Student Exploration: Titration
Vocabulary: By the end of the Gizmo, please familiarize yourself with the following
analyte
titrant
equivalence point
indicator
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gi
...
Student Exploration: Titration
Vocabulary: By the end of the Gizmo, please familiarize yourself with the following
analyte
titrant
equivalence point
indicator
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
There are several definitions of acids and bases. According to the
Brønsted-Lowry definition, an acid is a substance that is capable of
donating a proton to another substance. A base is a substance that
accepts protons. When an acid and a base are combined, the acid is
neutralized as the base accepts the protons produced by the acid.
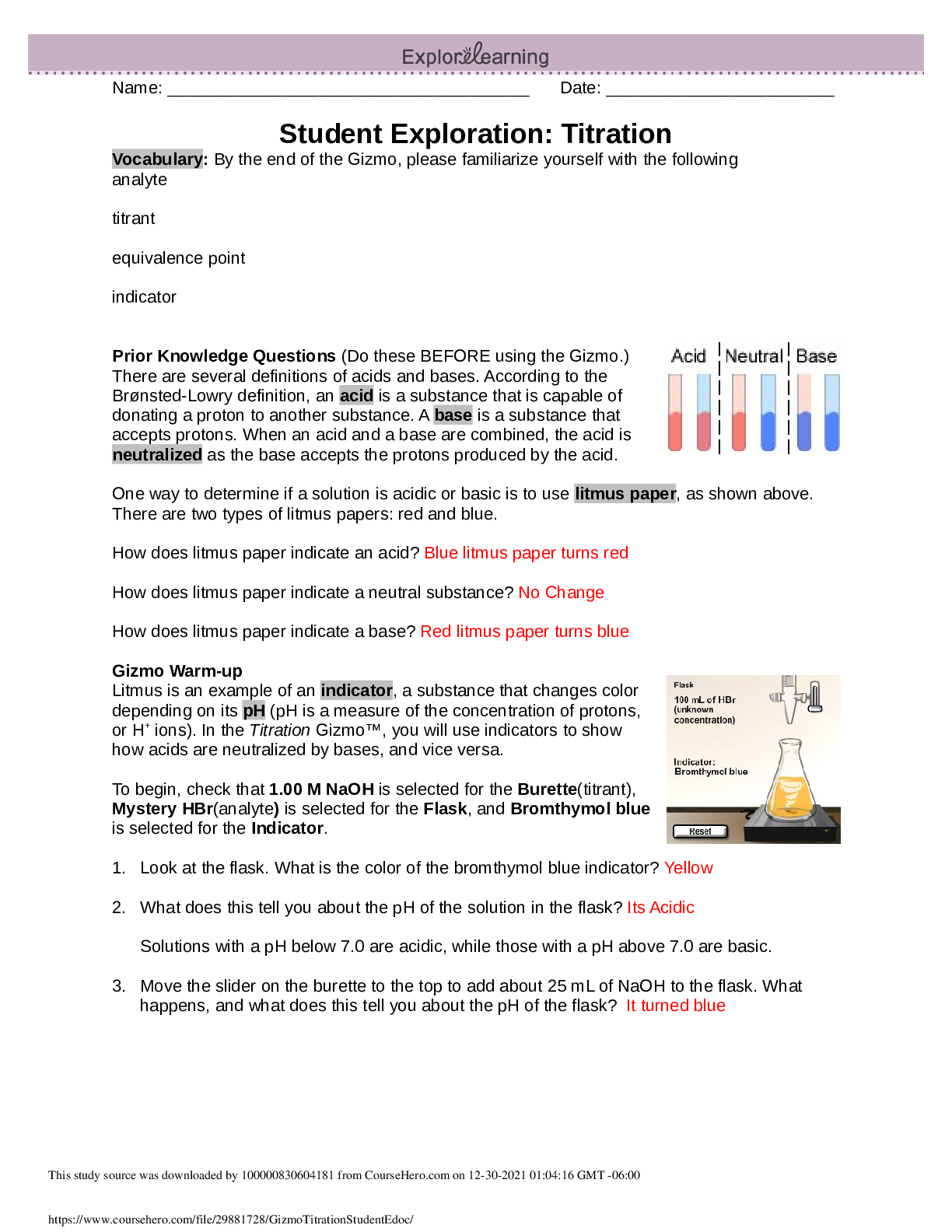
One way to determine if a solution is acidic or basic is to use litmus paper, as shown above.
There are two types of litmus papers: red and blue.
How does litmus paper indicate an acid? Blue litmus paper turns red
How does litmus paper indicate a neutral substance? No Change
How does litmus paper indicate a base? Red litmus paper turns blue
Gizmo Warm-up
Litmus is an example of an indicator, a substance that changes color
depending on its pH (pH is a measure of the concentration of protons,
or H+ ions). In the Titration Gizmo™, you will use indicators to show
how acids are neutralized by bases, and vice versa.
To begin, check that 1.00 M NaOH is selected for the Burette(titrant),
Mystery HBr(analyte) is selected for the Flask, and Bromthymol blue
is selected for the Indicator.
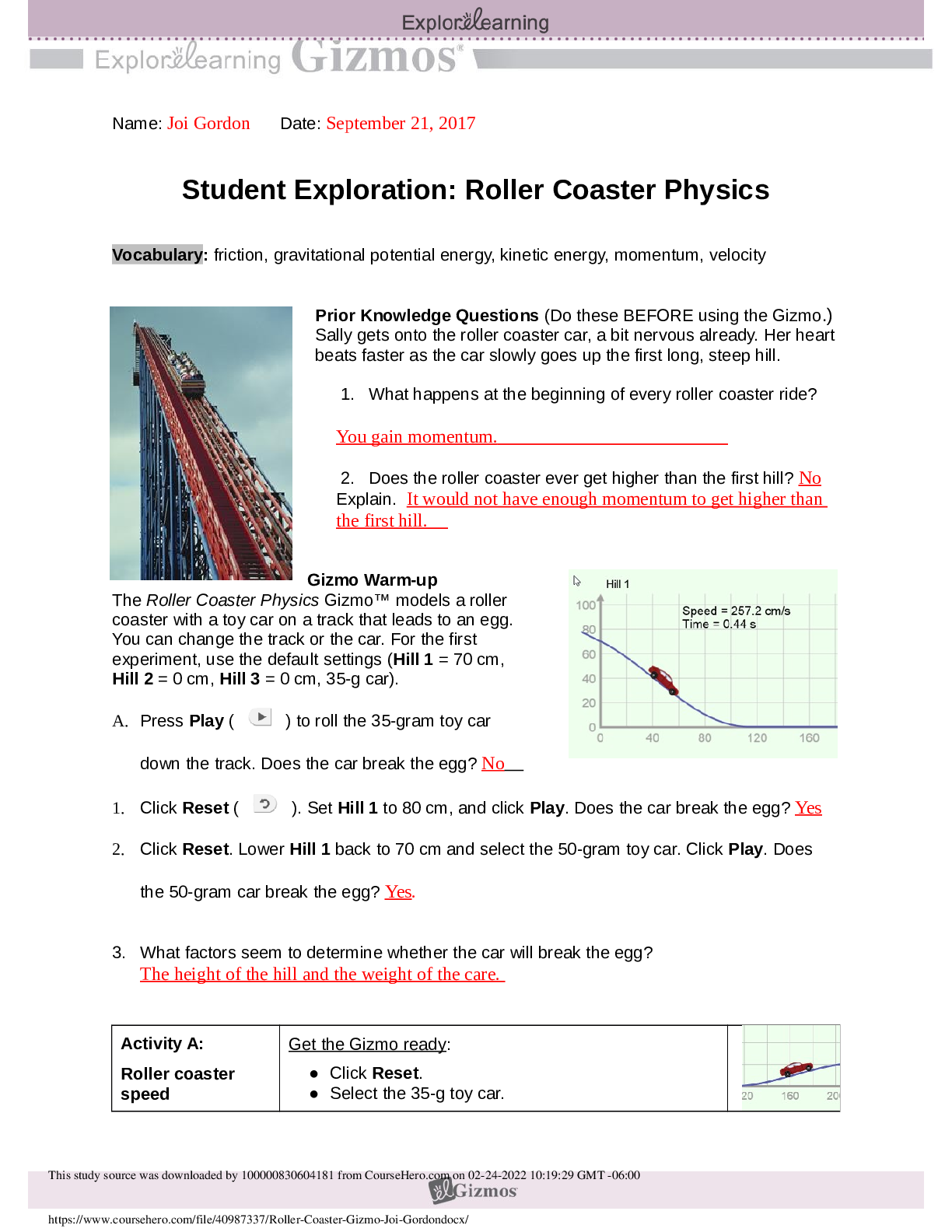
1. Look at the flask. What is the color of the bromthymol blue indicator? Yellow
2. What does this tell you about the pH of the solution in the flask? Its Acidic
Solutions with a pH below 7.0 are acidic, while those with a pH above 7.0 are basic.
3. Move the slider on the burette to the top to add about 25 mL of NaOH to the flask. What
happens, and what does this tell you about the pH of the flask? It turned blue
Activity A:
Acids and bases
Get the Gizmo ready:
Click Reset. Select 1.0 M HNO3 for the Burette
and Mystery NaOH for the Flask.
Select Phenolphthalein for the Indicator.
You will need a scientific calculator for this activity.
Introduction: When most acids dissolve in water, they dissociate into ions. For example, nitric
acid (HNO3) dissociates into H+ and NO3– ions.
Question: How do acids and bases interact in solution?
1. Calculate: Concentration is measured by molarity (M), or moles per liter. Brackets are also
used to symbolize molarity. For example, if 0.6 moles of HNO3 are dissolved in a liter of
water, you would say [HNO3] = 0.6 M.
A. Because HNO3 is a strong acid, it dissociates almost completely in water. That
means the concentration of H+ is very nearly equal to that of HNO3.
What is [H+] if [HNO3] is 0.01 M? 0.01M it is the same
B. The pH of a solution is equal to the negative log of H+ concentration: pH = –log[H+]
What is the pH of this solution? (Use the “log” button on your calculator.) 2
C. What is the pH of a 0.6 M HNO3 solution? 0.2
2. Describe: The equation for the reaction of nitric acid (HNO3) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
is shown on the bottom right of the Gizmo.
A. What are the reactants in this reaction? HNO3 and NaOH
B. What are the products of this reaction? NaNO3 and H2O
[Show More]