NR 507 Study Guide and P
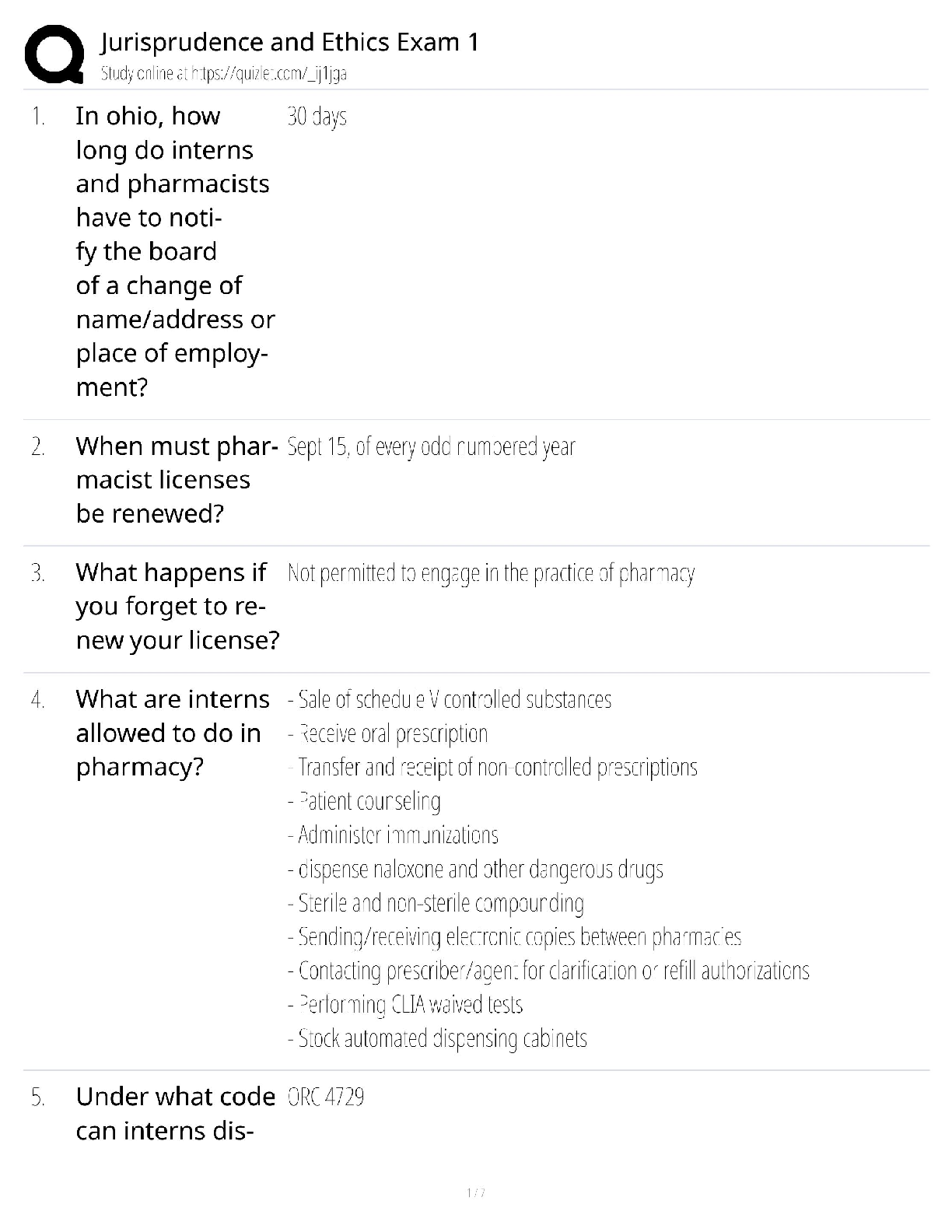
ractice questions
Types of immunity ch 7 & 8
Innate- natural epithelial barrier and inflammation the make innate resistance and protection pg. 191 Innate immunity includes two
lines of defens
...
NR 507 Study Guide and P
ractice questions
Types of immunity ch 7 & 8
Innate- natural epithelial barrier and inflammation the make innate resistance and protection pg. 191 Innate immunity includes two
lines of defense: Natural barriers and inflammation.
Natural barriers- physical, mechanical, and biochemical barriers at the body’s surfaces
Inflamation- associated with infection usually initiates an adaptive process that results in a long-term and very effective immunity
to the infecting microorganism, referred to a adaptive, acquired or specific immunity. Use of the Epithelial cells with no memory
function involved.
Adaptive/ acquired- immune response or immunity, after innate and inflammation, Third line of defense, initiated when innate
immune system signals the cells of adaptive immunity. There is a delay between primary exposure to antigen and maximum
response, however there is immediate action against secondary exposure. Response is specific toward antigen. Involves T
lymphocytes, B Lymphocytes, macrophages, and dentric cells. Specific immunologic memory by T and B lymphocytes
Active (Acquired) -after natural exposure to an antigen or after immunization pg. 227
Passive (Acquired)- preformed antibodies or t lymphocytes are transferred rom a donor to the recipient, maternal to fetus, or bone
marrow transplant pg. 227
Questions
What type of immunity is produced when an immunoglobulin crosses the placenta?
Passive-aquired immunity
The mucosal secretions of the cervix secrete which immunoglobulin?
IgA
A student nurse asks the clinician which cells are most primary in a patient's immunity. What is the clinician's best answer?
Lymphocytes.
A nurse recalls humoral immunity is generated through the process of:
producing antibodies.
While taking a health history, if a person has resistance to a disease from natural exposure to an antigen, how would the nurse
document this form of immunity?
Active acquired
What type of immunity will the nurse expect in an individual who is given a vaccine?
Active acquired immunity
A new mother asks the nurse about immunity of her newborn as she is breastfeeding. The nurse's response should include a
discussion on which type of immunity?
Passive
The nurse has been explaining to a student nurse about the different types of immunity. Which response indicates that the student
nurse has a good understanding of adaptive immunity?
Both the humoral and cell-mediated immunity develop memory cells
Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of adaptive immunity by
natural killer cells
The primary immune response ________.
has a lag period while B cells proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells
Which of the following is true about the number of binding sites per functional antibody unit?
IgM contains 10 binding sites.
Which cell of the immune system is absolutely required for an adaptive immune response?
Helper T cell
The adaptive immune system involves three major cell types: antigen-presenting cells, T cells, which constitute cell- mediated
immunity, and B cells, which govern humoral immunity.
The nurse understands that the function of IgG is as what?
A bond with target cells and a promoter of phagocytosis
The nurse understands that which type of immunity is the longest acting?
Natural active
Natural killer cells are specialized lymphocytes that are one of the major parts of which immunity?
Innate
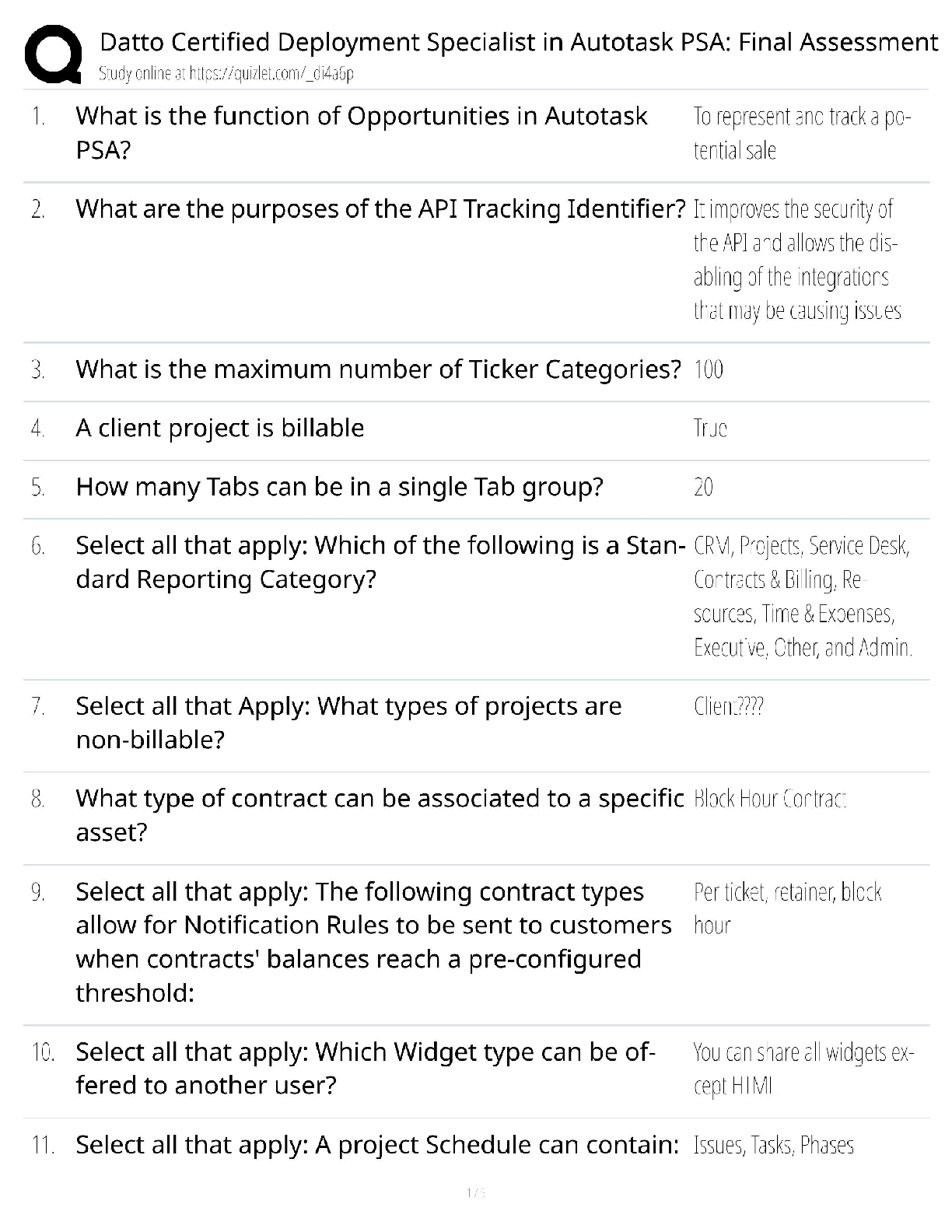
Alveolar ventilation/perfusion- pg. 1239 Ch 34 Effective gas exchange depends on an approximately even distribution of gas
(ventilation) and blood (perfusion) in all portion s of the lungs. The lungs are suspended from the hila in the thoracic cavity. When
the individual is in an upright position, gravity pulls the lungs down toward the diaphragm and compresses their lower portions or
bases.
Ratio between the amount of air getting into the alveoli and the amount of blood being sent to the lungs.
Questions
A consequence of alveolar hypoxia is:
Pulmonary artery vasoconstriction
The pressure required to inflate an alveolus is inversely related to:
Alveolus radius
The nurse is describing the movement of blood into and out of the capillary beds of the lungs to the body organs and tissues. What
term should the nurse use to describe this process?
Perfusion
A pulmonologist is discussing the base of the lungs with staff. Which information should be included? At the base of the lungs:
Arterial perfusion pressure exceeds alveolar gas pressure
When the pulmonologist discusses the condition in which a series of alveoli in the left lower lo
be receive adequate ventilation but do not have adequate perfusion, which statement indicates the nurse understands this
condition? When this occurs in a patient it is called:
Alveolar dead space
Which of the following conditions should the nurse monitor for in a patient with hypoventilation?
hypercapnia
A nurse is describing the pathophysiology of emphysema. Which information should the nurse include? Emphysema results in:
the destruction of alveolar septa and air trapping
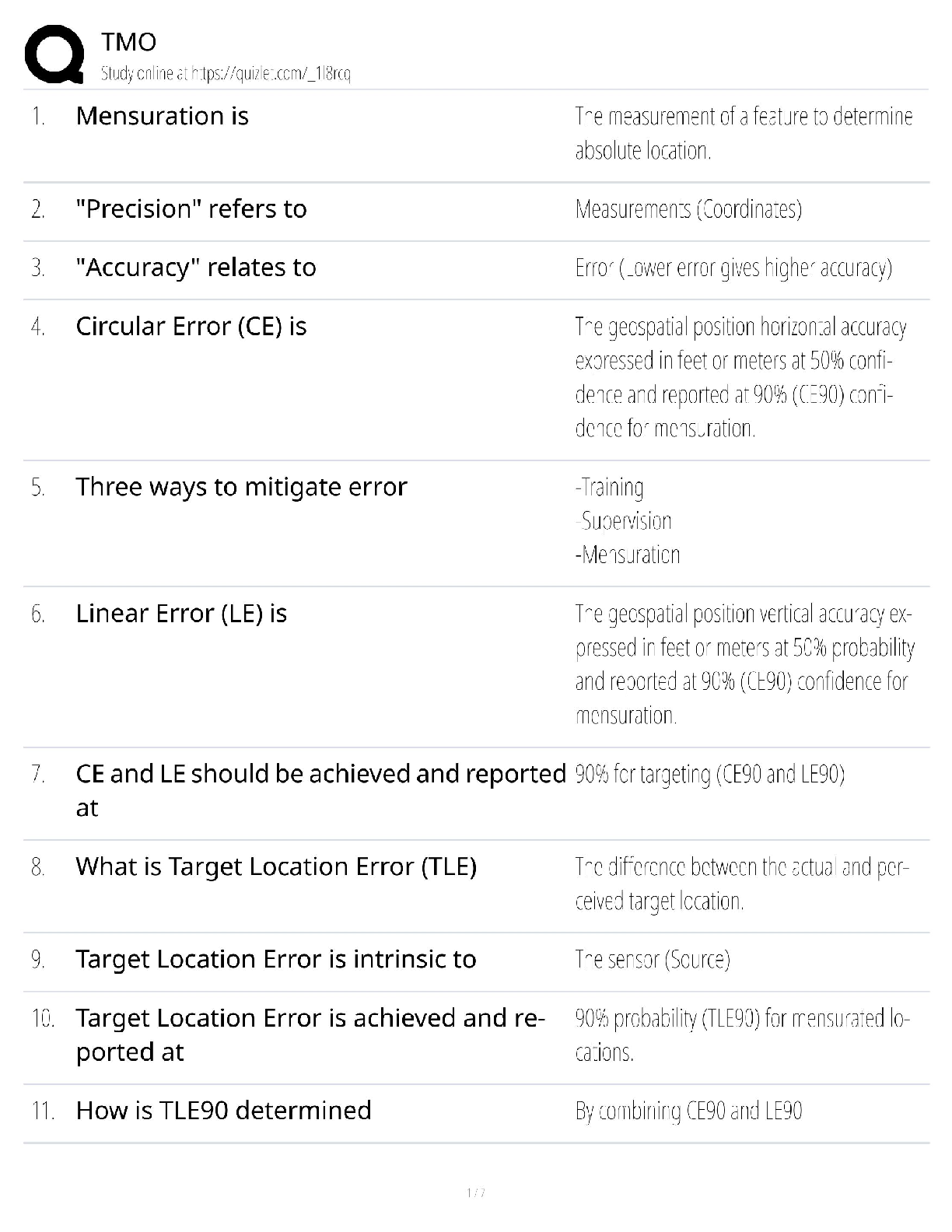
Dermatologic conditions and terminology ch. 46 pg. 1620,
macules- freckles, flat moles, change in color, less than1 cm,
nevi- moles pg. 1641,
pityriasis rosea- benign self-limiting inflammatory disorder that occurs in young adults, with seasonal peaks spring and fall.
Harmful in pregnancy. Associated with a virus, starts with a herald patch, circular. Salmon pink, and demarcated, usually on the
trunk, acyclovir and erythromycin, and corticosteroid creams for itching. Should go away within a few months.
Papule - An elevated, firm, circumscribed area less than 1 cm in diameter, Wart (verruca), elevated moles, lichen planus, fibroma,
insect bite
Patch - A flat, nonpalpable, irregular-shaped macule more than 1 cm in diameter, Vitiligo, port-wine stains, mongolian spots, caféau-lait spots
Plaque- Elevated, firm, and rough lesion with flat top surface greater than 1 cm in diameter, Psoriasis, seborrheic and actinic
keratosis
Wheal - Elevated, irregular-shaped area of cutaneous edema; solid, transient; variable diameter, Insect bites, urticaria, allergic
reaction
Nodule- Elevated, firm, circumscribed lesion; deeper in dermis than a papule; 1-2 cm in diameter, Erythema nodosum, lipomas
Tumor- Elevated, solid lesion; may be clearly demarcated; deeper in dermis; greater than 2 cm in diameter, Neoplasms, benign
tumor, lipoma, neurofibroma, hemangioma
Vesicle- Elevated, circumscribed, superficial, does not extend into dermis; filled with serous fluid; less than 1 cm in diameter,
Varicella (chickenpox), herpes zoster (shingles), herpes simplex
Bulla - Vesicle greater than 1 cm in diameter, Blister, pemphigus vulgaris
Pustule- Elevated, superficial lesion; similar to a vesicle but filled with purulent fluid, Impetigo, acne
Cyst - Elevated, circumscribed, encapsulated lesion; in dermis or subcutaneous layer; filled with liquid or semisolid material,
Sebaceous cyst, cystic acne
Telangiectasia - Fine (0.5-1.0 mm), irregular red lines produced by capillary dilation; can be associated with acne rosacea (face),
venous hypertension (spider veins in legs), systemic sclerosis, or developmental abnormalities (port-wine birthmarks),
Telangiectasia in rosacea
Questions
The physician instructs a mother to take her child out in the sun for approximately an hour or until the skin turns red (not
sunburned). This is a common medical treatment for
Pityriasis Rosea
The patient has a rash on her back that began about 10 days ago with a raised, scaly border and a pink center. Now she has similar
eruptions on both sides of her back. From these signs, the nurse would determine the rash to be
Pityriasis Rosea
A 28-year-old client comes to the office for evaluation of a rash. At first there was only one large patch, but then more lesions
erupted suddenly on the back and torso; the lesions itch. Physical examination reveals that the pattern of eruption is like a
Christmas tree and that various erythematous papules and macules are on the cleavage lines of the back. Based on this description,
what is the most likely diagnosis?
Pityriasis rosea
The nurse's assessment shows that the patient has a solid, elevated, circumscribed lesion that is less than 1 cm in diameter. In the
documentation the nurse would chart this as a
Papule
While waiting to see the physician, a patient shows the nurse skin areas that are flat, nonpalpable, and have had a change of color.
The nurse recognizes that the patient is demonstrating what?
macule
A young student comes to the school nurse and shows the nurse a mosquito bite. As the nurse expects, the bite is elevated and has
serous fluid contained in the dermis. How would the nurse classify this lesion?
A wheal is a primary skin lesion that is elevated and has fluid contained in the dermis
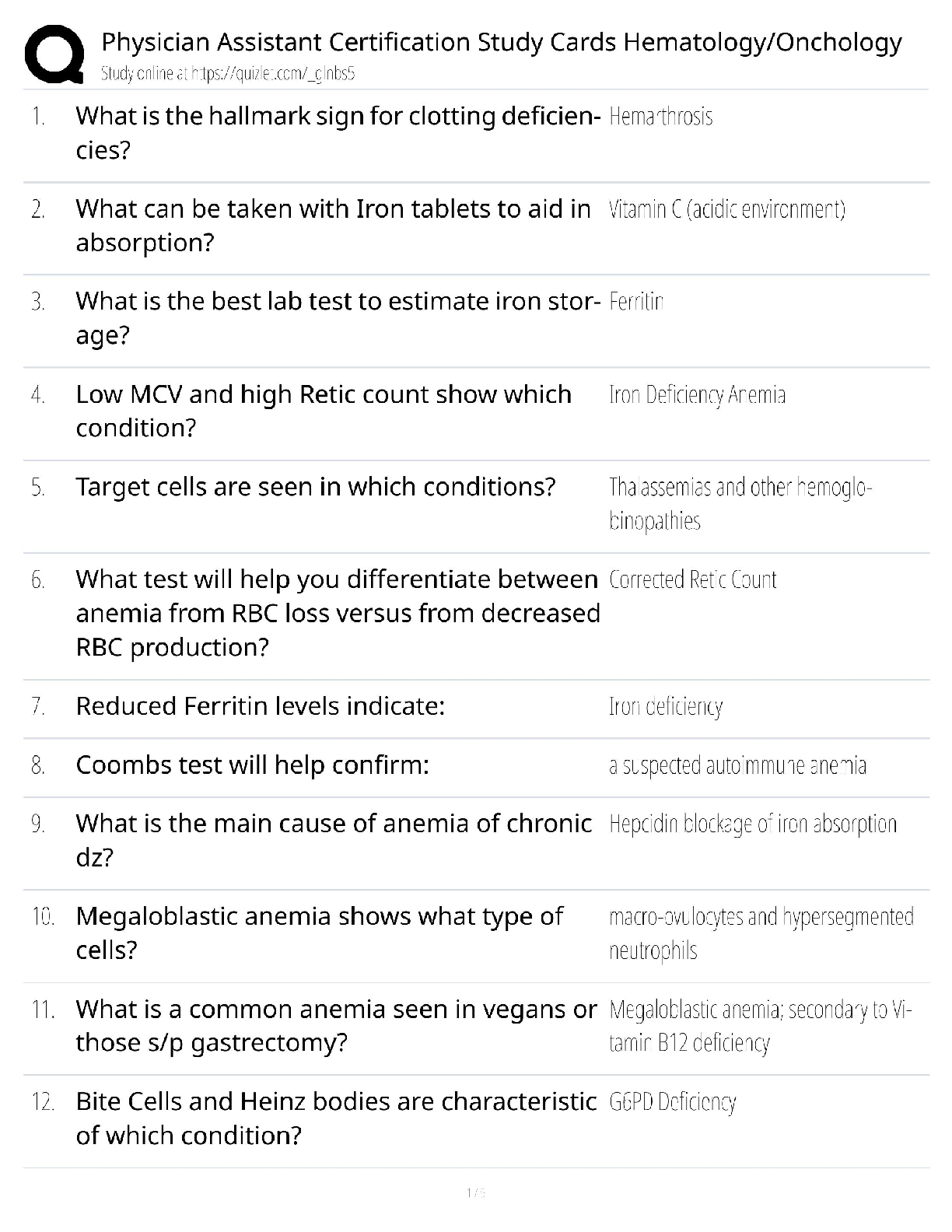
Croup- pg. 1294-1296 Croup illness can be divided into two categories
Acute laryngotracheobronchitisi
Spasmodic croup
Viral, barking cough, winter and spring months, usually affects children 6 mo to 3 yrs, peak at 2 years old, stridor, and fever, 2-5
days. human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs), RSV, viruses are airborne. Rest, humidity, and lots of fluids. Acute
laryngotracheobronchitis
Questions
The 3-year-old child is seen in the local clinic for croup. The child's parents ask the nurse what to do for the child at home to
alleviate symptoms. Which suggestions by the nurse is most appropriate?
"Stand with your child in front of an open freezer"
The nurse is assessing a child with croup in the emergency department. The child has a sore throat and is drooling. Examining the
child's throat using a tongue depressor might precipitate what condition?
[Show More]