Module 4 Final Quiz: Economic Strategy and Negotiation
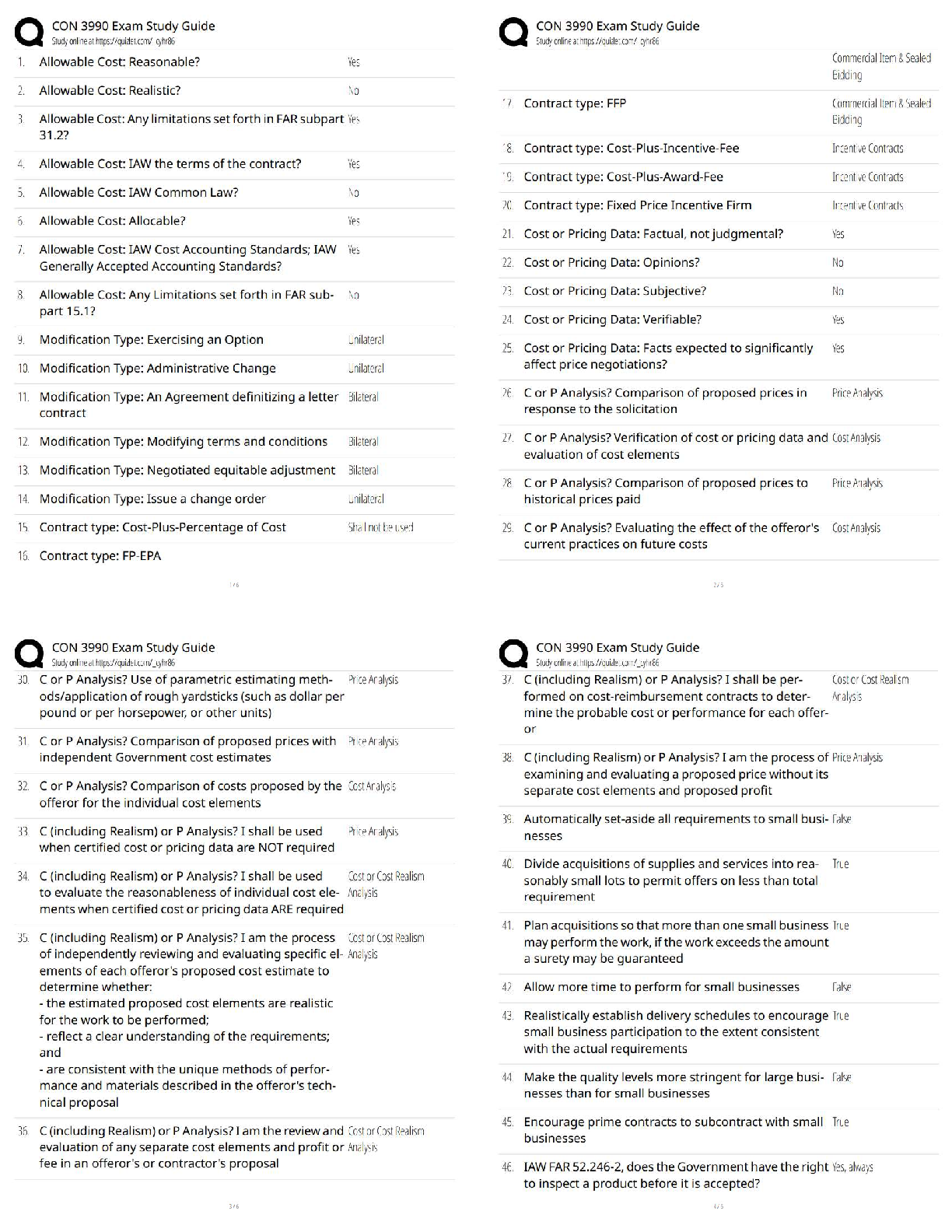
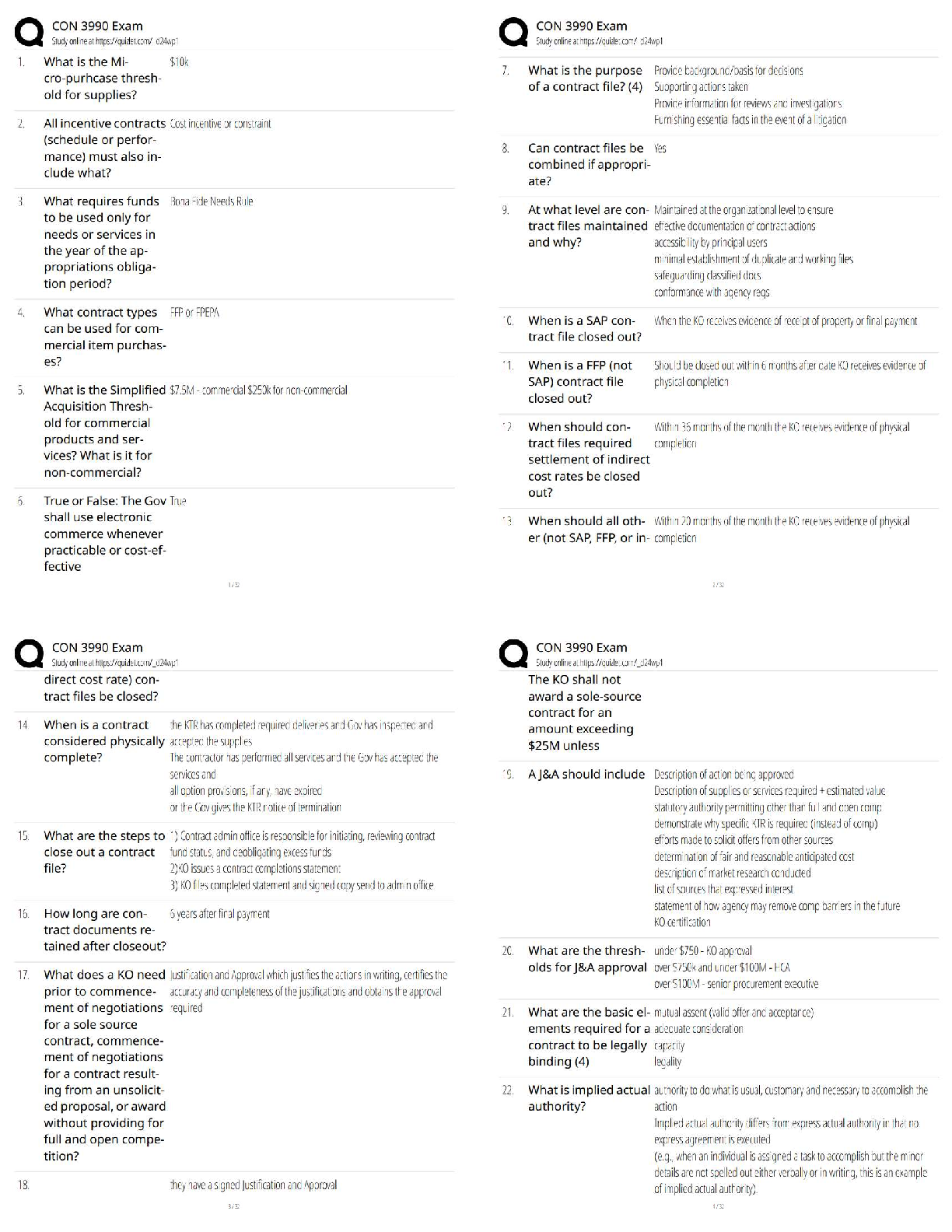
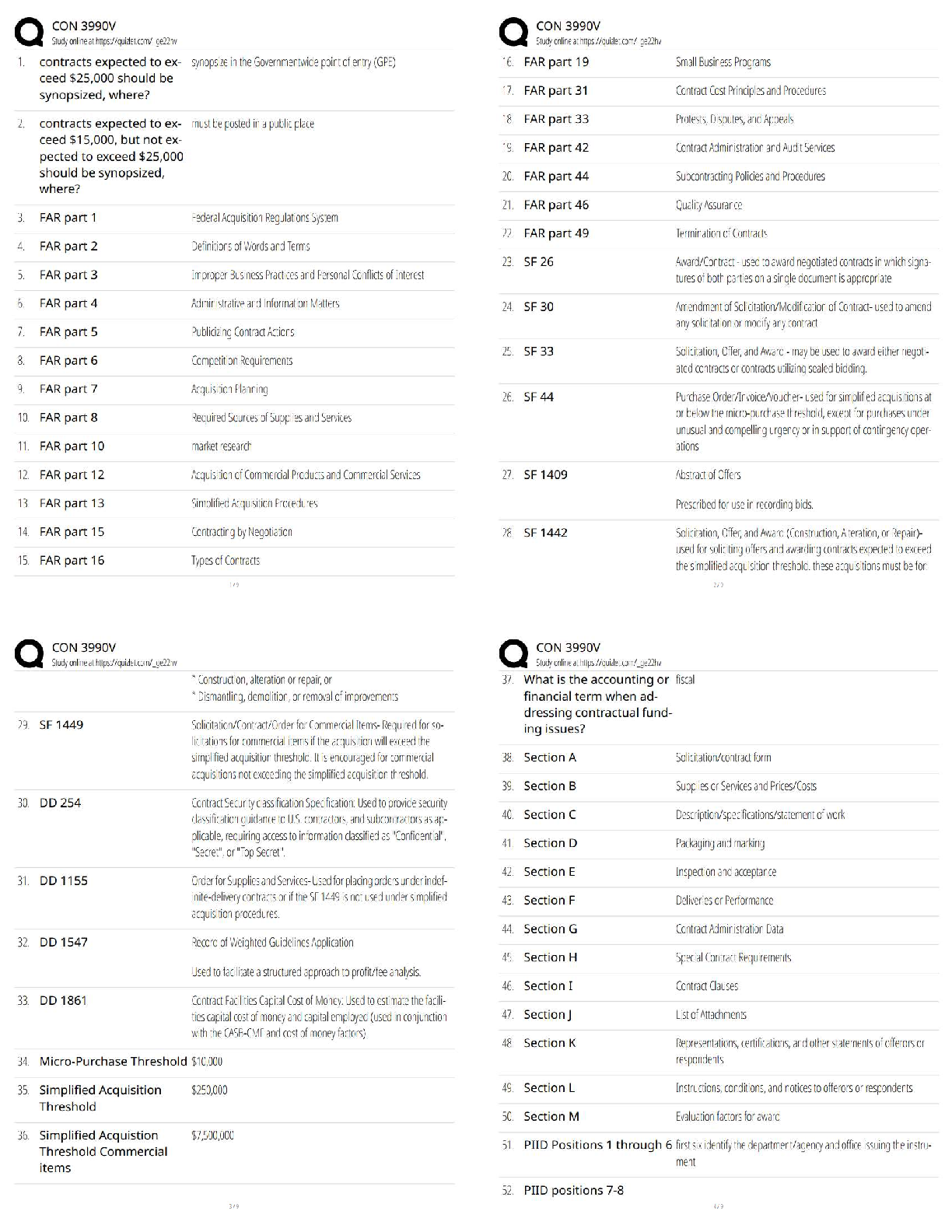
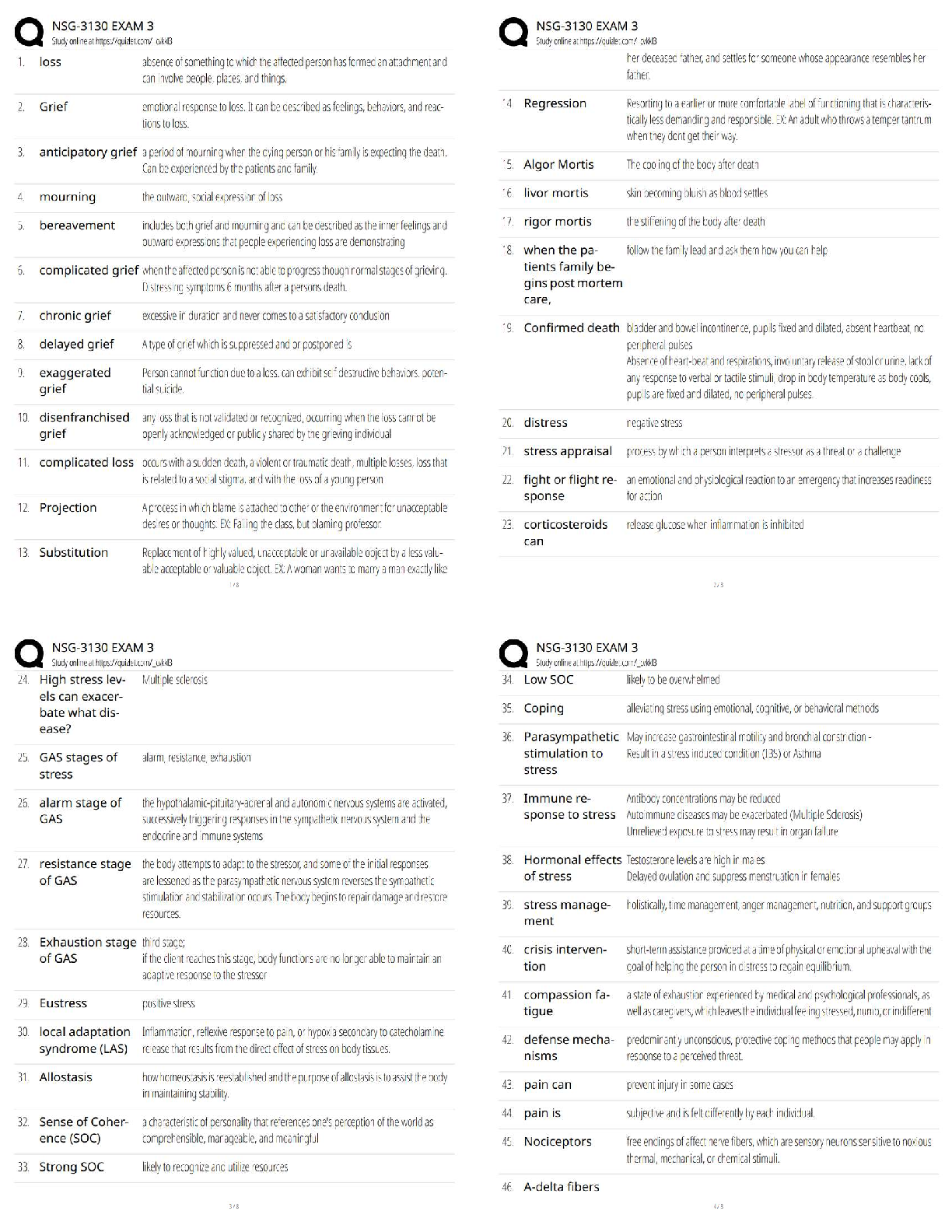
Module 4 Final Quiz
Due No due date Points 20 Questions 20 Time Limit 60 Minutes
Attempt History
Attempt Time Score
LATEST Attempt 1 17 minutes 20 out of 20
...
Module 4 Final Quiz: Economic Strategy and Negotiation
Module 4 Final Quiz
Due No due date Points 20 Questions 20 Time Limit 60 Minutes
Attempt History
Attempt Time Score
LATEST Attempt 1 17 minutes 20 out of 20
Correct answers are hidden.
Score for this quiz: 20 out of 20
Submitted May 2 at 16:23
This attempt took 17 minutes.
Question 1 1 / 1 pts
Doc and Brewster are in a negotiation over royalties. The negotiations proceed as follows. Doc
can make an offer that is either high (H), medium (M) or low (L). Having received the offer,
Brewster can either accept (A) or reject (R) any offer received. The payoffs are as follows. If an
offer of H is accepted, the payoffs are (30, 8) to Doc and Brewster, respectively. If an offer of H
is rejected, the payoffs are (18, 16). If an offer of M is made and accepted, the payoffs are (20,
8). If an M offer is rejected the payoffs are (5, 5). If a low offer is made and accepted the
payoffs are (30, 5) and if an of L is rejected the payoffs are (10, 15). In the subgame perfect
equilibrium outcome Brewster receives a payoff of .
8
Question 2 1 / 1 pts
Chrissie owns a vintage guitar that she values at $0. Mark would like to buy the guitar and
values it at $1000. The negotiations are as follows. Chrissie suggests a price to Mark. If Mark
agrees trade takes place at the agreed price. If Mark rejects the offer, Mark buys an identical
guitar from Angus for a price of $400 and Chrissie receives a payoff of $0. What is the
outcome of the negotiations?
Chrissie offers a price of $1000 and Mark accepts
Chrissie offers a price of $400 and Mark accepts
02/05/2020 Module 4 Final Quiz: Economic Strategy and Negotiation
https://canvas.sydney.edu.au/courses/23912/quizzes/94190 2/9
Chrissie offers a price of $0 and Mark accepts
Chrissie offers a price of $600 and Mark accepts.
Chrissie offers a price of $500 and Mark rejects.
Question 3 1 / 1 pts
Chrissie owns a vintage guitar that she values at $0. Mark would like to buy the guitar and
values it at $1000. The negotiations are as follows. Chrissie suggests a price to Mark. If Mark
agrees trade takes place at the agreed price. If Mark rejects the offer, negotiations end and
each party receives a payoff of $0. What is the outcome of the negotiations?
Trade takes place at a price of $1000.
Chrissie offers a price close to $1000 and Mark rejects the offer
Mark rejects any offer Chrissie makes.
Trade takes place at a price of $500
Trade takes place at a price of $0
Question 4 1 / 1 pts
JJ and PW are in a negotiation that involves each party simultaneously choosing their strategy.
JJ can either offer a high (H) or a low (L) price. PW can opt to Accept (A) or reject (R). If JJ
opts for H and PW A, the payoffs are 6 to JJ and 4 to PW. If JJ opts for H and PW R, the
payoffs are 4 to JJ and 6 to PW. If JJ goes L and PW A, the payoffs are 8 to JJ and 3 to PW.
Finally, if JJ goes L and PW R, the payoffs are 7 and 5, to JJ and PW, respectively. Which of
the following statements are true?
The Nash equilibrium is (L, R)
This negotiation resembles a prisoners’ dilemma.
The Nash equilibrium is (H, A)
JJ has a dominant strategy to set a high (H) price.
The Nash equilibrium in the negotiation is (H, R).
02/05/2020 Module 4 Final Quiz: Economic Strategy and Negotiation
https://canvas.sydney.edu.au/courses/23912/quizzes/94190 3/9
Question 5 1 / 1 pts
Consider the CBA negotiating with Myer regarding the rate of interest for a loan. The CBA can
offer any interest rate r between 0 and 10. If Myer accepts the payoff to the CBA is r, and the
payoff to Myer is 10 – r. If Myer rejects the offer the payoffs are 0 to both parties.
What is the strategy of Myer in any credible equilibrium?
Accept any offer r ≤ 10.
None of the answers are correct.
Accept any offer r ≥ 10
Accept any offer r ≥ 0
Accept any offer provided r = 0
Question 6 1 / 1 pts
Ainslie is in a team with Michelle and together they must produce a report for their boss. To
determine who will do the work, they engage in the following negotiations: Ainslie can propose
that either she does the work, or that Michelle does the work. Michelle can then accept or
reject Ainslie’s offer. If Ainslie offers to do the work, and Michelle accepts this offer, Ainslie gets
a payoff of 20 and Michelle a payoff of 40. If Michelle rejects this offer both get a payoff of 10. If
Ainslie suggests Michelle do the work and Michelle accepts, the payoffs are 50 to Ainslie and
20 to Michelle. If Michelle rejects Ainslie’s suggestion that Michelle is the one who should
complete the work, Ainslie has an opportunity to respond. At this juncture, Ainslie can opt not
to do the work, and both workers get a payoff of 10. If Ainslie chooses to do the work, she
receives a payoff of 15 and Michelle gets a return of 50. What is the outcome of this
negotiation process?
Ainslie suggests Michelle do the work, and Michelle accepts.
Ainslie suggests Michelle do the work, Michelle refuses; Ainslie then chooses not to do the work.
Ainslie suggests that she does the work herself, and Michelle refuses.
Ainslie suggests she does the work, and Michelle accepts.
Ainslie suggests Michelle do the work, and Michelle refuses; Ainslie then chooses to do the wor
[Show More]