Concise Introduction To Logic 13th Edition By Patrick J. Hurley, Lori Watson | TEST BANK
$ 18

Sophia Psychology Milestone 1
$ 11

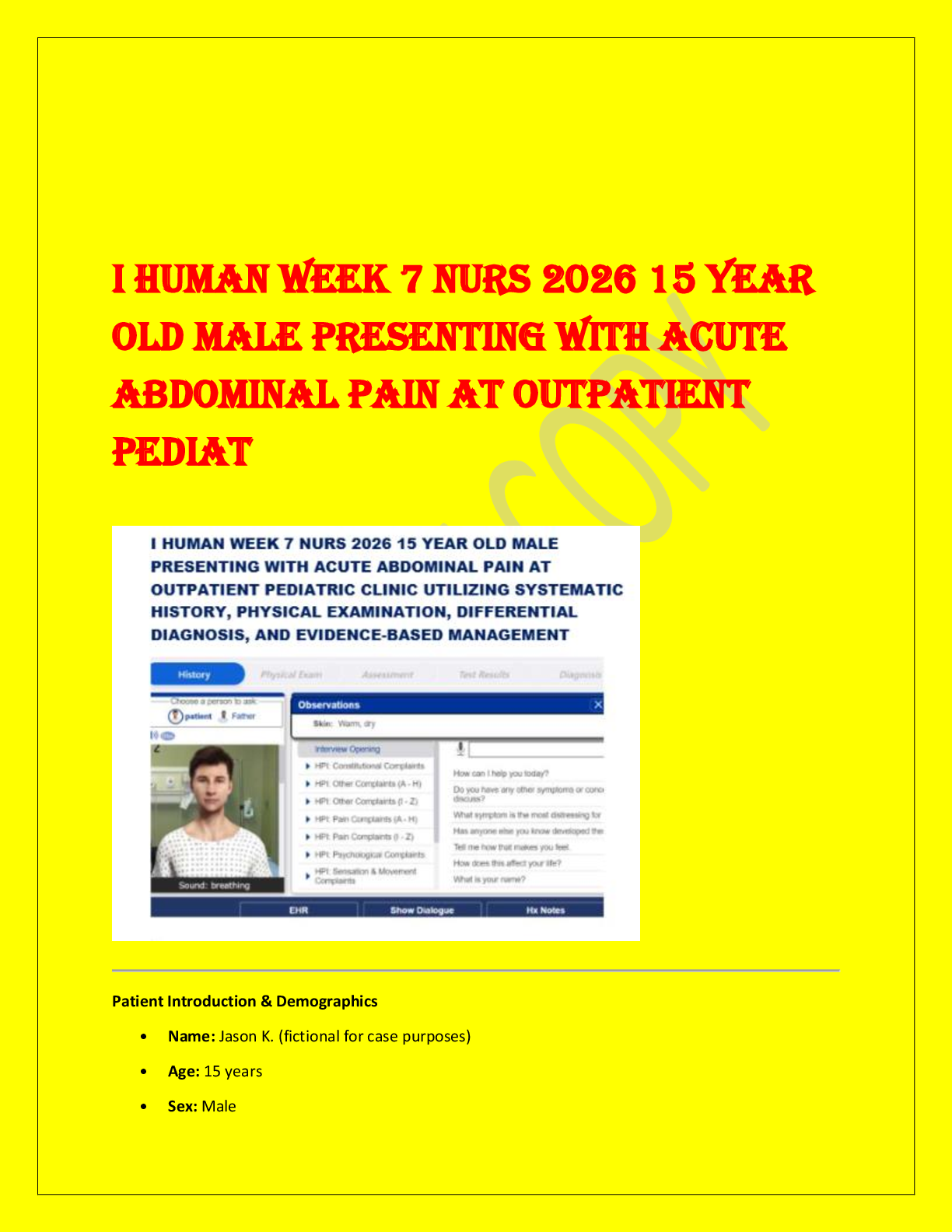
NR 602 MAX KING IHUMAN- LEAKING STOOL STUDY CASE LATEST UPDATE 2025
$ 22

CAT EXAM 1-HESI EXIT 2022
$ 10.5

AQA A-level CHEMISTRY 7405/2 Paper 2 Organic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 7

AQA A-level CHEMISTRY 7405/3 Paper 3 Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 7

3P CARDIOVASCULAR LATEST EXAM 2023.docx
$ 13

TEST_BANK_For_Edmunds'_Pharmacology_for_the_Primary_Care_Provider
$ 15

ATI Pharmacology Final Review 2021 Questions & Anwers
$ 15

BMGT380-MIDTERM ONE Exam Questions and Answers
$ 8

Solution Manuals for Absolute Java, 4E Walter Savitch
$ 23.5

CERTIFIED MEDICAL ASSISTANT PRACTICE EXAM COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE EXAM SOLUTION
$ 10

AQA June 2022 Question Paper A-level CHEMISTRY Paper 1 Inorganic and Physical Chemistry 7405/1
$ 7

REVISION SCIENCE TO EXCEL IN A-LEVEL PHYSICS A-levelPHYSICS7408/3BD Paper 3
$ 11.5

DPSS 0412 Research-Digest-Matrix 2020 – Saint Louis University | GPCOM: PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Final Examination
$ 11.5

WGU C201 Business Acumen Objective Assessment 2025 Study Guide
$ 16

EFM NCC Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
$ 10

LCDC IC&RC exam review 2017 test 1 Questions and answers. 100% accurate. Graded A+
$ 8
.png)
AZ NMLS Test Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

Sunny Hills HighBIO 420Elizabeth Kim - Unit 6 Review_ Gene Expression and Regulation. TOPIC 6.1 DNA and RNA Structure. Questions and Answers 2021 updated
$ 11

HESI CHEMISTRY V1/V2 - QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1.
$ 12.5

NUR 417 Final Genomics Study Guide, 279 Terms, Study Guide Material Questions and Answers with Explanations (latest Update), 100% Correct, Download to Score A
$ 35

Test Bank for Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation 7th Edition by Cairo Complete Solution
$ 15

US History I Unit 3 Challenge 1. | 100% CORRECT
$ 12

Understanding Pathophysiology 6th Edition Huether Test Bank|Huether & McCance: Understanding Pathophysiology, 6th Edition (complete A+ guide)
$ 18
.png)
> GCE History A Y212/01: The American Revolution 1740-1796 Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for Autumn 2021
$ 10
.png)
Sterile Processing - Final Exam, IAHCSMM CENTRAL SUPPLY STUDY GUIDE, Sterile Processing Study Material for Certification Exam
$ 15

Solution Manual for Concepts of Genetics 4th Edition
$ 23.5
CCRN VIDEO PRACTICE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NEW 2022 EXAM
$ 11.5

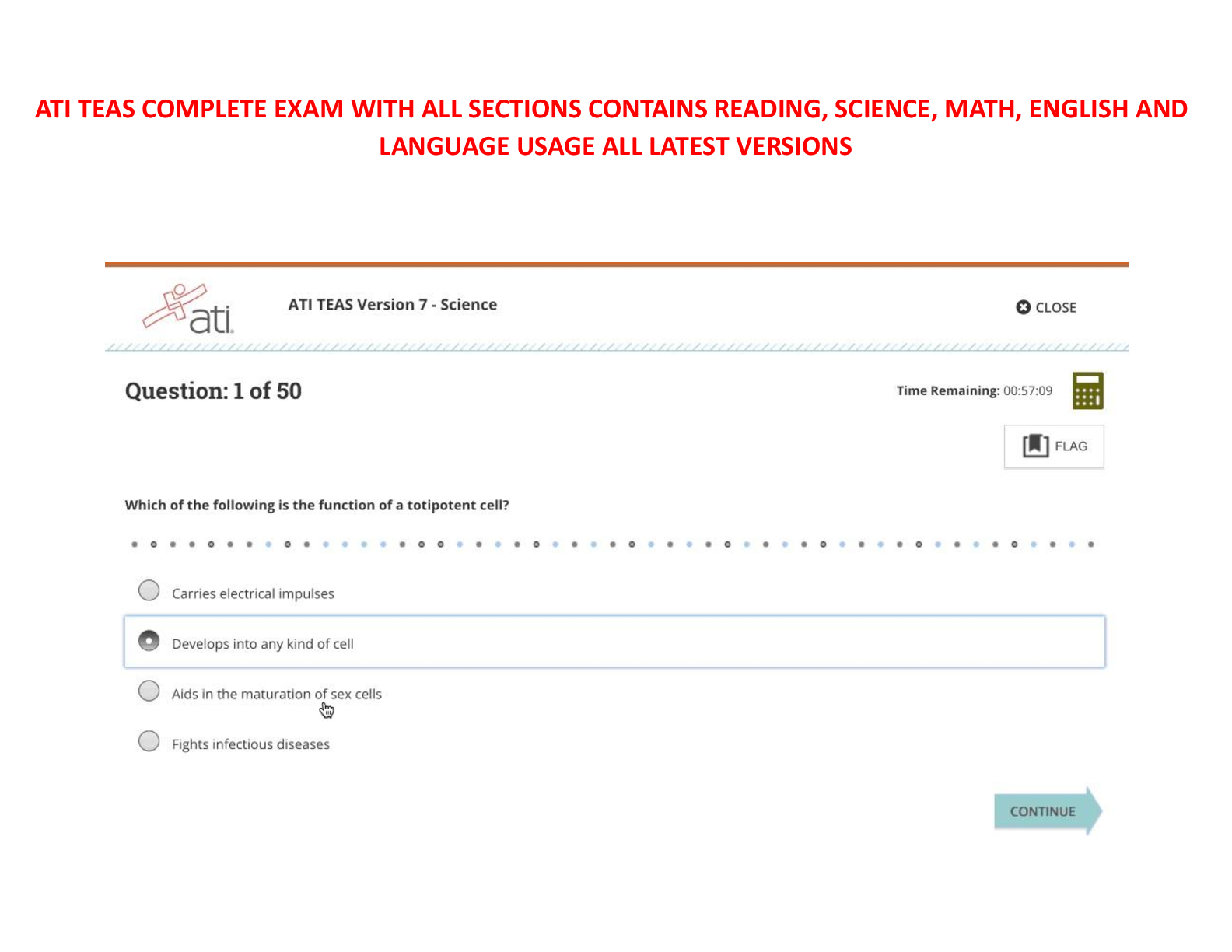
TEAS 7 READING V1&V2
$ 60

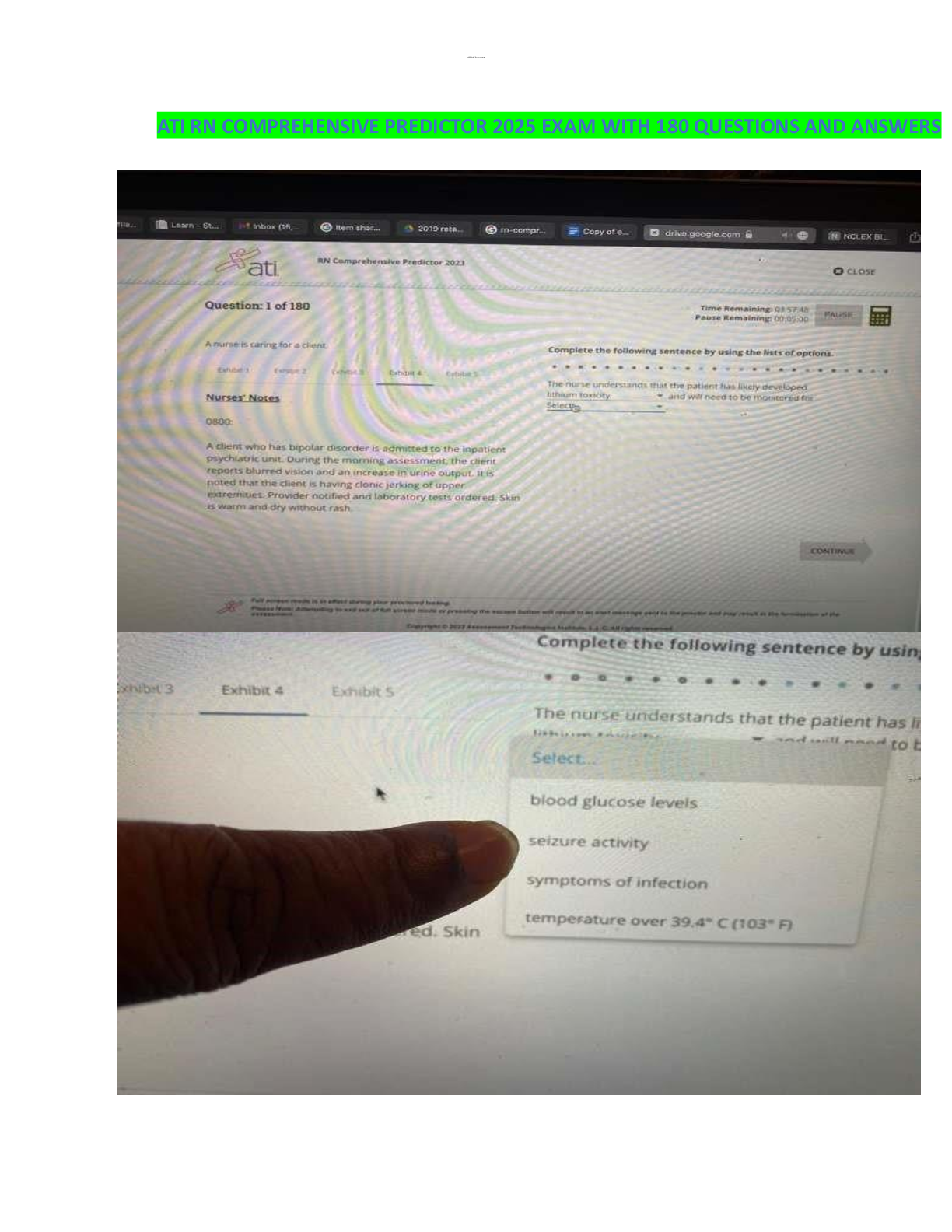
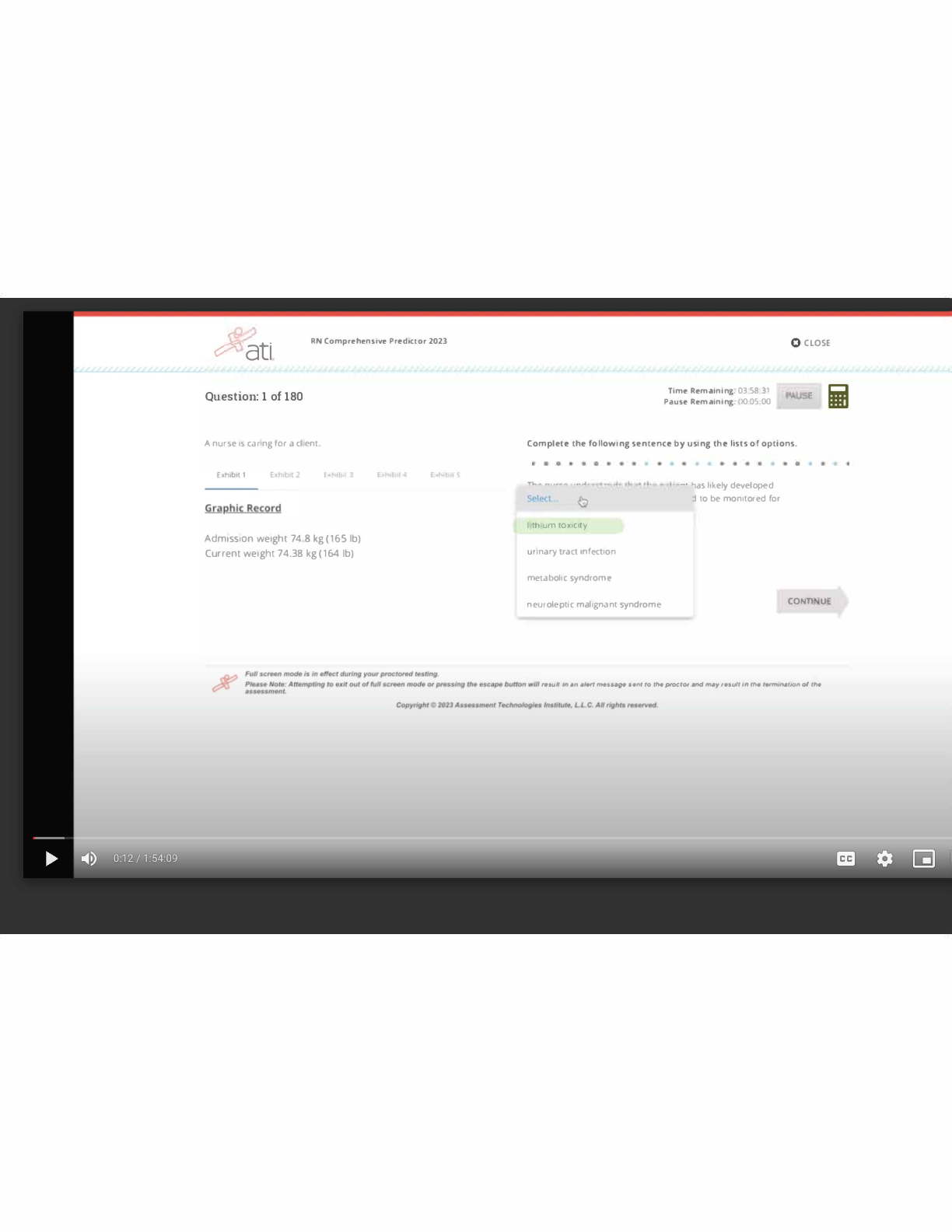
ATI nutrition, ATI Nutrition Proctored Exam Study Set Questions and Answers 2023/2024
$ 8

Pharm Exam 2 Pharmacological Basis For Nursing Interventions I
$ 10

Sophia – US History II – Milestone 3 Final,100% CORRECT
$ 14

NURS 501 Advanced Physiology and Pathophysiology Chapter 1: Cellular Biology Study Guide





.png)



.png)
.png)