Dennis Hermanzo - Talking Mental Stevens Magic
$ 20

PROJ586 Risk Event Case Study / DeVry University, Chicago - PROJ 586 week 5 presentation
$ 11

Summary Texas Commission on Law Enforcement > TCOLE Final review complete TCOLE Test: Answered Correctly.
$ 9

Solutions Manual with Test Bank Hospitality Management Accounting 9th Edition By Martin Jagels
$ 30

IGCSE Accounting Questions and Correct Answers
$ 11

Sepsis/Septic Shock UNFOLDING Reasoning Case Study
$ 10
 review NEW 2022 PRACTICE SOLUTION.png)
EKG for Medical Assisting (CCMA, RMA) review NEW 2022 PRACTICE SOLUTION
$ 13.5

023 AQA GCSE GERMAN 8668/RH Paper 3 Reading Higher Tier Question Paper & Mark scheme (Merged) June 2023 [VERIFIED] GCSE GERMAN Higher Tier Paper 3 Reading
$ 7

IB ESS Revision Exam Prep Question section and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+
$ 8

NURS 3632 HESI A2 V2 grammar Study Guide for 2022/2023 COMPLETED A
$ 7
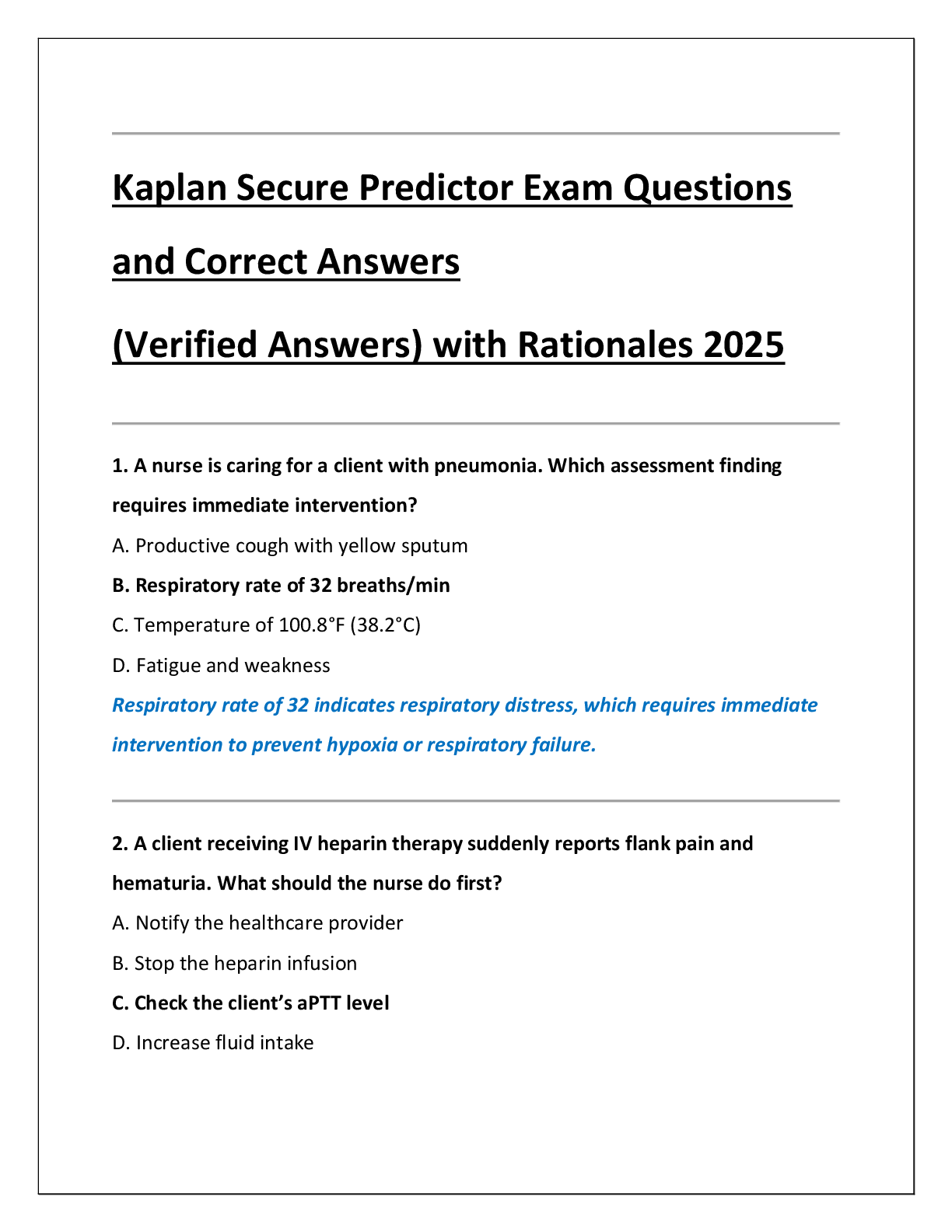
Kaplan Secure Predictor Exam Questions and Correct Answers (Verified Answers) with Rationales 2025
$ 16

PMP Project Management Fundamentals with all Correct & 100% Verified Answers |Latest Update |Already Graded A+
$ 10.5

STAT 200 Week 4 Homework Problems (summer 2022) complete solutions.
$ 8
 V1.png)
AQA GCSE 8462 Chemistry Chemical analysis and using resources (Higher) Answers and Commentaries. 2021 Assessment resources.
$ 9

QUAL 556 Human Aspects Continuous Improvement - Eastern Michigan University. CHAPTER 07—Designing Organizations for Performance Excellence
$ 5.5

FMCSA Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Latest Versions.
$ 4

Chem 210 Test 1 Questions and Answers 2023
$ 7

Lecture: Managing Project Teams. People In Projects
$ 7.5
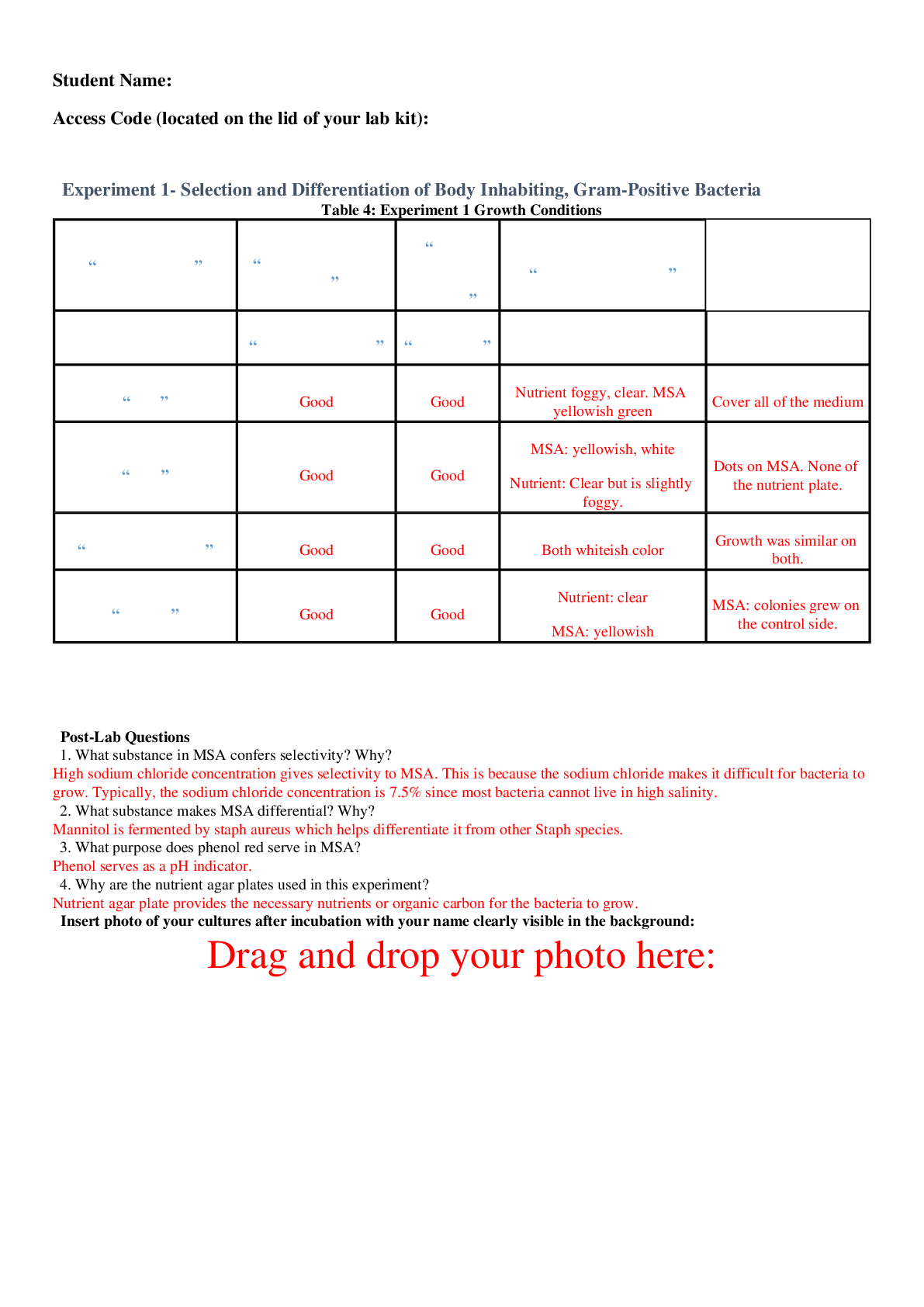
BIOLOGY LAB EXPERIMENT : Experiment 1- Selection and Differentiation of Body Inhabiting, Gram-Positive Bacteria
$ 10

How Plagiarism can Impact A Communication Manager Career
$ 2.5

CLG 0010 DOD GOV. COM. PUR. CARD OVERVIEW EXAM QUIZ & Answers.
$ 7

SSL AND TLS THEORY AND PRACTICE, INFORMATION SECURITY AND PRIVACY SERIES 4TH EDITION BY ROFL OPPLINGER
$ 21

eBook The Politicization of Police Stops in Europe 1st Edition By Jacques de Maillard, Kristof Verfaillie, Mike Rowe
$ 30

NUR 514 Topic 3 - Discussion Question 1
$ 5

(7037) AQA A-Level Geography Component 2 Human Geography Exam Guide Qns & Ans Updated Version 2024