
MGMT 404 Course Project: Getta Byte Software Project |Getta Byte Software project final.2020/2021|Devry University
$ 22

OCR_AS Level Mathematics A_H230/02 Question Paper Oct 2021 | Pure Mathematics and Mechanics
$ 8.5

2022 Real Estate Sales Person Exam Prep (California) with COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 10
.png)
WGU C175 Vocab Latest 2022 Graded A+
$ 7

A Level Media Studies_H409/01 Question Paper Oct 2021 | Media Messages
$ 7.5
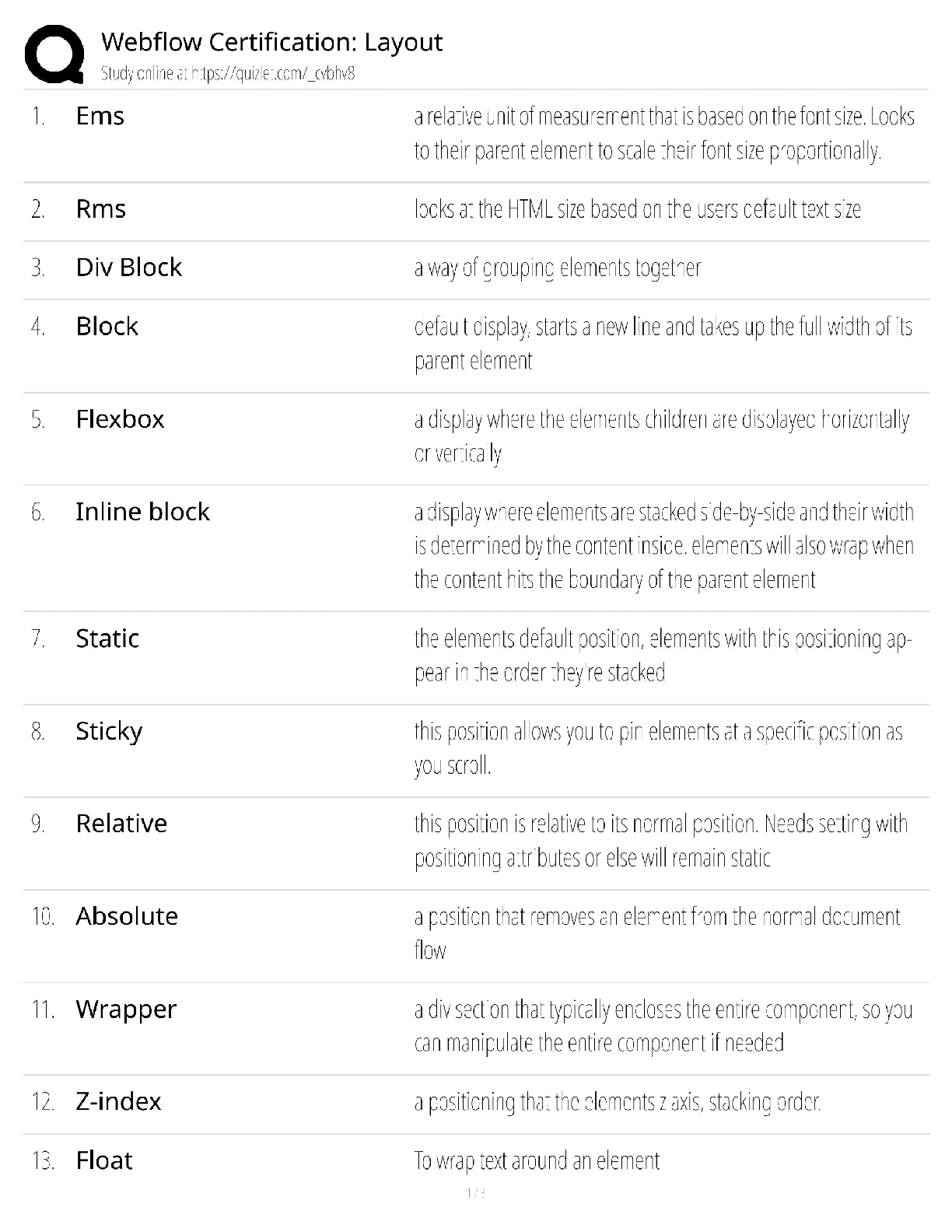
Webflow Certification Layout / Web Design & Development Guide / 2025 Update / Score 100%
$ 22

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY THE BIOLOGIC BASIS FOR DISEASE IN ADULTS AND CHILDREN 8th Edition TESTBANK
$ 7

GCSE (9–1) Mathematics J560/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier). November 2021. Question Paper.
$ 4.5

CALA REPL EXAM VERSION 1 2025
$ 19

BUSI 830 Overview of Case Study Types | 2025 Update with complete solutions. BUSI 830: Comparative Analysis of Case Study Types in Doctoral Research
$ 21.5
.png)
WGU C175 Data Management Foundation Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 5

Chapter 14 Information Security Certifications / CISSP, CISM, CompTIA Security+ / 2025 Study Guide / Score 100%
$ 11.5

FF2 Final Exam Questions And Answers( Complete best Solution Rated A)
$ 10

WGU C464 Introduction to Communication Questions and Answers with Complete Solutions
$ 7

[eBook] [PDF] Fluid Mechanics in 2nd EDition SI Units By Russell Hibbeler












.png)
.png)













