Meiosis GIZMO-ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
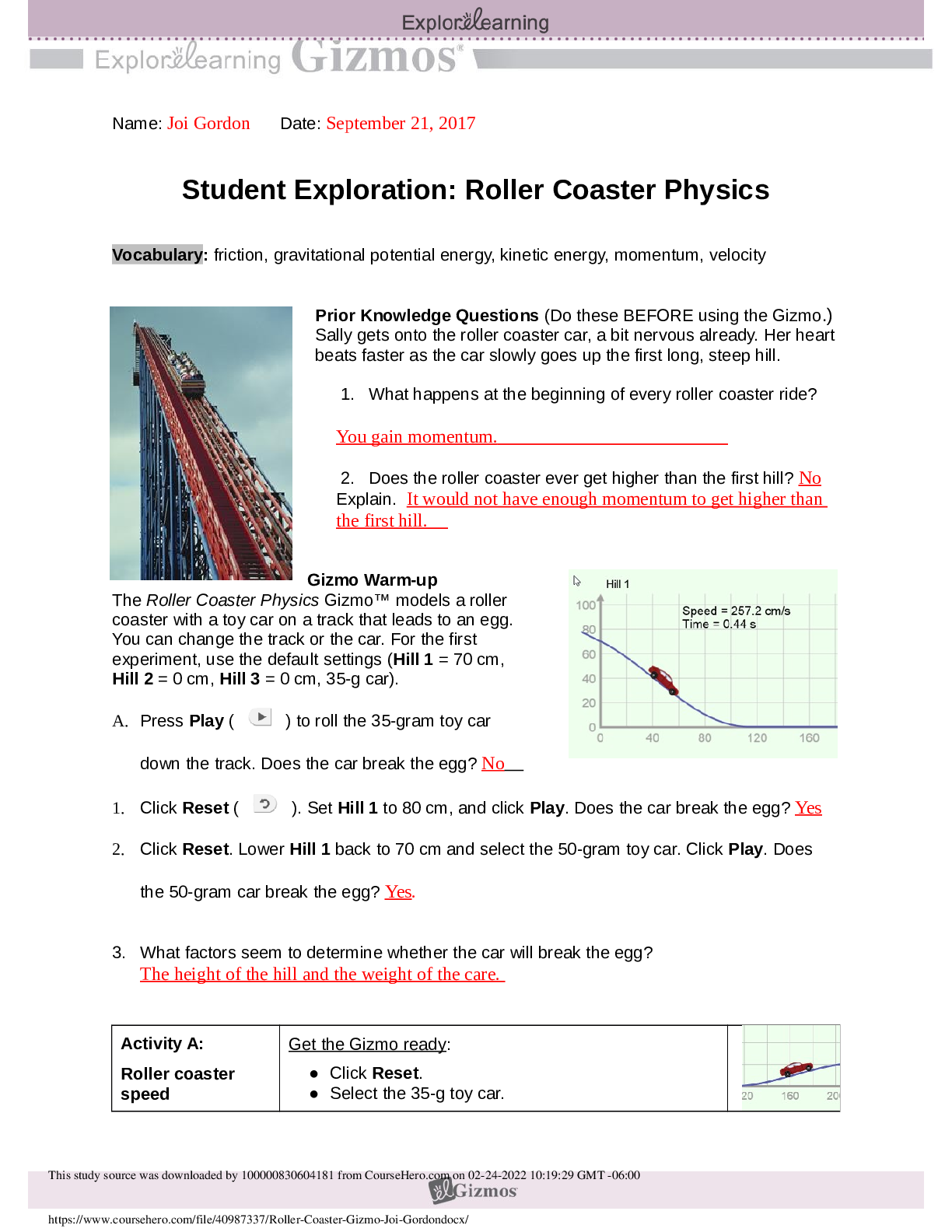
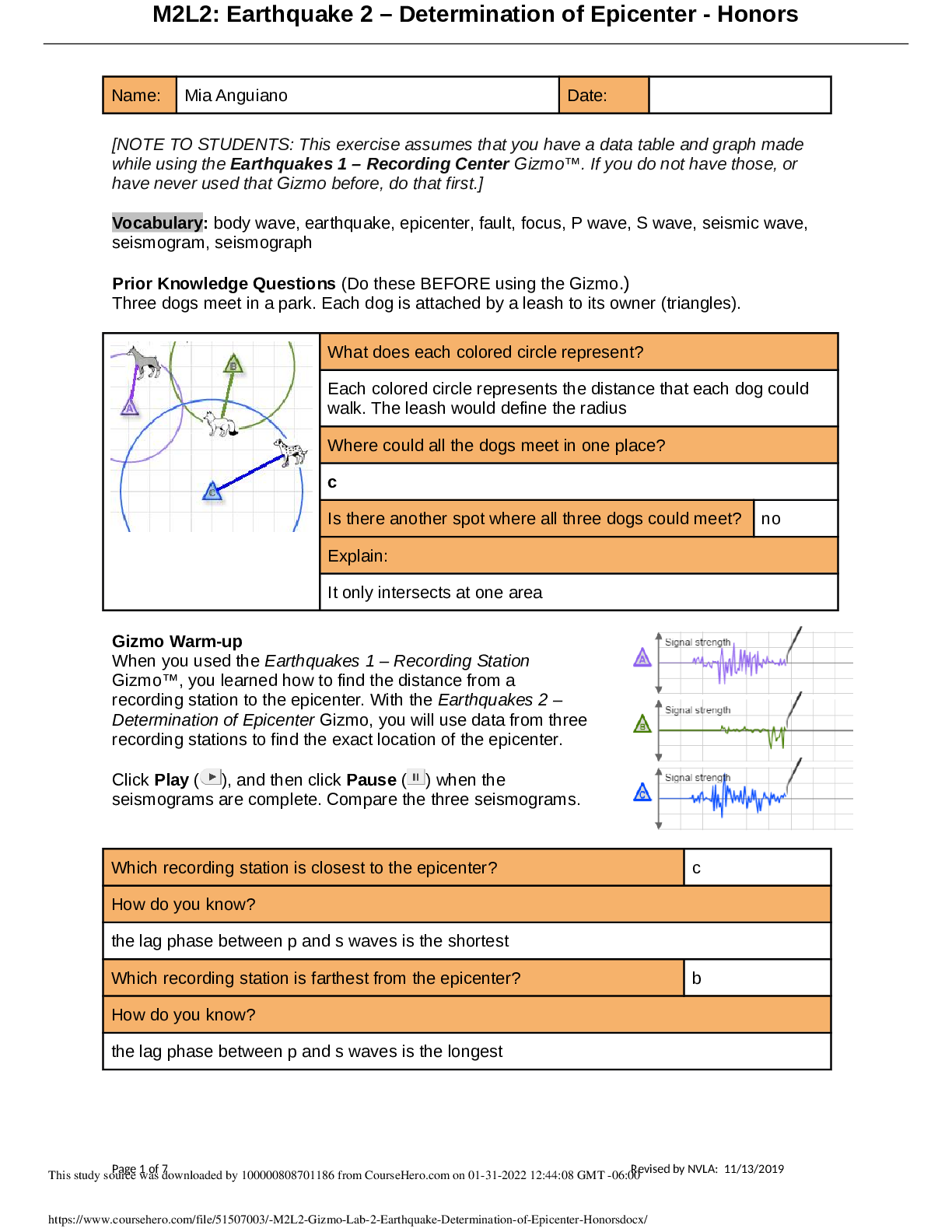
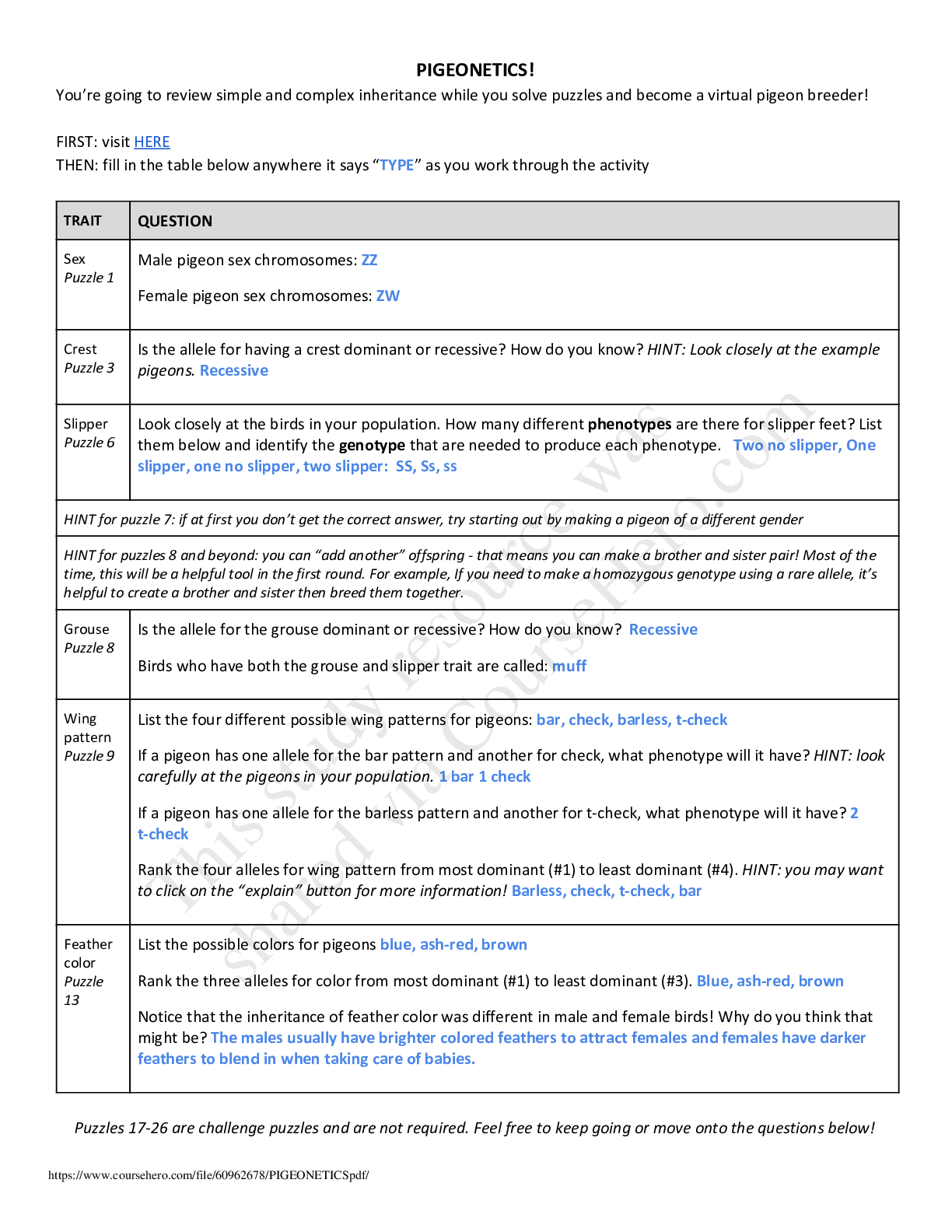
Student Exploration: Meiosis Vocabulary: anaphase, chromosome, crossover, cytokinesis, diploid, DNA, dominant, gamete, genotype, germ cell, haploid, homologous chromosomes, interphase, meiosis, meta... phase, mitosis, ovum, phenotype, prophase, recessive, sister chromatid, sperm cell, telophase, zygote Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. During mitosis, a single cell divides to produce two daughter cells. What must happen in the original cell so that each of the daughter cells has a complete set of chromosomes? The DNA must replicate 2. During sexual reproduction, two sex cells fuse to create a fertilized cell with a complete set of chromosomes. What must be true about the number of chromosomes in each sex cell? There must be 2 one x and one y or both X. Gizmo Warm-up Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells mature into gametes, or sex cells. In the Meiosis Gizmo, you will learn the steps in meiosis and experiment to produce customized sex cells and offspring. On the STEPS tab, click Male. You are looking at a germ cell, or a cell that will undergo meiosis to become gametes. 1. Read the description of interphase at the bottom of the Gizmo. What happens to the cell at the beginning of interphase? The cell grows in size and doubles its organelles. 2. Click on the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. Describe what happens. The DNA duplicates and allows the cell to continue to grow 3. Why is it necessary for the cell to grow and duplicate its DNA before the start of meiosis?Because when a parent cell undergoes mitosis it divides into two daughter cells and they all need DNA thats why before mitosis takes place there must be a duplicate of the DNA. Introduction: Unlike mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell, meiosis creates four unique daughter cells with half the amount of DNA as the parent cell. Question: How does meiosis create four daughter cells from one parent cell? 1. Observe: (Prophase I) Click on the nucleus to break it down then click on the DNA to condense it into chromosomes. Drag the centrosomes to the top and bottom of the cell. A. How many chromosomes does this cell have? 2 Each chromosome consists of a pair of sister chromatids, two identical strands of DNA that formed when DNA replicated during interphase. B. On the image to the right, draw two lines connecting the pairs of homologous chromosomes (chromosomes of similar size with a matching set of genes). In the Gizmo, drag the homologous chromosomes together. Click Continue. 2. Observe: (Metaphase I and Anaphase I) - Drag the groups of homologous chromosomes to the metaphase plate, then drag spindle fibers from each of the centrosomes to the chromosomes. Click the centrosome to pull the chromosomes apart. How do the chromosomes separate in anaphase I? The centrosomes attach spindle fibers to each mom the chromosomes to pull them apart and to opposites sides of the cell. 3. Compare: An image of the anaphase step in mitosis is shown to the right. A. How does anaphase I in meiosis differ from anaphase in mitosis? key difference between mitosis and meiosis is that sister chromatids remain joined during Activity A: Steps in meiosis Get the Gizmo ready: • Make sure the STEPS tab is selected. • If necessary, choose the Male cell. Click on the DNA to copy it to proceed to prophase I. !anaphase I in meiosis , whereas in ana [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 26, 2021
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 26, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
145














.png)
.png)


.png)




