Convection Gizmo Lab (1) Student Exploration: Convection Cells
Document Content and Description Below
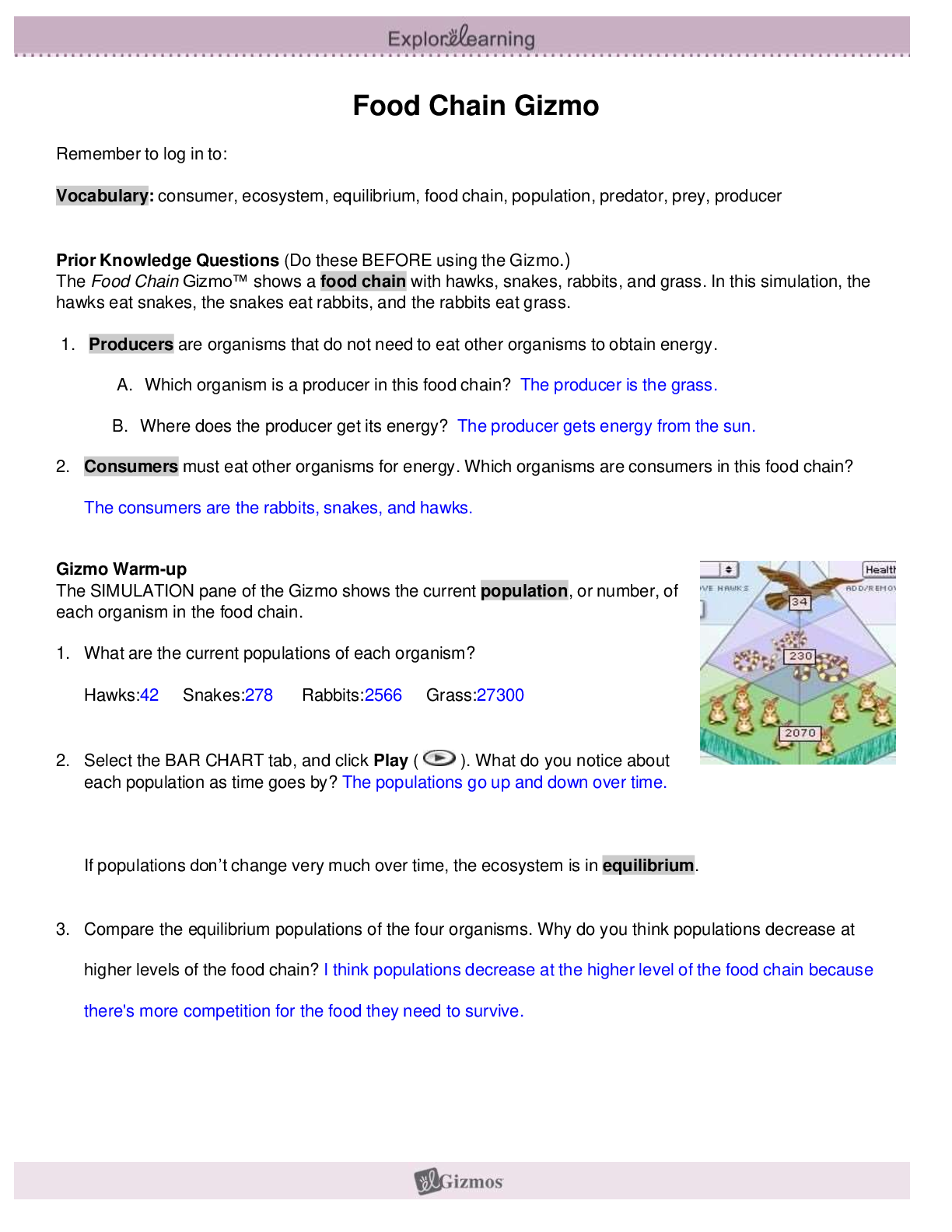
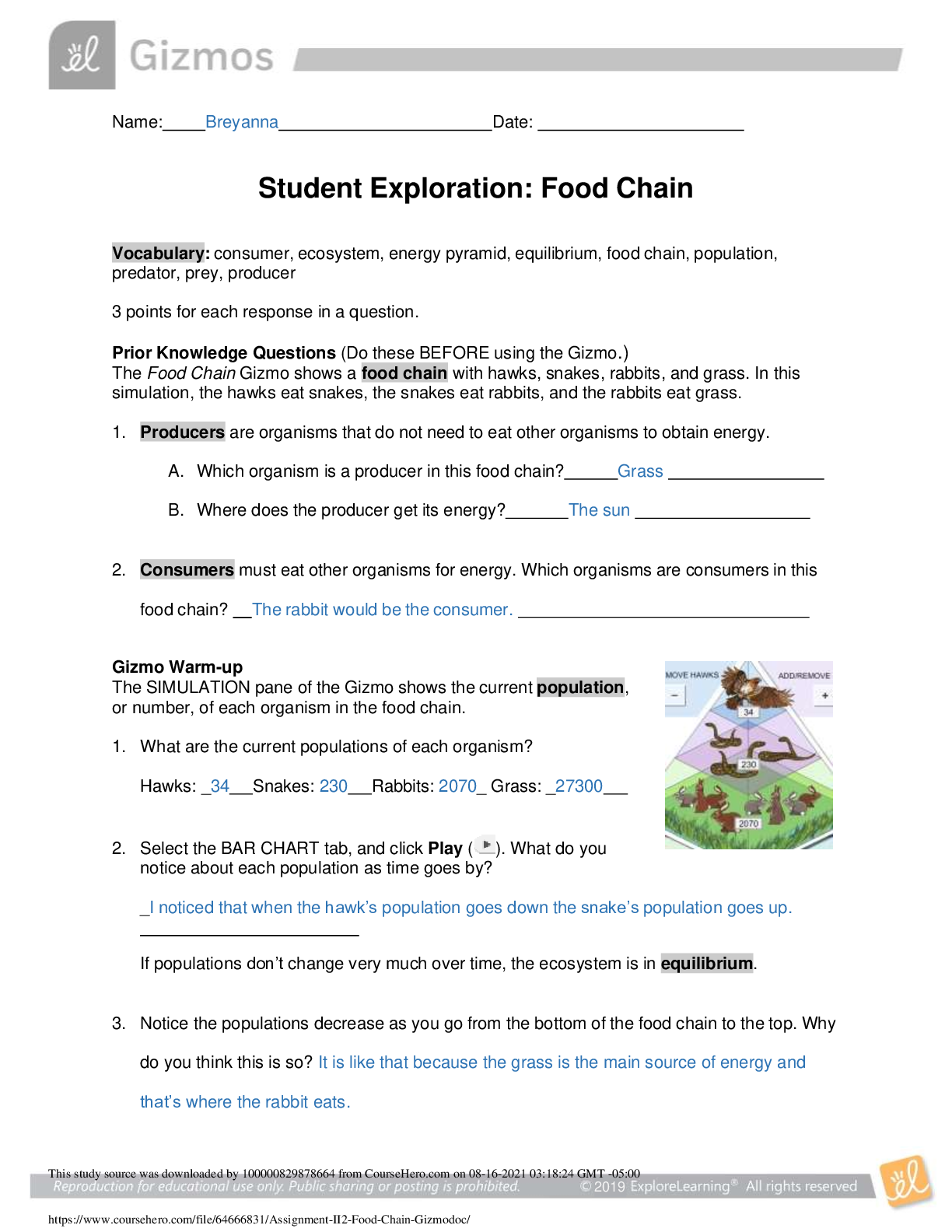
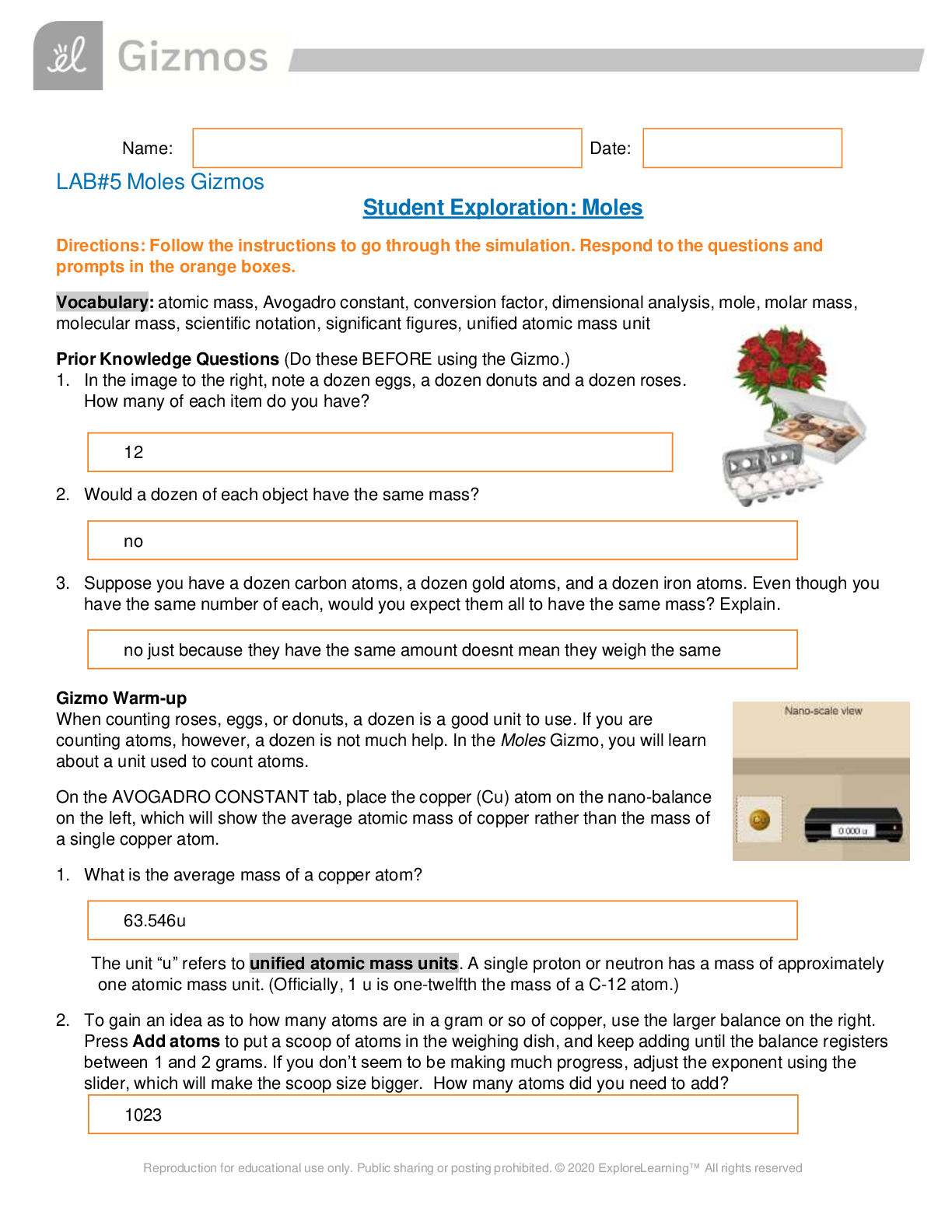
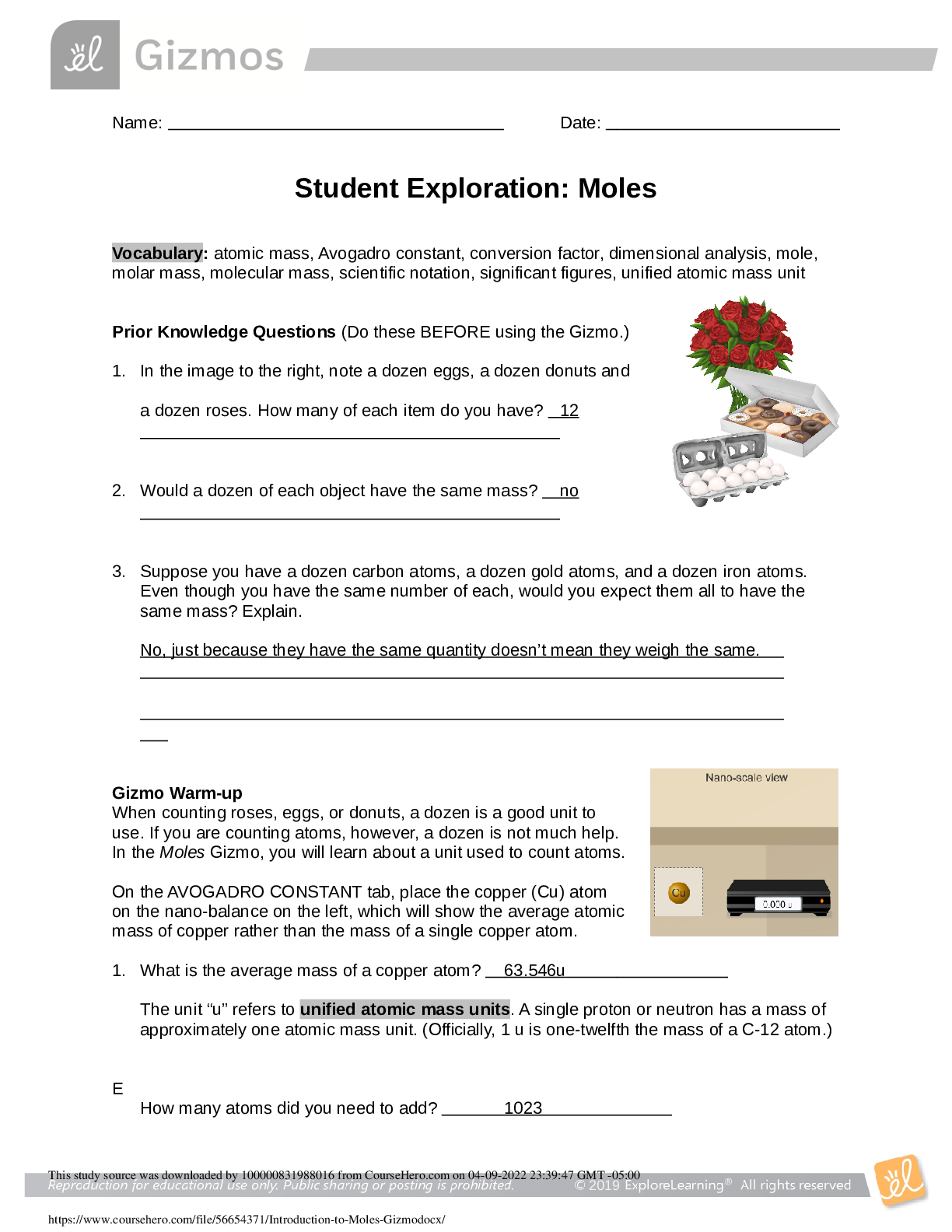
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Convection Cells Vocabulary: convection, convection cell, density, global conveyor belt, mantle, mid-ocean ridge, subduction zone, vector, viscosity ... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) You place a pot of soup on the stove. As the soup warms you notice some areas where soup is rising up and other areas where soup is sinking down. 1. Why do you think some of the soup is rising up? I think some of the soup is rising up because of the hot air pressure. 2. Why do you think some of the soup is sinking down? I think the soup is sinking because the temperature is cold and not hot but it is not the same temperature so it sinks. Gizmo Warm-up When fluids (gases or liquids) are heated, they tend to move. This motion is called convection. In the Convection Cells Gizmo, you will observe and experiment with convection both in a laboratory setting and in several real-world examples. To begin, note the laboratory setup on the MODEL tab. A beaker of liquid is placed above a gas burner. Click Play ( ). The burner is now heating the fluid. 1. What do you notice? 2. Drag the eyedropper into the beaker just above the burner and let go to release a drop of orange liquid into the beaker. What do you notice about the path of the drop? Question: What causes convection cells to form? 1. Hypothesize: Click Play, add a drop, and watch the motion of the liquid. Why do you think convection tends to occur in heated fluids? 2. Observe: Click Clear drop. Under Show, select Temperature. The temperature scale runs from red (hot) to dark blue (colder). A. Where is the hottest liquid located? B. Where is the coldest liquid located? C. Add a drop. Does the hottest liquid tend to rise or sink? D. Does the coldest liquid tend to rise or sink? 3. Observe: Click Clear drop, and then add a new drop to the liquid. Turn on Show micro view of drop. This view shows 21 molecules in the drop. Pay attention to how fast the molecules move and how much space they occupy as the drop moves around the beaker. (Note: If the drop gets stuck, add a new drop to the beaker.) A. In which part of the beaker do the liquid molecules move fastest? B. In which part are the liquid molecules most spread out? 4. Explore: Click Clear drop and drag the probe ( ) into the beaker. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is a measure of how tightly the particles of a substance are packed. Move the probe to different parts of the beaker, observing the temperature and density. A. What relationship do you observe between the temperature and density? ..................................................................................continued,...................................................................... [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 04, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 04, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
516