Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
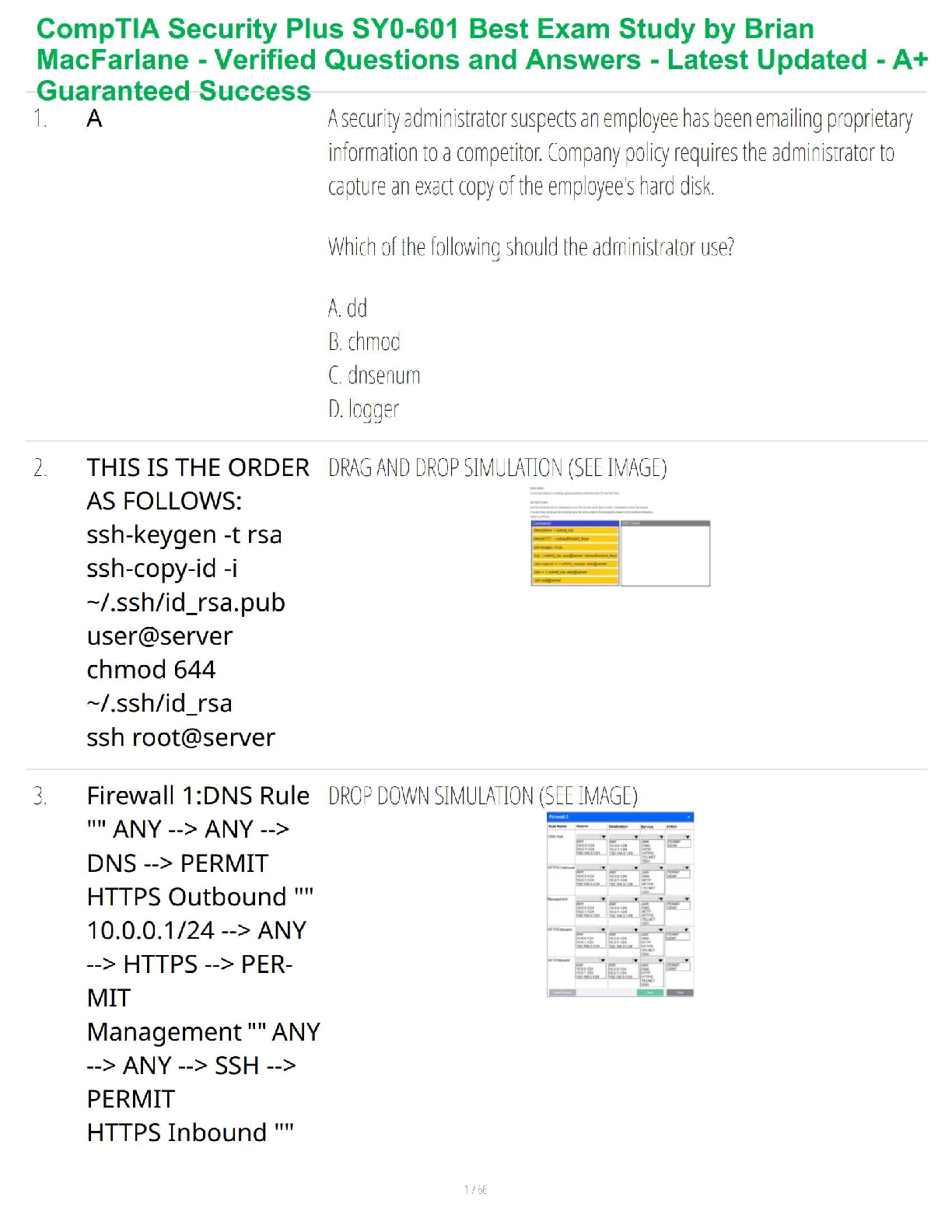
Ø Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions:
1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) Gained more than 15 pounds (7kg)
3.) Had
...
Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
Ø Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions:
1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) Gained more than 15 pounds (7kg)
3.) Had a full term pregnancy
4.) Had a second term abortion
o When you use a diaphragm, you need to use spermicide with every act of coitus
(withdrawal of penis from vagina prior to ejaculation). Every time you withdrawl, instill
more spermicide
o Diaphragm must stay inserted for 6hrs after act of coitus
Ø Hormonal Contraceptives (Oral)
o Side effects: Chest pain, SOB, Leg pain (from a possible clot), headache or eye problems
(from a stroke or hypertension)
o Contraindications: Women with a history of blood clots, stroke, cardiac problems, smoker,
breast or estrogen related cancers (pill contains estrogen)
Ø Depo-Provera/Medroxyprogesterone
o Injectable progestin
o Can cause decreased bone mineral density or loss of calcium
§ Nursing action: Ensure patient has adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
Ø IUD
o Increase risk for PID
o Can cause uterine perforation or ectopic pregnancy (increases risk for ectopic pregnancy)
o Look out for/Notify PCP:
§ Change in string length à IUD is moving and not in the right place
§ Foul smelling vaginal discharge
§ Pain with intercourse
§ Fever/Chills (infection)
Infertility is defined as an inability to conceive desire engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse for a
prolonged period of time or at least 12 months.
Ø Common factors associated with infertility include:
o Decreased sperm production (Sperm analysis)
o Endometriosis
o Ovulation disorders
o Tubal occlusions à If you test and use DYE (used in the fallopian tubes), make sure the woman
is not allergic to iodine or shellfish/seafood
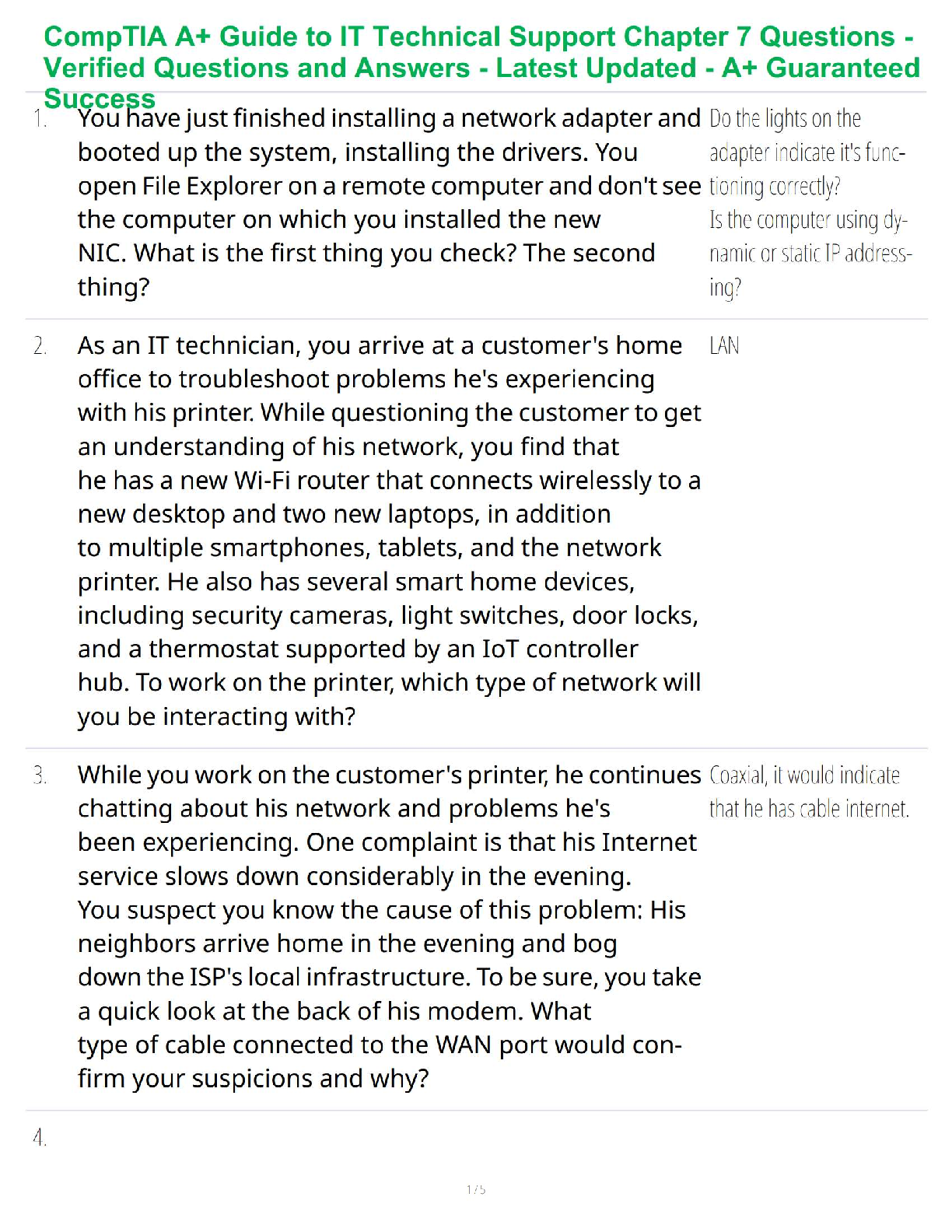
Video #2: Signs of Pregnancy
Presumptive: Can be defined by things/reasons other than pregnancy
Ø Amenorrhea à Can be anorexic or exercising too much
Ø Fatigue à Didn’t sleep well
Ø Nausea/Vomiting à Sick
Ø Urinary Frequency à UTI
Ø Quickening/Fluttering in stomach à Gas
Probable: Changes that make the examiner suspect a woman is pregnant (primarily related to physical
changes of the uterus).
Ø Abdominal enlargement: Related to changes in uterine size, shape, and position
Ø Hegar’s Sign: Softening and compressibility of the lower uterus
Ø Chadwick’s Sign: Deepend violet bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa
Ø Goodell’s Sign: Softening of cervical tip
Ø Ballottement: Rebound of unengaged uterus
Ø Braxton Hicks Contractions: False contractions that are painless, irregular, and usually relieved
by walking
Ø Positive Pregnancy Test: Woman’s hormonal level may not be normal
Ø Fetal Outline:
Positive: Very distinct things.
Ø Fetal Heart Sounds
Ø Fetal Heart Beat can be heard
Ø Can see the baby with ultrasound
Ø Can feel movement in the uterus
Naegele’s Rule: LMP – 3 months + 7 days + 1 year
Cathy’s Rule: + 9 months + 1 week
Know how to find out GTPAL numbers
G= Gravidity (# of times a woman has been pregnant PLUS current pregnancy)
T= Term Births (How many baby’s were delievered at term 38 WEEKS OR MORE)
P= Preterm Births (Below 38 weeks)
A= Abortion (spontaneous or not) or miscarriages
L= Living children
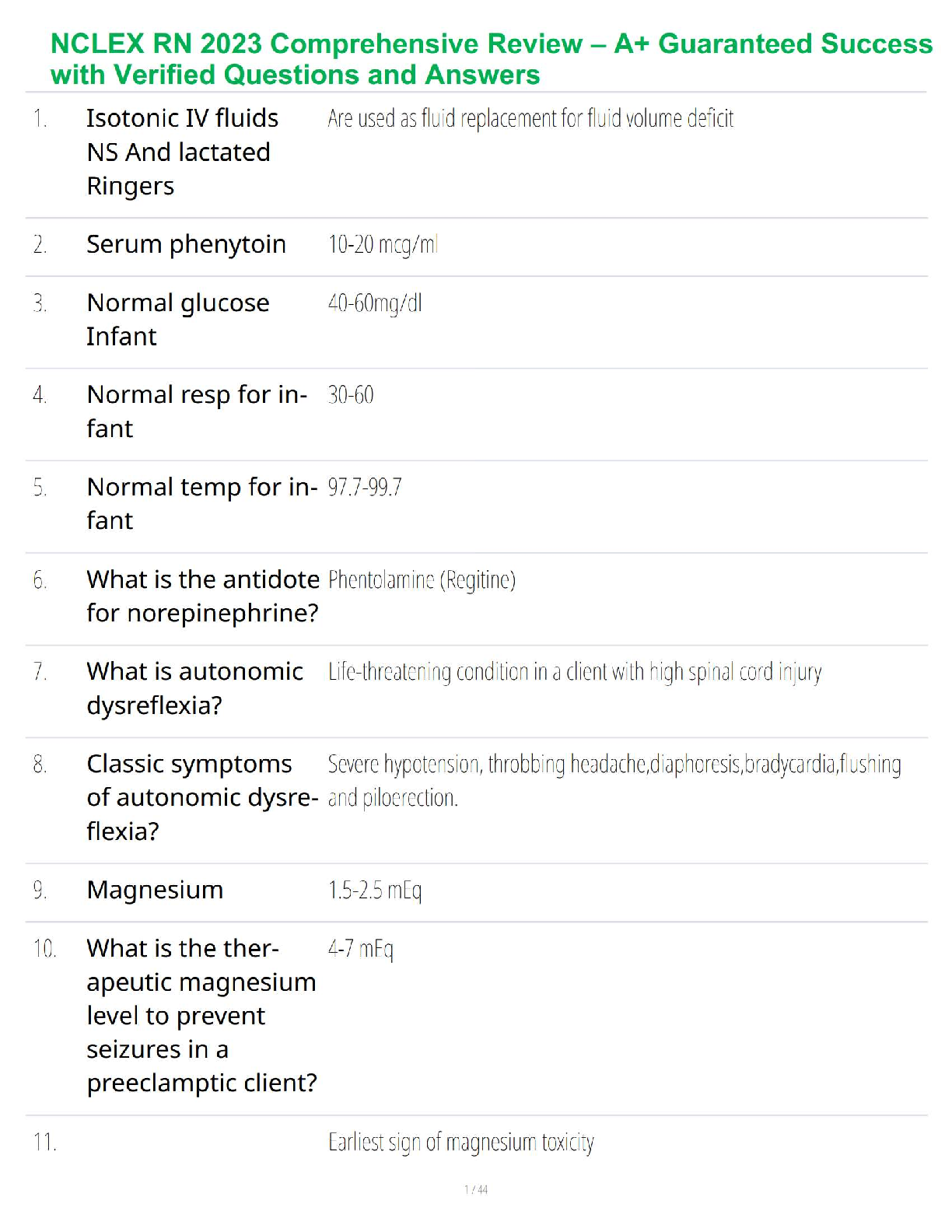
Video #3: Weight Gain & Nutrition During Pregnancy AND Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy
Weight Gain & Nutrition
Ø Normal weight gain = 25- 35 pounds
Ø Overweight person weight gain = 15- 25 pounds
Ø Underweight person weight gain = 28-40 pounds
Ø During 1st trimester à A woman should only gain 1-2 kg (2-4 pounds); A woman should not gain
1 pound per week.
Ø During 2nd trimester à 1 pound per week is normal; increase caloric intake by 340 calories per
day
Ø During 3rd trimester à 1 pound per week is normal ; increase caloric intake by 450 calories per
day
Ø If you are breastfeeding after pregnancy à You still need to eat an extra 300-400 calories per
day
Ø Intake of FOLIC ACID à Helps prevent Neural Tube Defects (NTD) à Sources: dark green leafy
veggies; orange juice
Ø Women should increase their fluid intake to 2-3L per day
Ø Women should limit their caffeine intake to à 300 mg per day
Ø No amount of alcohol is okay
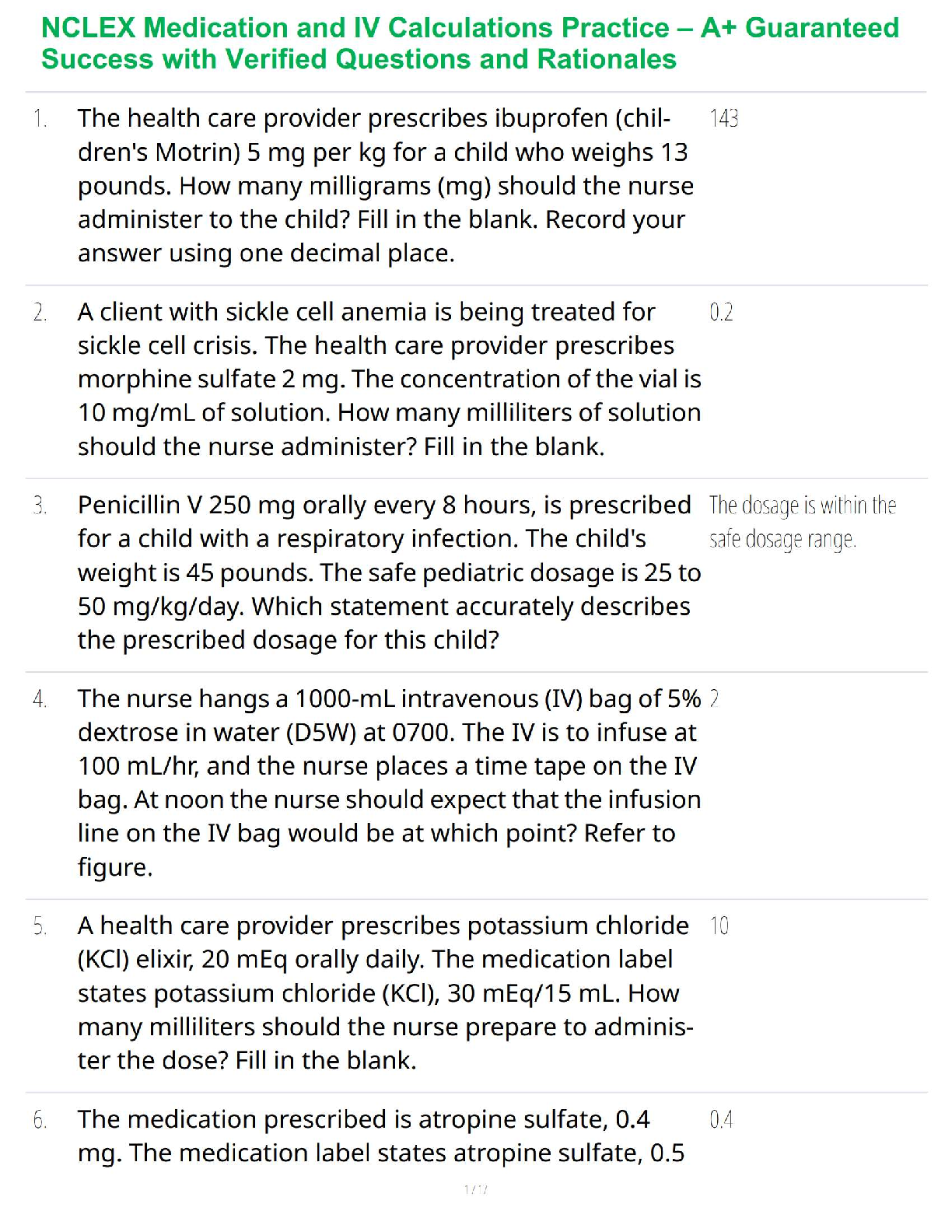
Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy
Noninvasive = Full Bladder
Invasive = Empty Bladder
Ultrasound à Bladder should be full to help sound waves resonate better
Amniocentesis à Bladder should be empty
[Show More]












.png)
.png)