Isotopes: Gizmo Lab
Activity A:
Isotope notation
Get the Gizmo ready:
Set protons to 2 and neutrons to 2.
Check that Show isotope notation is selected.
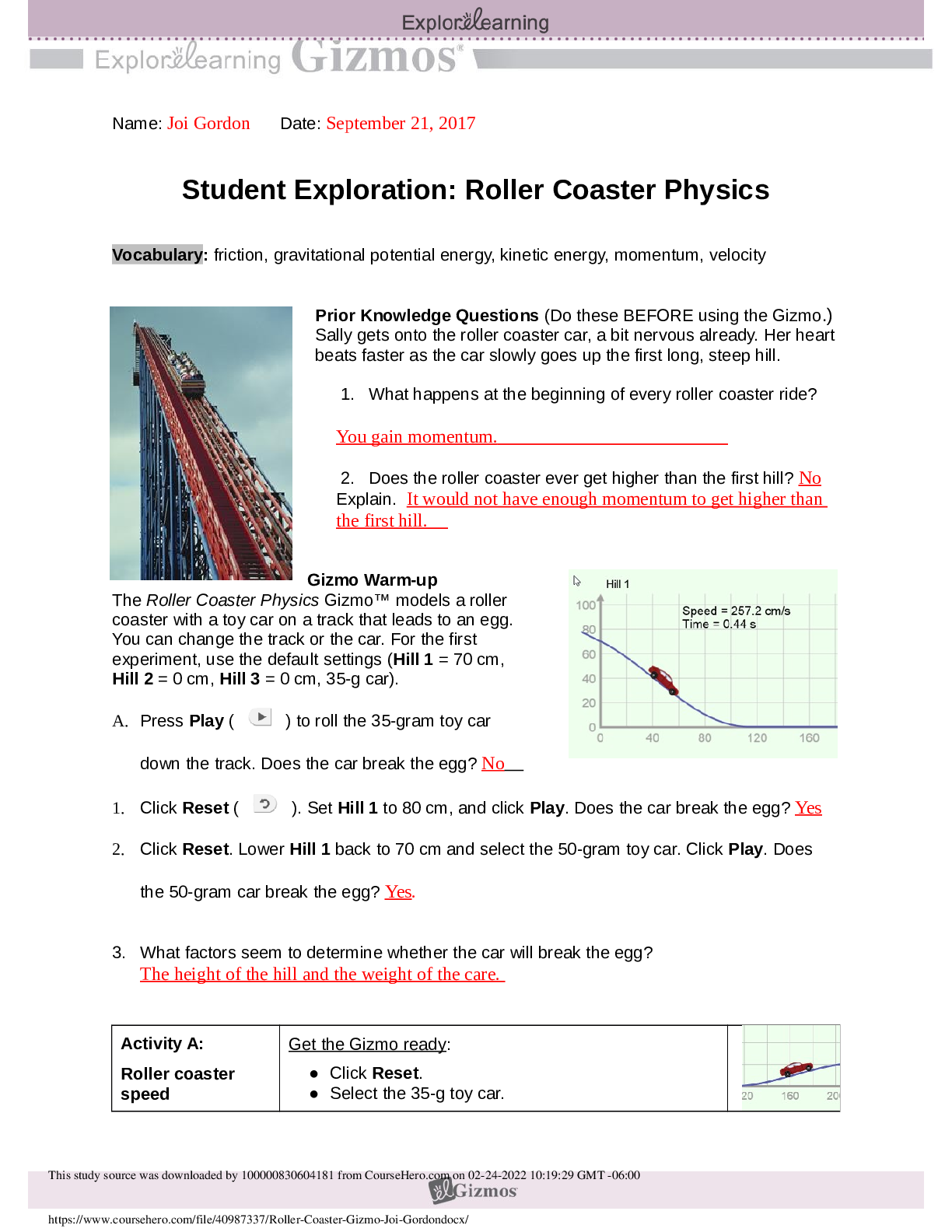
Question: How are isotopes written down?
1. Explore: Belo
...
Isotopes: Gizmo Lab
Activity A:
Isotope notation
Get the Gizmo ready:
Set protons to 2 and neutrons to 2.
Check that Show isotope notation is selected.
Question: How are isotopes written down?
1. Explore: Below the helium atom you see the isotope notation for helium-4. Add and
subtract protons and neutrons a few times using the arrow buttons. Notice how the isotope
notation changes when you do this.
A. What does the top number equal? Mass Number
B. Which particle determines the atomic number? Atomic Number
In isotope notation there are two numbers to the left of the element
symbol. The top number is the mass number (A). The mass number
is the sum of the protons and neutrons. The bottom number is the
atomic number (Z). The atomic number is the number of protons.
2. Apply: Turn off Show isotope notation. Set protons to 3 and neutrons to 4.
Write this isotope using isotope notation. Check your answer in the Gizmo.
7 3
Li
3. Observe: Set the protons to 8 and the neutrons to 9.
A. How is the isotope written at the top left of the gray box?
Oxygen – 17: Stable
This isotope makes up 0.38% of the element.
B. What does the number next to the element name indicate? Mass
4. Practice: Turn off Show isotope notation. Use what you have learned to fill in the table.
When you are finished, check your answers in the Gizmo.
Protons Neutrons Mass number Isotope notation Symbol
17 18 35 Chlorine-35 Cl
1 0 1 Hydrogen-1 H
26 30 56 Iron-56 Fe
14 17 31 Silicon-31 Si
95 148 243 Americium-243 Am
Activity B:
Band of stability
Get the Gizmo ready:
On the graph, make sure the x-axis and y-axis
range from 0-20. If not, click the [o] zoom control.
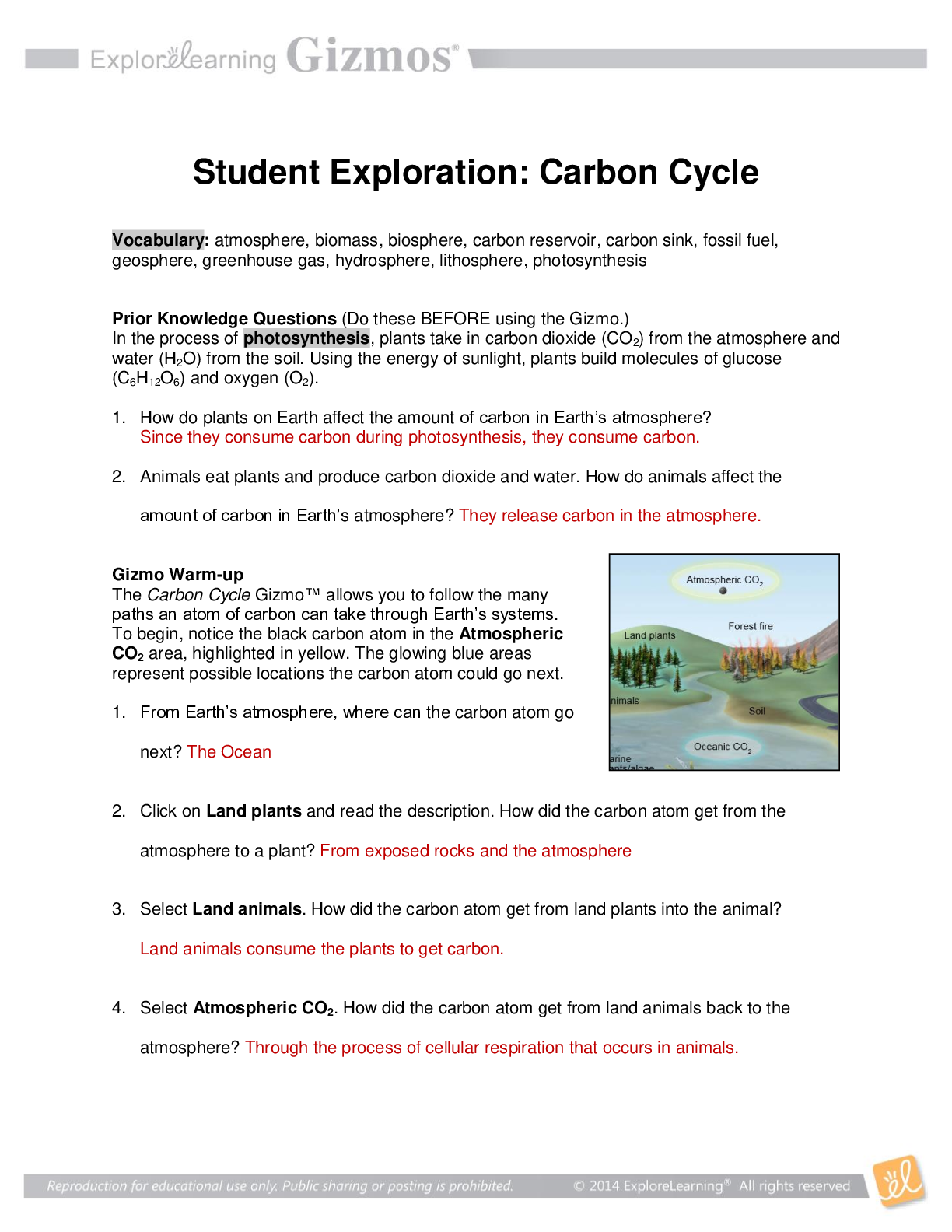
Introduction: Some atoms are stable, while others are radioactive. In a radioactive atom, the
nucleus has the potential to break down, or decay, and change into a different element. For
example, radon-222 is radioactive. When it decays, its nucleus loses enough protons and
neutrons to become polonium-218. Radioactive isotopes are also called radioisotopes.
Question: How can we predict whether an isotope will be stable or radioactive?
1. Observe: Use the Gizmo to create a carbon-12 isotope.
A. Is this isotope stable or radioactive? Stable
B. Add a neutron to create carbon-13. Is this isotope stable or radioactive? Stable
C. Add another neutron. Is this isotope stable or radioactive? Radioactive
D. What is the half-life of this isotope? 5730 yr.
The half-life of a radioisotope is the time it takes for 50% of the atoms in a sample to decay.
The shorter the half-life, the more unstable the nucleus
[Show More]