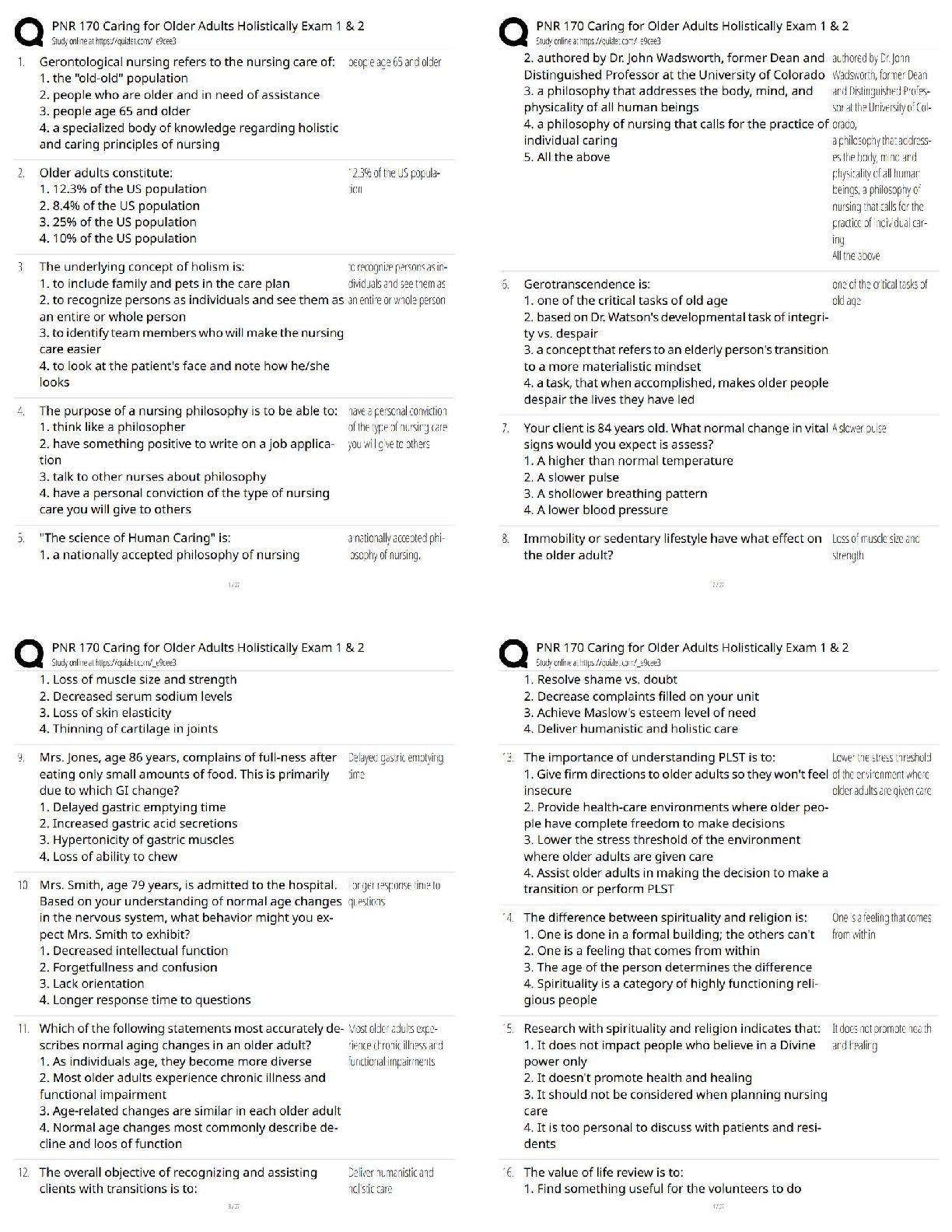
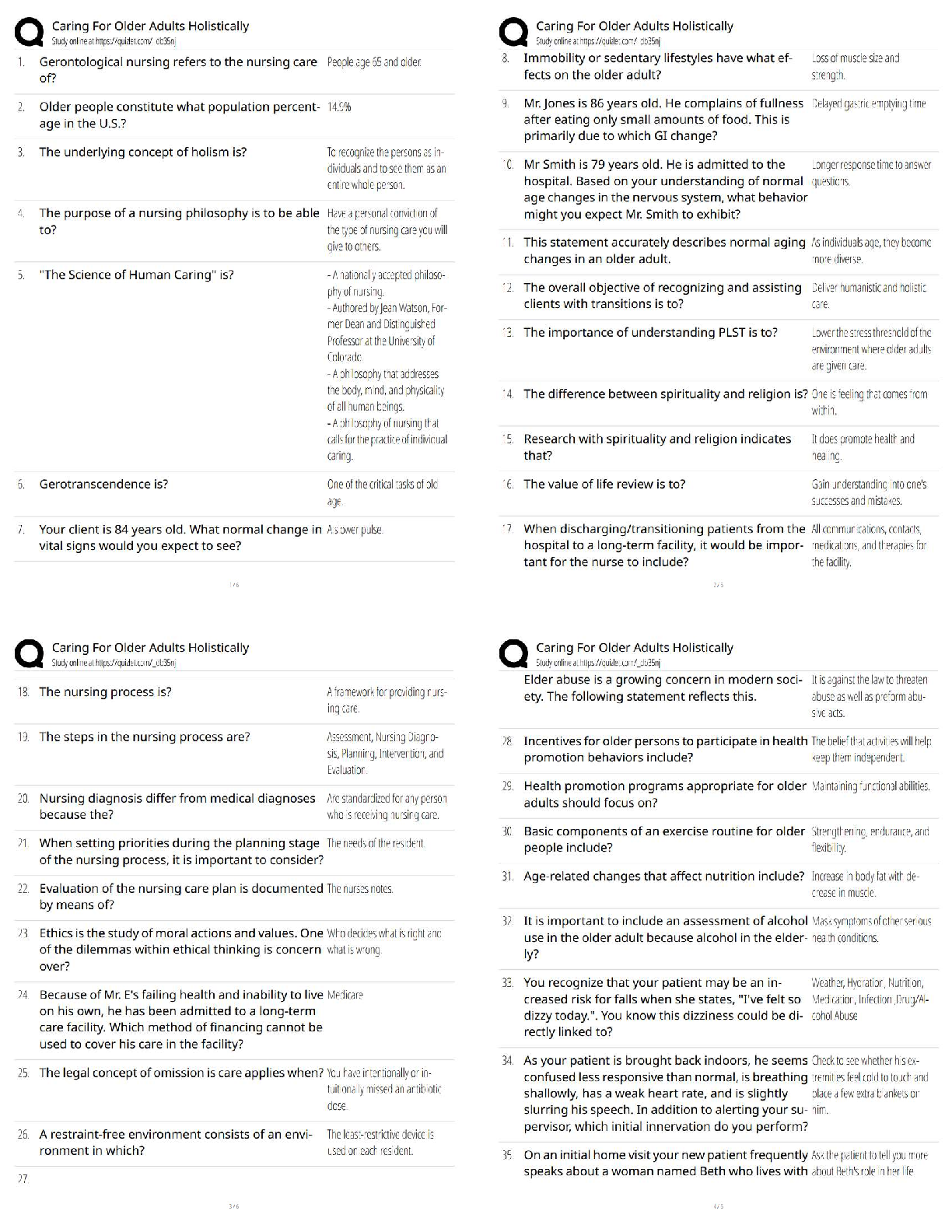
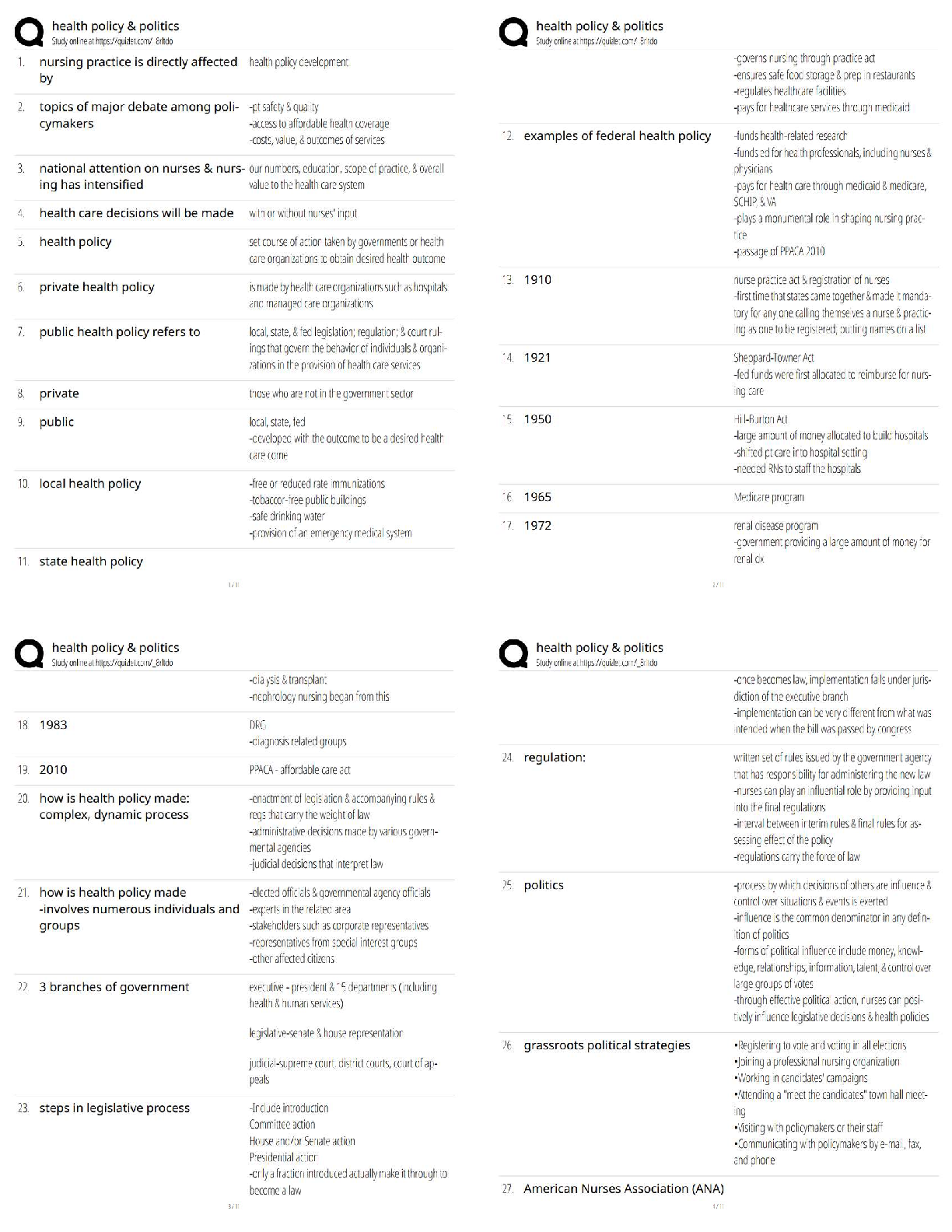
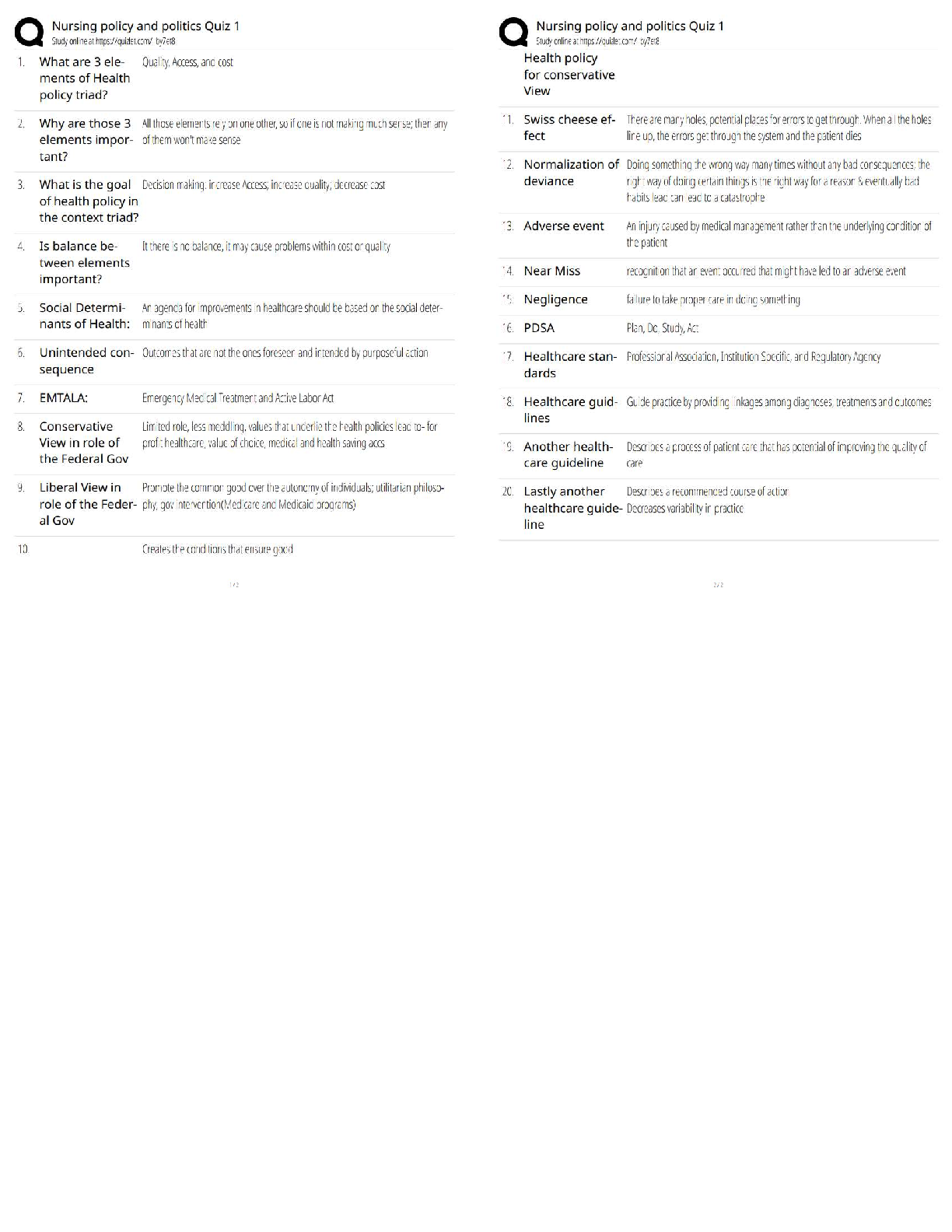
CHAPTER 10--
PARTNERSHIPS: FORMATION, OPERATION, AND BASIS
Student: ___________________________________________________________________________
1. A partnership is an association formed by two or more taxpayers (who m
...
CHAPTER 10--
PARTNERSHIPS: FORMATION, OPERATION, AND BASIS
Student: ___________________________________________________________________________
1. A partnership is an association formed by two or more taxpayers (who may be any type of entity) to carry on
a trade or business.
True False
2. In a limited liability company, all members are protected from all debts of the partnership unless they
personally guaranteed the debt.
True False
3. A limited partnership offers all partners protection from claims by the LP’s creditors.
True False
4. The primary purpose of the partnership agreement is to document the various tax elections made by the
partners regarding depreciation methods, treatment of research and experimental costs, calculation of the § 199
deduction, and the § 754 election.
True False
5. The taxable income of a partnership flows through to the partners, who report the income on their tax
returns.
True False
6. An example of the “aggregate concept” underlying partnership taxation is the fact that the partners (rather
than the partnership) pay tax on partnership income.
True False
7. Each partner’s profit-sharing, loss-sharing, and capital-sharing ownership percentages are always the same.
True False8. The “inside basis” is defined as a partner’s basis in the partnership interest.
True False
9. The partnership reports each partner’s share of income to the partner in a single amount on Form 1099.
True False
10. Section 721 provides that, in general, no gain or loss is recognized by the partnership or the partner on
contribution of appreciated or depreciated property to a partnership in exchange for an interest in the
partnership.
True False
11. Ken and Lars formed the equal KL Partnership during the current year, with Ken contributing $100,000 in
cash and Lars contributing land (basis of $60,000, fair market value of $40,000) and equipment (basis of $0, fair
market value of $60,000). Lars recognizes a $40,000 gain on the contribution and his basis in his partnership
interest is $100,000.
True False
12. Morgan and Kristen formed an equal partnership on August 1 of the current year. Morgan contributed
$60,000 cash and land with a basis of $18,000 and a fair market value of $40,000. Kristen contributed
equipment with a basis of $42,000 and a value of $100,000. Kristen and Morgan each have a basis of $100,000
in their partnership interests.
True False
13. Section 721 provides that no gain or loss is recognized on a contribution of property to a partnership in
exchange for an interest in the partnership. An exception might apply if the taxpayer receives a cash distribution
from the partnership soon after the property contribution is made.
True False
14. George received a fully-vested 10% interest in partnership capital and a 20% interest in future partnership
profits in exchange for services rendered to the GHP, LLC (not a publicly-traded partnership interest). The
future profits of the partnership are subject to normal operating risks. George will report ordinary income equal
to the fair market value of the profits interest, but the capital interest will not be currently taxed to him.
True False15. Laura is a real estate developer and owns property that is treated as inventory (not a capital asset) in her
business. She contributes a parcel of this land (basis of $15,000) to a partnership, also to be held as inventory.
The fair market value of the property is $12,000 at the contribution date. After three years, the partnership sells
the land for $10,000. The partnership will recognize a $5,000 ordinary loss on sale of the property.
True False
[Show More]










.png)

.png)