NUR 227 MN Oxygenation Notes.odt
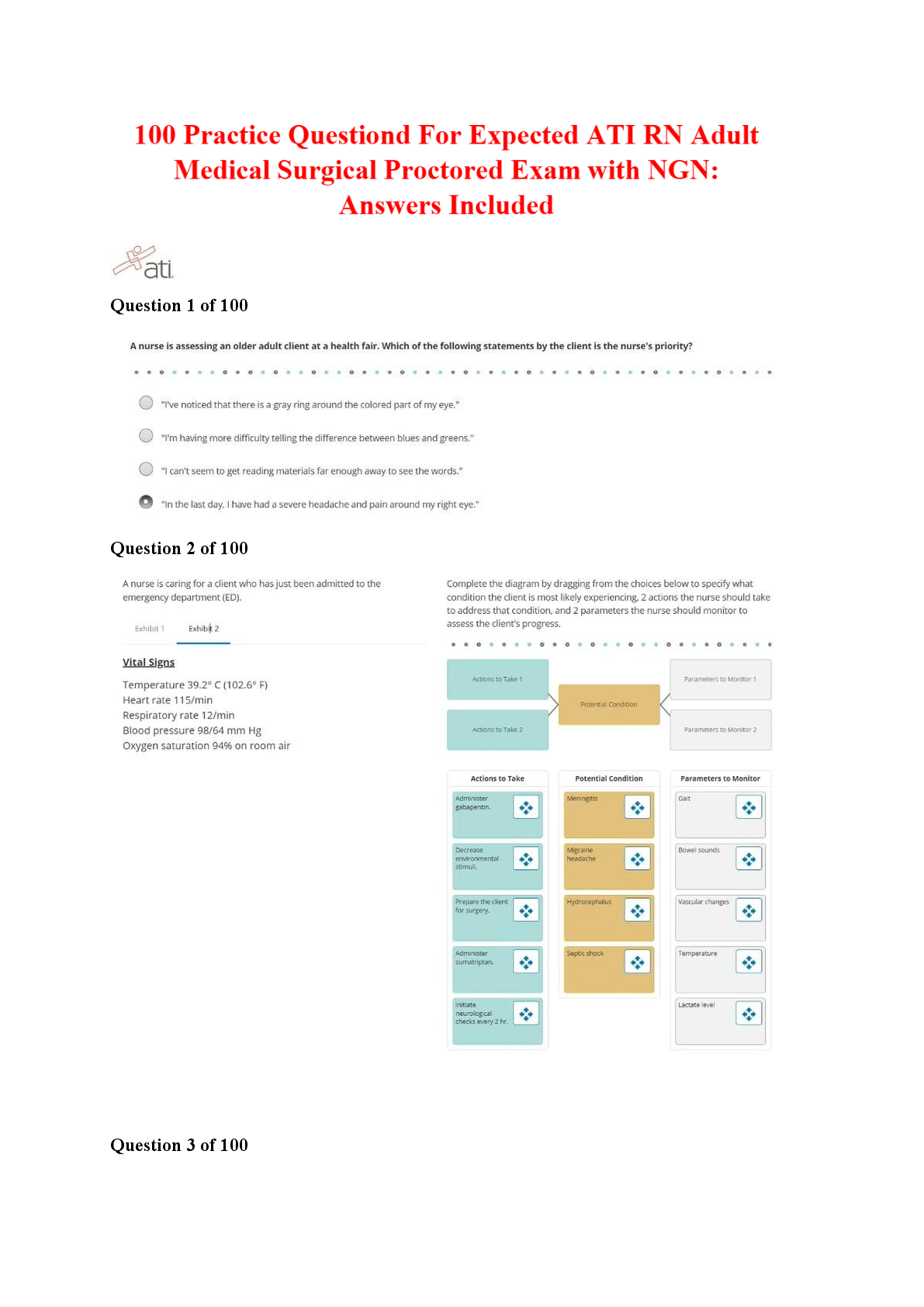
Extrauterine Transition of the Respiratory System
Step 1: In Utero
Step 2: During Labor & Delivery
Step 3: At Birth
o Crying at birth continues to promote positive pressure, air
...
NUR 227 MN Oxygenation Notes.odt
Extrauterine Transition of the Respiratory System
Step 1: In Utero
Step 2: During Labor & Delivery
Step 3: At Birth
o Crying at birth continues to promote positive pressure, air in the lungs, and therefore alveoli expansion.
o Gasping reflex stimulated from noise, light, cooler temperature, increased CO2, decreased O2, handling.
Newborn Respiratory Assessment
o Count Respiratory Rate
o Breath Sounds
o Oxygen Saturation
–
o Pattern
o Chest Expansion
– Expected: Symmetrical
– Deviations: Retractions
o Mucous Membranes
o Periodic Breathing
o Signs of Respiratory Distress
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
o Mild respiratory distress caused by a delay in lung fluid clearance that resolves in 24-72 hours.
o Risk factors:
– Mom heavily sedated during labor and delivery
– Born via cesarean section.
o Symptoms:
– Tachypnea
– Grunting
– Mild intercostal retractions
– Decreased breath sounds due to reduced air entry
– Labored respirations
– Nasal flaring
– Mild cyanosis
o Diagnosis:
– Chest x-ray
– ABG (arterial blood gas)- degree of gas exchange and acid-base balance.
o Nursing Management: Supportive care based on symptoms.
– Adequate oxygenation (O2 via NC or hood for good O2 sat)
– May need IV fluids or gavage feedings; PO feeds ONLY if respiratory rate WNL
– Neutral thermoenvironment
– Minimal stimulation to minimize O2 demand
Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Resulting from lung immaturity and lack of alveolar surfactant (reduces surface tension and prevents collapse of alveoli). Self-limiting, symptoms decline after 72 hrs.
o Risk factors: (All impact surfactant production!)
– Preterm birth
– Perinatal asphyxia
– Neonatal sepsis
– Born via cesarean section
– Male gender
– Maternal diabetes
o Symptoms are shown at birth or within a few hours:
– Grunting
– Nasal flaring
– Retractions
– Seesaw respirations
– Cyanosis
– Tachycardia
– Crackles
– Tachypnea
o Diagnosis:
o Presenting symptoms
o Chest x-ray
o Rule out any underlying causes such as infection, sepsis
o Nursing Management: Supportive based on symptoms
o O2 with mechanical vent, CPAP, NC, PEEP, surfactant therapy
o Maintain body temperature
o Maintain fluid balance
o Provide nutrition
o Maintain circulation for tissue perfusion
o Monitor O2 saturation
o Suction via bulb syringe or deep suction
o Cluster care
Antenatal Glucocorticoid Therapy
MEDICATION /
DOSE / ROUTE CLASS / ACTION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING
IMPLICATIONS
Betamethasone (Celestone)
12 mg IM for two doses 24 hours apart
(Oxygenatio n) Corticosteroid:
*Stimulates fetal lung maturity by promoting release of enzymes that induce production or release of lung surfactant
*To prevent or reduce respiratory *May worsen maternal conditions such as DM or HTN *Give deep IM in ventral gluteal or vastus lateralis muscle
*Assess blood glucose
*Administer two doses intramuscularly 24 hr apart.
distress for fetuses b/n 24-34 weeks *Monitor for maternal infection or pulmonary edema.
*Educate parents about potential benefits of drug to preterm infant.
Assess maternal lung sounds and monitor for signs of infection.
[Show More]




.png)