NSG5003 ADVANCED PATHOPHYSIOLOGY|WEEK 10 FINAL GUIDE 2021
$ 13.5

OCR A LEVEL JUNE 2022 HISTORY A - LIBERALS, CONSERVATIVES AND THE RISE OF LABOUR - QUESTION PAPER
$ 1

ATI TEAS 7 SCIENCE EXAM 2023 WITH ALL THE ANSWERS COMPLETE A+

.png)
.png)








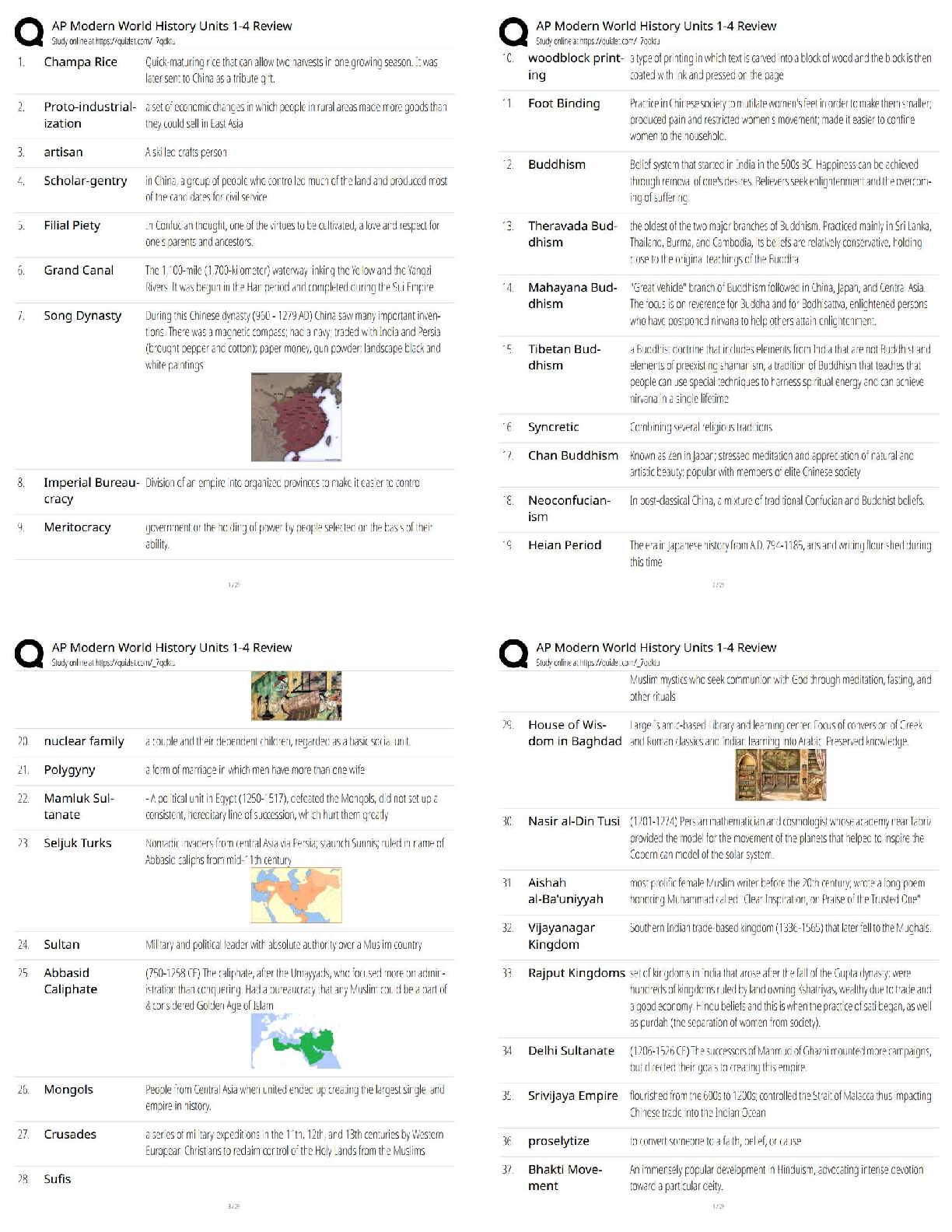
.png)

.png)