Finance > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > The University of SydneyFINC 6013FINC6013 Final Exam Practice Solutions ( ALL QUESTIONS WITH 100% CO (All)
The University of SydneyFINC 6013FINC6013 Final Exam Practice Solutions ( ALL QUESTIONS WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS/SOLUTIONS)
Document Content and Description Below
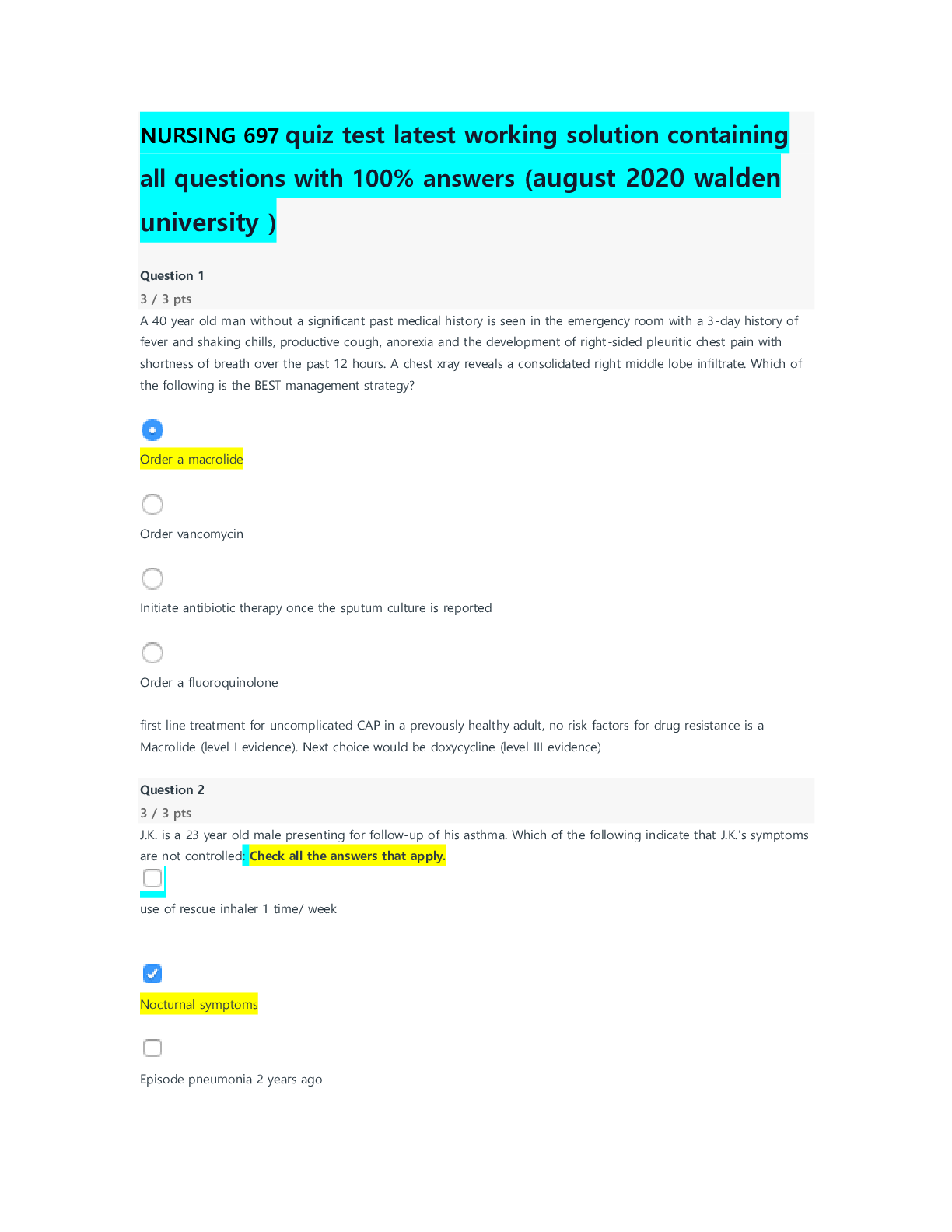
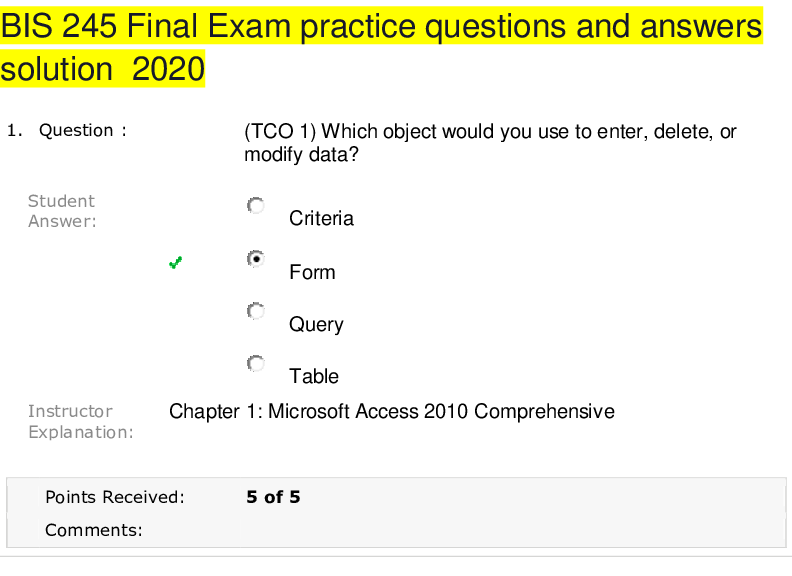
FINC6013 Final Exam Practice Questions PART A Choose the answer that is the MOST correct and fill out the multiple-choice answer sheet. Only one answer should be marked for each question. Failure t... o do so means zero marks for this section. 1) When translating from foreign currency to home currency, current/non-current method means that current accounts are translated at _______, while non-current accounts are translated at _______. A. current exchange rate; current exchange rate B. current exchange rate; historical exchange rate used to record the account C. historical exchange rate used to record the account; current exchange rate D. average historical exchange rate; historical exchange rate used to record the account E. current exchange rate; average historical exchange rate 2) Which of the following statements best describes diversifying foreign exchange risk and exposure via currency of invoicing? A. Firm invoices in local currency B. Firm invoices in foreign currency C. Firm invoices partly in local currency and partly in foreign currency D. Firm invoices in a currency basket unit or composite currency E. None of the above 3) In chartism, _______ level is the level that price has trouble falling below, and _______ level is the level that price has trouble rising above. These levels define a _______. A. support; resistance; trading range B. support; resistance; breakout C. resistance; support; trading range D. resistance; support; breakout E. lower; upper; breakout2 4) For a net exporter, a depreciation of foreign currency will result in a _______ of its profitability. The exporter can avoid this by _______ the foreign currency price of its products. However, the effect of this action is limited by _______ for its product. A. increase; increasing; price elasticity of demand B. decrease; decreasing; price elasticity of supply C. decrease; increasing; price elasticity of demand D. increase; decreasing; price elasticity of supply E. decrease; increasing; price elasticity of supply 5) Firms can manage transaction exposure using various hedging techniques. If foreign currency is expected to appreciate, domestic firm would like to _______foreign currency payables and _______foreign currency receivables. A. lead; lead B. lag; lag C. lead; lag D. lag; lead E. None of the above 6) An Australian superannuation fund decides to invest in New Zealand stock market. Which of the following risk(s) is/are most likely associated with this investment decision? (i) risk in Australian equity market (ii) risk in New Zealand equity market (iii) risk of AUD/NZD exchange rate A. (i) only B. (ii) only C. (i) and (ii) D. (ii) and (iii) E. (i), (ii) and (iii) 7) Which of the following is least likely a factor that determines international return correlations? A. Geographic proximity B. Trade pattern C. Industrial structure D. Tax system E. Irrational investor behaviour Note) The question is revised; “D. Economic cycle” is replaced by “D. Tax system.”3 8) Which of the following is least likely to be an investment puzzle in cross-border investment? A. Use of inflated hurdle rates B. Investing in low Sharpe-ratio countries C. Failure to abandon unprofitable investments D. Negative-NPV investments in emerging markets E. None of the above 9) A _______ draft is payable on presentation to the drawee. A. revocable B. confirmed C. unconfirmed D. sight E. time 10) If a multi-national company wants to reduce its income tax using transfer pricing, it should _______ taxable income in a country with _______ tax rate by charging _______ prices (than uncontrolled prices) on goods sold to its subsidiary in that country. A. maximize; high; higher B. maximize; high; lower C. maximize; low; higher D. minimize; high; higher E. minimize; low; lower Note) The question is revised: “… by charging high/low prices on goods …” is replaced by “… by charging higher/lower prices (than uncontrolled prices) on goods …”4 PART B (Part B has FOUR questions.) Question 1: A. It is shown that U.S. Sharpe ratio is higher than the Sharpe ratios for other G7 countries. Why U.S. investors should care about investing in international markets? [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 11, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 11, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
184

















 ansswers.png)

.png)




