*NURSING > EXAM > NURS 213 - New Final Exam Questions & Answers - Detailed Answer Key Guide (2020/2021) - City College (All)
NURS 213 - New Final Exam Questions & Answers - Detailed Answer Key Guide (2020/2021) - City Colleges of Chicago - Already Graded A.
Document Content and Description Below
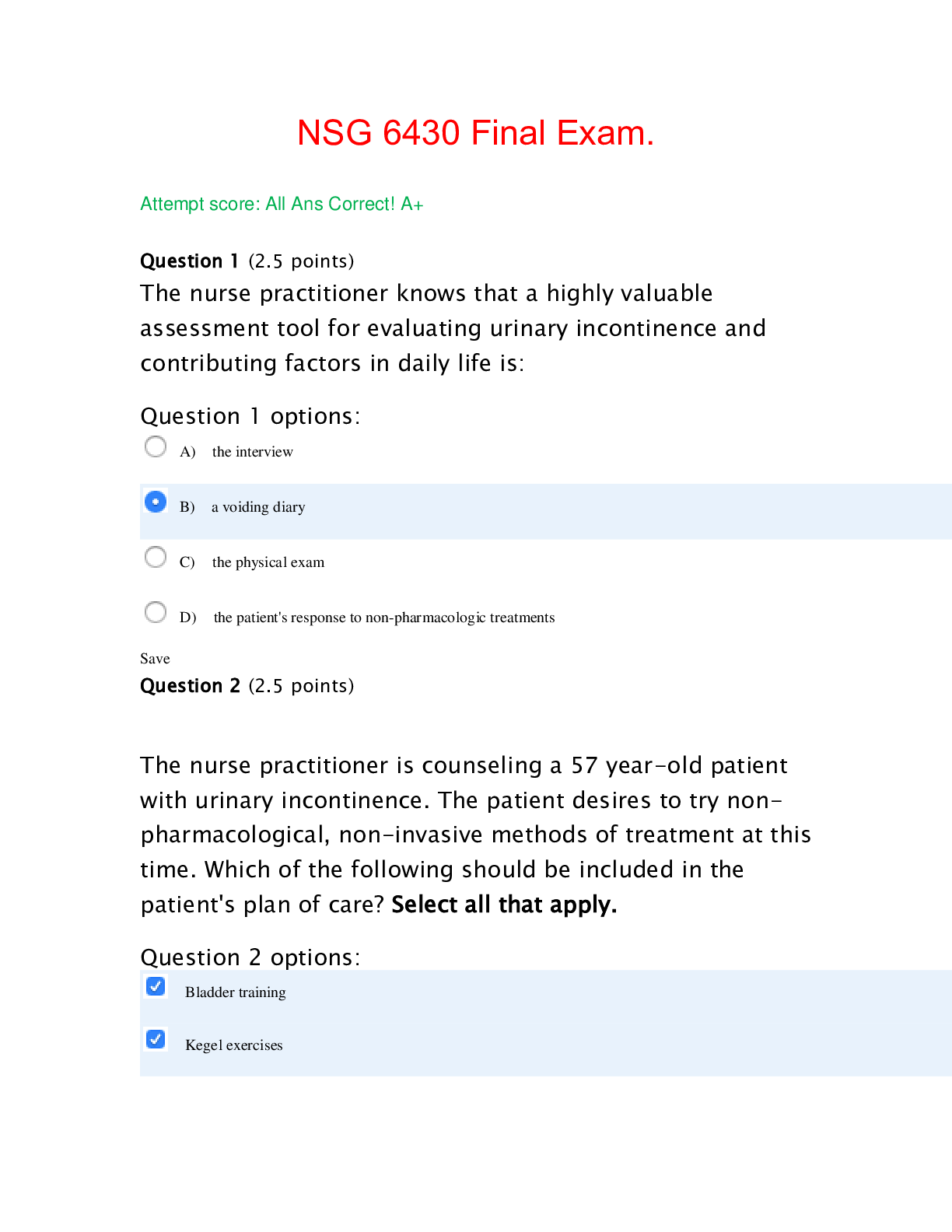
1. A nurse is caring for a client who has metastatic cancer and has become ventilator-dependent after palliative surgery. The client wants to have the ventilator withdrawn but the client's children wa... nt the client to keep it on. The client is examined by a psychiatrist who finds that the client is competent. The nurse is aware that continued treatment against the client's wishes is a violation of which ethical principle? A. Veracity Rationale: Veracity is the "duty to tell the truth." This ethical principle is not violated. B. Autonomy Rationale: In health care, autonomy is the principle underlying informed consent, the right to refuse treatment, and the right to appoint a surrogate decision-maker. C. Fidelity Rationale: Fidelity is the "duty to keep one's promises or word." It refers to the obligation to be faithful to the agreements, commitments, and responsibilities made to oneself and others. This ethical principle is not violated. D. Nonmaleficence Rationale: Nonmaleficence is the "duty to do no harm." This ethical principle is not violated. 2. A nurse is caring for a client who has an indwelling urinary catheter and is to receive catheter care twice a day. Which of the following is the appropriate nursing action to ensure the client's privacy? A. Pull the curtain around the client's bed. Rationale: Pulling the curtain provides the most privacy for the client. With the curtain pulled, anyone entering the client's room does not have visual access to the client or the treatment being performed. B. Cover the client's genitalia with a towel while performing catheter care. Rationale: This action is inappropriate. Performing catheter care includes cleansing and inspection of the urinary meatus. This cannot be properly accomplished if the client's genitalia are covered. C. Close the door to the client's room. Rationale: Anyone can open the door and unnecessarily expose the client to the person entering the room as well as others in the hallway. D. Ask the client's roommate to leave until the treatment is finished. Rationale: This action is inappropriate. It is not necessary for the client's roommate to leave the room while catheter care is performed. 3. A nurse is caring for several clients in a walk-in clinic. Which client should the nurse have the provider see immediately? A. A belligerent, vomiting teenager with alcohol on her breath. Rationale: This client does not have a life-threatening emergency. B. A screaming toddler with a freely bleeding forehead wound. Rationale: This client does not have a life-threatening emergency. C. A diaphoretic, obese middle-aged man with epigastric pain. Rationale: This client has two of the classic signs of a myocardial infarction (MI), diaphoresis and epigastric pain. It is possible the client is having an MI. D. Young adult with painful sunburned face and arms. Rationale: This client does not have a life-threatening emergency. 4. A nurse is caring for a client with a compression fracture of a spinal vertebra. Just prior to an hour-long transport to the hospital, the client was medicated with intravenous morphine sulfate (Duramorph). On arrival, the neurosurgeon determines that urgent surgical intervention is indicated for the fracture. The nurse realizes that consent for the surgery A. must be obtained from a relative of the client. Rationale: According to the case scenario, this client was given a narcotic that can alter the ability to understand within the subsequent 1 to 2 hr. Consequently, this client is not legally able to provide consent. B. can be inferred since the client consented to the transport. Rationale: Consent for transfer to another facility for evaluation by a specialist does not imply consent for any further procedures or care. C. should be obtained from the client immediately. Rationale: This client was given a narcotic that can alter the ability to understand within the subsequent 1 to 2 hr. Consequently, this client is not legally able to provide consent. D. will be delayed until the morphine is metabolized. Rationale: Delaying consent until the morphine is metabolized could be dangerous to the client and may increase the chance of a life-long disability. 5. An assistive personnel (AP) comes to work with a new set of highly polished acrylic nails. The nurse takes the AP aside and explains that acrylic nails are not permitted on the health care unit. Which of the following statements should the nurse tell the AP? A. "There is a higher risk of infection associated with acrylic nails." Rationale: Studies have shown that the wearing of acrylic nails is associated with an increased risk of infection. It is more difficult to perform adequate handwashing with acrylic nails and microorganisms can hide in small chips in the polish. In addition, acrylic nails make it more difficult to apply gloves properly and can increase the risk of tearing of the tips. B. "Polished acrylic nails have a very unprofessional appearance." Rationale: This is not the reason that acrylic nails are prohibited in the health care setting. C. "Acrylic nails may contribute to contact dermatitis." Rationale: This is not the reason that acrylic nails are prohibited in the health care setting. D. "Acrylic nails can break and injure the client." Rationale: This is not the reason that acrylic nails are prohibited in the health care setting. 6. A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled to have surgery. In preparing the client for surgery, which of the following actions is considered outside the responsibility of the nurse? A. Assess the current health status of the client. Rationale: This action is a nursing responsibility that helps collect baseline data on the client. B. Explain the operative procedure, risks, and benefits. Rationale: Explaining the procedure and any risks that may be associated with the procedure is the responsibility of the person performing the procedure. This is not a nursing responsibility. C. Review preoperative laboratory tests results. Rationale: This action is a nursing responsibility that determines if any abnormal values could cause surgical complications. D. Ensure that a signed surgical consent form was completed. Rationale: This action is a nursing responsibility that ensures proper surgical protocol is carried out. 7. A nurse takes the witness stand in a malpractice suit. While on the witness stand, the nurse states to the court, "any reasonable and prudent nurse would have questioned that order." In this situation, which of the following types of witness is the nurse testifying as? A. Defense Rationale: The case scenario does not give you enough information to determine if the nurse was giving testimony on the behalf of either the defense or the prosecution. B. Expert Rationale: The nurse in this situation is offering a professional opinion about a standard of practice: what a reasonable and prudent nurse would do in that same circumstance. A nurse, acting as an expert C. Character witness, is one who has a special skill, advanced education, or is part of a nursing specialty and is allowed by the court to offer an opinion based on professional expertise. Rationale: Character witnesses provide information describing the overall nature of a person, based on past experience and knowledge of that person's actions. D. Prosecution Rationale: The case scenario does not give you enough information to determine if the nurse was giving testimony on the behalf of either the defense or the prosecution. 8. A family member who is the primary caregiver of a client with multiple care needs is interested in a respite care program. The nurse should explain that the primary purpose of a respite care program is to provide which of the following? A. Pain management Rationale: This is not the primary purpose of a respite program. B. Temporary care Rationale: The primary purpose of respite is to give family members time and temporary relief from the stress they may experience while providing extra care for a family member with a disability. C. Palliative care Rationale: This is not the primary purpose of a respite program. D. Restorative care Rationale: This is not the primary purpose of a respite program. 9. A nurse reported to the nurse manager that another staff member was observed signing out meperidine hydrochloride (Demerol), which was not administered to the client. The nurse manager should know that potential opiate abuse by the employee may be manifested by which of the following symptoms? A. Tremors Rationale: Demerol is a synthetic narcotic analgesic. Tremors result from a buildup of normeperidine when repeated doses are given. B. Rhinorrhea Rationale: Rhinorrhea may occur with opiate withdrawal but is not an effect from the medication. C. Pale skin color Rationale: Pale skin color is not an effect of this medication. Integumentary effects include flushing. D. Dilated pupils Rationale: Pupillary changes that may be observed in opiate abuse would be constricted pupils, not dilated pupils. 10. A nurse is caring for a client who has constipation, and a soap suds enema is prescribed. As the nurse explains the procedure, the client states, "The doctor didn't tell me I was supposed to receive an enema." Which of the following nursing actions is appropriate at this time? A. Check the client's chart for the provider's prescription. Rationale: This option directly addresses the client's concern about whether or not an enema is prescribed. Looking at the provider's prescription will help to clarify the situation and will reassure the client that the procedure was prescribed. B. Explain to the client that the provider prescribed the procedure. Rationale: This option ignores the client's concern about whether or not an enema is prescribed. C. Assure the client that enemas are commonly prescribed for constipation. Rationale: This option ignores the client's concern about whether or not an enema is prescribed. D. Inform the charge nurse that the client refused the enema. Rationale: The client did not refuse the enema, so this action would be incorrect. 11. A nurse is caring for several clients on the unit. In which of the following situations is the nurse permitted to disclose information to an outside agency about the client or the client's circumstances? A. An older adult is admitted for the treatment of a spiral fracture. Rationale: This situation reflects elder abuse. Nurses are mandatory reporters of any client situation in which children or the elderly are being abused or neglected. B. A client is admitted for asthma and has track marks that may indicate IV drug abuse. Rationale: Although the use of street drugs is illegal, the track marks may be present from scarring due to prior use. The nurse would not be required to report this finding to law enforcement. C. A football star is admitted following a knee injury. Rationale: Information about the client's status and treatment cannot be shared outside of the health care team caring for this client without his permission. D. A local politician is admitted to an alcohol rehabilitation facility. Rationale: Information about the client's status and treatment cannot be shared outside of the health care team caring for this client. 12. A nurse is caring for several patients. The nurse should know that which of the following conditions makes a client an unsuitable organ donor? A. Older than age 65 Rationale: Age is not an automatic exclusion criterion, and most transplant centers will evaluate potential donors from newborn to 80 years old. B. Metastatic malignancy Rationale: The only clients who are always excluded from organ or tissue donation are those who have metastatic malignancies or communicable diseases such as hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus. C. Advanced cardiovascular disease Rationale: Although advanced cardiovascular disease may preclude the donation of some organs, it is not an automatic exclusion criterion. D. Type 1 diabetes mellitus Rationale: Although long-standing diabetes may preclude the donation of some organs, it is not an automatic exclusion criterion. 13. A nurse in the intensive care unit is caring for a client who has a tracheostomy and is on a ventilator. The client also has an indwelling urinary catheter to gravity drainage and a central venous catheter, and is on a heparin drip for a thrombophlebitis of the left leg. Which of the following specimens can the nurse delegate to assistive personnel (AP) to collect? A. Blood culture Rationale: Obtaining a blood culture is not within the scope of practice for an AP. B. Sputum culture Rationale: Collecting a sputum sample is not within the scope of practice for an AP. C. Arterial blood gas (ABG) Rationale: Collecting an ABG sample is not within the scope of practice for an AP. D. Fecal occult blood Rationale: Collecting a stool sample is within the scope of practice for an AP. 14. A hospital is participating in a disaster simulation in which a toxic substance is released into a crowded stadium. Multiple clients are transported to the hospital. Which of the following activities would be of lowest priority for the triage nurse in the event of a disaster? A. Preventing cross-contamination of clients Rationale: In a disaster, the nurse must be able to segregate clients to prevent contamination of a non-exposed client by an exposed client, thereby limiting the spread of an unknown toxin. B. Performing concise client assessment Rationale: In the triage setting, the nurse's priority is client assessment and control of client flow. C. Educating the client and family Rationale: The triage nurse should not use the limited time available with each client to provide education. Other health care team members will do this once treatment of the client is initiated. D. Maintaining calm amidst the chaos Rationale: The nurse should direct client flow in a calm, professional, and orderly manner in order to maintain a therapeutic environment for client care. 15. A nurse is caring for a client. The nurse demonstrates adherence to the ethical principle of fidelity in practice by doing which of the following? A. Keeping an appointment with a client. Rationale: Fidelity is the duty to keep one's promises or word. Keeping an appointment that the nurse has made with the client is an example of fidelity. B. Allowing a new mother to hold her stillborn infant. Rationale: Beneficence is the duty to do good for others. Allowing a grieving mother an opportunity to spend time with her infant helps her to process her loss and is an example of beneficence. C. Confirming that a client going for surgery has signed a consent form. Rationale: The ethical principle of autonomy describes an individual's right to choose. In health care, autonomy is the principle underlying informed consent, the right to refuse treatment, and the right to appoint a surrogate decision maker. D. Refusing to disclose information about a client to the media. Rationale: Confidentiality means that a client's personal health care information cannot be disclosed to unauthorized individuals or other entities. 16. A nurse is working with an assistive personnel (AP) to care for a group of clients on the pediatric floor. Which task should the nurse have the AP perform first? A. Collect a stool sample for ova and parasites from a 2-year-old child. Rationale: Although elimination is an important physiologic need, the nurse uses Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a guideline to identify a client with a more immediate need. The stool sample should be collected when available and sent to the laboratory for analysis. B. Ambulate a postoperative 5-year-old child to the playroom. Rationale: Although ambulation is an important physiologic need, the nurse uses Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a guideline to identify a client with a more immediate need. C. Assist the nurse in bathing a 14-year-old child who has a handicap. Rationale: Although provision of skin care is an important physiologic need, the nurse uses Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a guideline to identify a client with a more immediate need. D. Feed a 9-year-old child with bilaterally burned upper extremities. Rationale: In prioritizing the list of tasks, the nurse should have the AP perform the tasks that meet basic physiologic needs first. Using Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a guideline, the nurse should know that the client who needs to be fed is the most basic physiologic need listed. 17. Following a suicide bombing at a shopping mall, an unidentified, unconscious client is admitted to the emergency department with an acute intra-abdominal hemorrhage. The nurse should recognize that consent for the surgery A. should be obtained from an officer of the court. Rationale: Awaiting legal intervention could mean an inordinate delay until surgery is performed. B. must be obtained from a relative of the client. Rationale: In urgent situations, it is preferable for consent to be obtained from a relative or health care proxy (HCP). However, in this situation, the next of kin cannot be readily identified. C. can be inferred since the client is in critical condition. Rationale: The client is unconscious and in critical condition, and consequently, is incapable of providing consent. Preferably, consent should be obtained from a relative or health care proxy (HCP). However, the client is also unidentified, meaning the client could die while awaiting identification and next of kin. Therefore, consent should be implied and the surgery will be performed as an emergency life-saving procedure. D. will be delayed until the client is identified. Rationale: This is not an appropriate action. The client could die awaiting identification and next of kin. 18. A nurse is speaking to the nurse manager about a schedule request, and the nurse manager puts an arm around the nurse and says, "I bet you are a great lover." Which of the following is the appropriate response by the nurse? A. "Let's talk about something else." Rationale: While this appears to be a response meant to change the subject, this response does not make it clear that this type of sexually oriented conversation and physical contact is undesired by the nurse. B. "Whether or not I am a good lover is irrelevant." Rationale: While this appears to be a response meant to change the subject, this response does not make it clear that this type of sexually oriented conversation and physical contact is undesired by the nurse. C. "Speaking to me like that makes me uncomfortable." Rationale: This assertive response makes it clear that this type of sexually oriented conversation and physical contact is undesired by the nurse. D. "That is not what I am here to discuss." Rationale: While this appears to be a response meant to change the subject, this response does not make it clear that this type of sexually oriented conversation and physical contact is undesired by the nurse. 19. A female teen volunteer is assigned to the pediatric unit for the day and reports to the charge nurse for an assignment. Which of the following assignments is unsafe for the volunteer? A. Helping a 7-year-old client who has celiac disease make out the next day's menu Rationale: The volunteer may not be familiar with the dietary needs of a client with celiac disease. B. Playing a computer video game with a 15-year-old male client in skeletal traction Rationale: This is an appropriate and safe assignment for the volunteer that provides both socialization and diversional activity to the client in traction. C. Reading a book to a 4-year-old client who has AIDS Rationale: This is an appropriate and safe assignment for the volunteer that provides a diversional activity for the client. D. Refilling the ice pitchers for clients on the unit for the charge nurse Rationale: Refilling the ice pitchers for clients on the unit for the charge nurse is an appropriate and safe assignment for the volunteer to do under the supervision of the charge nurse. 20. When checking on a confused client, a nurse finds that the client has fallen out of bed after climbing over the side rails. After determining that the client is uninjured, the nurse assists the client back to bed and contacts the provider to assess the client. The nurse then completes a variance report detailing the incident. Which of the following should be the next nursing action the nurse completes? A. Make a copy of the variance report for the provider. Rationale: Variance reports are confidential tools used by the institution to improve client care. They are never copied. B. Submit the variance report to the nurse manager. Rationale: Variance reports are confidential tools used by the institution to improve client care. They are never copied, placed in, or referred to in a client's chart. Filing a variance report does not substitute for a complete entry in the client's chart documenting the incident. Once completed, the variance form is submitted to the nurse's most immediate supervisor such as the nurse manager. C. Place the variance report in the client's chart. Rationale: Variance reports are confidential tools used by the institution to improve client care. They are never placed in the client's chart. D. Document in the chart that a variance form has been filed. Rationale: Variance reports are confidential tools used by the institution to improve client care. They are never referred to in a client's chart. 21. A nurse manager notices that a nurse in the unit is not delivering care in accordance with a recent policy change. The effective approach for the nurse manager to take is to A. encourage the nurse to openly verbalize the reasons for resistance to the change. Rationale: The nurse manager should realize that resistance to change is likely if the people who must implement the change are not invested in the change process. The nurse manager should meet with the nurse to allow an open forum for the nurse to verbalize the reasons for reluctance to adopt the new policy. B. explain to the nurse the importance of implementing the new policy. Rationale: The nurse has likely rejected the change without critically thinking about the possible benefits; this is not the appropriate action by the nurse. C. ignore the resistance and allow peer pressure to facilitate change in the nurse's behavior. Rationale: The nurse manager should not ignore an individual who is refusing to implement a policy change. The nurse may act as a barrier to the change. D. threaten disciplinary consequences if the nurse does not implement the new policy. Rationale: Starting the meeting with a discussion of disciplinary consequences is unlikely to encourage open dialogue. 22. A nursing supervisor assigns a float nurse in an adult medical-surgical unit to work in a pediatric unit. This is the nurse's first time in a pediatric setting. Which of the following is an appropriate assignment for the nurse? A. Care for postoperative school-age clients. Rationale: Hospitalized school-aged children tend to have similar medical-surgical diagnoses to adults and are in an age group that is easier to care for than younger children or adolescents. The float nurse should be able to handle this assignment with minimal guidance. B. Function as an assistive personnel (AP). [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 29 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 09, 2021
Number of pages
29
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 09, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
99


.png)