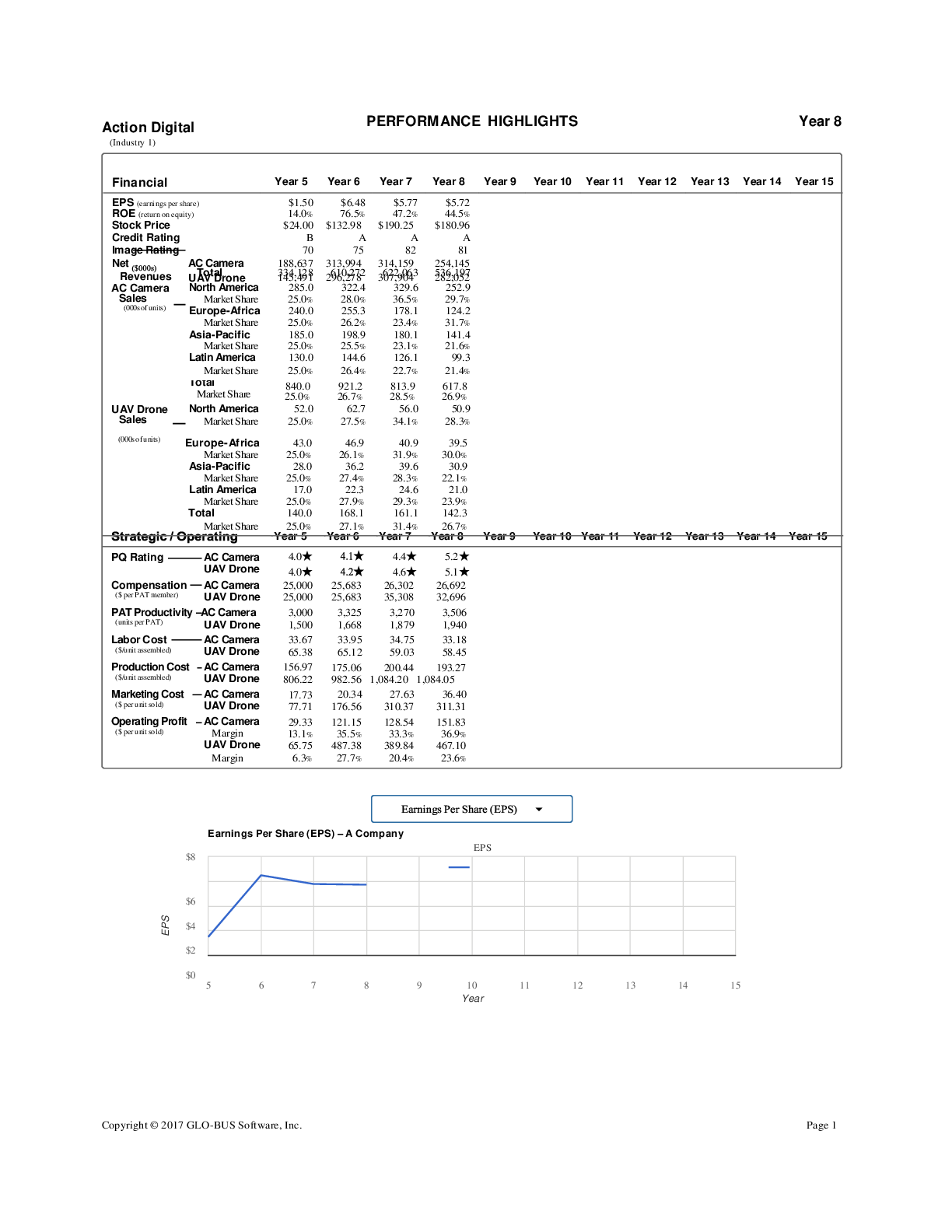1. DNA is used to tell people apart. What aspects of DNA do you think make this
possible?
- The lengths of the repeated sequences in DNA
- The DNA sequences themselves
2. What are some possible uses for technology th
...
1. DNA is used to tell people apart. What aspects of DNA do you think make this
possible?
- The lengths of the repeated sequences in DNA
- The DNA sequences themselves
2. What are some possible uses for technology that can identify people based on their
DNA?
- Gel electrophoresis
Gizmo Warm-up
DNA profiling does not just compare people’s entire genome side
by side. Instead, a very particular part of the DNA is compared. In
the DNA Profiling Gizmo you will learn about the differences in
DNA that make DNA profiling possible and you will use that
knowledge to design your own DNA profiling test.
Click on the crime lab in the Forensic training section. You are looking at a strand of DNA. DNA
contains genes and non-coding regions between genes. Click on Non-coding A.
1. You are looking at a portion of the non-coding A section for three different people.
Are these sections the same or different? Explain.
- The sections are different. Person 1 has the longest section, person 3 has the
second-longest section and person 2 has the shortest section.
a. Click Previous then click on Gene A. Are there differences in gene A for the three
people?
- Person 1 and Person 3 have identical sequences in their gene A. On the other hand, the
sequence of nucleotides in person 2 differs from both persons 1 and 3. In one section,
persons 1 and 3 have the base pair of C and G whereas person 2 has the base pair of A
and T.
Activity A:
Forensic training
Get the Gizmo ready:
● Click on Forensic training and Start again.
Introduction: In this activity, you will learn about the principles and techniques that make DNA
profiling possible. Genes code for specific traits. In people, the DNA sequences for most genes
are nearly identical, since any change could result in a harmful disorder. The areas between
genes do not code for any essential traits, so a change to the DNA sequence doesn’t have any
major consequences. As a result, these regions tend to be very different for different people.
Question: How can the differences in DNA be exploited to perform DNA profiling?
1. Observe: Click on non-coding A. What do you see in the middle of each of the three
DNA sequences?
- I see repeated sequences (TAAA and ATTT) in all three DNA sequences.
2. Compare: Turn on Show short tandem repeats (STRs). An STR is a short, repeated
sequence of DNA, like TAAA. They can be repeated any number of times without affecting
the traits of the person. Different people usually have different numbers of repeats.
What does this do to the length of each person’s non-coding regions?
- The more STRs a person has in their DNA, the longer their non-coding regions. Vice
versa, the fewer STRs a person has, the shorter their non-coding regions.
3. Create: Your goal is to make copies of the STR region. To do this, you will make primers
that surround the STR region. A primer is a short sequence of DNA that acts as a starting
point for DNA replication
[Show More]