5.2 Ionic Bonds Gizmo Student Exploration Thomas Bremigan
Document Content and Description Below
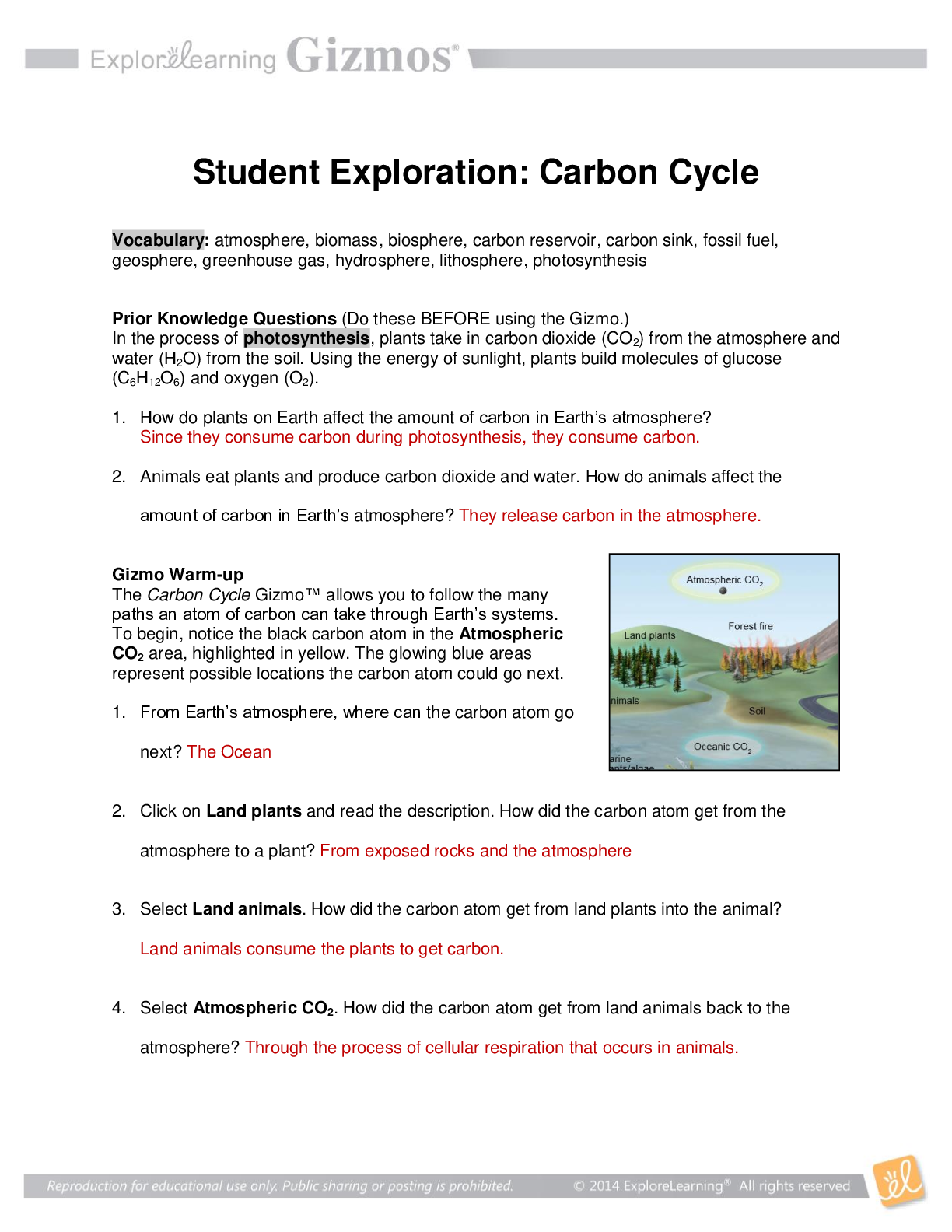
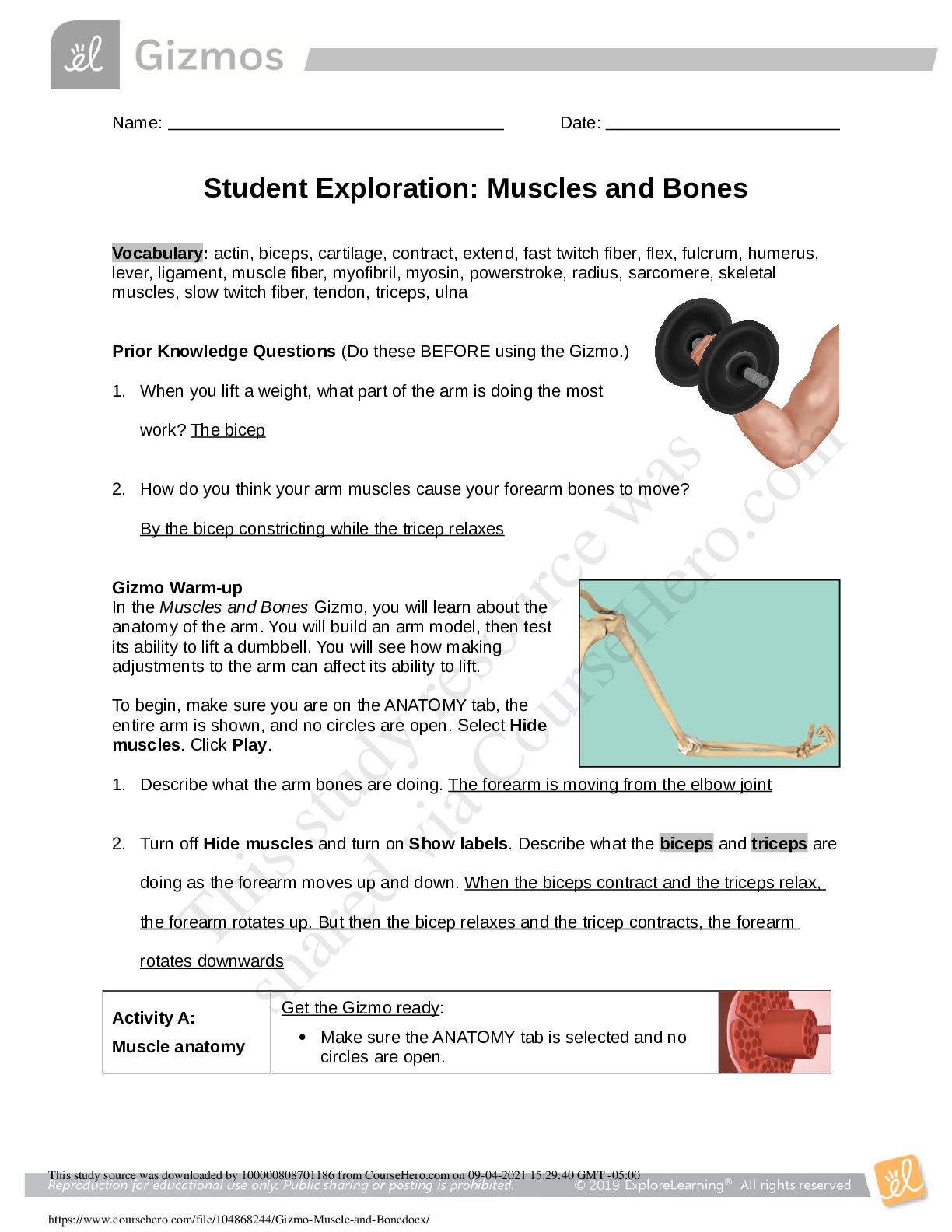
Student Exploration: Ionic Bonds Vocabulary: chemical family, electron affinity, ion, ionic bond, metal, nonmetal, octet rule, shell, valence electron Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE usi ... ng the Gizmo.) 1. Nate and Clara are drawing pictures with markers. There are 8 markers in a set. Nate has 9 markers and Clara has 7. What can Nate and Clara do so that each of them has a full set? Nate would have to give Clare one of his makers. 2. Maggie is sitting at a table with Fred and Florence. Maggie has 10 markers, but Fred and Florence each have only 7 markers. How can they share markers so each has 8? Maggie would have to give one of her makers to Fred and one to Florence. Gizmo Warm-up Just like students sharing markers, atoms sometimes share or swap electrons. By doing this, atoms form bonds. The Ionic Bonds Gizmo allows you to explore how ionic bonds form. To begin, check that Sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl) are selected from the menus at right. Click Play ( ) to see electrons orbiting the nucleus of each atom. (Note: These atom models are simplified and not meant to be realistic.) 1. Each atom consists of a central nucleus and several shells that contain electrons. The outermost electrons are called valence electrons. (Inner electrons are not shown.) How many valence electrons does each atom have? Sodium: __1____ Chlorine: __7____ 2. Click Pause ( ). Elements can be classified as metals and nonmetals. Metals do not hold on to their valence electrons very tightly, while nonmetals hold their electrons tightly. Electron affinity is a measure of how tightly the valence electrons are held. A. Try pulling an electron away from each atom. Based on this experiment, which atom is a metal? ______Sodium______________ Which is a nonmetal? _______Chlorine_____________ B. Try moving an electron from the metal to the nonmetal. What happens? ____The electrons moves over. ______ __________________________________________________________________ _ 201 9 Get Activity A: o Ion s nd chlorine are still selected. Introduction: Some of the particles that make up atoms have an electrical charge. Electrons are negatively charged, while protons are positively charged. Particles with opposite charges (+ and –) attract, while particles with the same charge (+ and + or – and –) repel. Question: What happens when atoms gain or lose electrons? They become ions. 1. Count: Electrons move around the nucleus of atoms in specific shells, shown by the rings around the atoms in the Gizmo. The first ring holds two electrons, and the second holds eight. (Electrons in the inner rings are not shown; you can assume these rings are full.) A. Observe the sodium and chlorine atoms. Assuming that the inner rings are full of electrons, how many electrons are there total in each atom? [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$6.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 20, 2021
Number of pages
5
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 20, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
80