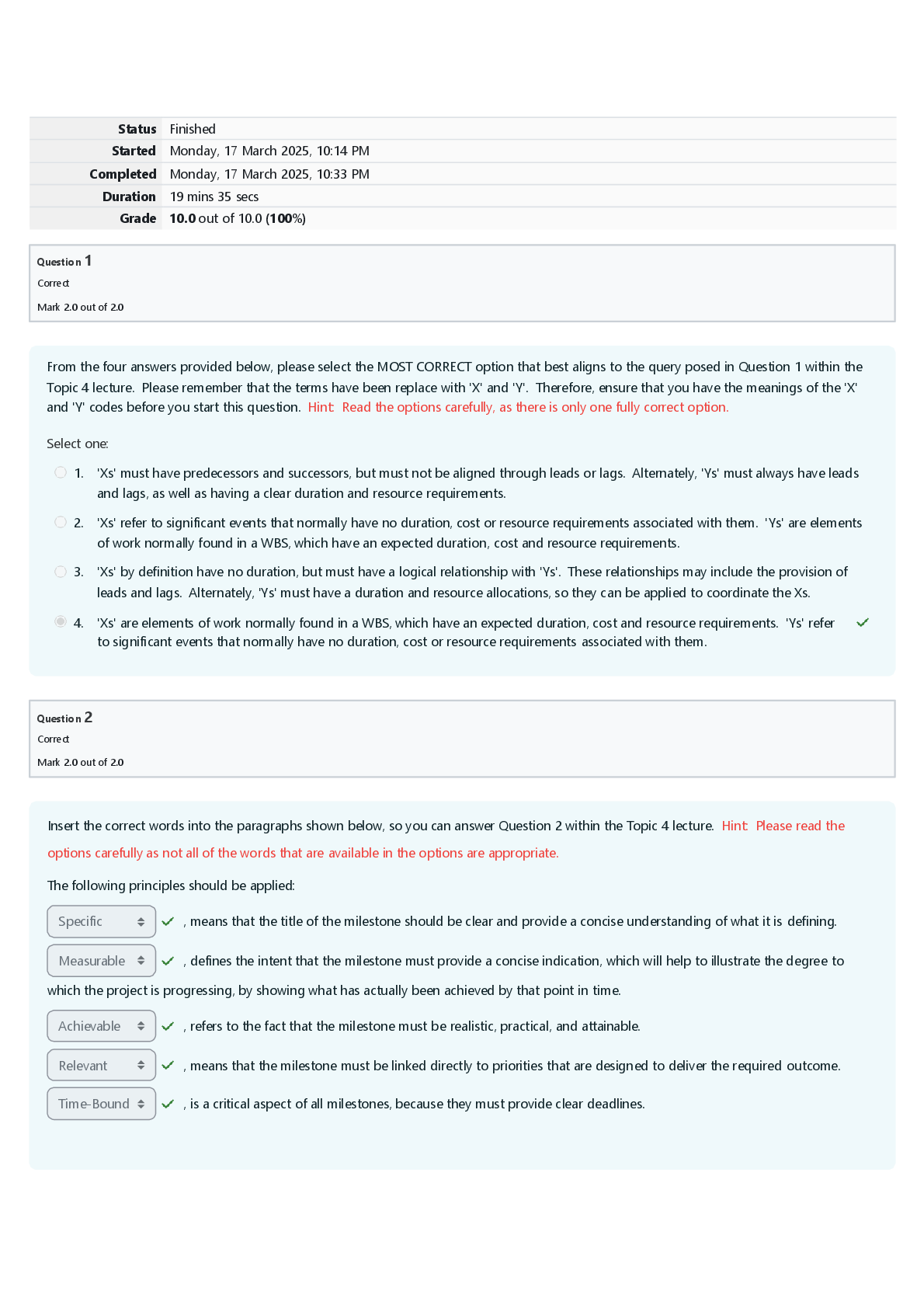
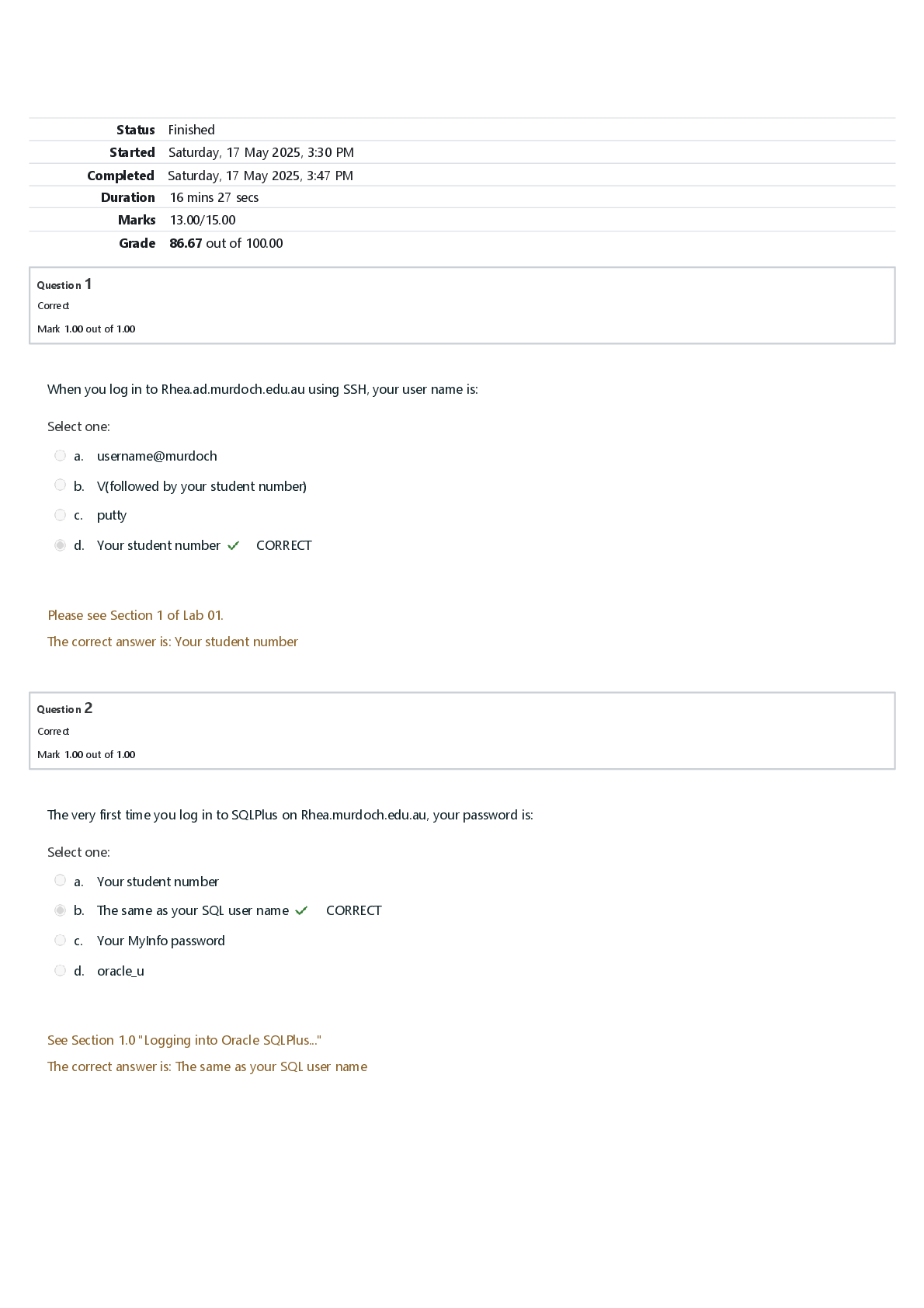
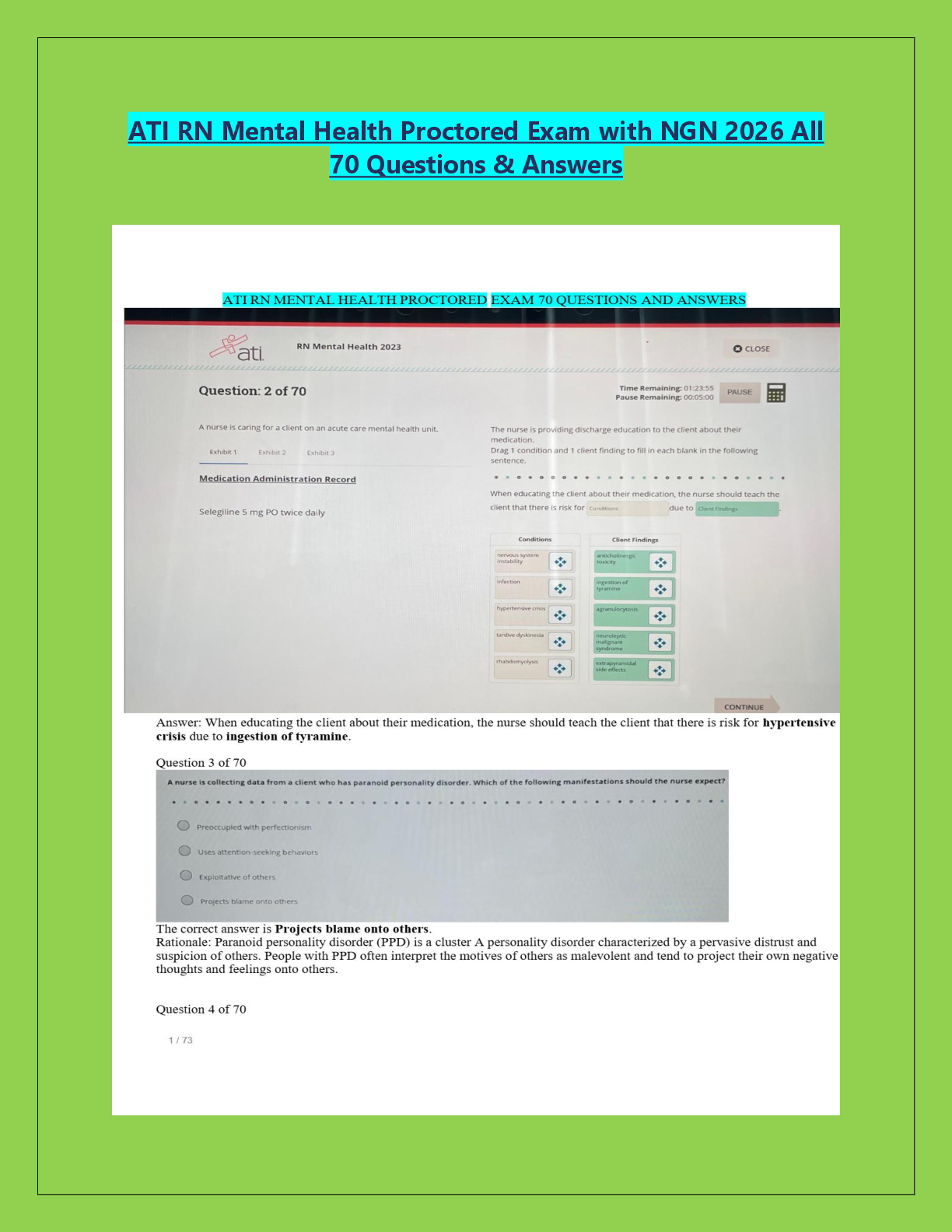
Module 1 Exam (Questions and Answers) Module 1 Questions 1. ID: 8482548610A nurse is providing information to a group of pregnant clients and their partners about the psychosocial development of an i ... nfant. Using Erikson's theory of psychosocial development, what should the nurse tell the group about the infants? Rely on the fact that their needs will be met Correct Need to tolerate a great deal of frustration and discomfort to develop a healthy personality Must have needs ignored for short periods to develop a healthy personality Need to experience frustration, so it is best to allow an infant to cry for a while before meeting his or her needs Rationale: According to Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development, infants struggle to establish a sense of basic trust rather than a sense of basic mistrust in their world, their caregivers, and themselves. If provided with consistent satisfying experiences that are delivered in a timely manner, infants come to rely on the fact that their needs are met and that, in turn, they will be able to tolerate some degree of frustration and discomfort until those needs are met. This sense of confidence is an early form of trust and provides the foundation for a healthy personality. Therefore the other options are incorrect. Test-Taking Strategy: Eliminate the option that contains the closed-ended word "must." Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and indicate that experiencing frustration is necessary. Review: Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development as it relates to the infant. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal- child nursing (4th ed., pp. 74-75). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Reproduction HESI Concepts: Developmental, Sexuality/Reproduction Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 2. ID: 8482544657A nurse is weighing a breastfed 6-month-old infant who has been brought to the pediatrician's office for a scheduled visit. The infant's weight at birth was 6 lb 8 oz. The nurse notes that the infant now weighs 13 lb. Which action should the nurse take? Tell the mother that the infant's weight is increasing as expected Correct Tell the mother to decrease the daily number of feedings because the weight gain is excessive Tell the mother that semisolid foods should not be introduced until the infant's weight stabilizes Tell the mother that the infant should be switched from breast milk to formula because the weight gain is inadequate Rationale: Infants usually double their birth weight by 6 months and triple it by 1 year of age. If the infant is 6 lb 8 oz, at birth, a weight of 13 lb at 6 months of age is to be expected. Semisolid foods are usually introduced between 4 and 6 months of age. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject in the question, the current weight of the infant. Recalling that infants double their weight by 6 months of age will direct you to the correct option. Review: the growth rate of an infant. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 488-489). St. Louis: Elsevier. Potter, P., Perry, A. G., Stockert, P. A., & Hall, A. M. (2013). Fundamentals of nursing. (8th ed., p. 143). St. Louis: Mosby. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Nutrition HESI Concepts: Developmental, Nutrition Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 3. ID: 8482548652A nurse performing a physical assessment of a 12-month-old infant notes that the infant's head circumference is the same as the chest circumference. Based on this finding, what should the nurse do? Suspect the presence of hydrocephalus Suggest to the pediatrician that a skull x-ray be performed Tell the mother that the infant is growing faster than expected Document these measurements in the infant's health-care record Correct Rationale: The head circumference growth rate during the first year is approximately 0.4 inch (1 cm) per month. By 10 to 12 months of age, the infant’s head and chest circumferences are equal. Therefore, suspecting the presence of hydrocephalus, telling the mother that the infant is growing faster than expected, and suggesting that a skull x-ray be performed are incorrect. Test-Taking Strategy: Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and indicate that the infant has a physiological problem. Review: the expected growth rate of an infant. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 69, 489-490). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Development HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Developmental Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 4. ID: 8482544621A new mother asks the nurse, "I was told that my infant received my antibodies during pregnancy. Does that mean that my infant is protected against infections?" Which statement should the nurse make in response to the mother? "Yes, your infant is protected from all infections." "If you breastfeed, your infant is protected from infection." "The transfer of your antibodies protects your infant until the infant is 12 months old." "The immune system of an infant is immature, and the infant is at risk for infection." Correct Rationale: Transplacental transfer of maternal antibodies supplements the infant’s weak response to infection until approximately 3 to 4 months of age. Although the infant begins to produce immunoglobulin (Ig) soon after birth, by 1 year of age the infant has only approximately 60% of the adult IgG level, 75% of the adult IgM level, and 20% of the adult IgA level. Breast milk transmits additional IgA protection. The activity of T-lymphocytes also increases after birth. Even though the immune system matures during infancy, maximal protection against infection is not achieved until early childhood. This immaturity places the infant at risk for infection. Test-Taking Strategy: Eliminate the option containing the closed-ended word "all." Recalling that breastfeeding alone does not protect the infant from infection will assist you in eliminating the option that suggests breastfeeding protects the infant. From the remaining options, use the strategy of selecting the umbrella option to answer correctly. Review: the physiological concepts related to the maturity of body systems in an infant. References: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 477-478). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Immunity HESI Concepts: Developmental, Immunity Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 5. ID: 8482544611A nurse is assessing the language development of a 9-month- old infant. Which developmental milestone does the nurse expect to note in an infant of this age? The infant babbles. The infant says "Mama." Correct The infant smiles and coos. The infant babbles single consonants. Rationale: An 8- to 9-month-old infant can string vowels and consonants together. The first words, such as "Mama," "Daddy," "bye-bye," and "baby," begin to have meaning. A 1- to 3-month-old infant produces cooing sounds. Babbling is common in a 3- to 4-month-old. Single-consonant babbling occurs between 6 and 8 months of age. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, the age of the infant. Recalling the language development that occurs during infancy will direct you to the correct option. Remember that an 8- to 9-month-old infant can string vowels and consonants together. Review: the developmental milestones related to language development in an infant. Reference:McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 94, 112). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Understanding Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Commuication, Development HESI Concepts: Communication, Developmental Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 6. ID: 8482544667The mother of a 9-month-old infant calls the nurse at the pediatrician's office, tells the nurse that her infant is teething, and asks what can be done to relieve the infant's discomfort. What should the nurse instruct the mother to do? Schedule an appointment with a dentist for a dental evaluation Rub the infant's gums with baby aspirin that has been dissolved in water Obtain an over-the-counter (OTC) topical medication for gum-pain relief Give the infant cool liquids or a Popsicle and hard foods such as dry toast Correct Rationale: Although sometimes asymptomatic, teething is often signaled by behavior such as nighttime awakening, daytime restlessness, an increase in nonnutritive sucking, excess drooling, and temporary loss of appetite. Some degree of discomfort is normal. It is unnecessary to obtain a dental evaluation, but a health-care professional should further investigate any incidence of increased temperature, irritability, ear-tugging, or diarrhea. The nurse may suggest that the mother provide cool liquids and hard foods such as dry toast, Popsicles, or a frozen bagel for chewing to relieve discomfort. Hard, cold teethers and ice wrapped in cloth may also provide comfort for inflamed gums. OTC medications for gum relief should only be used as directed by the healthcare provider. Home remedies such as rubbing the gums with aspirin should be discouraged, but acetaminophen (Tylenol), administered as directed for the child’s age, can relieve discomfort. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, teething and relieving the infant’s discomfort. First recall that it is unnecessary to consult with a dentist. Next, eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and involve administering medication to the infant. Review: the measures that will relieve the discomfort of teething. Reference:McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 105). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Comfort, Development HESI Concepts: Comfort—Pain, Developmental Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 7. ID: 8482544675A nurse is teaching the mother of an 11-month-old infant how to clean the infant's teeth. What should the nurse tell the mother to do? Use water and a cotton swab and rub the teeth Correct Use diluted fluoride and rub the teeth with a soft washcloth Use a small amount of toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush Dip the infant's pacifier in maple syrup so that the infant will suck Rationale: Because the primary teeth are used for chewing until the permanent teeth erupt and because decay of the primary teeth often results in decay of the permanent teeth, dental care must be started in infancy. The mother can use cotton swabs or a soft washcloth to clean the teeth. Appropriate amounts of fluoride are necessary for the development of healthy teeth, but infants usually receive fluoride when formula and cereal are mixed with fluoridated water or through fluoride supplementation. Toothpaste is not recommended because infants tend to swallow it, possibly ingesting excessive amounts of fluoride. Dipping the infant’s pacifier in maple syrup is unacceptable because of the risk of tooth decay. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, cleaning the teeth. Recalling the risk associated with tooth decay will help eliminate the option that identifies the use of maple syrup. To select from the remaining options, noting that the client in the question is an infant will direct you to the correct option. Review: the procedure for cleaning teeth in an infant. Reference:McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 105). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Development HESI Concepts: Developmental, Teaching and Learning/Client Education Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 8. ID: 8482544663A nurse provides information about feeding to the mother of a 6-month-old infant. Which statement by the mother indicates an understanding of the information? "I can mix the food in the my infant's bottle if he won't eat it." "Fluoride supplementation is not necessary until permanent teeth come in." "Egg white should not be given to my infant because of the risk for an allergy." Correct "Meats are really important for iron, and I should start feeding meats to my infant right away." Rationale: Egg white, even in small quantities, is not given to the infant until the end of the first year of life because it is a common food allergen. Fluoride supplementation may be needed beginning at of 6 months, depending on the infant’s intake of fluoridated tap water. Foods are never mixed with formula in the bottle. It may be difficult for the infant to consume the formula, and it will also be difficult to determine the infant’s intake of the formula. Solid foods may be introduced into the diet when the infant is 5 to 6 months old. Rice cereal may be introduced first because of its low allergenic potential; or, depending on the pediatrician’s preference, fruits and vegetables may be introduced first. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the words “indicates an understanding of the information.” Read each option carefully and think about the principles associated with feeding and nutrition. Recalling that allergy is a concern will direct you to the correct option. Review: the principles related to nutrition an infant. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 102). St. Louis: Elsevier. Hockenberry, M., & Wilson, D. (2013). Wong’s Essentials of pediatric nursing (9th ed., p. 329). St. Louis: Mosby. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluation Content Area: Nutrition Giddens Concepts: Development, Nutrition HESI Concepts: Developmental, Nutrition Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 9. ID: 8482548624A nurse provides instructions to a mother of a newborn infant who weighs 7 lb 2 oz about car safety. What should the nurse tell the mother? To secure the infant in the middle of the back seat in a rear-facing infant safety seat Correct To place the infant in a booster seat in the front seat of the car with the shoulder and lap belts secured around the infant That it is acceptable to place the infant in the front seat in a rear-facing infant safety seat as long as the car has passenger-side air bags That because of the infant's weight it is acceptable to hold the infant as long as the mother and infant are sitting in the middle of the back seat of the car Rationale: Infants should not be restrained in the front seats of cars. If a passenger-side air bag is deployed, the air bag may severely jolt an infant safety seat, harming the infant. Infants weighing less than 20 lb and those younger than 1 year should always be in the middle of the back seat in a rear-facing car safety seat. An infant must be placed in an infant safety seat and is never to be held by another person when riding in a car. Test-Taking Strategy: Eliminate the options that are comparable or alike and recommend placing the infant in the front seat. To select from the remaining options, keep safety in mind and remember that the infant should never be held and should be placed in an infant safety seat. Review: car safety principles for an infant. References: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 107-108). St. Louis: Elsevier. American Academy of Pediatrics for information on car safety www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Car-Safety-Seats- Information-for-Families.aspx. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Safety Giddens Concepts: Development, Safety HESI Concepts: Developmental, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 10. ID: 8482548616A nurse provides instructions to a mother about crib safety for her infant. Which statement by the mother indicates a need for further instructions? "I need to keep large toys out of the crib." "The drop side needs to be impossible for my infant to release." "Wood surfaces on the crib need to be free of splinters and cracks." "The distance between the slats needs to be no more than 4 inches wide to prevent entrapment of my infant's head or body." Correct Rationale: The distance between slats must be no more than 2 ⅜ inches to prevent entrapment of the infant’s head and body. The mesh in a mesh-sided crib should have openings smaller than ¼ inch. The drop side must be impossible for the infant to release, and wood surfaces should be free of splinters, cracks, and lead-based paint. The mother should avoid placing large toys in the crib, because an older infant may use them as steps to climb over the side, possibly resulting in serious injury. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic words "need for further instructions" in the query of the question. These words indicate a negative event query and the need to select the incorrect statement by the mother. Visualizing each of these options and keeping safety in mind will direct you to the correct option. Review: crib safety instructions. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 109). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Safety Giddens Concepts: Development, Safety points. HESI Concepts: Developmental, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible 11. ID: 8482548648The mother of a 2-year-old tells the nurse that she is very concerned about her child because he has developed "a will of his own" and "acts as if he can control others." The nurse provides information to the mother to alleviate her concern, recalling that, according to Erikson, a toddler is confronting which developmental task? Initiative versus guilt Trust versus mistrust Industry versus inferiority Autonomy versus doubt and shame Correct Rationale: According to Erikson, the toddler is struggling with the developmental task of acquiring a sense of autonomy while overcoming a sense of shame and doubt. Toddlers discover that they have wills of their own and that they can control others. Asserting their wills and insisting on their own way, however, often lead to conflict with those they love, whereas submissive behavior is rewarded with affection and approval. Toddlers experience conflict because they want to assert their own wills but do not want to risk losing the approval of loved ones. Trust versus mistrust is the developmental task of the infant. Initiative versus guilt is the developmental task of the preschool-age child. Industry versus inferiority is the developmental task of the school-age child. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject in the question, the behavior of a 2- year-old toddler. Note the relationship between the words "a will of his own" and the word "autonomy" in the correct option. Review: Erikson’s developmental stages. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 74). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Development HESI Concepts: Developmental, Teaching and Learning/Client Education Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 12. ID: 8482548618A nurse is planning care for a hospitalized toddler. To best maintain the toddler's sense of control and security and ease feelings of helplessness and fear, which action should the nurse take? Spend as much time as possible with the toddler Keep hospital routines as similar as possible to those at home Correct Allow the toddler to play with other children in the nursing unit playroom Allow the toddler to select toys from the nursing unit playroom that can be brought into the toddler's hospital room Rationale: The nurse can decrease the stress of hospitalization for the toddler by incorporating the toddler’s usual rituals and routines from home into nursing care activities. Keeping hospital routines as similar to those of home as possible and recognizing ritualistic needs gives the toddler some sense of control and security and eases feelings of helplessness and fear. Spending as much time as possible with the toddler and allowing the toddler to play with other children and select the toys he would like to play with may be appropriate interventions, but keeping the hospital routine as similar as possible to the routine at home will best maintain the toddler’s sense of control and security and ease feelings of helplessness and fear. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic word "best" in the question and focus on the subject, how to best maintain the toddler’s sense of control and security and ease feelings of helplessness and fear. This will assist you in selecting the correct option. Review: the psychosocial needs of the toddler with regard to hospitalization. Reference:McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 883). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Comfort, Development HESI Concepts: Comfort, Developmental Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 13. ID: 8482544677A nurse in a daycare setting is planning play activities for 2- and 3-year-old children. Which toy is most appropriate for these activities? Blocks and push-pull toys Correct Finger paints and card games Simple board games and puzzles Videos and cutting-and-pasting toys Rationale: Toys for the toddler should meet the child’s needs for activity and inquisitiveness. The toddler enjoys objects of different textures such as clay, sand, finger paints, and bubbles; push-pull toys; large balls; sand and water play; blocks; painting; coloring with large crayons; large puzzles; and trucks or dolls. Card games, simple board games, videos, and cutting-and-pasting toys are more appropriate play activities for the preschooler. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic words “most appropriate.” Remember that all parts of an option need to be correct for the option to be correct. Focusing on the age of the child will direct you to the correct option. Review: age-appropriate toys for the toddler. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 123, 126, 137). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Safety HESI Concepts: Developmental, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 14. ID: 8482548634A mother of twin toddlers tells the nurse that she is concerned because she found her children involved in sex play and didn't know what to do. What should the nurse tell the mother? To separate her children during playtime That if the behavior continues, she will need to bring her children to a child psychologist That if she notes the behavior again she should casually tell her children to dress and to direct them to another activity Correct To tell her children that what they are doing is bad and that they will be punished if they are caught doing it again Rationale: Sex play and masturbation are common among toddlers. Parents should respect the toddler’s curiosity as normal without judging the toddler as bad. Parents who discover children involved in sex play may casually tell them to dress and direct them to another play activity, thereby limiting sex play without producing feelings of shame or anxiety. Bringing the children to a child psychologist, separating them at play, and punishing them are all inappropriate. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, toddlers. Recalling that sex play and masturbation are common among toddlers will direct you to the correct option. Review: psychosexual development in the toddler. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 127). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Sexuality HESI Concepts: Developmental, Sexuality/Reproduction Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 15. ID: 8482548638A nurse is assessing the motor development of a 24-month-old child. Which activities would the nurse expect the mother to report that the child can perform? Select all that apply. Put on and tie his shoes Align two or more blocks Correct Dress himself appropriately Go to the bathroom without help Turn the pages of a book one at a time Correct Rationale: By 24 months of age, the toddler can put on simple items of clothing but cannot differentiate front and back. Some other activities that children at this age can perform include zipping large zippers, putting on shoes, washing and drying their hands, aligning two or more blocks, and turning the pages of a book one at a time. The fine motor skill needed to tie shoes is not yet developed. By the age of 4 to 5 years, the child is more independent and can dress, eat, and go to the bathroom without help. Test-Taking Strategy: Focusing on the subject, the age of the child, and thinking about developmental stages will help direct you to the correct options. Review:: motor development in the 24-month-old. References: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal- child nursing (4th ed., pp. 122-123, 126). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Understanding Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Development HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Developmental Awarded 2.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 16. ID: 8482548604A nurse is assessing language development in a toddler from a bilingual family. What should the nurse expect about the child’s language development? Is slower than expected Correct Is developing as expected Is more advanced than expected Will require assistance from a speech therapist Rationale: Although the age at which children begin to talk varies widely, most can communicate verbally by the second birthday. The rate of language development depends on physical maturity and the amount of reinforcement the child has received. Children of bilingual families, twins, and children other than firstborns may have slower language development. A child from a bilingual family does not require assistance from a speech therapist to ensure language development. Test-Taking Strategy: Note that there are no data in the question to indicate that the child needs assistance from a speech therapist. When selecting from the remaining options, noting the word "bilingual" in the question and recalling the factors that affect language development will direct you to the correct option. Review: the factors that affect language development. Reference: Hockenberry, M., & Wilson, D. (2013). Wong’s Essentials of pediatric nursing (9th ed., p. 49). St. Louis: Mosby. McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal- child nursing (4th ed., pp. 71-72, 124). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Understanding Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Cultural Awareness Giddens Concepts: Communication, Development HESI Concepts: Communication, Developmental Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 17. ID: 8482548661A mother asks the nurse when her child should have his first dentist visit. What should the nurse tell the mother? At age 3 Just before beginning kindergarten Twelve months after the first primary tooth erupts Soon after the first primary tooth erupts, usually around 1 year of age Correct Rationale: The child should see the dentist soon after the first primary tooth erupts at around 1 year of age. Therefore the remaining options are incorrect. Parents should be aware of the dental guidelines for children and should not delay necessary dental care. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, the age of the first dental visit, and recall the importance of dental care. Answer correctly by selecting the option that provides dental care at the earliest age. Review: dental care guidelines. Reference:McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 129-130). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Development HESI Concepts: Developmental, Teaching and Learning/Client Education Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 18. ID: 8482544661The mother of a toddler asks the nurse when she will know that her child is ready to start toilet training. The nurse should tell the mother that which observation is a sign of physical readiness? The child has been walking for 2 years. The child can eat using a fork and knife. The child no longer has temper tantrums. The child can remove his or her own clothing. Correct Rationale: Signs of physical readiness for toilet training include the following: The child can remove her own clothing; is willing to let go of a toy when asked; is able to sit, squat, and walk well; and has been walking for 1 year. Using a fork and knife, walking for 2 years, and an absence of temper tantrums are not signs of physical readiness. Test-Taking Strategy: Noting the words "physical readiness" in the question will assist you in eliminating the option that addresses temper tantrums. To select from the remaining options, visualize each to help direct you to the correct option. Review: the signs of physical readiness for toilet training. Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 137). St. Louis: Elsevier. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Development, Elimination HESI Concepts: Developmental, Elimination Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 19. ID: 8482548640The mother of a 9 year old child who is 5 feet 1 inch in height asks a nurse about car safety seats. What should the nurse tell the mother to use? Front booster seat Rear convertible seat Forward-facing car seat Rear seat using lap and shoulder seat belts Correct Rationale: All infants and toddlers should ride in a Rear-Facing Car Seat until they are at least 2 years of age or until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by their car seat's manufacturer. Any child who has outgrown the rear-facing weight or height limit for their convertible car seat should use a Forward-Facing Car Seat with a harness for as long as possible, up to the highest weight or height allowed by their car seat manufacturer. All children whose weight or height is above the forward-facing limit for their car seat should use a Belt- Positioning Booster Seat until the vehicle seat belt fits properly, typically when they have reached 4 feet 9 inches in height and are between 8 and 12 years of age. When children are old enough and large enough for the vehicle seat belt to fit them correctly, they should always use Lap and Shoulder Seat Belts for optimal protection. All children younger than 13 years should be restrained in the rear seats of vehicles for optimal protection. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the subject, a 9 year old child who is 4 feet 11 inches in height. . Keeping the subject of safety in mind and visualizing each of the options will direct you to the correct option. Review: car safety measures. Reference: Potter, P., Perry, A. G., Stockert, P. A., & Hall, A. M. (2013). Fundamentals of nursing. (8th ed., pp. 366-367). St. Louis: Mosby. American Academy of Pediatrics for information on car safety www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Car-Safety-Seats- Information-for-Families.aspx . Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Safety Giddens Concepts: Development, Safety HESI Concepts: Developmental, Safety Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 20. ID: 8482546322The mother of a 5-year-old asks the nurse how often her child should undergo a dental examination. When should the nurse tell the mother the child should have dental examinations? Once a year Every 3 months Every 6 months Correct Whenever a new primary tooth erupts Rationale: Dental examinations for a 4- to 5-year-old child should be conducted every 6 months. Every 3 months, once a year, and whenever a new primary tooth erupts are all incorrect. Test-Taking Strategy: Knowledge regarding the schedule for dental examinations for a 5-year-old child is needed to answer this question. Recalling the general principles related to dental care and thinking about dental health care of an adult will help direct you to the correct option. Review: dental-care principles for a child. Reference: Hockenberry, M., & Wilson, D. (2013). Wong’s Essentials of pediatric nursing (9th ed., p. 394). St. Louis: Mosby. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Developmental Stages Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Development HESI Concepts: Developmental, Teaching and Learning/Client Education .............................................Continued............................................. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 59 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

NURSING 2362 - Module 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,&10 Exams (Questions & Answers)
Module 1 Exam|Module 3 Exam|Module 4 Exam|Module 5 Exam|Module 6 Exam|Module 7 Exam|Module 8 Exam|Module 9 Exam|Module 10 Exam
By Ajay25 4 years ago
$75
9
Reviews( 0 )
$18.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 28, 2021
Number of pages
59
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 28, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
138