PN2 Final Practice Quiz with (GRADED A) answers | 100% GUARANTEED PASS.
Document Content and Description Below
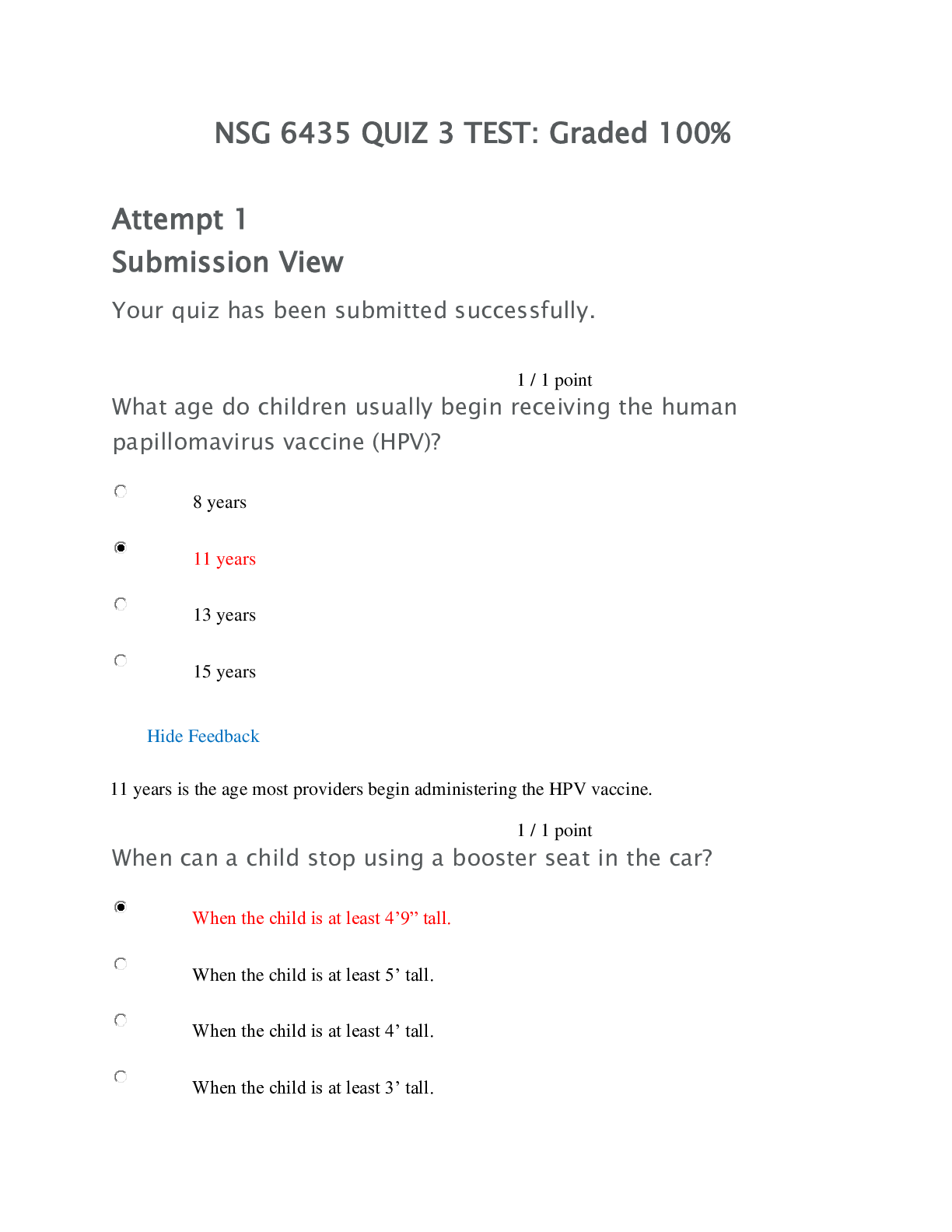
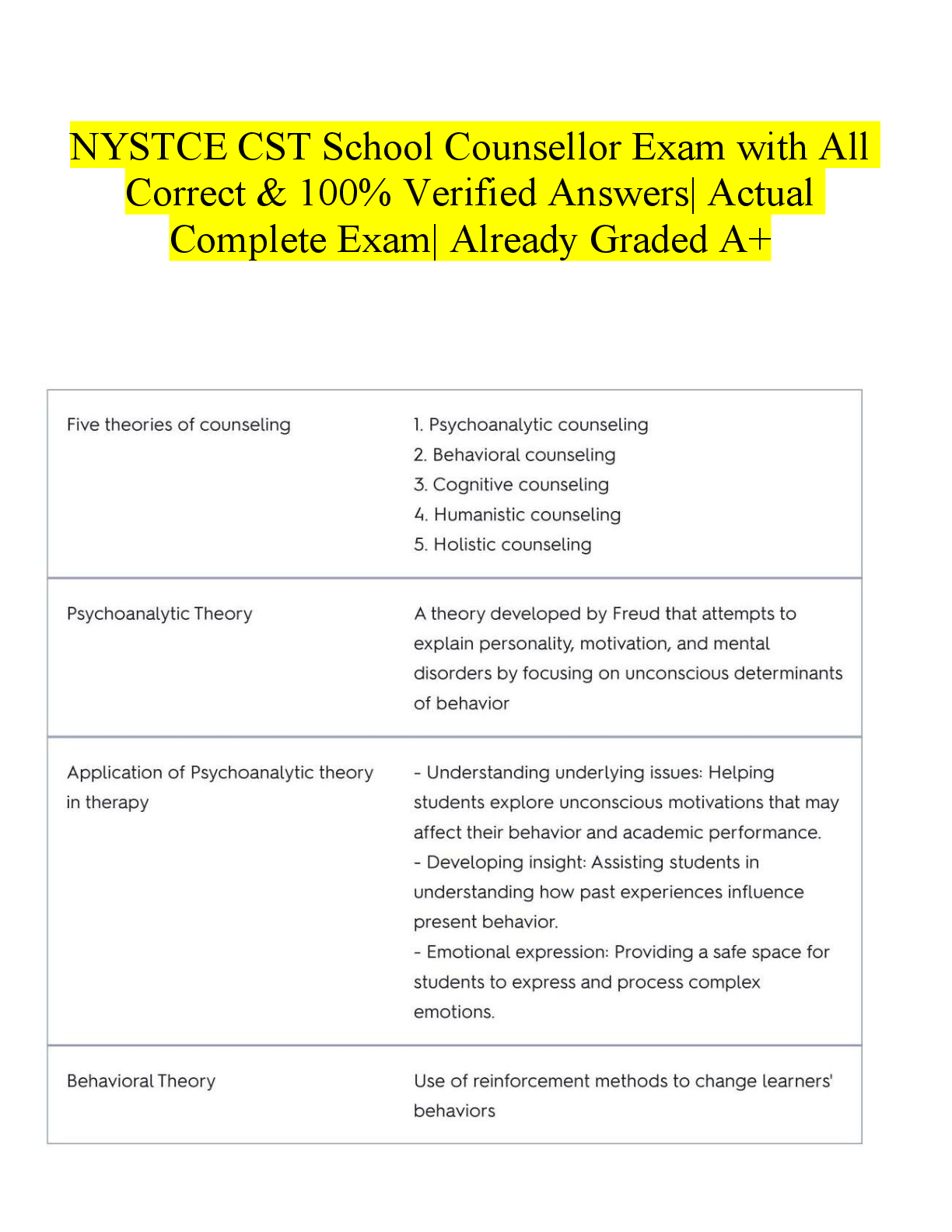
Final Practice Quiz PN2 1. What intervention is most important to teach the client about identifying the onset of dehydration? a. Converting ounces to milliliters b. Obtaining and c ... harting daily weight * c. Measuring abdominal girth d. Selecting food items with high water content 0.2 points Question 2 1. A client has hypokalemia. Which question by the nurse obtains the most information on a possible cause? a. “Do you use sugar substitutes?” b. “Have your bowel habits changed recently?” c. “Do you use diuretics or laxatives?” * d. “Do you have any kidney disease?” 0.2 points Question 3 1. A client has been treated for hypokalemia. Which clinical manifestation or condition indicates that treatment has been effective? a. Having a bowel movement daily* b. Gaining 2 lb during the past week c. Fasting blood glucose level of 106 mg/dL d. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showing inverted T-waves 0.2 points Question 4 1. Which client statement indicates the need for more teaching regarding identification of the early manifestations of hypokalemia? a. “When I am constipated, I drink more fluids.”* b. “I check my pulse each morning and each night.” c. “When my muscles feel weak, I eat a banana.” d. “I have been weighing myself every day.” 0.2 points Question 5 1. A client is being discharged and needs to self-monitor for the development of hyperkalemia. Which intervention is most important for the nurse to teach the client? a. Assessing radial pulse for a full minute twice a day* b. Weighing self daily at the same time of day c. Ensuring an oral intake of a least 3 L of fluids per day d. Restricting sodium as well as potassium intake 0.2 points Question 6 1. In evaluating the electrocardiogram (ECG) in a client with acidosis, the nurse correlates which ECG change with effectiveness of therapy? a. P-wave preceding the QRS complex b. Heart rate decreased to 62 beats/min c. Small U-waves present after each complex d. T-waves present, normal height * 0.2 points Question 7 1. The nurse correlates which condition with the following arterial blood gas values: pH 7.48, HCO – 22 mEq/L, PCO 28 mm Hg, PO 98 mm Hg? a. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease b. Anxiety-induced hyperventilation* c. Diarrhea and vomiting for 36 hours d. Diabetic ketoacidosis and emphysema 0.2 points Question 8 1. The home care nurse is making a follow-up visit to a client who had total hip replacement surgery 2 weeks ago. Which client statement indicates a need for clarification regarding postoperative routine? a. “Now that my hip doesn’t hurt, I can cross my legs like a lady again.” * b. “I take 200 mg of Motrin (ibuprofen) at bedtime so that I can sleep.” c. “My daughter helps me put on my elastic TED (thromboembolic deterrent) hose every day.” d. “Each day, I try to increase my walking time by at least 10 minutes.” 0.2 points Question 9 1. A nurse is caring for a client who has had rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for 5 years. Which laboratory value requires the most immediate intervention by the nurse? a. Hemoglobin (Hg), 10.6 g/dL b. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), 16 mg/dL c. Creatinine, 3.2 mg/dL * d. White blood cell count (WBC), 3800/mm3 0.2 points Question 10 1. The nurse is teaching a postmenopausal client about the risk of acquiring HIV infection. The client states, “I’m an old woman! I cannot possibly get HIV.” What is the nurse’s best response? a. “You might be right. How often do you engage in sexual activities?” b. “Women in your age-group are the fastest growing population of AIDS clients today.” * c. “Your vaginal walls become thicker after menopause, which increases your risk.” d. “Hormonal fluctuations after menopause make it harder to fight off infection.” 0.2 points Question 11 1. A client with asthma reports “not being able to take deep breaths.” The nurse auscultates decreased breath sounds in the bases, and no wheezes. What is the nurse’s best action? a. Have the client cough forcefully. b. Assess the client’s oxygen saturation. * c. Encourage the client to stay calm and take deep breaths. d. Document the findings and continue to monitor. 0.2 points Question 12 1. A client diagnosed with asthma has not responded well to medication. The client is concerned and asks the nurse, “What is wrong with me, and why am I not getting better?” What is the nurse’s best response? a. “It is possible that genetic testing may help.” * b. “You should try homeopathic medicine.” c. “The medication dose has to be increased.” d. “You just weren’t used to the medication yet.” 0.2 points Question 13 1. The nurse is assessing a client with lung disease. Which symptom does the nurse intervene for first? a. The client has bilateral dependent leg edema. * b. The client’s anterior-posterior chest diameter is 2:2. c. Clubbing of the finger tips is noted. d. The client is pale. 0.2 points Question 14 1. The nurse is worried that a client who is not entirely reliable is being discharged home on therapy for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. What strategy is the best to use for this client? a. IV drug administration b. Remaining in the hospital c. Directly observed therapy* d. Isolation 0.2 points Question 15 1. A nurse is about to administer the first dose of captopril (Capoten) to a client with hypertension. Which is the priority nursing intervention? a. Place the client in Trendelenburg position to facilitate blood flow to the heart. b. Educate the client to sit on the side of the bed for a few minutes before rising*. c. Instruct the client to drink 3 L of fluid daily when taking this medication. d. Take the client’s apical pulse for 1 full minute before drug administration. 0.2 points Question 16 1. The nurse is assessing a client who reports claudication after walking a distance of one block. The nurse notes a painful ulcer on the fourth toe of the client’s right foot. What condition do these findings correlate with? a. Deep vein thrombosis b. Peripheral arterial disease* c. Peripheral venous disease d. Diabetic foot ulceration 0.2 points Question 17 1. The new graduate nurse is assessing a client with an unrepaired abdominal aortic aneurysm. What assessment technique requires further education by the supervising nurse? a. Measurement of abdominal girth b. Palpation of the abdominal midline area * c. Observation of abdominal wall movement d. Auscultation of any area of the abdomen 0.2 points Question 18 1. The nurse is providing health education to a client with chronic venous stasis ulcers. What priority instruction does the nurse include? a. “Remove and reapply a new DuoDerm dressing to your ulcers each day.” b. “Take 1 low-dose aspirin (81 mg) daily to prevent inflammation.” c. “Clean venous ulcers with Betadine before applying a dressing.” d. “Apply antiembolism stockings before getting out of bed in the morning.*” 0.2 points Question 19 1. The nurse assesses a client’s legs. Which assessment finding indicates arterial insufficiency? a. Ankle discoloration and pitting edema b. Pain with activity but not while resting c. Full veins present in dependent extremity d. Dependent mottling and absence of hair * 0.2 points Question 20 1. The nurse is assessing a client with a history of migraines. Which clinical manifestation is an early sign of a migraine with aura? a. Lethargy b. Numbness of the tongue c. Visual disturbances * d. Vertigo 0.2 points Question 21 1. The nurse is assessing a client with a cluster headache. Which clinical manifestation does the nurse expect to find? a. Exophthalmos b. Ipsilateral tearing of the eye * c. Abrupt loss of consciousness d. Neck and shoulder tenderness 0.2 points Question 22 1. The daughter of a client with Alzheimer’s disease asks, “Will the medication my mother is taking improve her dementia?” How does the nurse respond? a. “It will not improve dementia but can help control emotional responses.” * b. “It is used to halt the advancement of Alzheimer’s disease but will not cure it.” c. “It will provide a steady improvement in memory but not in problem solving.” d. “It will help your mother live independently once more.” 0.2 points Question 23 1. The nurse assesses a client who has myasthenia gravis. Which clinical manifestation does the nurse expect to observe in this client? a. Absent deep tendon reflexes b. Lateralization to the affected side during the Weber test c. Impaired stereognosis d. Inability to perform the six cardinal positions of gaze* 0.2 points Question 24 1. A client with a ruptured tympanic membrane asks the nurse whether hearing will be affected permanently. Which is the nurse’s best response? a. “Yes. Any time the eardrum is ruptured it will form a scar, which will cause some degree of permanent hearing loss.” b. “Possibly. The eardrum usually heals in 1 to 2 weeks. Any persistent hearing problem should be evaluated.” * c. “Yes. It will be important for you to be fitted with a hearing aid as soon as possible.” d. “No. Antibiotics will help resolve the infection and cure your hearing impairment.” 0.2 points Question 25 1. Which client does the nurse assess most carefully for the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease? a. Postoperative client who has a nasogastric (NG) tube * b. Client with atrial fibrillation who drinks decaffeinated coffee c. Client who has lost 20 pounds through diet and exercise d. Diabetic client taking oral hypoglycemic agents 0.2 points Question 26 1. Which statement indicates that the client understands the management of his or her sliding hiatal hernia? a. “I will remain upright for several hours after each meal.” * b. “I will lie flat for 30 minutes after each meal.” c. “I will have my blood count done in 2 weeks to check for anemia.” d. “I will sleep at night while lying on my left side to prevent reflux.” 0.2 points Question 27 1. The nurse is caring for a client who presents with chronic epigastric pain, heartburn, and anorexia. The client asks the nurse how the doctor can best determine whether the symptoms are caused by gastritis. Which is the nurse’s best response? a. “The doctor will take a look inside your stomach using a tube with a light on the end of it.”* b. “A blood sample will be sent to the laboratory to determine whether you have a stomach infection or bleeding.” c. “A CT scan of your abdomen will show whether inflammation is present in your stomach.” d. “You will be asked to drink a barium solution while x-rays are taken of your stomach.” 0.2 points Question 28 1. A client has hypothyroidism. Which problem does the nurse address as a priority for this client? a. Heat intolerance b. Body image problems c. Obesity d. Depression and withdrawal* 0.2 points Question 29 1. The nurse is assessing a client with Graves’ disease and finds that the client’s temperature has risen 1° F. Before notifying the health care provider, which action by the nurse takes priority? a. Administer a dose of acetaminophen (Tylenol). b. Turn the lights down in the client’s room and shut the doo*r. c. Calculate the client’s apical-radial pulse deficit. d. Call for an immediate electrocardiogram (ECG). 0.2 points Question 30 1. Three hours after surgery, the nurse notes that the breath of the client with type 1 diabetes has a “fruity” odor. Which is the nurse’s best first action? a. Perform pulmonary hygiene. b. Increase the IV fluid flow rate. c. Document the finding in the client’s chart. d. Test the serum for ketone bodies. * 0.2 points Question 31 1. A diabetic client has numbness and reduced sensation. Which intervention does the nurse teach this client to prevent injury? a. “Examine your feet daily using a mirror.” b. “Use a bath thermometer to test the water temperature*.” c. “Rotate your insulin injection sites.” d. “Wear white socks instead of colored socks.” 0.2 points Question 32 1. In a client with less than the normal amount of bicarbonate in the blood and other extracellular fluids, what response does the nurse anticipate? a. Increased risk for acidosis* b. Decreased risk for acidosis c. Decreased risk for alkalosis d. Increased risk for alkalosis 0.2 points Question 33 1. Which response is an example of compensation for an acid-base imbalance? a. Increase in the rate and depth of respirations when exercising * b. Increased urinary output when blood pressure increases during exercise c. Increased release of acids from kidneys during exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) d. Increased thirst when spending time in an excessively dry environment 0.2 points Question 34 1. A client has moderate acidosis. Which assessment does the nurse perform first? a. Perform assessments of musculoskeletal strength. b. Determine whether the client is awake, alert, and oriented. c. Assess respiratory rate and depth and work of breathing. d. Take the client’s pulse and blood pressure, and analyze the electrocardiogram (ECG) strip. * 0.2 points Question 35 1. Which action by the nurse is most effective to prevent becoming exposed to the human immune deficiency virus (HIV)? a. Wash hands before and after contact with clients who are HIV positive. b. Convert parenteral medications to an oral form for clients who are HIV positive. c. Place clients who are HIV positive in Contact Precautions. d. Always use Standard Precautions with all clients in the workplace.* 0.2 points Question 36 1. The nurse is caring for a young client who has acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a very low CD4+ cell count. The nurse is teaching the client how to avoid infection at home. Which statement by the client indicates that additional teaching is needed? a. “It will seem funny but I’ll run my toothbrush through the dishwasher.” b. “My brother will change the kitty litter box from now on.” c. “I will not drink juice that has been sitting out for longer than an hour.” d. “I will let my sister clean my pet iguana’s cage from now on.”* 0.2 points Question 37 1. The nurse is caring for a young woman at the primary health care clinic. Which assessment finding leads the nurse to question the client about risk factors for HIV? a. Six vaginal yeast infections in the last 12 months* b. Very heavy periods and breakthrough bleeding c. Unable to become pregnant for the last 2 years d. Severe cramping and irregular periods 0.2 points Question 38 1. A client who is positive for HIV presents with confusion, fever, headache, blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. What does the nurse do first? a. Assess the client’s deep tendon reflexes. b. Start an IV line with normal saline. c. Assess the client’s pupil reaction. d. Ask the client to place his chin on his chest*. 0.2 points Question 39 1. A client is admitted with early-stage heart failure. Which assessment finding does the nurse expect? a. An increase in heart rate and respiratory rate * b. An increase in creatinine and extremity edema c. A decrease in respirations and oxygen saturation d. A decrease in blood pressure and urine output 0.2 points Question 40 1. The nurse is assessing clients on a cardiac unit. Which client does the nurse assess most carefully for developing left-sided heart failure? a. Middle-aged man with pulmonary hypertension b. Middle-aged woman with aortic stenosis * c. Older woman who smokes cigarettes daily d. Older man who has had a myocardial infarction 0.2 points Question 41 1. The nurse is assessing a client in an outpatient clinic. Which client statement alerts the nurse to possible left-sided heart failure? a. “I have been awakened by the need to urinate at night.” b. “I have been drinking more water than usual.” c. “I have experienced blurred vision on several occasions.” d. “I have to stop halfway up the stairs to catch my breath.” * 0.2 points Question 42 1. A client with atherosclerosis asks a nurse which factors are responsible for this condition. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “A combination of platelets and fats accumulates, narrowing the artery and reducing blood flow.” * b. “Excess sodium causes injury to the arteries, reducing blood flow and eventually causing obstruction.” c. “Injury to the arteries causes them to spasm, reducing blood flow to the extremities.” d. “Excess fats in your diet are stored in the lining of your arteries, causing them to constrict.” 0.2 points Question 43 1. The nurse is assessing for skin changes in an African-American client admitted with peripheral arterial disease. What does the nurse monitor for? a. Cyanosis of the nail beds* b. Loss of toenails c. Excess hair growth d. Pitting edema in the feet 0.2 points Question 44 1. The nurse is talking to the family of a client who has Parkinson’s disease. Which statement indicates that the family has a good understanding of the changes in motor movement associated with this disease? a. “She has trouble chewing so I will offer bite-sized portions.” * b. “I think this disease makes her nervous. She perspires all the time.” c. “I can never tell what she’s thinking. She hides behind a frozen face.” d. “She drools all the time so I just can’t take her out anywhere.” 0.2 points Question 45 1. The nurse is caring for a client with Parkinson’s disease. Which intervention does the nurse implement to prevent respiratory complications in the client? a. Ensure fluid intake of at least 3 L/day. b. Teach the client pursed-lip breathing techniques. c. Maintain the head of the bed at 30 degrees or greater*. d. Keep an oral airway at the bedside. 0.2 points Question 46 1. Which dietary modification does the nurse provide for a client with hyperthyroidism? a. Decreased calories and proteins and increased carbohydrates b. Supplemental vitamins and reduction of calories c. Elimination of carbohydrates and increased proteins and fats d. Increased calories, proteins, and carbohydrates * 0.2 points Question 47 1. Twelve hours after a total thyroidectomy, the client develops stridor. Which is the nurse’s priority intervention? a. Hyperextend the client’s neck and apply oxygen. b. Document the finding and assess the client hourly. c. Prepare for emergency tracheostomy and call the health care provider*. d. Reassure the client that the voice change is temporary. 0.2 points Question 48 1. Which ethnic groups should the nurse screen specifically for hypocalcemia? (Select all that apply.) a. Asians * b. Hispanics c. Blacks * d. American Indians* e. Whites 0.2 points Question 49 1. The nurse is reviewing a client’s laboratory results. The nurse correlates elevations in which values as risk factors for atherosclerosis? (Select all that apply.) a. Serum albumin, 4 g/dL b. Triglycerides, 200 mg/dL * c. Total cholesterol, 280 mg/dL* d. Low-density cholesterol, 160 mg/dL* e. High-density cholesterol, 50 mg/dL 0.2 points Question 50 1. The nurse is performing health screening in a local mall. Which people does the nurse counsel to be tested for diabetes? (Select all that apply.) a. Woman with a 30-pound weight gain during pregnancy b. African-American or American Indian * c. Person with history of pancreatic trauma d. Middle-aged woman with physical inactivity most days of the week * e. Young woman who gave birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds* f. Male with a body mass index greater than 25 kg/m2 ** [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

HESI ADV MED SURG 2019 v2 Study Guide|ADVANCED HESI MED SURG TEST BANK|HESI FUNDAMENTALS RATIONALES MEDICAL SURGICAL VERSION 2|Hesi Fundamentals RN |Hesi Fundamentals Practice Questions|Hesi Fundamentals EXIT|PN2 HESI Exam 2|PN3 HESI Exam 3|Mental Health
HESI ADV MED SURG 2019 v2 Study Guide|ADVANCED HESI MED SURG TEST BANK|HESI FUNDAMENTALS RATIONALES MEDICAL SURGICAL VERSION 2|Hesi Fundamentals RN |Hesi Fundamentals Practice Questions|Hesi Fundament...
By Prof. Goodluck 4 years ago
$14.5
13
Reviews( 0 )
$14.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 11, 2021
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 11, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
103






 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)