Physical Education > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BCRPA PT-ICE Study Guide Exam test bank. Questions with accurate answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ (All)
BCRPA PT-ICE Study Guide Exam test bank. Questions with accurate answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
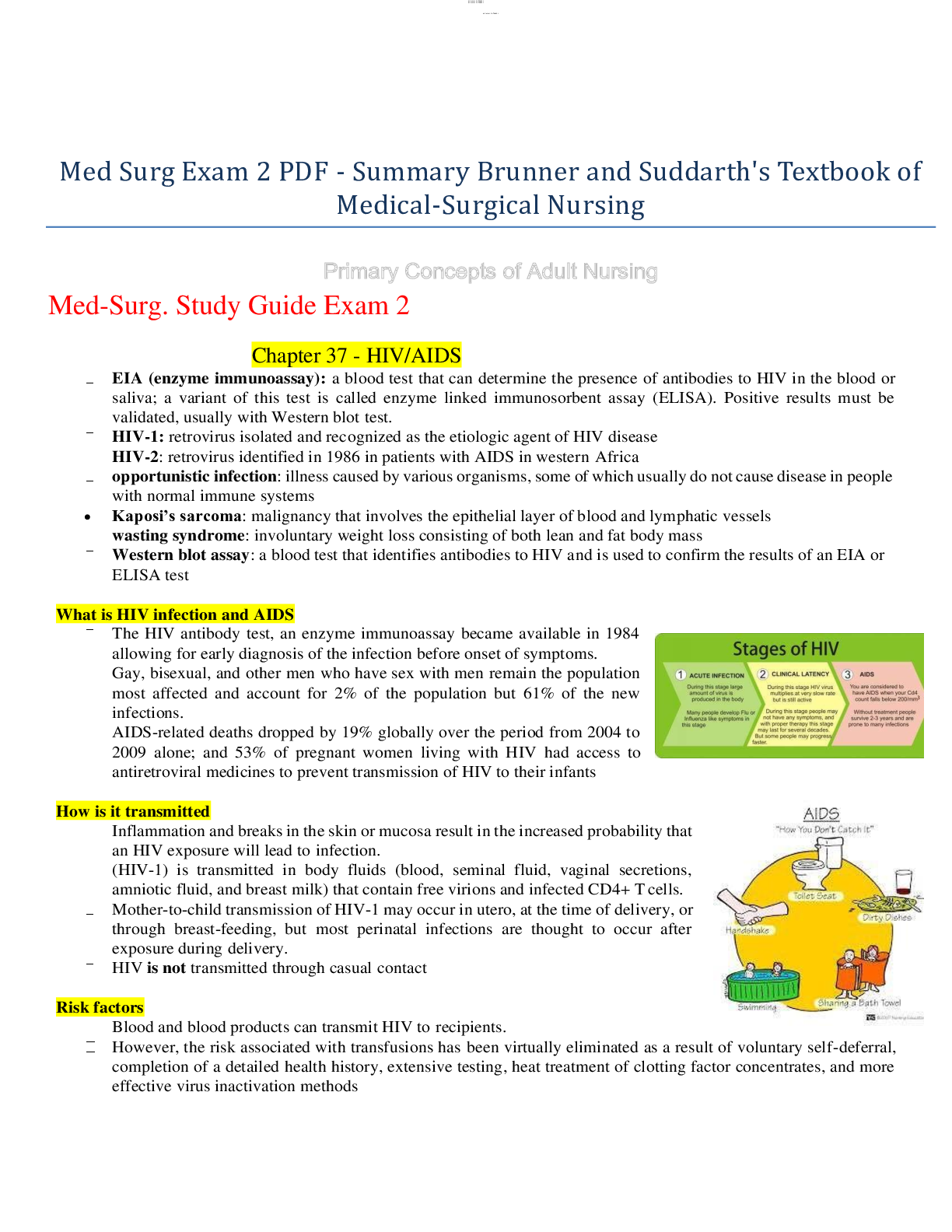
BCRPA PT-ICE Study Guide Exam test bank. Questions with accurate answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ Exercise Physiology 1) A person exercises for 40 minutes at an intensity of 50% of MaxVO2. Compa... red to the first 10 minutes of exercise, the last 10 minutes of exercise affect his/her fat and carbohydrate utilization in which of the following manners a) Fat Utilization: Decreases Carbohydrate Utilization: Decreases b) Fat Utilization: Decreases Carbohydrate Utilization: Increases c) Fat Utilization: Increases Carbohydrate Utilization: Increases d) Fat Utilization: Increases Carbohydrate Utilization: Decreases d) Fat Utilization: Increases Carbohydrate Utilization: Decreases The longer an aerobic activity the more the body relies on fat and less on carbohydrates. Exercise Physiology 2) To improve the cardiovascular fitness level of a 30 year old healthy adult female with a RHR of 70, it is recommended that she begin aerobic exercise at an intensity of: a) 30-40% of heart rate resolve b) 40-50% of heart rate reserve c) 50-60% of heart rate reserve d) 70-85% of heart rate reserve c) 50-60% of heart rate reserve Health people start at 50-60% HRR, only extremely unfit people start lower, she is not. Exercise Physiology 3) Generally, to improve the cardiovascular fitness level of a sedentary, healthy adult female, she needs to exercise for a minimum aerobic overload duration of does not include warm-up or cool down): a) 5-10 minutes b) 15-20 minutes c) 25-30 minutes d) 35-40 minutes b) 15-20 minutes This is the minimum duration to receive a PHYSIOLOGICAL cardiovascular effect. Exercise Physiology 4) Bill Big and Harry Huge are training partners. harry, the smaller of the two displays greater strength during the 1 RM Bench Press Test. Which of the following might explain this occurrence? a) an anatomical leverage advantage for Harry b) greater synchronous recruitment of motor units by Harry c) greater storage of glycogen in the muscles of Harry d) a & b d) a & b an anatomical leverage advantage for Harry & greater synchronous recruitment of motor units by Harry 1 RM's rely on the ATP-CP system, this activity is very short, maximal activity; Glycogen isn't used. Exercise Physiology 5) Which of the following are associated with the neuromuscular junction. Which of the following are associated with the neuromuscular junction: a) acetylcholine b) cholinesterase c) motor end plates d) all of the above d) all of the above All components play a role at the neuromuscular junction in order to cause muscular contraction. Exercise Physiology 6) The Sliding Filament Theory is thought to be: a) actin muscle FIBRES sliding along the myosin MYOFIBRILS b) actin MYOFILAMENTS being pulled and then sliding alon teh myosin MYOFILAMENTS c) myosin projections attaching to and pulling on the active sites of actin, forming cross-bridges. d) b & c d) actin MYOFILAMENTS being pulled and then sliding alon teh myosin MYOFILAMENTS; & myosin projections attaching to and pulling on the active sites of actin, forming cross-bridges. Exercise Physiology 7) The amount of force that is generated during a muscular contraction is dependent on a) the size and number of muscle fibres b) the size and number of motor units c) the frequency of the neuro-impulses discharged to the contracting muscle d) all of the above d) all of the above Exercise Physiology 8) Muscular fatigue may be caused by a) a depletion in ATP-CP stores b) accumulation of waste products c) dehydration d) all of the above d) all of the above Exercise Physiology SHORT ANSWER: 1) Describe the Myotatic Stretch Reflex from start to finish and the key players or mechanisms inolved in it (6 pts). A ballistic stretch will cause the stretched muscle to contract and not to relax. During a ballistic stretch, the muscle spindles, sensory organs that lie parallel to the muscle fibers, perceive and then transmit the rate and length of the stretch to the CNS. The CNS the analyzes the info and sends a neural impulse to the muscle belly to contract, thereby stopping the joint from continuing to move and the muscle to stretch further and risk injury. The force of the contraction is determined by the force of the stretch, the greater the stretch the greater the contraction. the entire process from stretch to muscle contraction is called the Myotatic Stretch Reflex. Exercise Physiology SHORT ANSWER: 2) Describe why ballistic stretching can be dangerous (4 pts). On the 2nd bounce is when injury can occur, since the muscle is being stretch in one direction while the contraction of the muscle occurs in the opposite direction. Now, there are two opposing forces occurring at the same time in both directions, causing increased tension on the muscle structure and increasing the risk of injury. HUMAN ANATOMY 1) SITS stands for: a) Supraspinatus, Internalis, Teres Major, Subscapularis b) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Major, Subscapularis c) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis d) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Major/Minor, Subscapularis c) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis HUMAN ANATOMY 2) The Trapezius, Rhomboids, Serratus Anterior and Levator Scapulae all act on: a) Gleno-Humeral Joint b) Sterno-Clavicular Joint c) Acromio-Clavicular Joint d) Scapulo-Thoracic Joint d) Scapulo-Thoracic Joint This is a real term used to describe the soft-tissue joint known as the Scapulo-thoracic joint. HUMAN ANATOMY 3) A sagittal plane divides the body into: a) right and left sections b) superior and inferior sections c) anterior and posterior sections d) ventral and dorsal sections a) right and left sections HUMAN ANATOMY 4) Which statement is correct? a) Motor nerve cells carry information away from the Central Nervous System (CNS). b) Sensory Nerve cells carry information to the Central Nervous System (CNS). c) Motor Nerve cells carry information to the Central Nervous System (CNS). d) a & b d) a & b Motor nerve cells carry information away from the Central Nervous System (CNS). & Sensory Nerve cells carry information to the Central Nervous System (CNS). HUMAN ANATOMY 5) The exchange of oxygen from the blood to the cells is called: a) Cellular Respiration b) Internal Respiration c) External Respiration d) Hemoglobular/Myoglobular exchange b) Internal Respiration Cellular respiration is all the processes that go inside the cell, while external respiration is the transferring of external oxygen into the lungs and then into the blood. HUMAN ANATOMY 6) Match Up. a) Sagittal Plane b) Coronal Plane c) Transverse Plane d) Median Palne e) Proximal f) Distal _____ : Jumping Jacks b) Coronal Plane HUMAN ANATOMY 6) Match Up. a) Sagittal Plane b) Coronal Plane c) Transverse Plane d) Median Palne e) Proximal f) Distal _____ : Lateral Condyle f) Distal HUMAN ANATOMY 6) Match Up. a) Sagittal Plane b) Coronal Plane c) Transverse Plane d) Median Palne e) Proximal f) Distal _____ : Cross Country Skiing a) Sagittal Plane HUMAN ANATOMY 6) Match Up. a) Sagittal Plane b) Coronal Plane c) Transverse Plane d) Median Palne e) Proximal f) Distal _____ : Greater Trochanter e) Proximal HUMAN ANATOMY 6) Match Up. a) Sagittal Plane b) Coronal Plane c) Transverse Plane d) Median Palne e) Proximal f) Distal _____ : Bench Press (type of movement) c) Transverse Plane HUMAN ANATOMY 7) Match Up. a) Humerus Socket b) Hip Socket c) Radio-Ulnar d) Extension e) Flexion f) Gliding _____ : Acromio-Clavicular (type of joint?) f) Gliding HUMAN ANATOMY 7) Match Up. a) Humerus Socket b) Hip Socket c) Radio-Ulnar d) Extension e) Flexion f) Gliding _____ : Pivot (type of joint?) c) Radio-Ulnar HUMAN ANATOMY 7) Match Up. a) Humerus Socket b) Hip Socket c) Radio-Ulnar d) Extension e) Flexion f) Gliding _____ : Front Deltoid Raise (type of movement?) e) Flexion HUMAN ANATOMY 7) Match Up. a) Humerus Socket b) Hip Socket c) Radio-Ulnar d) Extension e) Flexion f) Gliding _____ : Glenoid Fossa (type of socket?) a) Humerus Socket HUMAN ANATOMY 7) Match Up. a) Humerus Socket b) Hip Socket c) Radio-Ulnar d) Extension e) Flexion f) Gliding _____ : Acetabulum (what type of joint is it connected to?) b) Hip Socket HUMAN ANATOMY 8) you've shown your client Biff, two stretches for the calf area; one is a gastrocnemius stretch that involves keeping the knee straight and the other is a soleus stretch keeping the knee bend at a 90º angle. Explain why one stretch needs to have the knee straight to be effective and the other stretch needs to have the knee bent. This is due to the origins of the muscles. The origin of the Gastrocnemius is above the knee, while the origin of the Soleus is below the knee. When the knee is straight the Gastroc's origin is furthest from its insertion on the Calcaneus. When the knee is bent, the Gastroc's origin is closer to its insertion, which causes the muscle to slacken. With the knee bent at 90 degrees, the Soleus will now experience most of the stretch. I suggest that you tape these muscles' origins and insertions, connect them with tape and watch what happens when you bend the knee. KINESIOLOGY 1) a) Transverse Adduction (Shoulder flexed to 90º) holding-up 30lb Hand Weights (Elbow bent to 90º). Standing: This exercise RESEMBLES a Pec Deck movement Muscles: ___________ a) Deltoid (ant, mid) KINESIOLOGY 1) b) Standing: External Rotation of Shoulder (neutral alignment with 30lb DB Hand Weights (Elbow bent to 90º). Standing with elbows in by our Side; elbows bent to 90 degrees. Muscles: ___________ [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 48 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)

BCRPA BUNDLE, TOP QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS, VERIFIED
BCRPA Fitness Theory, Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+. APPROVED.
By Topmark 2 years ago
$32
10
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 12, 2023
Number of pages
48
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 12, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
109


















.png)


 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)

