
MARK SCHEME – GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY – 8464/B/1H – JUNE 2020
$ 16

FRENCH 1 TEST
$ 6

Case Solutions/ Notes for MARU BATTING CENTER CUSTOMER LIFETIME VALUE by Julie Hennessy Evan Meagher
$ 15
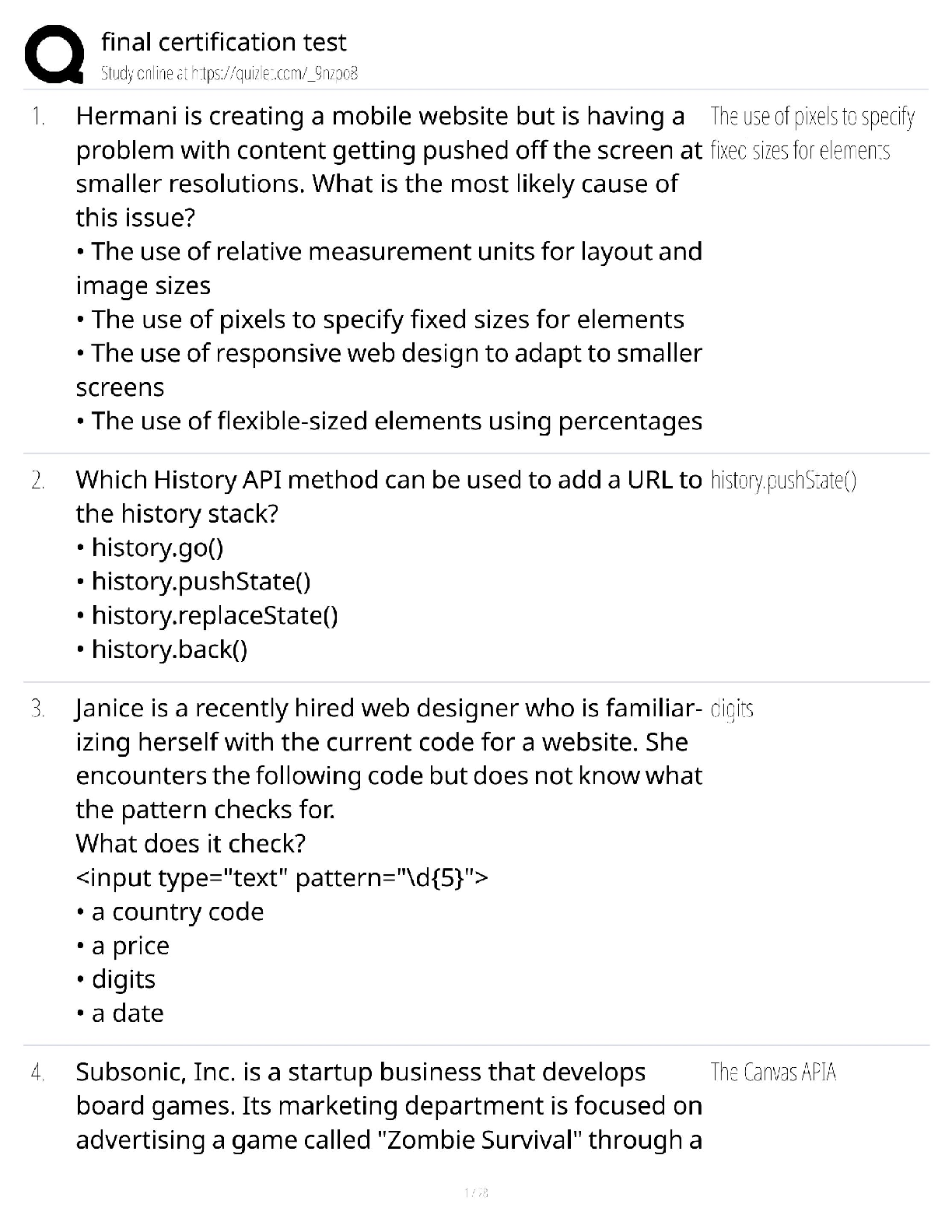
[Certification Name] Final Certification Test / 2025 Complete Prep Guide / Practice Exams & Pro Tips / Pass Guaranteed
$ 9.5

eBook PDF for Artificial Intelligence_ A Modern Approach 4th Edition By Stuart Russell_ Peter Norvig
$ 29

Statistic Final for maths 225N QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS latest 2020-2021(graded A)
$ 12.5

Gizmo Density Laboratory
$ 6.5
.png)
Midterm 2A Study Guide and Notes
$ 12.5

COM1501- Fundamentals of Communications (Semesters 1 & 2)
$ 12

> GCSE (9–1) Mathematics J560/01 Question Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) November 2021
$ 6

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS (Foundation Tier) 8300/2F) PAPER 2 MARK SCHEME FOR NOVEMBER 2022
$ 13

CPCS Certified Provider Credentialing Specialist Exam Study Questions. 96 Questions with 100% Correct Answers – COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 7

eBook The Lives of Sharks 1st Edition By Daniel Abel, Dr.R.Dean Grubbs
$ 30

>_AS LEVEL Mathematics A_H230/01 Mark Scheme NOV 2021 | Pure Mathematics and Statistics
$ 6.5

LAB REPORT PHYSICS
$ 10

WINDOWS Operating Systems
$ 4
.png)
CHC Practice Test Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 10

eBook Birds of the Middle East 3rd Edition By Richard Porter,Oscar Campbell , AbdulRahman Al-Sirhan
$ 30

Week 5 Case Study Fetal Distress/Cesarean Section RAPID Reasoning Luella Jones, 25 years old
$ 11
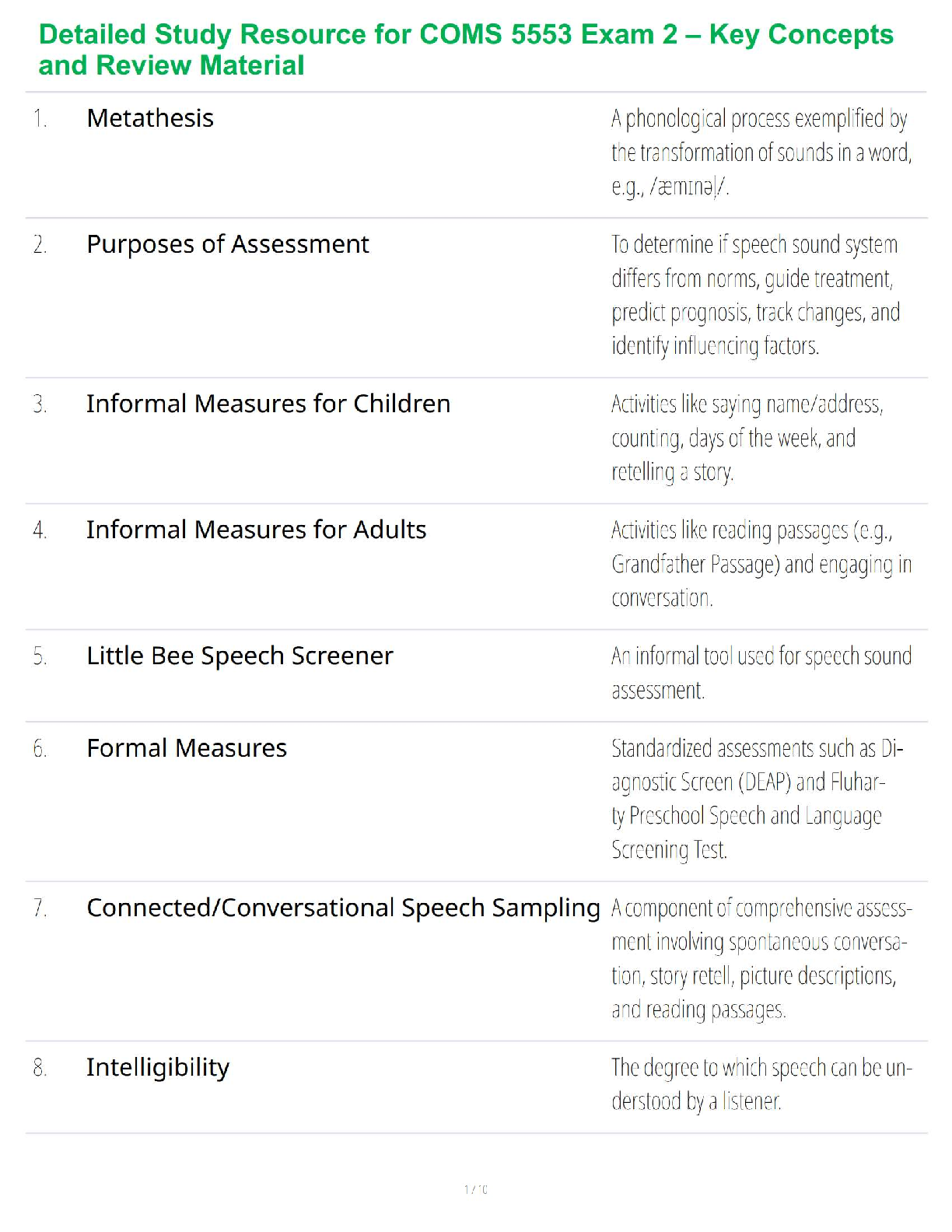
Detailed Study Resource for COMS 5553 Exam 2 – Key Concepts and Review Material
$ 7.5

eBook [PDF] Heat Exchangers Volume I Classification, Selection, and Thermal Design 3rd Edition By Kuppan Thulukkanam
$ 20

HE Summer Exam 22
$ 3

Rasmussen College - MAT GAM- 02 Mathematics of Games Math Pre Test ONE Rated A
$ 15

WGU C170 - PRE-ASSESSMENT Exam 100% Correct/WGU C170 - PRE-ASSESSMENT Exam 100% Correct
$ 12

eBook PDF for Modern control systems 14th globel Edition By Robert H. Bishop_ Richard C. Dorf
$ 29

OCR A Level Mathematics B (MEI) H640/01 Pure Mathematics and Mechanics QUESTION PAPER Tuesday 7 June 2022 – Afternoon
$ 9

Introduction to Programming
$ 1

MATH 225N Week 3 Lab Assignment: Article on Concussion|Latest 2020/2021 Complete Verified solution.
$ 9
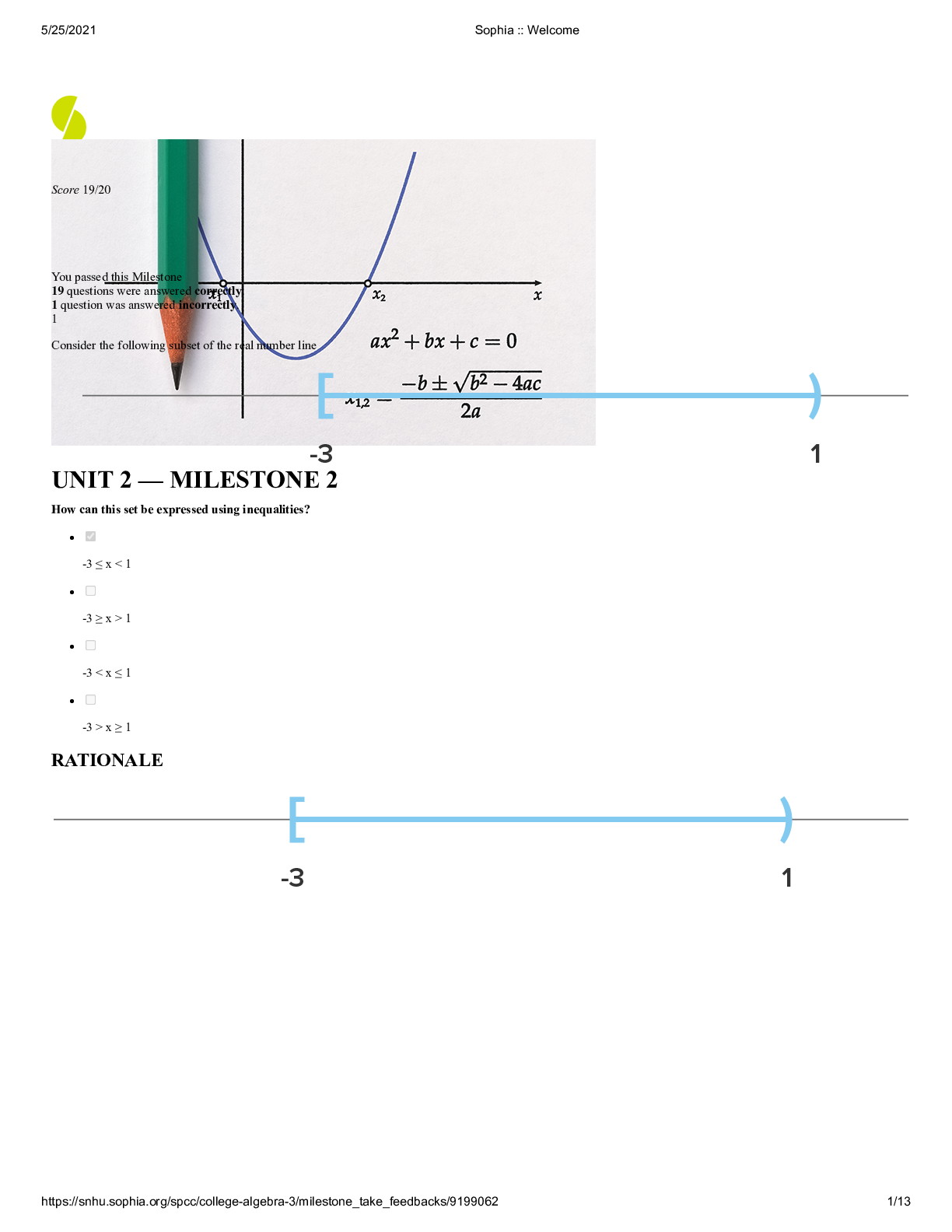
Sophia Unit 2 Milestone 2 College Algebra with correct answers
$ 14

NURS 231 MODULE 8 EXAM GRADE A+ CORRECT
$ 18

Solutions Manual for Applied Numerical Methods with Python for Engineers and Scientists 1st Edition By Steven Chapra
$ 26

Nasm CPT Final Exam Study Guide 100% Correct
$ 13

TEST BANK for Choices & Connections An Introduction to Communication, 2nd Edition by Steven McCornack, Joseph Ortiz
$ 24

EconomicsMcqsPdfByPakmcqs
$ 18

Week 2 - Study guide
$ 9.5

WGU C170 VHT2 TASK 1: NORMALIZATION AND DATABASE DESIGN
$ 11

Patho All Module Exams
$ 11

A Level Further Mathematics A_Y541/01 Mark Scheme Oct 2021 | Pure Core 2











.png)
















