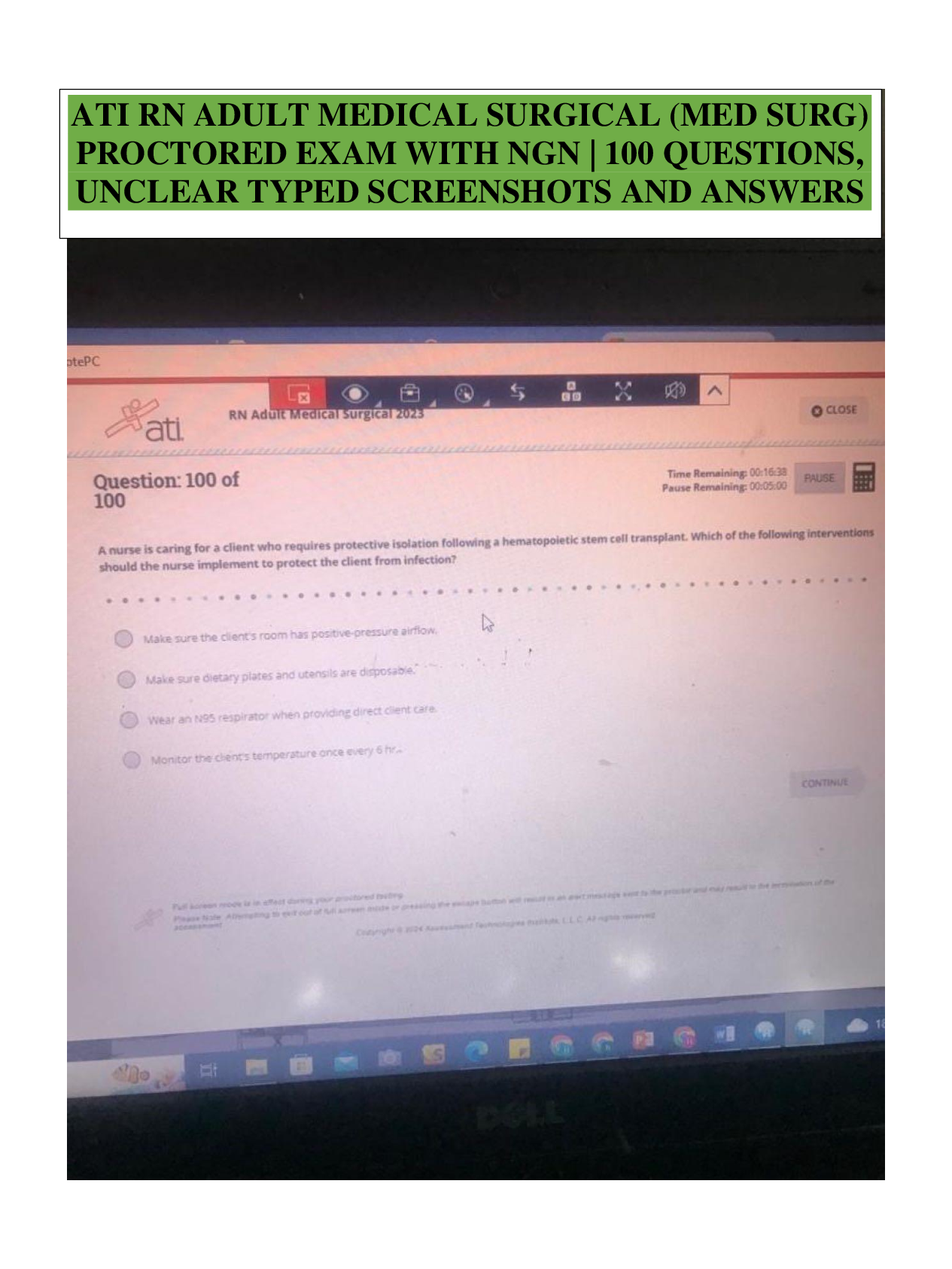
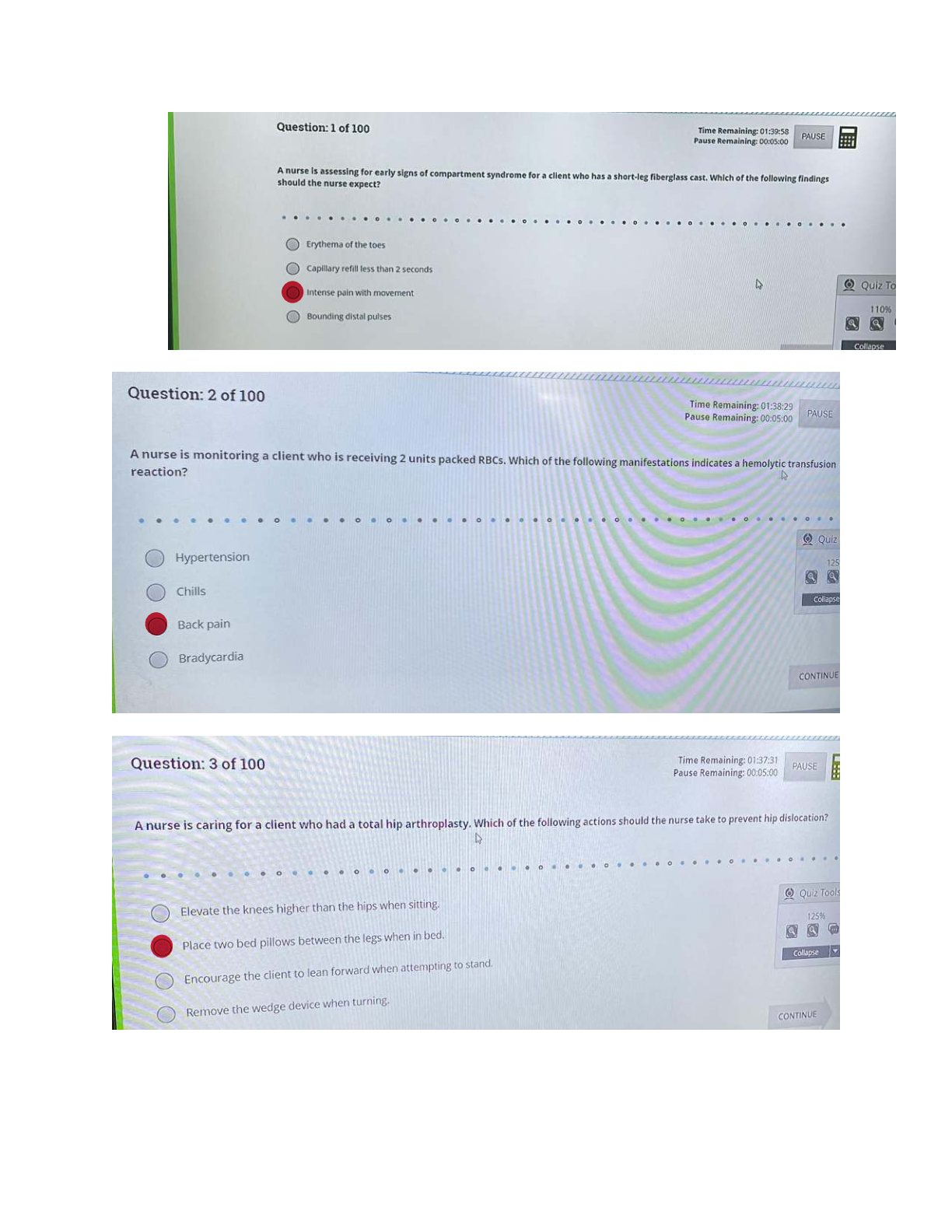
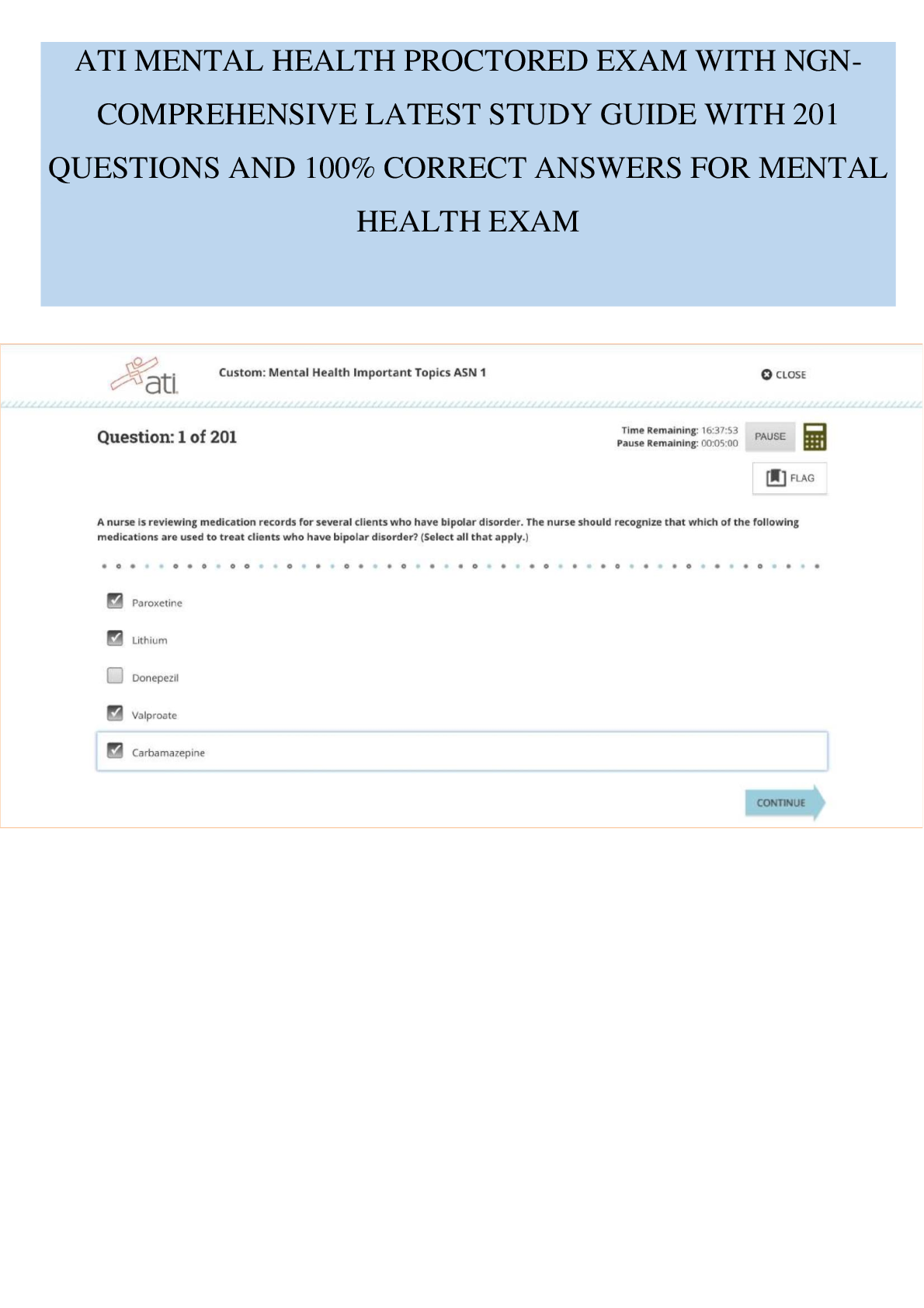
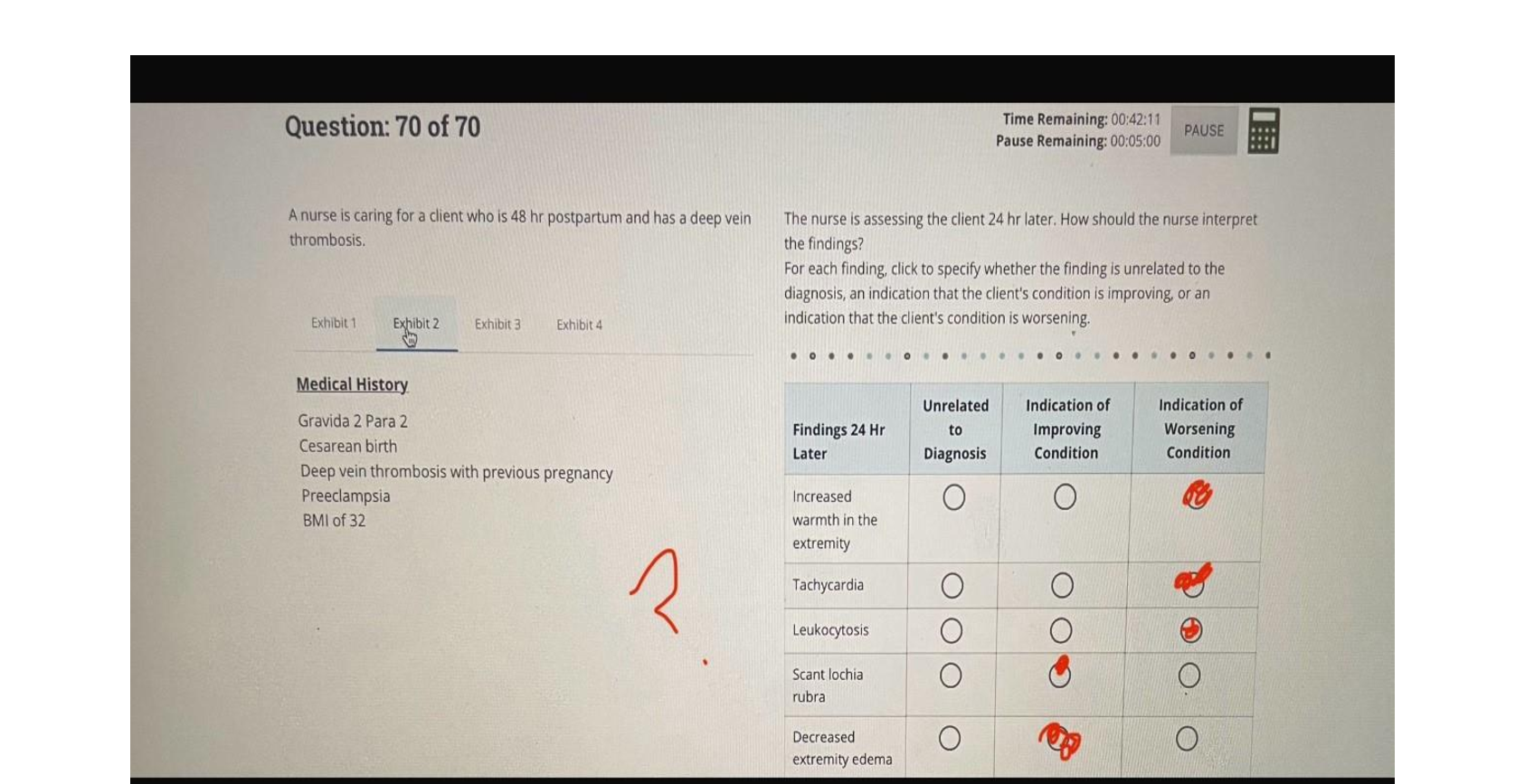
La'Vonn rolled a die 100 times. His results are below.
Number Times Rolled
1 18
2 20
3 15
4 17
5 14
6 16
What is the relative frequency for La'Vonn rolling a 3? Answer
choices are rounded to the hundredths place
...
La'Vonn rolled a die 100 times. His results are below.
Number Times Rolled
1 18
2 20
3 15
4 17
5 14
6 16
What is the relative frequency for La'Vonn rolling a 3? Answer
choices are rounded to the hundredths place.
0.01
0.15
0.38
0.07
RATIONALE
The relative frequency of a 3 is:
CONCEPT
Relative Frequency Probability/Empirical Method
2
A basketball player makes 60% of his free throws. We set him on the free
throw line and asked him to shoot free throws until he misses. Let the
random variable X be the number of free throws taken by the player until he
misses.
Assuming that his shots are independent, find the probability that
he will miss the shot on his 6th throw.
0.04666
0.03110
0.00614
0.01866
RATIONALE
Since we are looking for the probability until the first success, we will use the following
Geometric distribution formula:
The variable k is the number of trials until the first success, which in this case, is 6
throws.
The variable p is the probability of success, which in this case, a success is considered
missing a free throw. If the basketball player has a 60% of making it, he has a 40%, or
0.40, chance of missing.
CONCEPT
Geometric Distribution
3
For a math assignment, Michelle rolls a set of three standard dice at the
same time and notes the results of each trial.
What is the total number of outcomes for each trial?
18
216
27
36
RATIONALE
We can use the general counting principle and note that for each step, we simply
multiply all the possibilities at each step to get the total number of outcomes. Each diehas 6 possible outcomes. So the overall number of outcomes for rolling 3 die with 6
possible outcomes each is:
CONCEPT
Fundamental Counting Principle
4
Paul went to a blackjack table at the casino. At the table, the dealer has just
shuffled a standard deck of 52 cards.
Paul has had good luck at blackjack in the past, and he actually got three
blackjacks with Kings in a row the last time he played. Because of this lucky
run, Paul thinks that Kings are the luckiest card.
The dealer deals the first card to him. In a split second, he can see that it is a
black card, but he is unsure if it is a King.
What is the probability of the card being a King, given that it is a
black card? Answer choices are in a percentage format, rounded to
the nearest whole number.
23%
8%
50%
67%
RATIONALE
The probability of it being a King given it is a Black card uses the conditional formula:
Note that in a standard deck of 52 cards, half of the cards are black, or 26 out of 52. Of
those 26 black cards, only two are Kings.
CONCEPT
Conditional Probability
5Which of the following is an example of a false positive?
Test results confirm that a patient does not have cancer.
Test results indicate that a patient has cancer when, in fact, he does not.
Test results confirm that a patient has cancer.
Test results indicate that a patient does not have cancer when, in fact, he does.
RATIONALE
Since the test results indicate positively that the patient has cancer, when in fact cancer
is not present, this is a false positive.
CONCEPT
False Positives/False Negatives
6
Select the foll
[Show More]