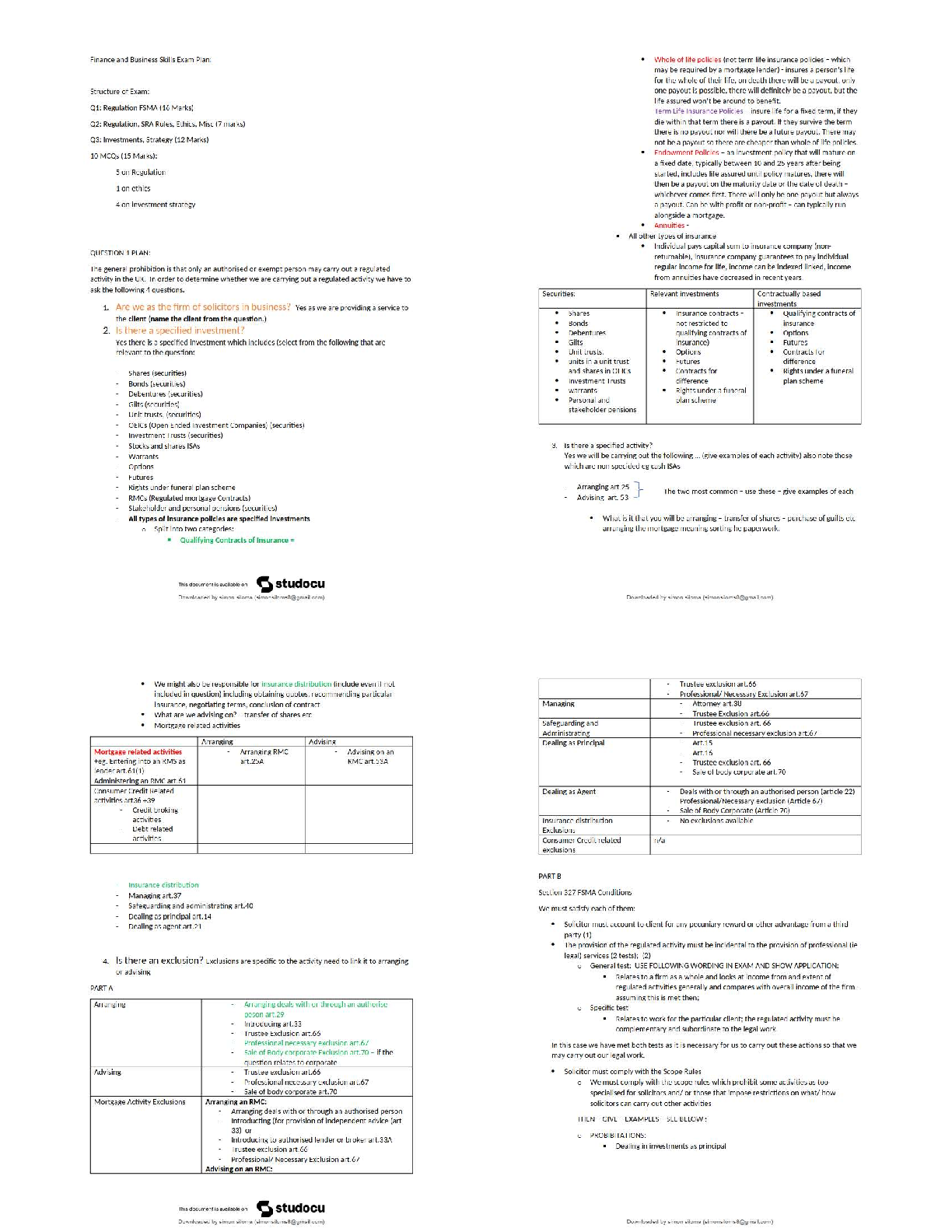
Chapter 3—The Marketing Research Process
TRUE/FALSE
1. Research is the process of developing and deciding among alternative ways of resolving a problem or
choosing from among alternative opportunities.
ANS: F
This i
...
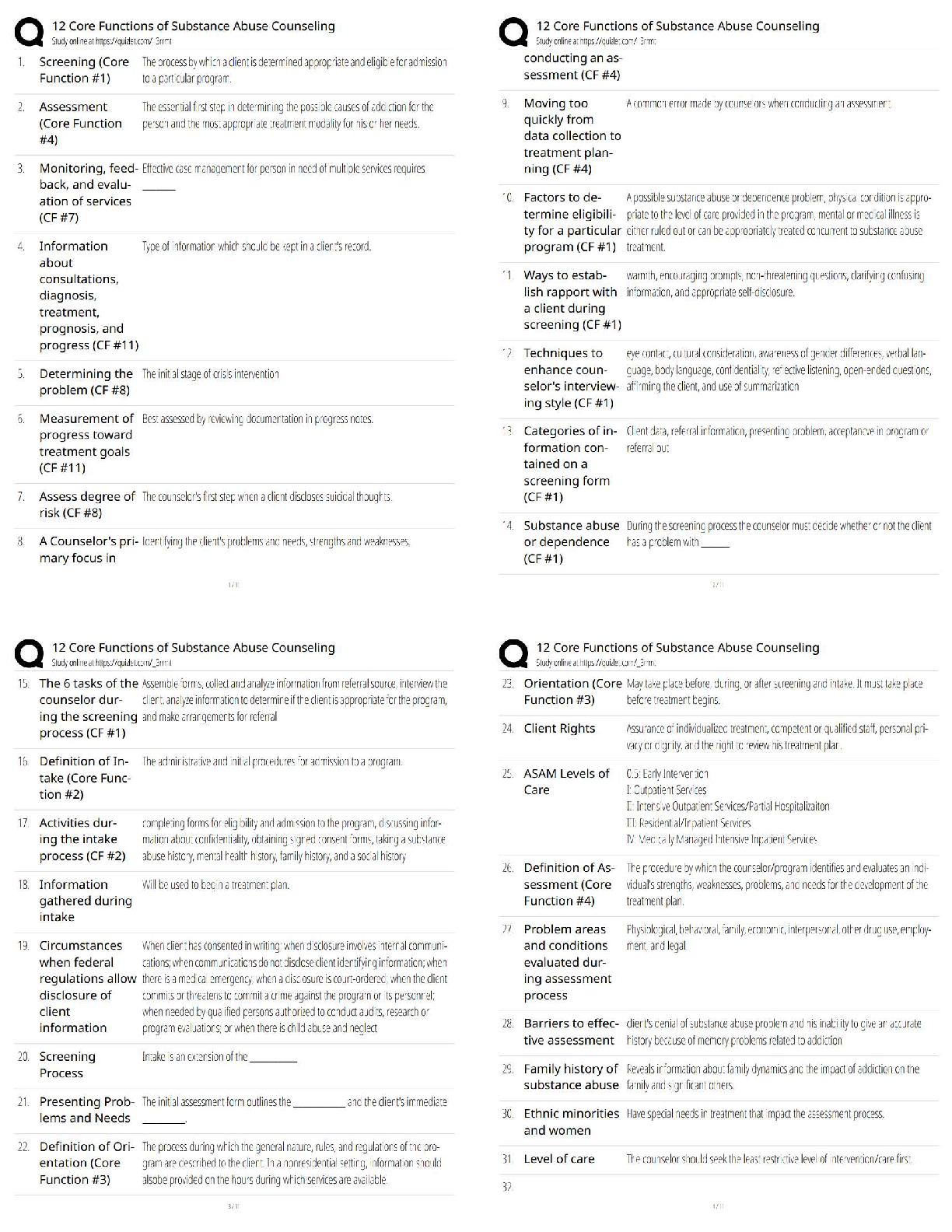
Chapter 3—The Marketing Research Process
TRUE/FALSE
1. Research is the process of developing and deciding among alternative ways of resolving a problem or
choosing from among alternative opportunities.
ANS: F
This is decision making.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 47 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2. A market opportunity is a situation that makes some potential competitive advantage possible.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 47
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3. The purpose of exploratory research is to provide conclusive evidence for a particular marketing action.
ANS: F
Exploratory research is conducted to clarify ambiguous situations or discover ideas that may be potential business opportunities. It is not intended to provide conclusive evidence from which to determine
a particular course of action.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 50 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
4. Descriptive research often helps describe market segments.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 51
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5. Descriptive studies are conducted with a considerable understanding of the situation being studied.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 53
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6. Concomitant variation is sufficient evidence to determine causality in experiments.
ANS: F
Concomitant variation is only one piece of causal evidence--temporal sequence and nonspurious association are also necessary.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 54 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7. Absolute association means any covariation between a cause and an effect is true and not simply due
to some other variable.
ANS: F
This is called nonspurious association.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 54 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking8. Terminal causality means the cause is necessary and sufficient to bring about the effect.
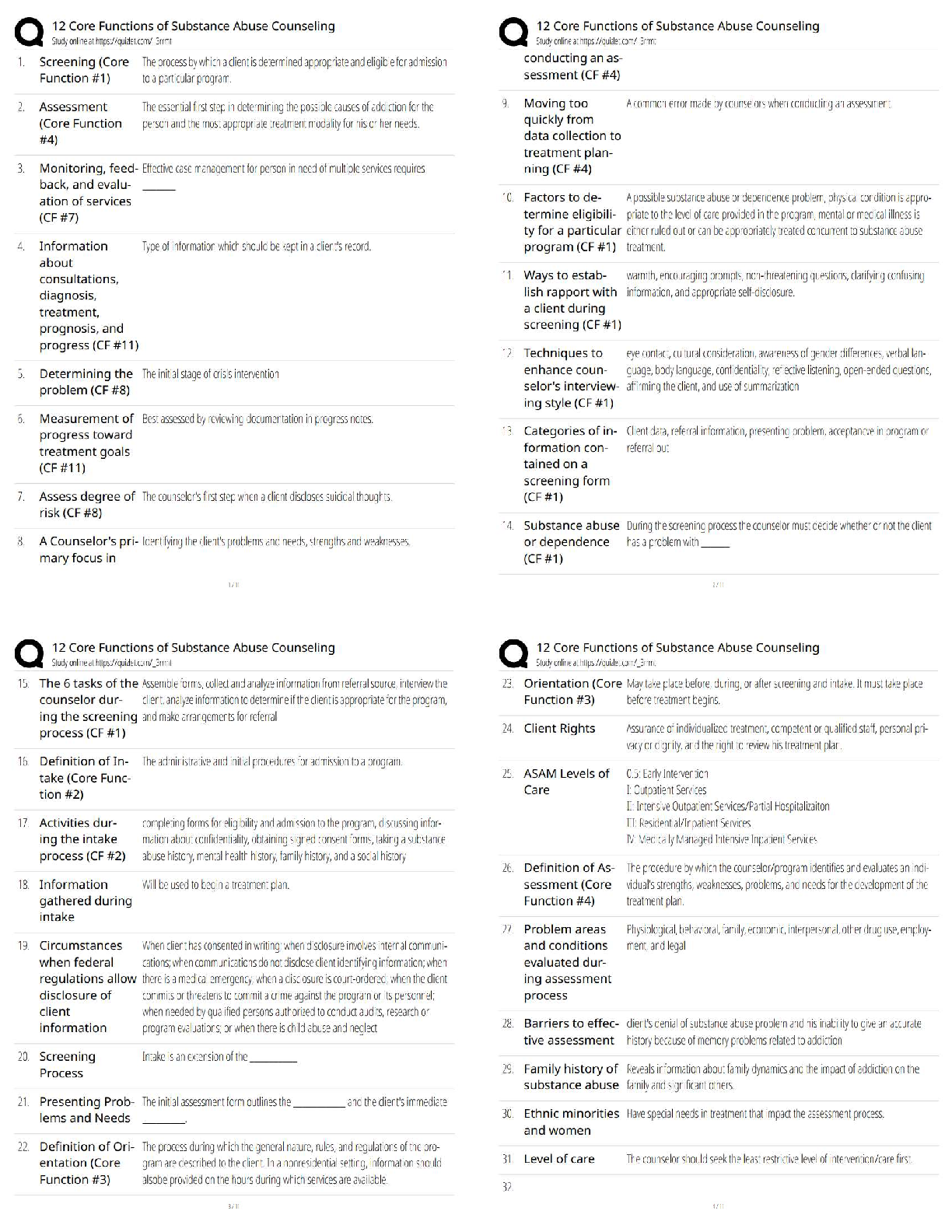
ANS: F
This is referred to as absolute causality.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 55 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
9. An experiment is a carefully controlled study in which the researcher manipulates a proposed cause
and observes any corresponding change in the proposed effect.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 55
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
10. Test marketing studies are a form of experimental research.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 55
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
11. Exploratory research is typically conducted in the early stages of decision-making.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 56
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
12. The first stage in the research process is planning a research design.
ANS: F
This is the second stage in the research process. The first stage is to define the research objectives.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 57 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
13. Properly defining a problem can be more difficult than solving it.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 60
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
14. The purpose of exploratory research is to refine and narrow the scope of the research topic.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 60
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
15. A directed search of published works, including periodicals and books, that discusses theory and
presents empirical results that are relevant to the topic at hand is called a literature review.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 61
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
16. Pilot studies are a formal research method that produce precise results.
ANS: F
A pilot study is a small-scale research project that collects data from respondents similar to those that
will be used in the full study. It can serve as a guide for a larger study or examine specific aspects of
the research to see if the selected procedures will actually work as intended.PTS: 1 REF: p. 61 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
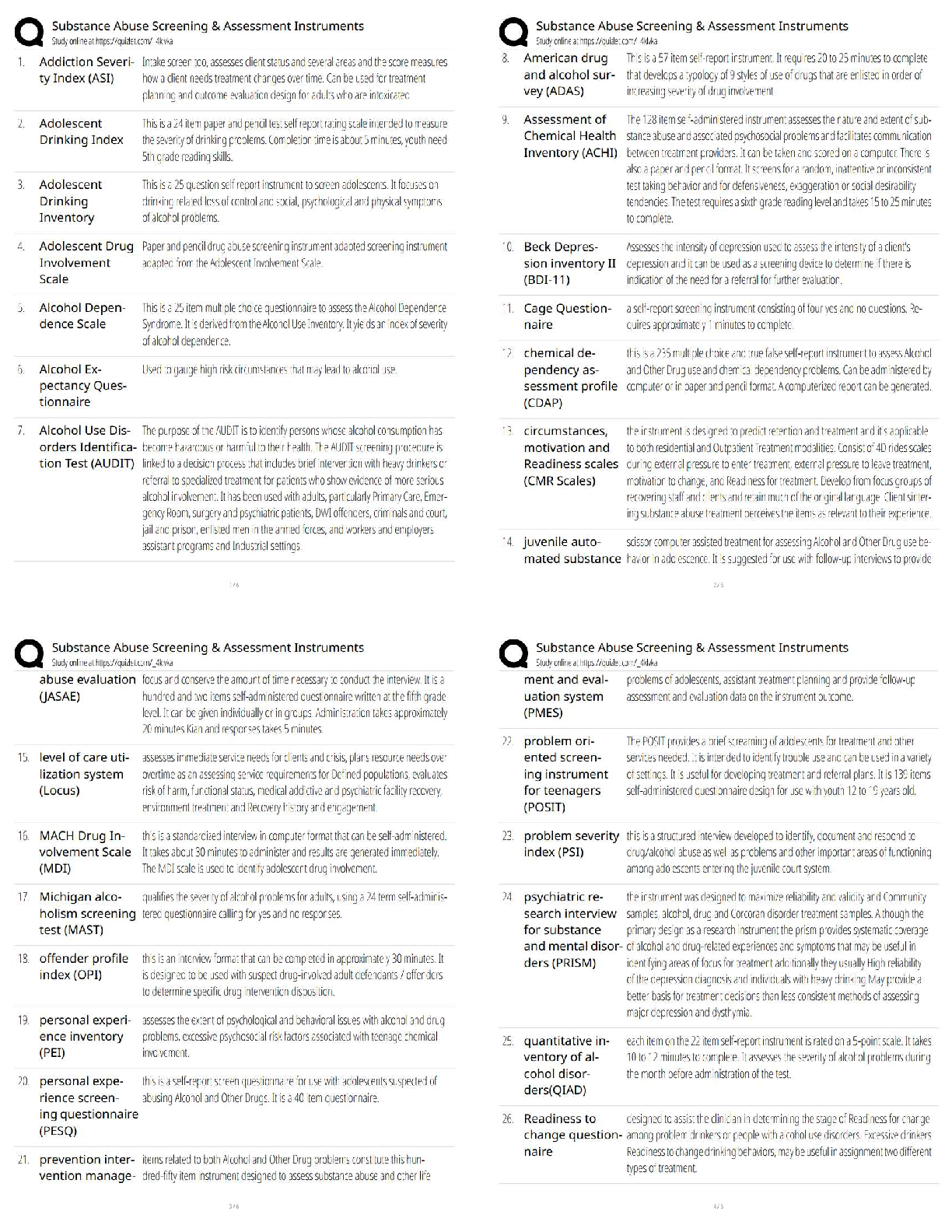
17. In its simplest form, a research hypothesis is a “guess” about the outcome of a research study.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 63
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
18. Statistics can be used to prove that a research hypothesis is true.
ANS: F
Statistics cannot prove a hypothesis is true. Because our results is based on statistics, there is always
the possibility that our conclusion is wrong.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 63 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
19. One of the major advantages of observation studies is that they record actual behavior rather than relying on reports of behavior from respondents.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 64
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
20. There is always one best research design for a marketing research study.
ANS: F
The researcher often has several alternatives that can accomplish the stated research objectives.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 65 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
21. A sample of respondents is a subset of the population of interest to the researcher.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 65
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
22. Unobtrusive methods of data gathering are those in which the subjects do not have to be disturbed for
data to be collected.
ANS: T PTS: 1 REF: p. 66
NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
23. Coding is the application of reasoning to understand the data that have been gathered.
ANS: F
This is data analysis.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 66 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
24. Management is most interested in detailed reporting of the research design and statistical findings.
ANS: F
Frequently, management is not interested in detailed reporting of the research design and statistical
findings, but wishes only a summary of the findings.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 67 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking25. A research project refers to numerous related studies that come together to address issues about a single company.
ANS: F
This is referred to as a research program.
PTS: 1 REF: p. 68 NAT: AACSB: Reflective Thinking
[Show More]










.png)

.png)