1. Signs of Pregnancy
a. Presumptive – subjective
i. Amenorrhea, fatigue, breast tenderness, N/V, quickening, urinary
frequency, and uterine and breast enlargement
b. Probable – objective
i. Positive pregnancy test,
...
1. Signs of Pregnancy
a. Presumptive – subjective
i. Amenorrhea, fatigue, breast tenderness, N/V, quickening, urinary
frequency, and uterine and breast enlargement
b. Probable – objective
i. Positive pregnancy test, ballottement (sharp upward pushing against the
uterine wall with a finger inserted into the vagina for diagnosing
pregnancy by feeling the return impact of the displaced fetus), Goodell’s
sign (softening of the cervix), Chadwick’s sign (bluish purple vaginal and
cervical mucosa), Hegar’s sign (softening of the lower uterine segment),
and Braxton hicks contractions
c. Positive
i. Ultrasound verification, auscultation of fetal heart tones, fetal movement
felt by experienced clinician
2. Integumentary System Adaptations
a. Hyperpigmentation – breast, genitalia, face (melisma)
b. Linea nigra – darker pigment mid abdomen
c. Striae gravidarum – stretch marks
d. Nails – faster growth, brittle
e. Hair – initial growth followed by hair loss
3. G’s – a pregnant woman
a. Gravida 1 (primigravida) = first pregnancy
b. Gravida 2 = second pregnancy
c. Multigravida = third or more pregnancy
4. P’s – a woman who has produced one or more viable offspring carrying a pregnancy 20
weeks or more
a. Primipara = one pregnancy of at least 20 weeks
b. Multipara = two or more pregnancies resulting in viable offspring
c. Nullipara = no viable offspring, para 0
5. GPTPAL
a. G – total number of pregnancies
b. T – full-term pregnancies (37-40 weeks)
c. P – preterm deliveries (20-36 weeks)
d. A – abortions and miscarriages (before 20 weeks)
e. L – living children
6. Calculating Due Date – Nagele’s Rule
a. Use first day of last menstrual period – 11/21/2020
b. Subtract 3 months – 8/21/2020
c. Add 7 days – 8/28/2020
d. Add 1 year – 8/28/2021 = EBD or EDD
e. Exception: sometimes the EDD will fall within the year of conception
7. Prenatal Schedule
a. Every 4 weeks up to 28 weeks
b. Every 2 weeks up to 29-36 weeks
c. Every week from 37 weeks to birth
8. True vs. False Labor
a. True Labor
i. Contractions – becoming stronger, lasting longer, becoming regular, and
continue despite use of comfort measures
ii. Cervix – becomes softener, effaces, and dilates
iii. Fetus – engaged in pelvis
b. False Labor
i. Contractions – irregular, often stop with walking, hydration, position
changes, and can be stopped with comfort measures
ii. Cervix – no significant change
iii. Fetus – presenting part usually not in pelvis
9. Preterm Labor – regular uterine contractions with cervical effacement and dilation
between 20-37 weeks gestation
10. Post-term Labor – pregnancy continuing past end the 42 weeks gestation
11. Stages of Labor
a. First Stage
i. Begins with onset of regular uterine contractions that intensify (true labor)
ii. Ends with full cervical effacement and dilation
iii. The longest stage
iv. Divided into 3 phases
1. Latent 0-3 cm – most 1st time moms go to hospital during this
phase
2. Active 4-7 cm
3. Transition 8-10 cm (most intense phase) – most multiparous moms
go during this phase
b. Second Stage
i. Begins with full cervical dilation and effacement
ii. Pushing occurs during this stage
iii. Spontaneous vs direct pushing
iv. This is the delivery stage
v. Ends with birth of baby
c. Third Stage
i. Begins with placenta separation
ii. Firmly contracting fundus
iii. Uterus changes in shape
iv. Gushes of blood
v. Umbilical cord begins to elongate
vi. Ends with placenta expulsion
d. Fourth Stage
i. Begins with recovery of patient
[Show More]
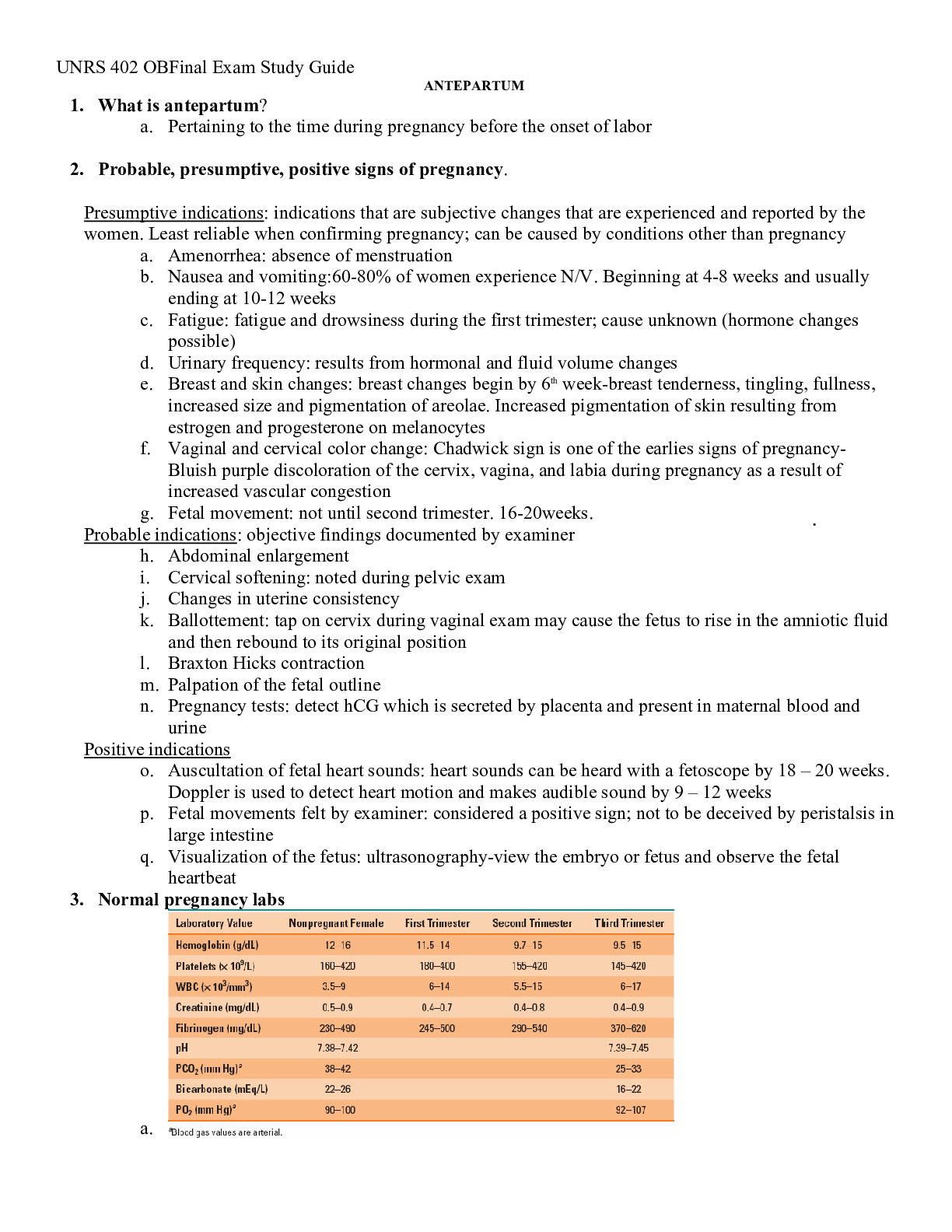











.png)
.png)













