*NURSING > EXAM > NUR 6531 final exam 1 (Microsoft.com Account Team) | Walden University (Correct Answers Marked in Ye (All)
NUR 6531 final exam 1 (Microsoft.com Account Team) | Walden University (Correct Answers Marked in Yellow)
Document Content and Description Below
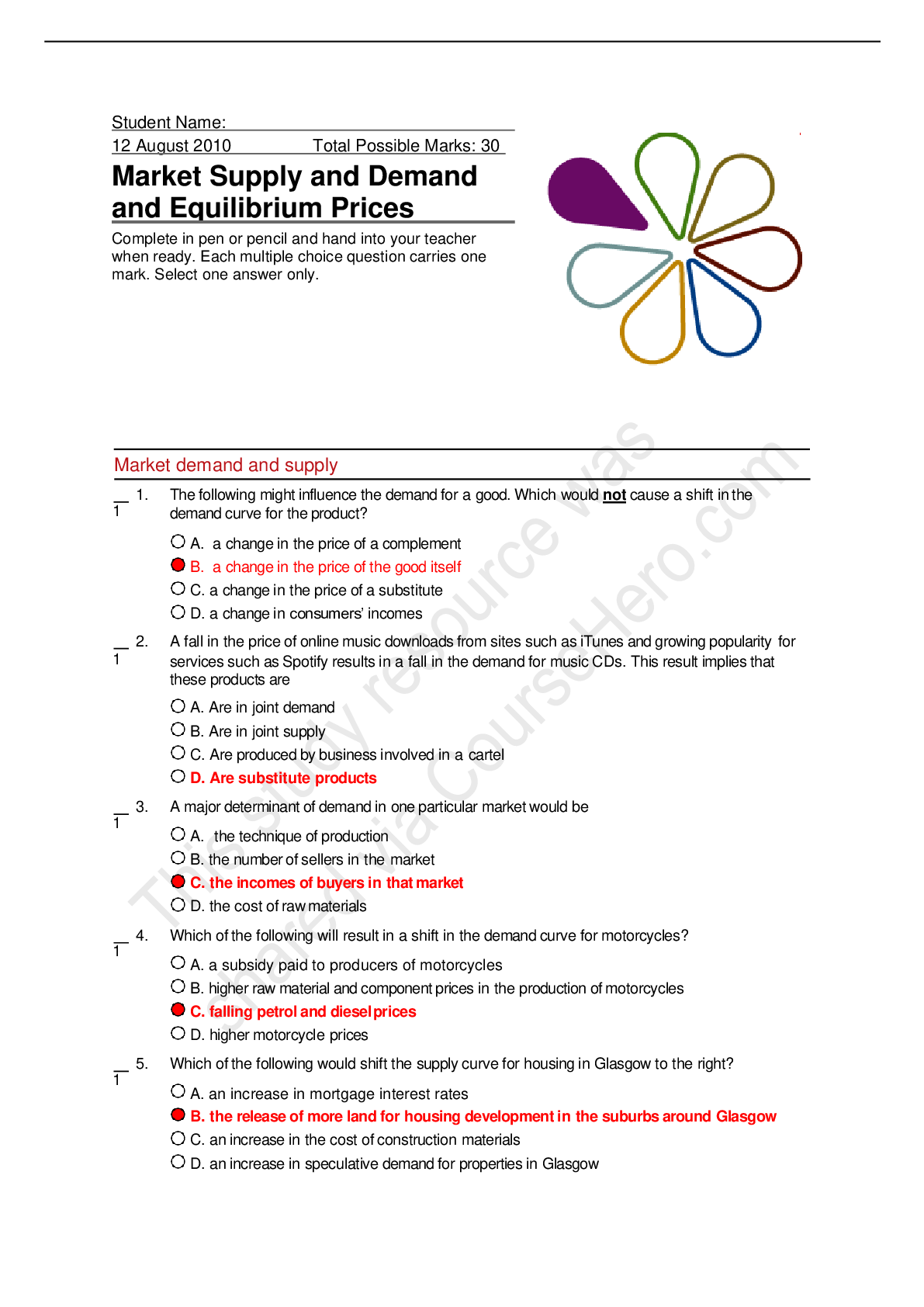
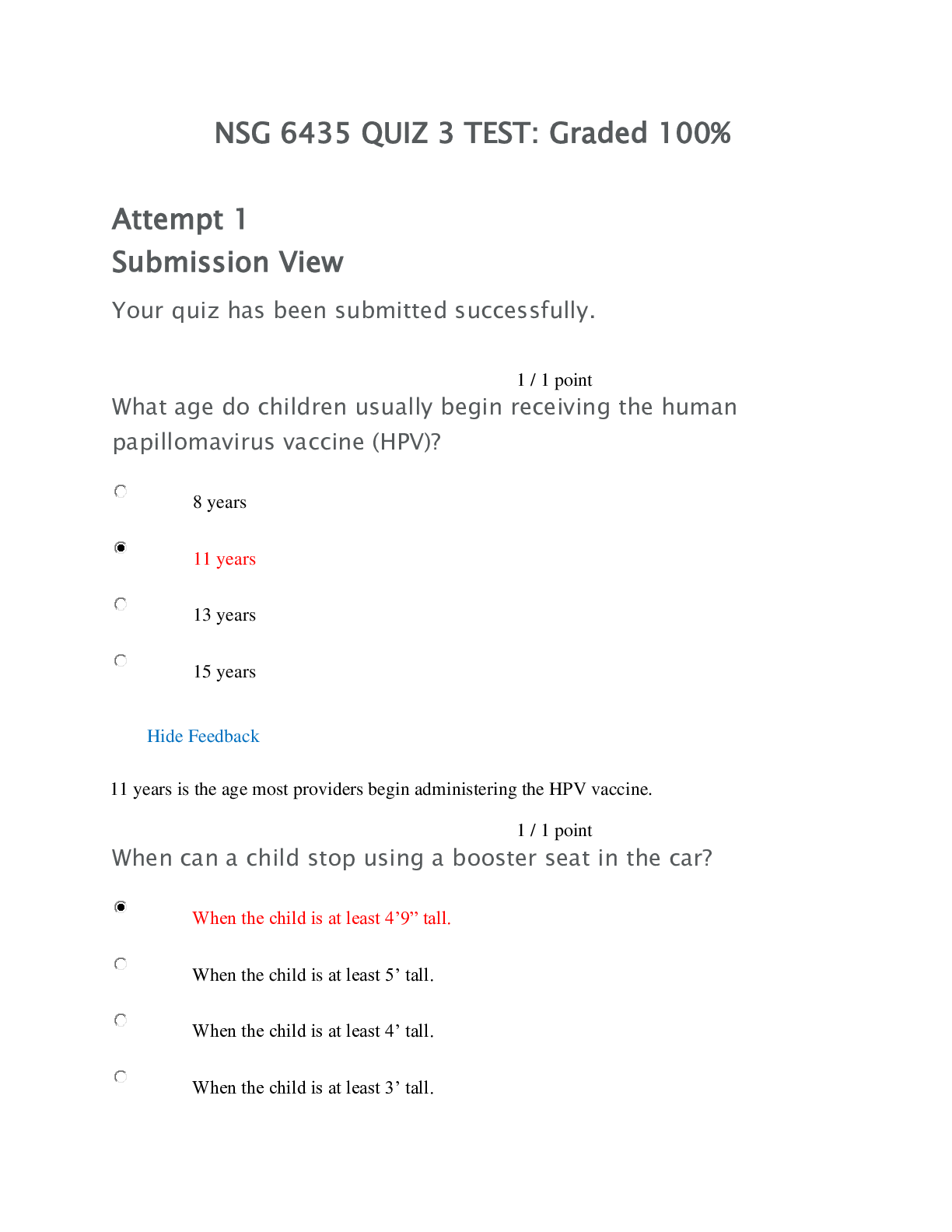
Central obesity, “moon” face, and dorsocervical fat pad are associated with: A . Metabolic syndrome B . Unilateral pheochromocytoma C . Cushing’s syndrome D . None of the above ... Question 3 1 out of 1 points An elderly man is started on lisinopril and hydrochlorhiazide for hypertension. Three days later, he returns to the office complaining of left great toe pain. On exam, the nurse practitioner notes an edematous, erythematous tender left great toe. The likely precipitant of this patient’s pain is: A . Trauma B . Tight shoes C . Arthritis flare D . Hydrochlorothiazide Question 4 1 out of 1 points The most effective treatment of non-infectious bursitis includes: Conservative treatment includes rest, cold and heat treatments, elevation, administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), bursal aspiration, and intrabursal steroid injections Question 5 1 out of 1 points What conditions must be met for you to bill “incident to” the physician, receiving 100% reimbursement from Medicare? Selected Answer: The physician must be on-site and engaged in patient care Answers: You must initiate the plan of care for the patient The physician must be on-site and engaged in patient care You must be employed as an independent contractor You must be the main health care provider who sees the patient Question 6 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is not a risk factor associated with the development of syndrome X and type 2 diabetes mellitus? The metabolic syndrome refers to the co-occurrence of several known cardiovascular risk factors, including insulin resistance, obesity, atherogenic dyslipidemia and hypertension. Question 7 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is not a common early sign of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)? A. Nocturia B. Urgency incontinence C. Strong urinary stream flow D. Straining to void Question 8 1 out of 1 points Steve, age 69, has gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). When teaching him how to reduce his lower esophageal sphincter pressure, which substances do you recommend that he avoid? Food that is very hot or very cold Fatty or fried foods Peppermint or spearmint, including flavoring Coffee, tea, and soft drinks that contain caffeine Spicy, highly seasoned foods Fried food DT caffeine, chocolate and anticholinergics Question 9 1 out of 1 points Which drug category contains the drugs that are the first line Gold standard therapy for COPD? Beta antagonist Question 10 1 out of 1 points The most commonly recommended pharmacological treatment regimen for low back pain (LBP) is: Nsaid Question 11 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is not appropriate suppression therapy for chronic bacterial prostatitis? Erythromycin Question 12 1 out of 1 points A patient presents with dehydration, hypotension, and fever. Laboratory testing reveals hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and hypoglycemia. These imbalances are corrected, but the patient returns 6 weeks later with the same symptoms of hyperpigmentation, weakness, anorexia, fatigue, and weight loss. What action(s) should the nurse practitioner take? .A Obtain a thorough history and physical, and check serum cortisol and ACTH levels. B. Perform a diet history and check CBC and FBS. C. Provide nutritional guidance and have the patient return in one month. D. Consult home health for intravenous administration Question 16 1 out of 1 points You are assessing a patient after a sports injury to his right knee. You elicit a positive anterior/posterior drawer sign. This test indicates an injury to the: he A. lateral meniscus B. cruciate ligament C. medial meniscus D. collateral ligament. Question 17 1 out of 1 points A 32 year old female patient presents with fever, chills, right flank pain, right costovertebral angle tenderness, and hematuria. Her urinalysis is positive for leukocytes and red blood cells. The nurse practitioner diagnoses pyelonephritis. The most appropriate management is: Include 500 mg of oral ciprofloxacin (Cipro) twice per day for seven days; 1,000 mg of extended-release ciprofloxacin once per day for seven days; or 750 mg of levofloxacin (Levaquin) once per day for five days. Question 19 1 out of 1 points A middle-aged man presents to urgent care complaining of pain of the medial condyle of the lower humerus. The man works as a carpenter and describes a gradual onset of pain. On exam, the medial epicondyle is tender and pain is increased with flexion and pronation. Range of motion is full The most likely cause of this patient’s pain is: epicondylitis Question 21 1 out of 1 points The best test to determine microalbuminuria to assist in the diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy s to measure albumin in a spot urine sample, collected either as the first urine in the morning or at random, for example, at the medical visit. This method is accurate,:Early morning Question 22 1 out of 1 points What is the first symptom seen in the majority of patients with Parkinson’s disease? Tremor at rest Question 23 1 out of 1 points The most commonly recommended method for prostate cancer screening in a 55 year old male is: digital rectal exams, Question 24 1 out of 1 points Martin, age 24, presents with an erythematous ear canal, pain, and a recent history of swimming. What do you suspect? Otitis externa/ swimmer’s ear Question 25 1 out of 1 points Which of the following symptoms suggests a more serious cause of back pain? Pain associated with lying down at night Question 28 1 out of 1 points A patient taking levothyroxine is being over-replaced. What condition is he at risk for? osteoporosis Question 29 1 out of 1 points Which of the following is the most common cause of low back pain? A . Lumbar disc disease B . Spinal stenosis C . Traumatic fracture D . Osteoporosis Question 30 1 out of 1 points Which is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States? Diabetes Question 31 1 out of 1 points A 77-year-old female presents to the office complaining a sudden swelling on her right elbow. She denies fever, chills, trauma, or pain. The physical exam reveals a non-tender area of swelling over the extensor surface over the right elbow with evidence of trauma or irritation. The nurse practitioner suspects: A . Arthritis B . Ulnar neuritis C . Septic arthritis D . Olecranon bursitis Questi [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 37 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (2)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WALDEN UNIVERSITY - NRNP 6635/ NURS 6630 Mid term & Final Exams
NUR 6531 final exam 1 (Microsoft.com Account Team) | Walden University (Correct Answers Marked in Yellow) NRNP 6531 Final Exam - 100 Percent Grade | Walden University Walden University NURS 6521...
By d.occ 4 years ago
$45
9

NURS 6531 Final Exam (3 Versions), NURS 6531 Midterm Exam (3 Versions): (100 Q & A in Each Version) & NURS 6531 Week 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11 Quiz: Walden University |2021/2022|
NURS 6531 Final Exam (3 Versions), NURS 6531 Midterm Exam (3 Versions): (100 Q & A in Each Version) & NURS 6531 Week 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11 Quiz: Walden University |2021/2022|
By d.occ 4 years ago
$45
12
Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 24, 2021
Number of pages
37
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 24, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
149