*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 340 Week 6 Assignment: Clinical Simulation Prep Packet | 100% Verified PASS. (All)
NR 340 Week 6 Assignment: Clinical Simulation Prep Packet | 100% Verified PASS.
Document Content and Description Below
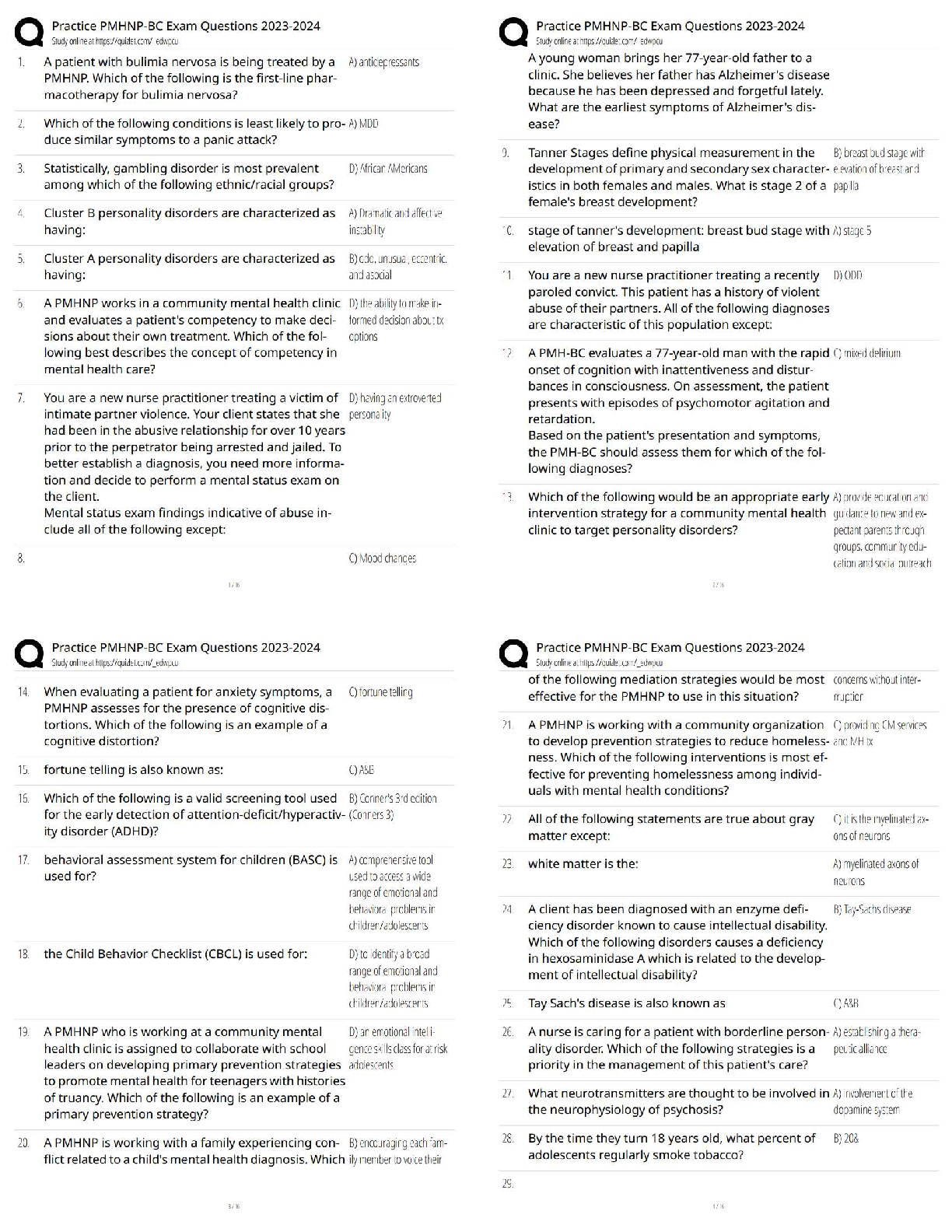
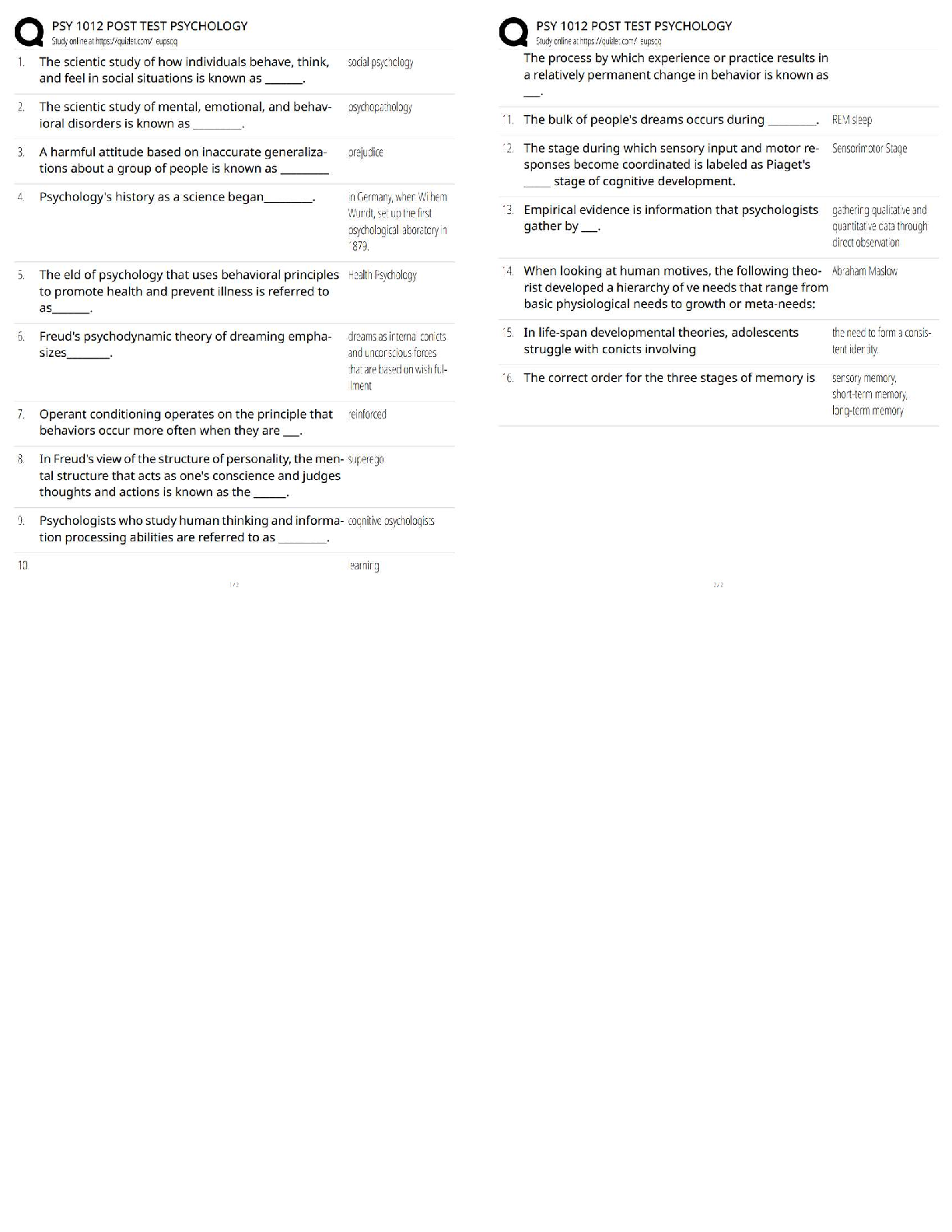
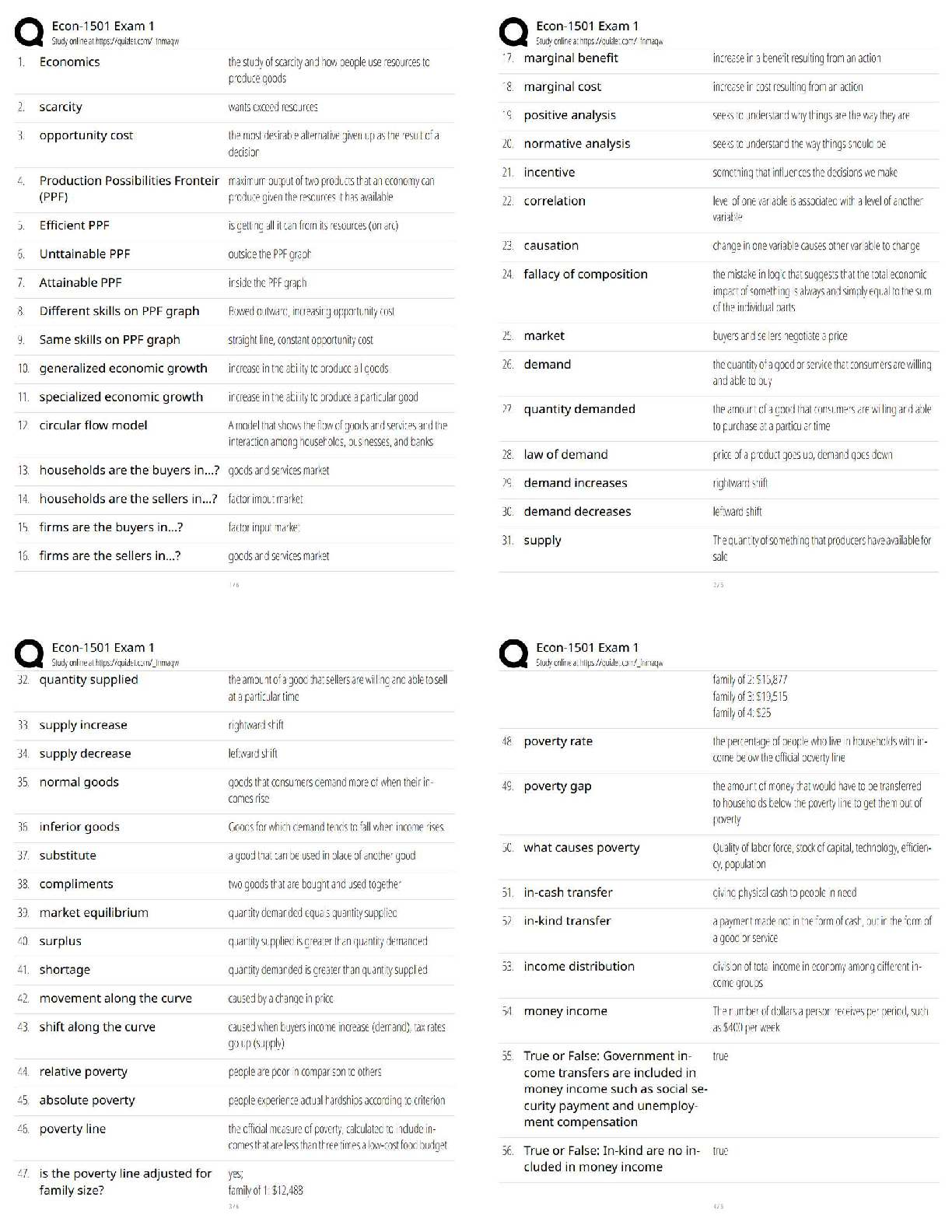
Name Date 2021 (RETAKE) Directions: This assignment is to be completed independently (it is not a group assignment!) and turned in on your assigned clinical simulation day. Late submissions wi ... ll not be accepted. The purpose of this assignment is to prepare you to complete the corresponding clinical simulation scenarios related to coronary artery disease and hypertensive crisis respectively. Resources to complete this assignment include the following: A. Lewis Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9th edition. Prevention of osteoporosis (p. 1555) and hip replacement post-operative management (p.1526-1527). B. Sole textbook Pulmonary Embolism (p. 423-425) and thrombolytic candidates (p. 382). C. Stroke/TPA articles posted on shell This assignment is worth 50 points. 1. What is the nurse’s role in providing family centered care during and after a crisis? (1 point) The nurse’s role in communication with family members and patients is to be involved during and after a crisis. The nurse should share information with family and patient that is clear and avoid using medical jargon, the nurse should also be truthful and show respect for the family and patients needs and listen to what information they have to provide. The nurse should also provide comfort and support to the family members, be aware of family strengths, and have respect for different methods of coping. 2. What pharmacological and non-pharmacological comfort measures can be used for a post- operative patient? (2 points) Pharmacological: Opoids - morphine, dilaudid, fentanyl Non-pharmacological: Guided imagery, relaxation or breathing techniques, active listening, re-positioning, and therapeutic touch, sedative music, limit noise and lighting, explanation of all procedures and interventions. 3. What vital nursing assessment data should be gathered on a patient post hip replacement surgery? (3 points) Pain level (0-10), vital signs, check surgical site dressing for drainage and signs of infections, bowel sounds, lungs sounds and perfusion 4. Describe the major complications that can arise for patients who are post-operative hip injury/replacement? (3 points) DVT, PE, stroke, infection, falls 5. Describe the pathophysiologic process of a pulmonary embolism. Include the typical origin site of a pulmonary embolism. (3 points) Name Date 7/26/16 There is a blockage in a blood vessel that forms a blood clot (thrombus). The thrombus dislodges from the blood vessel and travels through the blood until it becomes stuck in a blood vessel in the lungs and occludes blood flow. Pulmonary embolism happens most commonly due to mobilization of a clot from deep venous thrombosis in the lower leg. 6. What are 3 signs and symptoms associated with a pulmonary embolism? (2 points) Shortness of breath (SOB), chest pain, coughing (possibly bloody) 7. What medical treatments can be used to treat a pulmonary embolism? (2 points) Treatment includes anticoagulants (heparin), thrombolytics (tpa), or possibly surgery. 8. What immediate nursing interventions should the nurse perform for a patient who is experiencing a pulmonary embolism? (3 points) ✓ Rapid Response ✓ Bed Rest ✓ Order for stat chest x-ray ✓ Give supplemental oxygen 9. Describe the actions, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dose range and method of administration for the following medications: (6 points) Drug Actions Indications Contraindicatio ns Adverse effects Dose range Method of administration Heparin Potentiates the inhibitory effect of Prophylaxis and treatment Hypersensitivity, uncontrolled Bleeding, heparin-induced IV: Intermittent bolus 10,000 IV, Sub-Q antithrombin on of various bleeding, severe thrombocytopenia units followed factor Xa and thromboembol thrombocytopeni , pain at injection by 5,000-10,000 thrombin. In low ic disorders. a site, fever units q 4-6 hr. doses, prevents the Ex: PE, A fib Continuous conversion of infusion 5,000 prothrombin to units (35-70 thrombin by its units/kg) effects on factor followed by Xa. Higher doses 20,000-40,000 neutralize units infused thrombin, over 24 hrs. prevention the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Therapeutic effect: Prevention of thrombus formation. Name Date 7/26/16 Cefazolin Bind to the bacterial cell wall Treatment of the following Hypersensitivity to Seizures, pseudomembrano Powder for injection: 500 IV, IM membrane, causing infections cephalosporins, us colitis, steven- mg/vial, 1 g/vial, cell death. caused by serious johnson 10 g/vial, 20 Therapeutic susceptible sensitivity to syndrome, g/vial, Premixed effects: bactericidal organisms: penicillins anaphylaxis, containers: 1 action against skin, urinary, serum sickness, g/50 mL D5W, 2 susceptible respiratory, diarrhea, nausea, g/50 mL D5W bacteria. intra- vomiting, abdominal, thrombocytopenia bone, & septicemia. Enoxaparin Prevents conversion of Prevention of DVT and PE Hypersensitivity to this drug, Fever, confusion, nausea, edema, SubQ: 30 mg BID given 12-24 Sub-Q fibrogen to fibrin in hip and heparin, or pork; hypochromic hr post-op for 7- and prothrombin to knee hemophilia, anemia, 10 days provided thrombin by replacements leukemia with thrombocytopenia that hemostasis enhancing bleeding, PUD, , bleeding, has been inhibitory effects heparin-induced ecchymosis established of antithrombin III; thrombocytopeni produces higher a ratio of antifactor Xa to antifactor IIa Valsartan Blocks the vasoconstrictor and Hypertension, alone or in Hypersensitivity, pregnancy, Dizziness, insomnia, MI, PO: 80-160 mg q daily alone or in Oral aldosterone- combination severe hepatic dysrhythmias, combination secreting effects of disease, bilateral hepatotoxicity, with other angiotensin II. renal artery nephrotoxicity, antihypertensive stenosis cramps, cough s Triamterene Acts on distal tubule and cortical Edema, HTN, diuresis, CHF, Hypersensitivity to thiazides or Uremia, glucosuria, PO: 25-100 mg/day Oral thick ascending edema in sulfonamides, headache, limb of loop of corticosteroid, anuria, renal dizziness, Henle by estrogen decomposition, hepatitis, aplastic increasing therapy hypomagnesemi anemia, excretion of water, a leukopenia, sodium, chloride, agranulocytosis, and potassium thrombocytopenia , neutropenia Acetaminop hen/Hydroco done Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as meditators of pain and fever, primarily in the CNS. Therapeutic effects: analgesia, antipyretic Treatment of: mild, moderate, or severe (with opioid analgesics), fever Pervious hypersensitivity, products containing alcohol, aspartame, severe hepatic impairment/activ e liver disease Hepatotoxicity, fatigue, insomnia, HTN, hypotension, headache, constipation, anxiety, increased agitation PO: 325-600 mg q 6 hr IV: 1000 mg q 6 hr or 650 mg q 4 hr not to exceed 1000 mg/dose Oral, IV Naomi Reed Simulation Scenario Name Date 7/26/16 10. Differentiate the pathophysiological processes and treatment options used in the 2 major types of stroke. (5 points) Ischemic: Artery that is carrying oxygenated blood to the brain is occulded. The treatment for ischemic strokes is administration of tPA, if within the designated time frame, and anticoagulants not within 24hrs of stroke and antihypertensives. The two types of ischemic strokes include: thrombotic, when damaged cerebral arteries become blocked by the formation of a blood clot within the brain. Embolism, caused by a clot in an artery but that does not form in the brain but in another part of the body and travels to the brain. Hemorrhagic: A weakened blood vessel in the brain breaks or a aneurysm within the brain bursts. Blood pours into the brain or around the brain causing swelling and increased pressure. Treatment includes administration of anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, and diuretics. Hemorrhagic strokes include: intracerebral, blood pools into the surrounding brain tissue from a leak of a vessel in the brain. Subarachnoid, bleeding around the brain into the tissue that covers the brain. 11. What is the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)? Briefly explain in 2-3 sentences what is assessed on the NIHSS and the scoring system. (2 points). The NIHSS is a 15-item neurologic examination used when someone suffers from a stroke to evaluate the effect of acute cerebral infarction on the levels of consciousness, language, neglect, visual-field loss, extraocular movement, motor strength, ataxia, dysarthria, and sensory loss. A trained observer rates the patent’s ability to answer questions and perform activities. 12. Provide 3 nursing considerations for administration of tissue plasminogen activator (rTPA). What may result if administration of TPA is too fast or too slow? (3 points) • Prior to tPA infusion, the patient’s systolic BP should be less than 185 mm Hg and the diastolic BP should be less than 110 mm Hg • tPA is not compatible with other medications and requires a its own I.V. line • tPA is dosed based on patient weight 13. List 5 contraindications for the administration of TPA. (2 points) ✓ Serious head trauma ✓ Subarachnoid hemorrhage ✓ Recent stroke ✓ Recent or history of intracranial surgery ✓ Uncontrolled HTN, systolic greater than 185, diastolic greater than 110 ✓ Active internal bleeding ✓ Intracranial aneurysm Name Date 7/26/16 14. Sample TPA calculation. 0.9 mg/kg over 60 minutes (not to exceed 90 mg) with 10% of the total dose administered as an initial IV bolus over one minute. Patient weighs 130 lbs. TPA comes in a premixed bag: 75mg in 75 ml. Calculate the infusion dose (in mg) and the bolus dose (in mg). (2 points). Infusion dose: 47.9 mg Bolus dose: 5.3 mg 15. How often are vital signs and neuro checks performed once TPA has been started? (2 points) Assess and document vital signs, cardiac rhythm, neurological status, and for signs/symptoms of bleeding for the first 2 hours after initiating tPA administration, then every 30 minutes for 6 hours, then every hour for 16 hours and during tPA administration monitor BP every 15 minutes. 16. What nursing interventions need to be avoided once TPA administration has started? (2 points) ✓ Do not administer heparin, aspirin, or warfarin sodium for 24 hours after tPA infusion due to increased risk for bleeding ✓ Do not perform arterial or central venous lines, IM injections, NG tubes, or foley catheters for 24 hours post tPA administration unless procedure is life-saving 17. What are potential complications of TPA therapy the nurse will need to assess for? (2 points) ✓ Uncontrolled bleeding is the most serious complication of tPA therapy. Internal and peripheral bleeding can occur in the brain, GI tract, GU tract, gums, retroperitoneum, inside the nose, at puncture and catheter sites, and under the skin causing ecchymosis ✓ Other complications include seizures and neurotoxicity 18. What is the desired outcome of TPA? (2 points) The desired outcome of administering tPA include: ✓ Dissolve cerebral blood clot(s) thereby limiting cerebral ischemia and reducing the risk for cerebral infarction ✓ Maintain blood flow to the brain 19. Describe the actions, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dose range and method of administration for the following medications: (3 points) Name Date 7/26/16 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

NR 340 Critical Care Nursing (NR 340 Course Exams Week 1 – 8) , Study Guides and Quizzes BUNDLE | 100% GUARANTEED PASS.
NR 340 Critical Care Nursing (NR 340 Course Exams Week 1 – 8) , Study Guides and Quizzes BUNDLE | 100% GUARANTEED PASS.
By Prof. Goodluck 4 years ago
$13
9
Reviews( 0 )
$11.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 08, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
119


 And LETRS Unit 8 Final Assessment Test.png)