Mechanical Engineering > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > 230772512-Reviewer-15 Visayas State University - Isabel, Leyte Campus ME MISC (All)
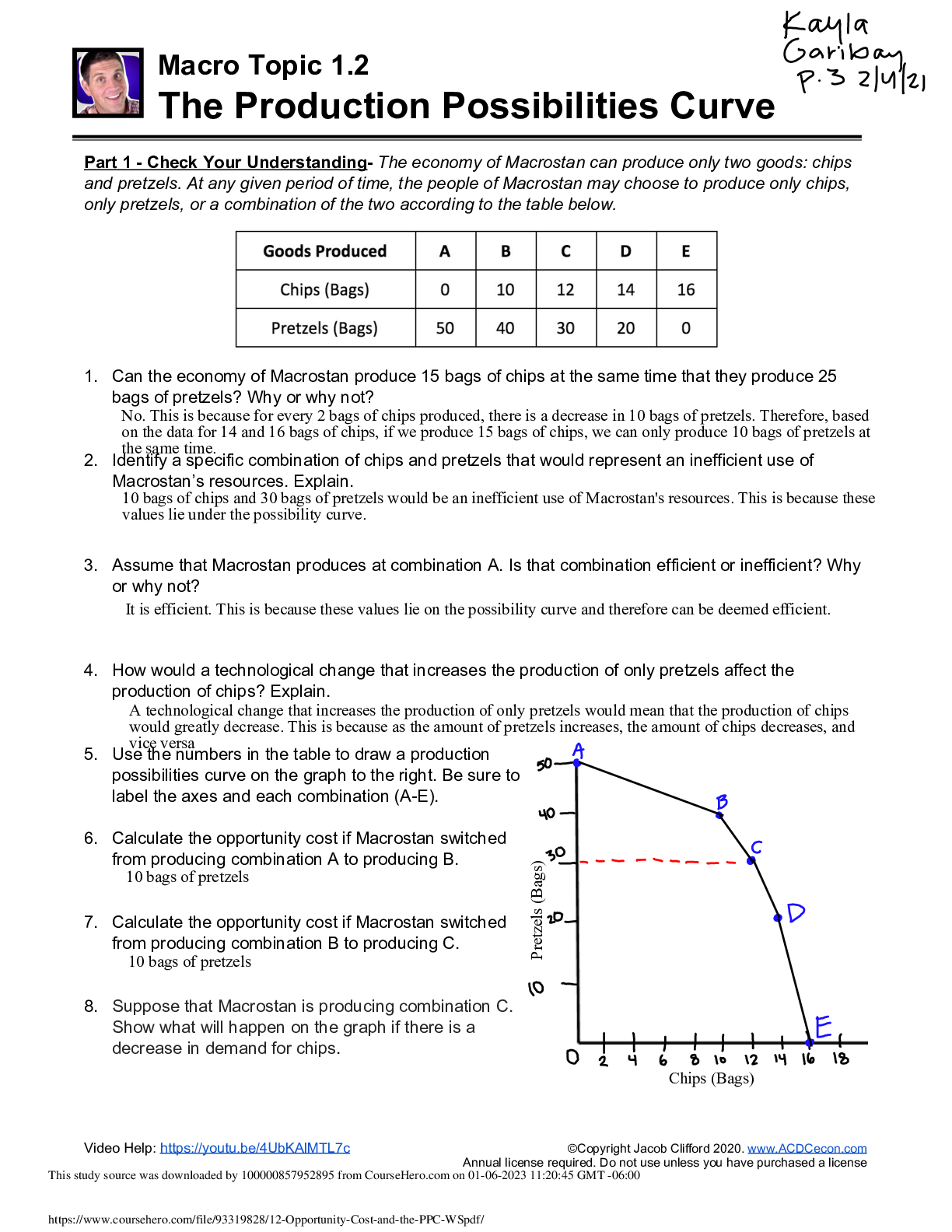
230772512-Reviewer-15 Visayas State University - Isabel, Leyte Campus ME MISC
Document Content and Description Below
Reheating process in Brayton cycle, the turbine work will a. Increase b. Decrease c. Remains the same d. None of these Ans. A Which of the following is the chemical formula of ethanol? a. C7H16... b. C2H6O c. C7H8 d. C6H12 Ans. B Which of the following is the chemical formula of heptane? a. C7H16 b. C2H6O c. C7H8 d. C6H12 Ans. A Which of the following is the chemical formula of hexane? a. C7H16 b. C2H6O c. C7H8 d. C6H12 Ans. D Which of the following is the chemical formula of toluene? a. C7H16 b. C2H6O c. C7H8 d. C6H12 Ans. C As the air passes through a nozzle, which of the following will increase? a. Temperature b. Enthalpy c. Internal energy d. Mach number Ans. D As the air passes through a diffuser, which of the following will decrease? a. Temperature b. Enthalpy c. Internal energy d. Mach number Ans. D As the air passes through a nozzle, which of the following will decrease? a. Temperature b. Enthalpy c. Internal energy d. Mach number Ans. C As the air passes through a diffuser, which of the following will increase? a. Density b. Entropy c. Mach number d. Velocity Ans. A As the air passes through a diffuser, which of the following will NOT be affected? a. Density b. Entropy c. Mach number d. Velocity Ans. B After passing through a convergent-divergent nozzle the temperature of air will: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Remains the same d. None of these Ans. B After passing through a convergent-divergent nozzle the density of air will: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Remains the same d. None of these Ans. B After passing through a convergent-divergent nozzle the mach number of air will: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Remains the same d. None of these Ans. B By increasing the temperature source of Carnot cycle, which of the following will not be affected? a. Efficiency b. Work c. Heat added d. Heat rejected Ans. D By decreasing the temperature source of Carnot cycle, which of the following will not be affected? a. Efficiency b. Work c. Heat added d. Heat rejected Ans. C By superheating the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle with useful cooling, which of the following will increase? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Condenser pressure b. Evaporator pressure c. Quality after expansion d. Heat rejected from condenser Ans. D By superheating the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle with useful cooling, which of the following will decrease? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Refrigerated effect b. COP c. Compressor power d. Mass flow rate Ans. D By superheating the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle without useful cooling, which of the following will decrease? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Heat rejected b. COP c. Compressor power d. Specific volume at suction Ans. B By superheating the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle without useful cooling, which of the following will increase? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Heat rejected b. COP c. Compressor power d. Specific volume at suction Ans. C By superheating the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle without useful cooling, which of the following will not be affected? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Refrigerated effect b. COP c. Compressor power d. Mass flow rate Ans. C By sub-cooling the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle at condenser exit, which of the following will increase? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Refrigerated effect b. Specific volume at suction c. Compressor power d. Mass flow rate Ans. A By sub-cooling the refrigerant in vapor compression cycle at condenser exit, which of the following will decrease? (use per unit mass analysis) a. Refrigerated effect b. Specific volume at suction c. Compressor power d. Mass flow rate Ans. D By increasing the vaporizing temperature in vapor compression cycle, which of the following will increase? (Use per unit mass analysis) A. mass flow rate B. COP C. specific volume at suction D. compressor work Answer: B By increasing the vaporizing temperature in vapor compression cycle, which of the following will decrease? (Use per unit mass analysis) A. Refrigeration effect B. COP C. evaporator temperature D. Temperature difference between evaporator and compressor Answer: D By increasing the condenser pressure in vapor compression cycle, which of the following will increase? (Use per unit mass analysis) A. moisture content after expansion B. compressor power C. heat rejected from condenser D. mass flow rate Answer: A If the pressure drop in the condenser Increases in a vapor compression cycle, which of the following will increase? (Use per unit mass analysis) A. mass flow rate B. compressor power C. heat rejected in the condenser D. specific volume of suction Answer: C If the pressure drop in the condenser increases in a vapor compression cycle, which of the following wil [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 30 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 09, 2022
Number of pages
30
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 09, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
104





.png)




.png)


