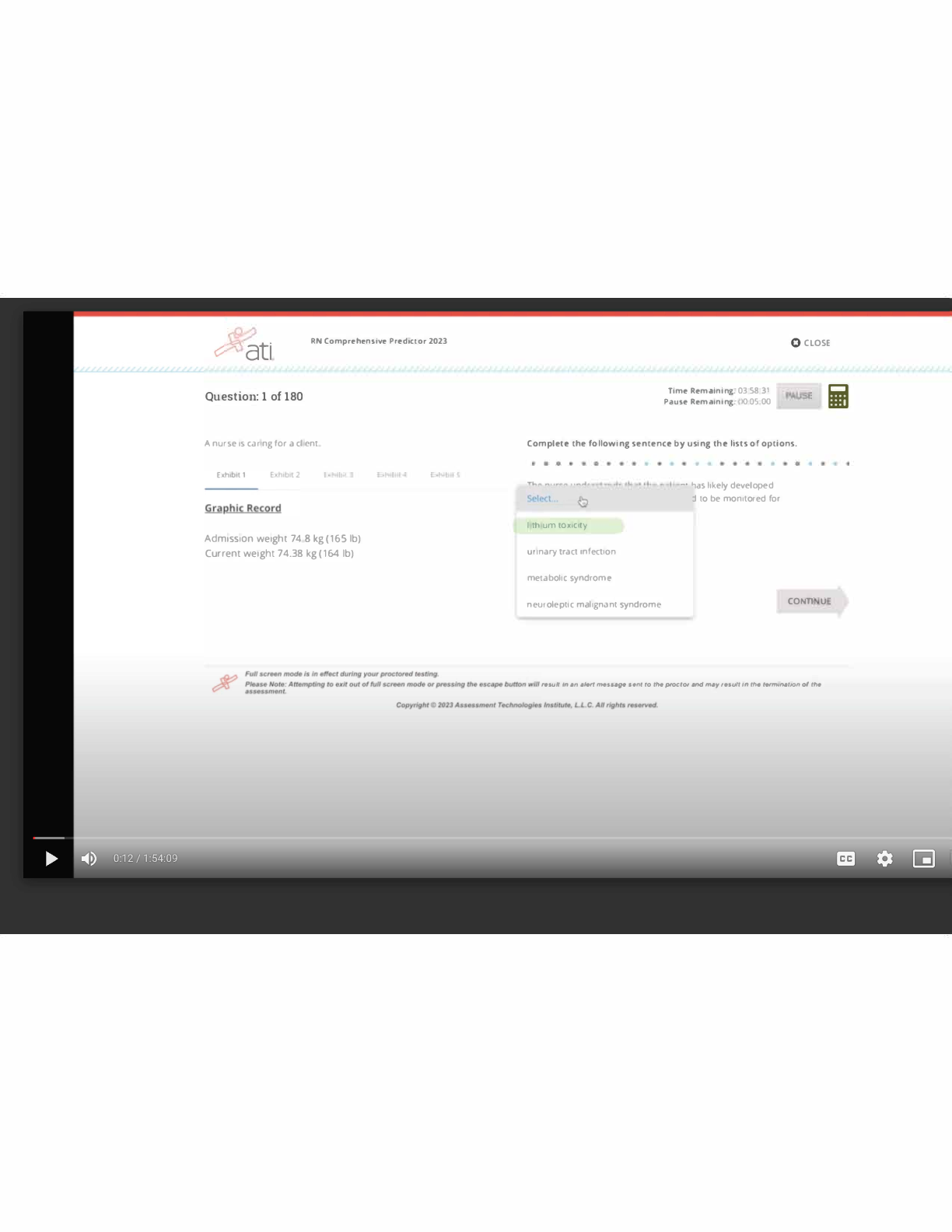
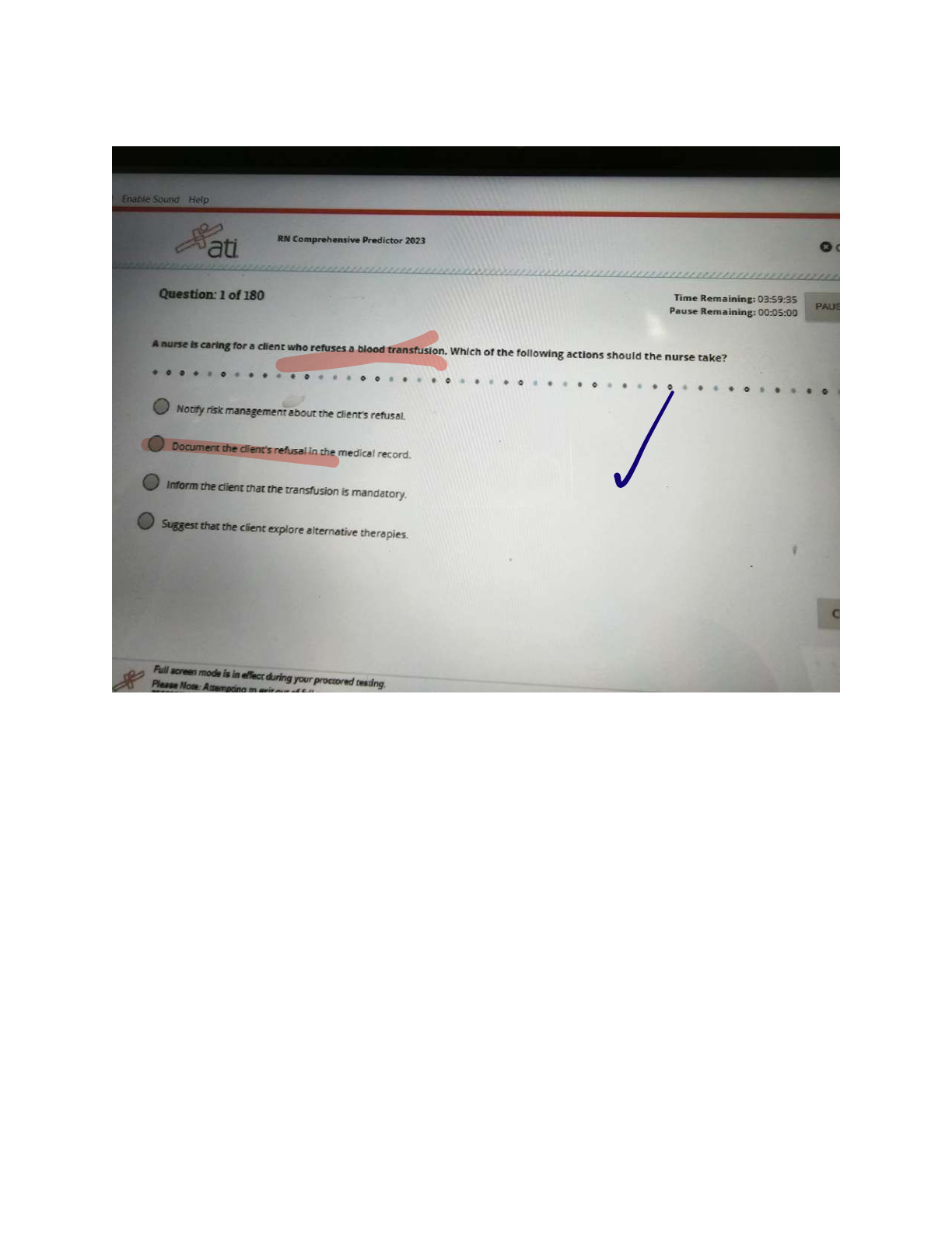
Which of the following is the most common cause of heartburn-type epigastric pain?
2. An older patient reports burning pain after ingestion of many foods and large meals. What assessment would assist the nurse practit
...
Which of the following is the most common cause of heartburn-type epigastric pain?
2. An older patient reports burning pain after ingestion of many foods and large meals. What assessment would assist the nurse practitioner in making a diagnosis of GERD?
3. Your patient complains of lower abdominal pain, anorexia, extreme fatigue, unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds in last 3 weeks, and you find a positive hemoccult on digital rectal examination. Laboratory tests show iron deficiency anemia. The clinician needs to consider:
4. A 22-year-old female comes to your office with complaints of right lower quadrant abdominal pain, which has been worsening over the last 24 hours. On examination of the abdomen, there is a palpable mass and rebound tenderness over the right lower quadrant. The clinician should recognize the importance of:
5. A nurse practitioner reports that your patient’s abdominal X-ray demonstrates multiple air-fluid levels in the bowel. This is a diagnostic finding found in:
6. Which of the following conditions is the most common cause of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea?
7. A 56-year-old male complains of anorexia, changes in bowel habits, extreme fatigue, and unintentional weight loss. At times he is constipated and other times he has episodes of diarrhea. His physical examination is unremarkable. It is important for the clinician to recognize the importance of:
8. A 59-year-old patient with history of alcohol abuse comes to your office because of ‘throwing up blood”. On physical examination, you note ascites and caput medusa. A likely cause for the hematemesis is:
9. An 82-year-old female presents to the emergency department with epigastric pain and weakness. She admits to having dark, tarry stools for the last few days. She reports a long history of pain due to osteoarthritis. She self-medicates daily with ibuprofen, naprosyn, and aspirin for joint pain. On physical examination, she has orthostatic hypotension and pallor. Fecal occult blood test is positive. A likely etiology of the patient’s problem is:
10. When counseling clients regarding the use of antidiarrheal drugs such as Imodium anti-diarrheal and Kaopectate, the nurse practitioner advises patients to:
11. When teaching a group of older adults regarding prevention of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms, the nurse practitioner will include which of the following instructions?
13. Helicobacter pylori is implicated as a causative agent in the development of duodenal or gastric ulcers. What teaching should the nurse practitioner plan for a patient who has a positive Helicobacter pylori test?
14. An obese middle-aged client presents with a month of nonproductive irritating cough without fever. He also reports occasional morning hoarseness. What should the differential include?
15. Which of the following findings would indicate a need for another endoscopy in clients with peptic ulcer disease?
16. A 20-year-old engineering student complains of episodes of abdominal discomfort, bloating, and episodes of diarrhea. The symptoms usually occur after eating, and pain is frequently relieved with bowel movement. She is on a “celiac diet” and the episodic symptoms persist. Physical examination and diagnostic tests are negative. Colonoscopy is negative for any abnormalities. This is a history and physical consistent with:
[Show More]












.png)