*NURSING > EXAM > NURS 5352 Advanced health assessment test 1 with complete solution | 100% VERIFIED (All)
NURS 5352 Advanced health assessment test 1 with complete solution | 100% VERIFIED
Document Content and Description Below
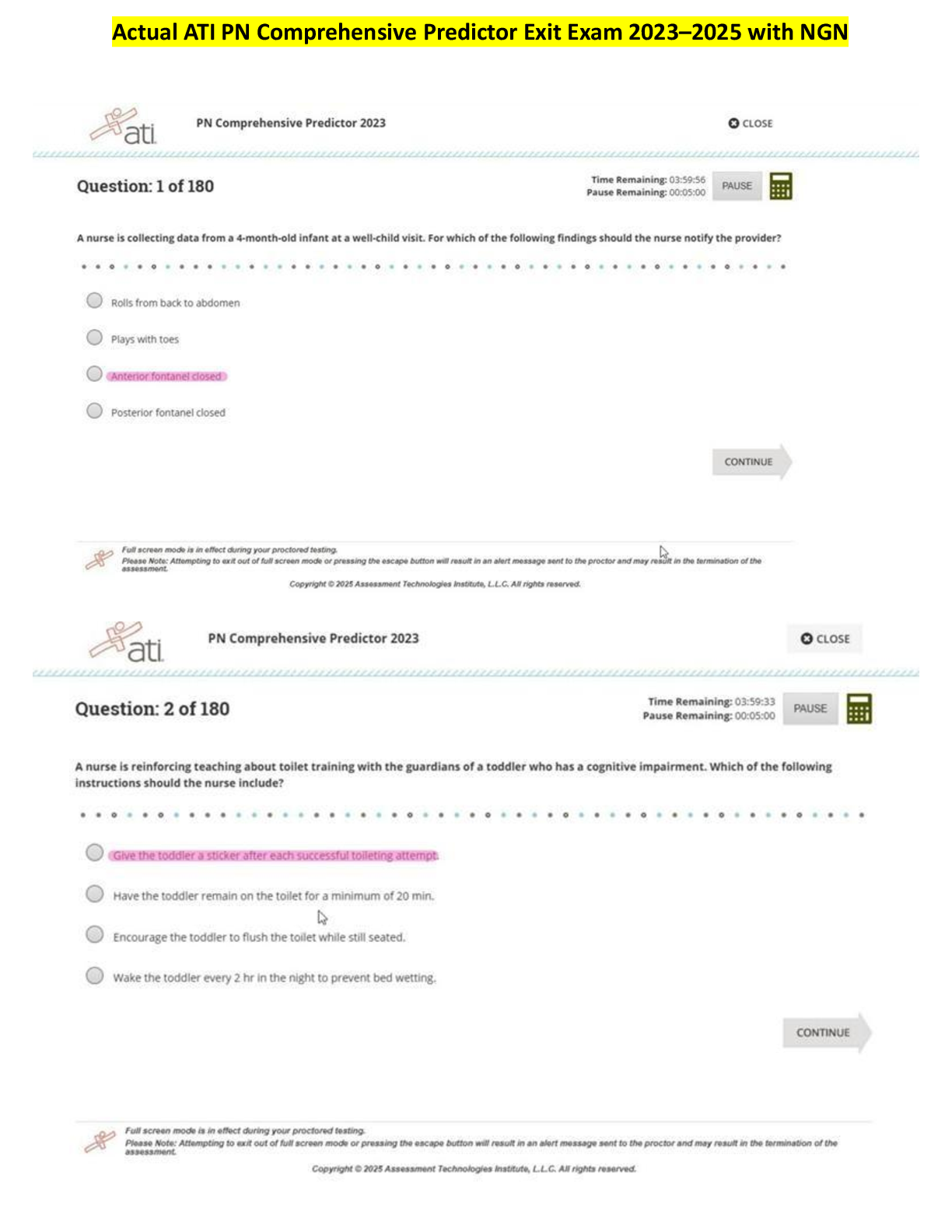
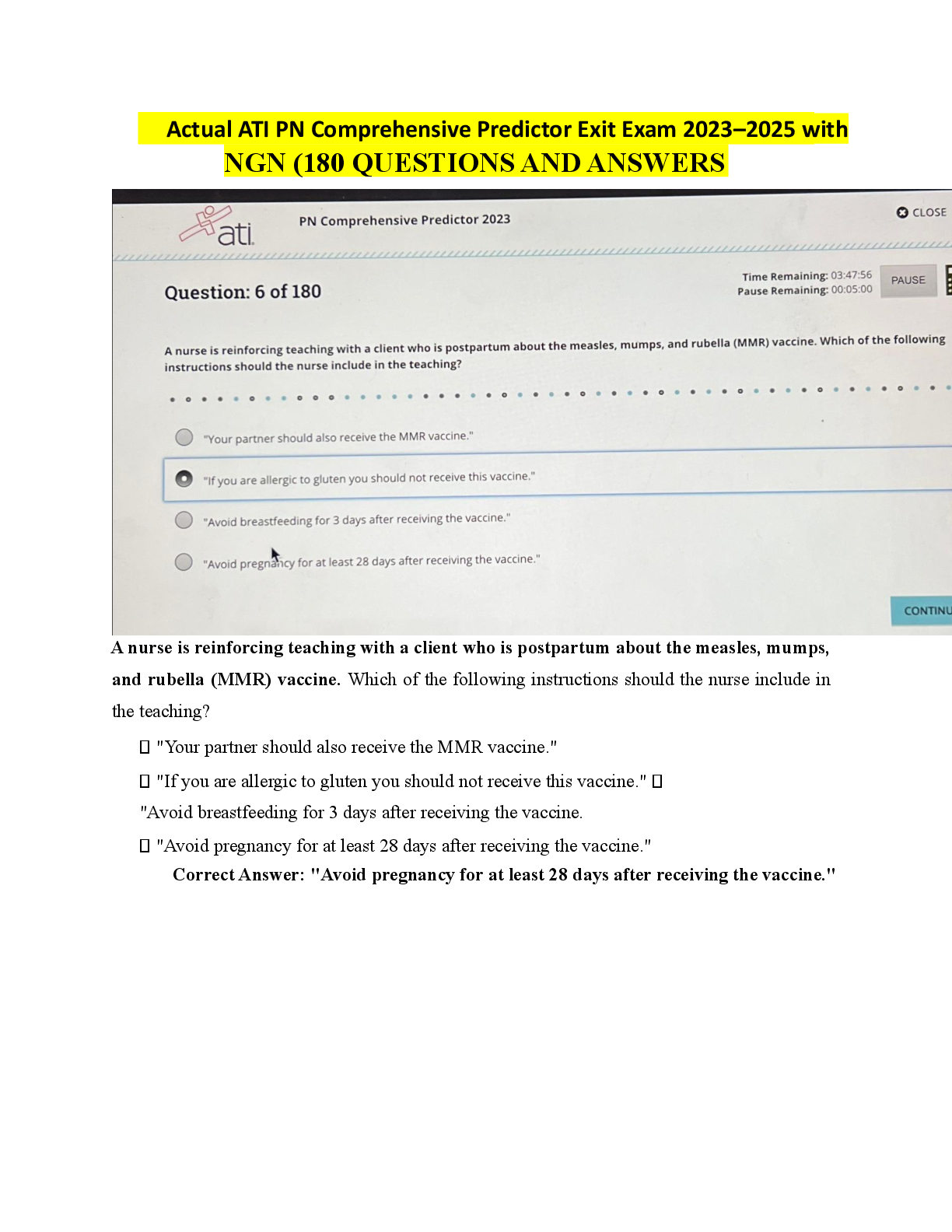
NURS 5352 Advanced health assessment test 1 with complete solution | 100% VERIFIEDAttempt History Attempt Time Score LATEST Attempt 1 59 minutes 88 out of 100 Correct answers are hidden. Score ... for this quiz: 88 out of 100 Submitted Feb 8 at 2:09pm This attempt took 59 minutes. In children what is a common cause of hair loss? Endrocrine disorders Tinea capitis fetal alcohol syndrome genetic disorders HEAD: In children, a common cause of hair loss is tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp. Seidel (2011), P. 248 Which of the following benign condition is characterized by bright red blood in a sharply defined area surrounded by healthy appearing conjunctiva? Hemorrhagic conjunctivis Subconjunctival hemorrhage allergic conjuctivitis bacterial conjuctivitis EYE: While allergic conjunctivitis is benign it is characterized by itchy eyes with clear discharge not blood. Bacterial cojunctivitis is characterized by errythemious conjunctiva often being in the entire conjuctiva and not clear borders and not bright red blood. Hemorrhagic conjunctivitis is found with Ebola and is a late sign in the disease which is definately not benign by this point but rather often fatal and also will not have clear borders. Seidel (2011), p. 274. Peripheral vision is assessed by which test? Confrontation Pupillary reaction Accomodation Snellen E chart EYE: The confrontation test measures peripheral vision. The examiner sits or stands across from the patient and asks the patient to close one eye while the examiner closes the opposite eye. The examiner then proceeds to wave the fingers while moving the extended arms from a lateral to a central position along both the temporal and the nasal fields. The pupillary reaction test is done by observing the pupil’s response to light. The accommodation test deals with pupil reaction to light, whereas the Snellen chart measures visual acuity. The swinging flashlight test evaluates the health of the optic nerve by looking for an afferent pupillary defect. Seidel, p. 271 Nasal symptoms that imply an allergic response include: Deviated septum Bluish grey or pale pink turbinates Purulent nasal discharge Small atrophied nasal mucous membranes NOSE: An allergic finding includes bluish gray or pale pink nasal turbinates that are swollen and boggy and a transverse crease at the junction between the cartilage and the bone of the nose. Seidel, p. 312 Intense pain with movement of the pinna is most closely associated with: Otitis media with effusion Otitis externa Temporomandibular joint syndrome Bacterial otitis media EAR: suspect otitis externa (swimmer’s ear) when pulling of the pinna reproduces ear pain. The other conditions do not commonly cause the same finding. Seidel, p. 327 A smooth red tongue with a slick appearance may indicate: Fungal infection Niacin or B12 deficiency Recent use of antibiotics Geographic tongue THROAT: A smooth red tongue with a slick appearance may indicate a niacin or vitamin B12 deficiency. Oral cancer involves lesions; recent use of antibiotics can turn the tongue yellowbrown to black and hairy; and fungal infections result in slightly raised white, creamcolored, or yellow spots in the mouth. Geographic tongue has irregular areas of whitish and red areas. Seidel, 316317 Bulging of an amber tympanic membrane with decreased mobility is consistent with: Healed tympanic membrane perforation Impacted cerumen in the external auditory canal Pseudomonas infection of the external auditory canal Middle ear effusion EAR: An amber color, with bulging of the tympanic membrane and without mobility or redness, most often indicates the presence of fluid in the middle ear. Seidel, p. 310 The head and chest circumference should be about the same on a patient until what age? 6 years 2 years 4 years 1 year CHEST & LUNGS: Seidel 361 and tegrity lecture. There are variations based on the maturity of the infant at birth noted in Seidel but they should generally be the same until age two or further investigation is needed. A 29yearold white woman presents to the clinic for evaluation. She is concerned because her skin, palms and soles of her feet are really yellow. You order blood work including LFTs and a hepatitis profile. The results of all her blood work are negative for hepatitis and her LFTs are within normal limits. With this in mind, what would the nurse practitioner want to ask this patient to explore other differential diagnoses, since hepatitis and other forms of liver disease are ruled out? If she takes a lot of Iron? If she has a history of diabetes mellitus If she eats a lot of yellow and orange vegetables Whether she has unusual bleeding problems SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: In the absence of liver disease, another cause of jaundice is increased carotene pigmentation. Diets high in carrots, sweet potatoes, and squash are high in carotene and can make the skin appear to be jaundiced. Seidel, p. 162 Wellcircumscribed silvery plaques on the trunk and extensor surfaces of the body is most consistent with which skin disorder? Psoriasis Pityriasis Rosea Tinea Eczema SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: Unlike other skin conditions, silvery plaques characterize psoriasis. Seidel, p. 190 A 17yearold student complains of a "rash for 3 days." After a complete history and ROS, the patient admits that there was a solitary oval plaque (Known as a "Herald Patch") on his upper chest about a week prior to the onset of this rash. Upon examination, you note pale, erythematous oval plaques over the trunk. They have fine scales and are arranged in a "christmas tree" pattern on his trunk. What is highest on your list of differential diagnoses? Tinea Contact Dermatitis Seborrheic Dermatitis Pityriasis Rosea SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: The described rash is the typical presentation of pityriasis rosea. The rash is not infectious or contagious, does not involve the palms and soles, and usually lasts for several weeks. Pityriasis rosea begins with a sudden primary (herald) patch, with the generalized eruption to the trunk and extremities following 1 to 3 weeks later. SEIDEL, P. 190 A shiny, elevated nodule that is pearly or translucent, with tiny blood vessels noted on the surface describes this most common cutaneous neoplasm. What is the name of this lesion? Malignant melanoma. Squamous cell carcinoma Seborrheic keratosis. Basal cell carcinoma. SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. It occurs more frequently on sunexposed parts of the body. Seidel, p. 195 A 5yearold child presents with discrete cloudy vesicles on an erythematous base (dew drops on a rose petal appearance) that began near her scalp and are spreading to the trunk. There are some vesicles that are umbilicated and others that are beginning to crust over. The child has a lowgrade fever and feels tired. What common childhood illness is most consistent with these findings? Rubeola Varicella Acne Vulgaris. Impetigo SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: The description of this child's complaint is a varicella rash, not acne, impetigo or rubeola. Chickenpox is a highly communicable disease and can be prevented by immunization. The period of communicability lasts from 1 or 2 days before onset of the rash until all the vesicles have crusted over, which usually takes about a week. Seidel, p. 207 Question 14 2 / 2 pts You are seeing a 5 year old boy in the clinic. The mother states that her son developed a small red bump on his upper lip 3 days ago, with increase in size and drainage. He has also been complaining of intense itching. Your inspection reveals crusted over vesicles with honeycolored exudate on his nares, and upper lip. Which condition is consistent with the above findings? Drug eruption Acne Vulgaris Chicken Pox Impetigo SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: Impetigo causes intense pruritus, regional lymphadenopathy, and honeycolored exudative crusting as the vesicles or bullae rupture and dry. Seidel, p. 206 A 24 year old male is brought in to the emergency room for evaluation. He was reportedly mumbling incoherently, and telling bystanders that he hears voices of people who are following him. His physical appearance is unkempt, with poor hygiene, and he is pacing in the exam room while you are talking with him. What disorder would BEST fit this description? Obsessive/Compulsive Disorder Schizophrenia. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Expressive Aphasia Psychiatric/Mental Assessment: Expressive Aphasia is the inability to speak words; ADHD is a problem of impaired attention and hyperactive behavior - fidgeting, short attention-span, disruptive behavior, etc.; Obsessive/Compulsive disorder is a problem with compulsive behaviors, such as repetitive hand-washing, cleaning, etc. Schizophrenia is associated with paranoid thoughts, delusions, incoherent speech, poor hygiene, and hallucinations - such as described with this patient. Seidel, p. 85 The nurse practitioner asks the patient to draw a clock and place the time at "ten minutes after eleven o'clock." What is the purpose of this exam? to determine the patient's level of mental retardation. to detect disturbances in the norepinephrine and serotonin neurotransmitters. To measure function of the parietal lobe of the brain to measure cognitive, motor, and perceptual function Question 17 2 / 2 pts A wise practitioner will never assume a psychiatric diagnosis, until all physical causes are ruled out. The mnemonic THINCMED is useful when evaluating for underlying medical conditions. The "T" in this mnemonic stands for: Tumor Thyroid Trauma Thrombosis Psych/Mental Health Assessment: The medical mnemonic THINCMED is used to evaluate for underlying medical conditions that may mimic psychiatric disorders. The "T" stands for Tumor. H - Hormones, including thyroid; I - Infection/Immune diseases; N-Nutrition (B-Vitamins, Iron); C - CNS (head trauma, MS, seizures, Parkinsons); M - Miscellaneous (sleep apnea, anemia, CHF); E - Electrolytes and toxins; D - Drugs (Dr. Petersen's Psych/Mental Health lecture) A 22-year-old female nurse is interviewing an 86-year-old male patient. The patient avoids eye contact and answers questions only by saying, "Yeah," "No," or "I guess so." Which of the following is appropriate for the interviewer to say or ask? “Why are you so depressed?” “It’s hard for me to gather useful information because your answers are so short.” “Does your religion make it hard for you to answer my questions?” “Are you uncomfortable talking with me?” CULTURE: It is all right to ask if the patient is uncomfortable with any aspect of your person and to talk about it; the other choices are less respectful. Seidel: p 40 An aspect of traditional Western medicine that may be troublesome to many Hispanics, Native Americans/American Indians, Asians, and Arabs is Western medicine's attempts to: use a "holistic" approach that views a particular medical problem as part of the bigger picture. retrieve balance in an individual's life. establish harmony between a person and the entire cosmos. determine a specific cause for every problem in a precise way. CULTURE: United States is Activity Oriented. Seidel, p. 39 A naturalistic or holistic approach to health care often assumes: a reductionist view that looks to a very narrow cause and effect. there are supernatural forces that determine one's fate. there are external factors that must be kept in balance. that “hot” conditions require treatment with a “hot” remedy. CULTURE: A naturalistic or holistic approach often assumes that there are external factors—some good, some bad—that must be kept in balance if we are remain well. Seidel, p. 42 The attitudes of the health care professional are largely: enculturated and cannot be changed. difficult for the patient to sense. uninfluenced by patient behavior. culturally derived. CULTURE: The attitude of the health care provider is foundationally derived from one's own culture but we should be aware that this can cause stereotypical judgments to be made; understanding this is relevant to the success of patient relationships. Attitudes of the health care professional are easily detected by others, and they influence patient behavior. Seidel, p. 36 The Rosenbaum card is used to measure: A. distance perception. B. near vision. D. the ability to identify colors. C. peripheral distortion. The Rosenbaum card is best used to measure nearsightedness because the patient holds the card at a comfortable distance and reads from the card. The Rosenbaum card is not used to measure distance perception because distance perception cannot be accurately measured with a card held close. Peripheral vision is assessed by an examiner with hand movements. Color identification can be measured with color cards. Which type of speculum should be used to examine a patient's tympanic membrane? 1. The smallest speculum that will illuminate the ear 2. The largest speculum that will fit comfortably in the ear 3. The shortest speculum available 4. Any speculum that will fit the otoscope head The largest speculum that will fit comfortably in the ear canal should be used for optimal visualization. (Seidel, p. 67). The nurse practitioner notes a number of important physical findings when conducting the physical examination. In which section of the record should these findings be recorded? in the objective section in the subjective section in the assessment section in the section designated for the plan A detailed description of the symptoms related to the chief complaint is presented in the: Personal and Social History Past Medical History. General Patient Information History of Present Illness. Hx&Interviewing/SOAP: The signs and symptoms, and historical data of the patient's experience that lead up to the chief complaint is placed in the history of present illness. Seidel, p. 799 Which question would be considered a "leading question?" “What do you think is causing your headaches?” “You don’t get headaches often do you?” “On a scale of 1 to 10, how would you rate the severity of your headaches?” “At what time of the day are your headaches the most severe?” Hx&Interviewing/SOAP: This question would limit the information in the patient's answer. The other choices reflect open-ended questions. Seidel, p. 5 Periods of silence during the interview can serve important purposes, such as: Providing time for the patient to reflect and gather their thoughts. Promoting a calm environment. allowing the provider time to think of more questions to ask Letting the interviewer take a break Hx&Interviewing/SOAP: Silence is a useful tool during interviews for the purpose of reflection, summoning of courage, and displaying compassion. It is usually a clue for you to go slower and not to push too hard. Seidel, p. 7 Mr. F. is speaking with you, the health care provider, about his respiratory problem. Mr. F. says, "I've had this cough for 3 days, and it's getting worse." You reply, "Tell me more about your cough." Mr. F. states, "I wish I could tell you more. That's why I'm here. You tell me what's wrong!" Which caregiver response would be most appropriate for enhancing communication? “I’ll have to examine you to figure out what the problem is.” “I understand. After 3 days, you’re tired of coughing. Have you had a fever?” “ Your symptoms are so vague, it will take a while to figure it out.” “There's no need to get angry. Let me ask you some history questions. Where were you born?” Hx&Interviewing/SOAP: This is the only response aimed at focusing on the chief compliant, to gather more data and does not digress from the issue. Seidel, p. 8 A 50-year-old man comes to the primary care clinic. He tells you he is worried because he has had severe chest pains for the past 2 weeks. Which question below corresponds to the "C" in " OLDCARTS"? “Can you describe the pain?” “When did the pain start?” “Does the pain radiate to your arm, back or neck?” “What makes the pain better or worse?” Hx&Interviewing/SOAP: OLDCARTS is a mnemonic that helps make sure all characteristics of a problem are described. The "C" in OLDCARTS" describes the character of a problem. This question is asking about the character of the pain - is is sharp, dull, constant, etc. The other questions describe other components of "OLDCARTS" such as onset, location, associated and relieving factors.... Seidel, p. 799 A postoperative patient who recently underwent an appendectomy reports pain and a nurse medicates him for presumed incisional pain. When she goes back in thirty minutes to evaluate the patient she finds he is in acute respiratory distress. A code is called and on EKG, he is found to be experiencing ACS, acute coronary syndrome and is transferred to ICU. This patient's condition would have been detected sooner if the nurse had followed which principle of pain assessment? Trauma usually is associated with pain. The intensity of the pain should always be evaluated. A patient who appears to be resting comfortably may still be experiencing pain. There may be more than one cause of pain. A genogram is drafted for the purpose of obtaining: ethnic and cultural backgrounds genetic and familial health problems growth and developmental status the present medical history A genogram is a pictorial display of a person's family relationshipsLinks to an external site. and medical historyLinks to an external site.. It provides more information than a traditional family treeLinks to an external site. by outlining important hereditary patterns and psychological factors. It can be used to identify recurring medical conditions and/or hereditary tendencies A fixed image of any group that rejects its potential for originality or individuality is known as a(n): stereotype acculturation norm ethos Your new patient is a 40-year-old Middle Eastern man with the complaint of new abdominal pain. You are concerned about violating a cultural prohibition when you prepare to do his rectal examination. The best tactic would be to: do the exam as it is a necessary part of the physical examination ask a colleague from the same geographic area if this examination is acceptable forego the examination for fear of violating cultural norms inform the patient of the reason for the examination and ask if it is acceptable to him Recognizing the possible problem and talking about it, evoking feelings sooner rather than later, makes it easier. It is permissible to ask if the patient is uncomfortable with you or your background and to talk about it. Also, when any aspect of the patient's person disturbs you, you must try to understand why. When cultural differences exist, be certain that you grasp exactly what the patient means and know exactly what the patient thinks you mean in words and actions. Asking the patient if you are not sure is far better than making a damaging mistake. Avoid assumptions about cultural beliefs and behaviors made without validation from the patient. Knowledge of the culture or cultures represented by the patient should be used to: form a sense of the patient based on prior knowledge help make the interview questions more pertinent form a standard practice procedure for that culture draw conclusions regarding individual patient needs Cultural humility involves the ability to recognize one's limitations in knowledge and cultural perspective and be open to new perspectives. Rather than assuming all patients of a particular culture fit a certain stereotype, the health care provider should view each patient as an individual. In doing so, cultural humility helps equalize the imbalance in the patient-provider relationship. A provider may know many specific details about a patient's particular culture yet not show cultural humility. Cultural humility involves self- reflection and self-critique with the goal of having a more balanced, mutually beneficial relationship. Being open to understanding a patient's belief systems and developing a partnership is much more important than knowing everything about a patient's specific culture. Which technique is used during both the history taking and the physical examination process? auscultation inspection percussion palpation Perform an overall inspection of the entire body. This starts when you first enter the room, greet the patient and introduce yourself. The inspection process continues for each body system during the physical exam. A comprehensive health history is an essential guide for the rest of the examination, but not if the patient cannot communicate it. There is any number of reasons for this lack of communication: age, trauma, language difficulties, or simply that the patient is uncooperative. When documenting this type of data, the healthcare practitioner should: Assess the symptoms and use her own judgment in interpreting the history Write it down in the patient's own words Not write it down Write it down, but note that she feels that the patient is unreliable Chapter: 1 Difficulty: Easy Feedback: Ideally in such a case, a person other than the patient will be on hand to provide the history. When that is not the case, however, the healthcare practitioner should record the source of the data and his judgment about that source's reliability. Choose the most correct statement regarding focused and comprehensive physical examinations: A comprehensive (head to toe) exam should be performed on all nonemergent, new patients who will be receiving ongoing primary care form a particular provider or group of clinicians. A focused physical exam is performed only in non-emergent situations and if the patient does not have usual provider follwing their care. A comprehensive and focused exam should never be done in the same office visit. A comprehensive exam should take no longer than 10 minutes. Choose the most correct statement regarding preparing to do a physical examination: Develop a pattern that is systmeatic and comfortable for the patient and that will prompt you not to omit parts of the exam. Learn to adapt to the situation and establish a routine that feels comfortable and natural to you. A third party should be allowed in the room to make the patient more comfortable. all of the above. All of these statements are correct. See page 23 of the Rhoads & Petersen text Which of the following is true regarding the data taken in a health history? Subjective data, being inherently less accurate, is of less value than objective data. A successful individualized plan of care must incorporate subjective data. Most health history data is objective and measurable. Objective data is error-free, quantifiable data. The Objective component of the exam begins with: the diagnostic testing the interview process the physical exam, which includes inspection of the patient when the clinician first sees them, whether sitting on the exam table or walking into the room. the hands-on physical exam The objective component begins with the physical exam, including the review of systems and physical exam, which should match each other. An important piece of the objective information includes the initial inspection of the patient when first observed. Concise accurate documentation of all findings is imperative in the physical exam. Correct terminology, accurate descriptions, appropriate legends, and completeness are vital components within the physical exam. Legally, the standard rule is: If it was not documented, it either was not assessed or not done. Hence, omissions can be critical. See Rhoads & Petersen, page 37. During an interview, tears appear in the patient's eyes and his voice becomes shaky. Initially, you should: ask him if he would like some time alone. offer a tissue and let him know it is all right to cry. explain to the patient that you will be able to help him more if he can control his emotions. ask the patient what he is upset about. Empathy and understanding should be first in caring for an emotional patient. Never leave the patient. Let him know it is alright to cry, and offer him a tissue, which is an example of empathy. Asking him why he is upset is not as appropriate as asking 'would you like to talk about what is making you upset?' See Rhoades & Petersen, pgs. 4-8. After you ask a patient about her family history, she says, "Tell me about your family now." Which response is generally most appropriate? Give a brief, undetailed answer. Ask the patient why she needs to know. Ignore the patient’s comment and continue with the interview. Ask a direct question that re-focuses the patient on the chief complaint. Ignoring the patient’s comment and continuing with the interview would only cause friction in the developing clinician/patient relationship. Clinicians should strive to build a friendly and professional relationship. Giving a brief, undetailed answer is generally the most effective way to show the patient that you are listening, while still providing only minimal information and proceeding with the interview at hand. This is the correct answer. Asking a direct question that re-focuses the patient on the chief complaint would come across as ignoring the patient's question. This would not be correct. Asking the patient why she needs to know would only cause friction in the conversation and eventually prolong the interview, which is not what the goal should be. See Rhoads & Petersen, chapter 1. Fluorescing lesions are best distinguished by using a(n): Wood's light magnifying glass transilluminator incandescent bulb Wood's light is used mainly in the examination of epidermal pigmentary disorder and cutaneous infections. Applying the light to the skin in a dark room causes epidermal pigment to appear accentuated while dermal pigmentary disorders with normal epidermal findings are obscured. Depigmentation will similarly be exaggerated against normal skin, appearing chalky white. Rhoades & Petersen, pg. 83 In a sun-exposed area of the body, a shiny, elevated nodule that is pearly or translucent, with tiny blood vessels noted on the surface describes this most common cutaneous neoplasm. What is the name of this lesion? Basal cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma Malignant melanoma. Seborrheic keratosis. SKIN/HAIR/NAILS: Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. It occurs more frequently on sun-exposed parts of the body. Seidel, p. 195 Which of the following occurs when firm pressure is used to apply the stethoscope's bell end-piece to the skin? Most sounds are amplified. It functionally converts to a diaphragm endpiece. It transmits low-pitched sounds. Assessment findings are more accurate. The bell of the stethoscope is built to utilize the dead space between the patient's skin and the hollow inside of the bell. If firm pressure is applied, the patient's skin may come into contact with the interior of the bell. This eliminates this hollow space and it functions as a diaphragm, eliminating the ability to auscultate vascular sounds any better than a diaphragm would. See Module 1 in Canvas. Mr. S presents with eye pain. He points to a specific location in his eye and says, “ It feels like I have something in my eye.” Which is the most appropriate question for the healthcare practitioner to ask? Is the foreign body sensation in one or both eyes? When did you last have something to eat? When was your last eye exam? Have you always been near-sighted? Asking whether the foreign body sensation is bilateral will help narrow down your diagnoses. Ask about onset, have the patient rate the discomfort, ask about associated symptoms, any activities associated with exposure to foreign bodies, and what may relieve the symptoms. Rhoads & Petersen, pg 97 When examining the eyes of a neonate, it is important to remember: that the eyes of the fetus are not formed until late in gestation. that the neonates visual acuity is about 20/200 that central vision is fully developed at birth. ocular mobility is not measured in the infant since it develops later in the first year of life. During the first 8 weeks of gestation, the fetus's eyes are formed. Neonates have a visual acuity of 20/200. Peripheral vision is fully developed at birth; however, central vision develops later. Rhoads & Petersen, pg 113 Which statement is most correct: Near sightedness is known as diplopia Testing vision with a Snellen Eye Chart tests peripheral vision Ishihara plates are used to test visual fields. Acuity is expressed as two numbers. The first number describes the patient's distance from the chart, and the second describes the distance at which the normal eye can read the line of letters or symbols. Acuity is expressed as two numbers (eg. 20/40). The first number describes the patient's distance from the chart, and the second describes the distance at which the normal eye can read the line of letters or symbols. The Snellen eye chart tests the optic nerve for central vision. Near sightedness is known as presbyopia Ishihara plates are used to test color blindness. Rhoads & Petersen, pgs 100-101 How is Impetigo best characterized at assessment? serous exudation and crusting; contagious; caused by Staph aureu chronic excoriated dermatitis Papules and pustules flat, usually found on extensor surfaces exposed to repeated traumas Impetigo is best characterized as serous exudation and crusting; contagious; caused by Staph aureus. Seller & Symons, Figure 29-2. Which of the following assessment pieces directly provides data best categorized by the healthcare provider as part of a patient's social history? Before seeing the healthcare provider, Ms. F fills out a form describing her illnesses, on which she includes having been diagnosed with hypertension and diabetes. During the health assessment, Mr. K says that he never received any childhood immunizations because of his mother's mistrust of them. Prior to a follow-up visit, Mr. D returns a document on which he has recorded his food and beverage intake for a typical week. As part of the patient interview, Ms. G reports that all four of her grandparents are alive and well. Submission Details: Quiz Score: 88 out of 100 [Show More]
Last updated: 10 months ago
Preview 5 out of 34 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 22, 2023
Number of pages
34
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 22, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
291






 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)